Anatomy of a MapReduce Job
In MapReduce, a YARN application is called a Job. The implementation of the Application Master provided by the MapReduce framework is called MRAppMaster.
Timeline of a MapReduce Job
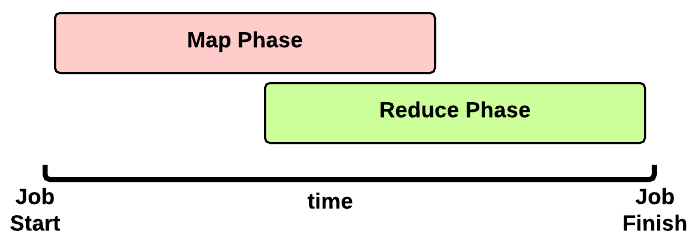 This is the timeline of a MapReduce Job execution:
This is the timeline of a MapReduce Job execution:
- Map Phase: several Map Tasks are executed
- Reduce Phase: several Reduce Tasks are executed
Notice that the Reduce Phase may start before the end of Map Phase. Hence, an interleaving between them is possible.
Map Phase
We now focus our discussion on the Map Phase. A key decision is how many MapTasks the Application Master needs to start for the current job.
What does the user give us?
Let’s take a step back. When a client submits an application, several kinds of information are provided to the YARN infrastucture. In particular:
- a configuration: this may be partial (some parameters are not specified by the user) and in this case the default values are used for the job. Notice that these default values may be the ones chosen by a Hadoop provider like Amanzon.
- a JAR containing:
- a
map()implementation - a combiner implementation
- a
reduce()implementation
- a
- input and output information:
- input directory: is the input directory on HDFS? On S3? How many files?
- output directory: where will we store the output? On HDFS? On S3?
The number of files inside the input directory is used for deciding the number of Map Tasks of a job.
How many Map Tasks?
The Application Master will launch one MapTask for each map split. Typically, there is a map split for each input file. If the input file is too big (bigger than the HDFS block size) then we have two or more map splits associated to the same input file. This is the pseudocode used inside the method getSplits() of the FileInputFormat class:
num_splits = 0
for each input file f:
remaining = f.length
while remaining / split_size > split_slope:
num_splits += 1
remaining -= split_size
where:
split_slope = 1.1
split_size =~ dfs.blocksize
Notice that the configuration parameter mapreduce.job.maps is ignored in MRv2 (in the past it was just an hint).
MapTask Launch
The MapReduce Application Master asks to the Resource Manager for Containers needed by the Job: one MapTask container request for each MapTask (map split).
A container request for a MapTask tries to exploit data locality of the map split. The Application Master asks for:
- a container located on the same Node Manager where the map split is stored (a map split may be stored on multiple nodes due to the HDFS replication factor);
- otherwise, a container located on a Node Manager in the same rack where the the map split is stored;
- otherwise, a container on any other Node Manager of the cluster
This is just an hint to the Resource Scheduler. The Resource Scheduler is free to ignore data locality if the suggested assignment is in conflict with the Resouce Scheduler’s goal.
When a Container is assigned to the Application Master, the MapTask is launched.
Map Phase: example of an execution scenario
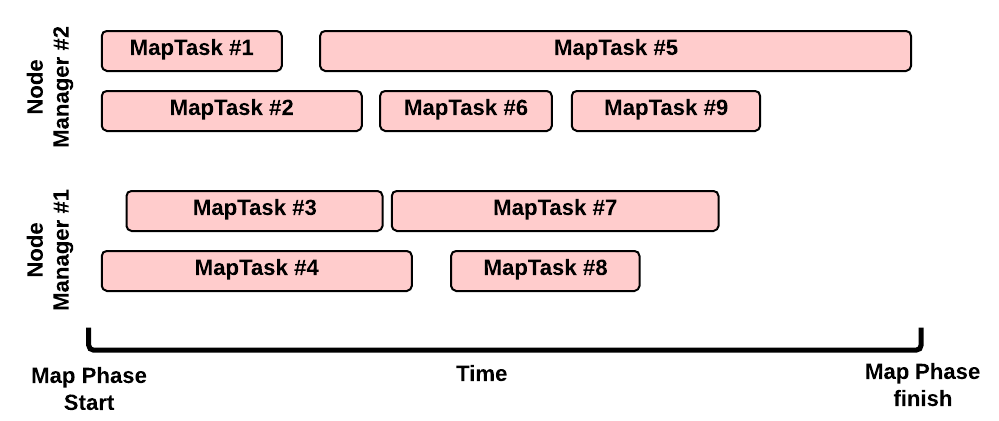
This is a possible execution scenario of the Map Phase:
- there are two Node Managers: each Node Manager has 2GB of RAM (NM capacity) and each MapTask requires 1GB, we can run in parallel 2 containers on each Node Manager (this is the best scenario, the Resource Scheduler may decide differently)
- there are no other YARN applications running in the cluster
- our job has 8 map splits (e.g., there are 7 files inside the input directory, but only one of them is bigger than the HDFS block size so we split it into 2 map splits): we need to run 8 Map Tasks.
Map Task Execution Timeline
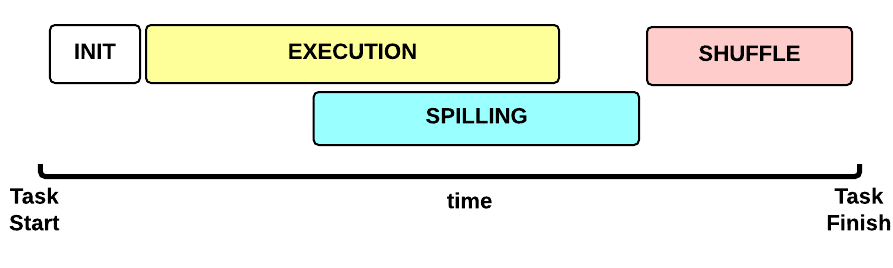 Let’s now focus on a single Map Task. This is the Map Task execution timeline:
Let’s now focus on a single Map Task. This is the Map Task execution timeline:
- INIT phase: we setup the Map Task
-
EXECUTION phase: for each (key, value) tuple inside the map split we run the
map()function - SPILLING phase: the map output is stored in an in-memory buffer; when this buffer is almost full then we start (in parallel) the spilling phase in order to remove data from it
- SHUFFLE phase: at the end of the spilling phase, we merge all the map outputs and package them for the reduce phase
MapTask: INIT
During the INIT phase, we:
- create a context (
TaskAttemptContext.class) - create an instance of the user
Mapper.class - setup the input (e.g.,
InputFormat.class,InputSplit.class,RecordReader.class) - setup the output (
NewOutputCollector.class) - create a mapper context (
MapContext.class,Mapper.Context.class) - initialize the input, e.g.:
- create a
SplitLineReader.classobject - create a
HdfsDataInputStream.classobject
MapTask: EXECUTION
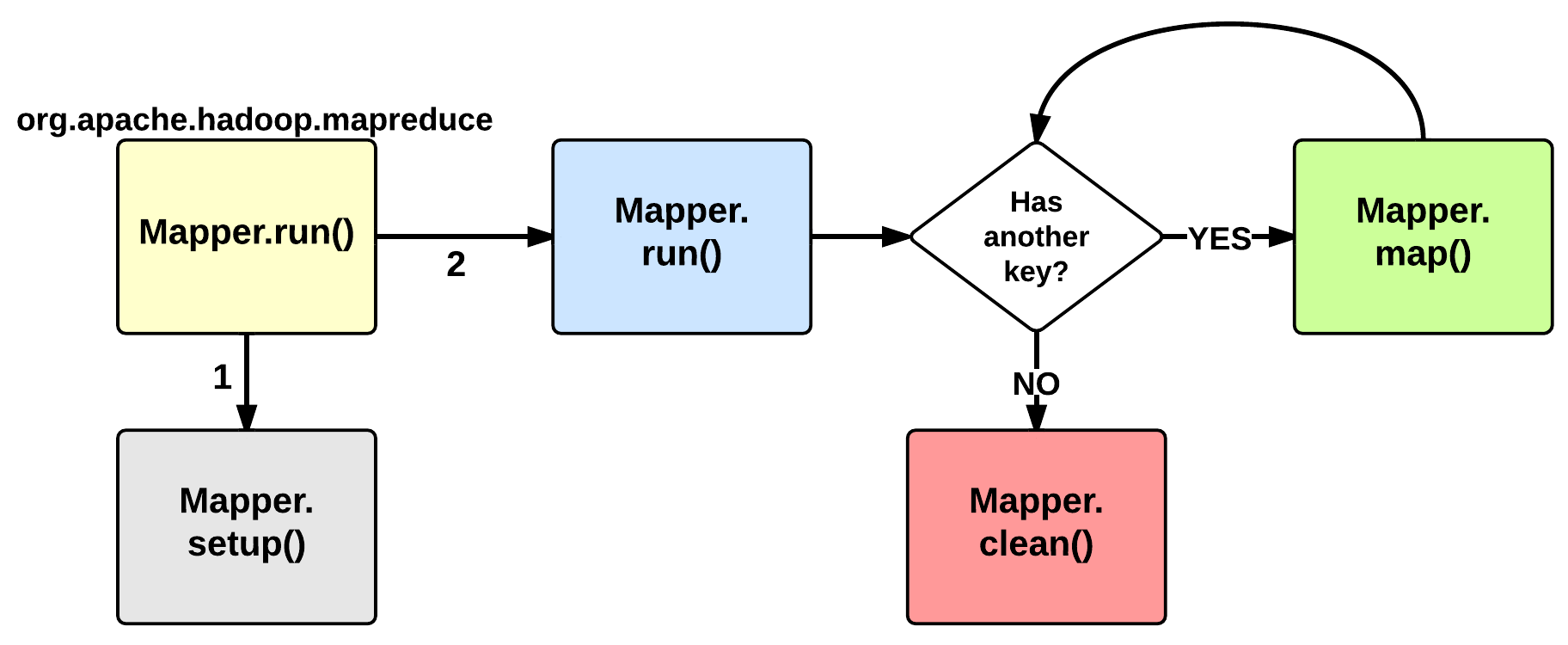
The EXECUTION phase is performed by the run method of the Mapper class. The user can override it, but by default it will start by calling the setup method: this function by default does not do anything useful but can be override by the user in order to setup the Task (e.g., initialize class variables). After the setup, for each <key, value> tuple contained in the map split, the map() is invoked. Therefore, map()receives: a key a value, and a mapper context. Using the context, a map stores its output to a buffer.
Notice that the map split is fetched chuck by chunk (e.g., 64KB) and each chunk is split in several (key, value) tuples (e.g., usingSplitLineReader.class). This is done inside the Mapper.Context.nextKeyValue method.
When the map split has been completely processed, the run function calls the clean method: by default, no action is performed but the user may decide to override it.
MapTask: SPILLING
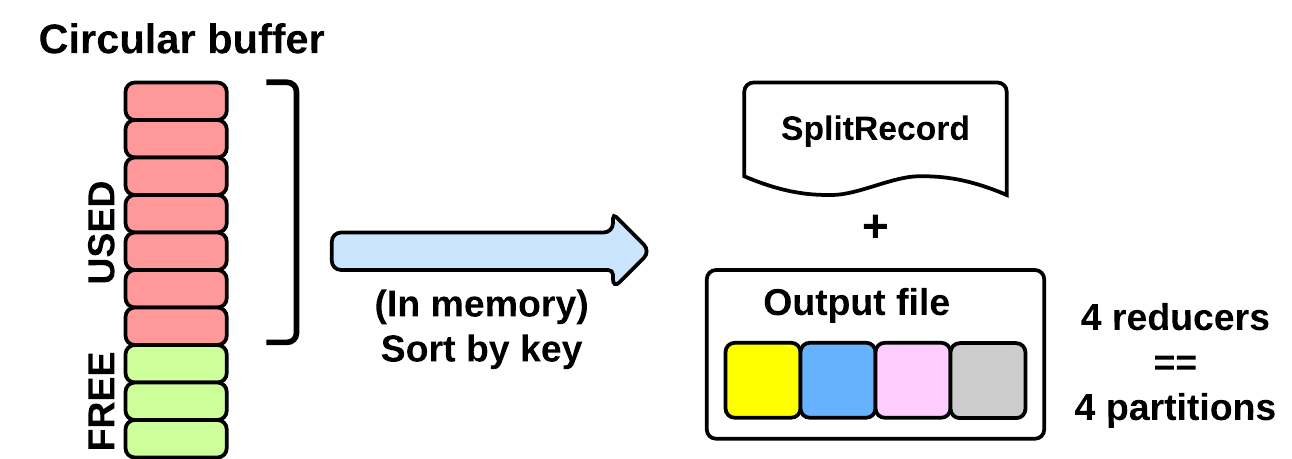
As seen in the EXECUTING phase, the map will write (using Mapper.Context.write()) its output into a circular in-memory buffer (MapTask.MapOutputBuffer). The size of this buffer is fixed and determined by the configuration parametermapreduce.task.io.sort.mb (default: 100MB).
Whenever this circular buffer is almost full (mapreduce.map. sort.spill.percent: 80% by default), the SPILLING phase is performed (in parallel using a separate thread). Notice that if the splilling thread is too slow and the buffer is 100% full, then the map() cannot be executed and thus it has to wait.
The SPILLING thread performs the following actions:
- it creates a
SpillRecordandFSOutputStream(local filesystem) - in-memory sorts the used chunk of the buffer: the output tuples are sorted by (partitionIdx, key) using a quicksort algorithm.
- the sorted output is split into partitions: one partition for each ReduceTask of the job (see later).
- Partitions are sequentially written into the local file.
How Many Reduce Tasks?
The number of ReduceTasks for the job is decided by the configuration parameter mapreduce.job.reduces.
What is the partitionIdx associated to an output tuple?
The paritionIdx of an output tuple is the index of a partition. It is decided inside the Mapper.Context.write():
partitionIdx = (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReducers
It is stored as metadata in the circular buffer alongside the output tuple. The user can customize the partitioner by setting the configuration parameter mapreduce.job.partitioner.class.
When do we apply the combiner?
If the user specifies a combiner then the SPILLING thread, before writing the tuples to the file (4), executes the combiner on the tuples contained in each partition. Basically, we:
- create an instance of the user
Reducer.class(the one specified for the combiner!) - create a
Reducer.Context: the output will be stored on the local filesystem - execute
Reduce.run(): see Reduce Task description
The combiner typically use the same implementation of the standard reduce() function and thus can be seen as a local reducer.
MapTask: end of EXECUTION
At the end of the EXECUTION phase, the SPILLING thread is triggered for the last time. In more detail, we:
- sort and spill the remaining unspilled tuples
- start the SHUFFLE phase
Notice that for each time the buffer was almost full, we get one spill file (SpillReciord + output file). Each Spill file contains several partitions (segments).
MapTask: SHUFFLE
Reduce Phase
[…]
YARN and MapReduce interaction
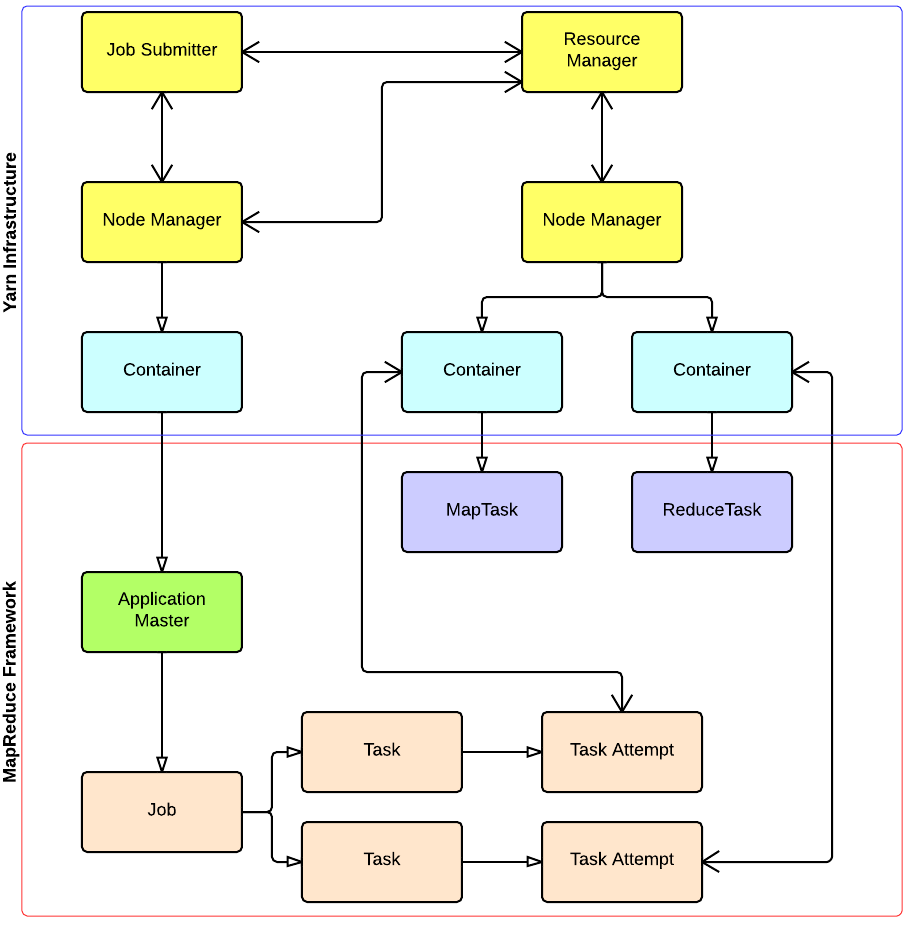
出处:http://ercoppa.github.io/HadoopInternals/Container.html







相关推荐
电机效率Map是电机性能分析中的一个重要概念,它用于描述电机在不同工况下运行的效率分布情况。在本文中,我们将深入探讨电机效率Map的绘制方法、意义以及如何利用工具进行计算。 电机效率是指电机输出的机械功率与...
电机效率MAP的绘制涉及到多个步骤和计算,首先需要收集电机在不同工况下的运行数据。这包括电机在各种转速下对应的输出转矩、输入电流、电压以及功率等信息。通过这些数据,我们可以计算出电机在每个工况点的效率,...
3. **运行安装程序**:在解压后的文件夹中找到Setup.exe或其他类似名称的可执行文件,双击启动安装向导。安装向导将引导你完成整个安装过程。 4. **接受许可协议**:安装过程中,你需要阅读并接受GeoMap4.0的许可...
用户只需运行该工具,并指定待转换的.map文件,map2dbg就会自动生成对应的.dbg文件。这样,开发者就可以在WinDBG中利用.dbg文件进行深入的调试和分析,包括查看函数调用栈、设置断点、检查内存状态等。 使用map2dbg...
`EasyXmlUtil`中很可能包含了一个名为`xmlToMap`的方法,用于执行这个过程。 接下来,Map到XML的转换则需要构建XML文档结构。我们可以利用`javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory`和`javax.xml.transform.dom....
1. **运行程序**:运行此程序时,由于存在除0错误,会导致程序崩溃。 2. **获取崩溃地址**:在出现“非法操作”对话框时,点击“详细信息”按钮,记录下崩溃的地址。 3. **查看MAP文件**:找到生成的MAP文件,分析...
- 运行时编辑:在游戏运行过程中,可以根据游戏逻辑动态修改TileMap,实现如地形变化、生长植被等效果。 - 故事进展:随着玩家在游戏中推进,TileMap可以揭示新的区域,隐藏或显示内容,增加探索感。 6. 性能优化...
文件列表中的"MapBrowser 1.2"可能包含了程序的主程序文件,用户下载后解压即可运行。安装和使用过程中,用户需要注意的是,尽管MapBrowser 提供了便利,但提取游戏资源应遵循游戏的使用协议,尊重知识产权,避免...
首先,我们来了解GEOMAP3.5的安装过程。在提供的压缩包文件中,包含了以下三个关键组件: 1. GeoMap35SuperPro.exe:这是主应用程序的安装文件,负责将GEOMAP3.5的核心功能部署到您的计算机上。运行这个文件,按照...
本文档将详细介绍 MapServer 的安装和配置过程,包括 GIS 服务器的设置、PostgreSQL 数据库的安装、PostGIS 空间数据库工具的安装、Shape 图层文件的导入、QGIS 工具的使用、Mapfile 编辑工具的使用等。 一、安装 ...
MapStruct的映射过程是基于编译时生成的代码,这种方式比反射调用性能更高,且由于在编译时就进行了类型检查,因此具有更高的类型安全性。 #### MapStruct的主要功能和优势: - 类型安全的映射:MapStruct使用...
GeoMap3.6支持在多种Windows操作系统环境下运行,包括Windows2000、WindowsXP、Windows2003和Windows7。 在安装方面,GeoMap3.6的运行环境需满足一定的系统需求,如内存、硬盘空间和兼容的操作系统。安装过程简单...
本实例主要探讨如何在Java项目中配置和使用MapServer,以及解决配置过程中遇到的问题。 首先,我们需要理解MapServer的基本概念。MapServer的核心是地图定义文件(Mapfile),它包含了地图的各种层(Layers)、样式...
4. **脚本接口**:MapMagic提供了丰富的脚本API,使得开发者可以利用C#编写自定义脚本来控制地形生成过程或与其他Unity组件交互。这增强了工具的灵活性和可扩展性。 5. **地形编辑器**:内置的地形编辑器允许用户在...
在这个“HI_MPI_IVE_Map”的例子中,我们将看到如何用这个函数打印像素值的变化,以便直观地理解映射过程。 在描述中提到的“ive_map的小demo”是一个精心设计的代码示例,它会创建一个输入图像,然后调用HI_MPI_...
总的来说,GoMap是AR游戏开发领域的一款强大工具,它简化了3D地图的创建过程,使得开发者可以专注于游戏的玩法设计和用户体验优化。通过充分利用GoMap的功能,我们可以期待未来出现更多创新且引人入胜的AR游戏作品,...
Shuffle过程描述着数据从map task输出到reduce task输入的这段过程。在Hadoop这样的集群环境中,大部分map task与reduce task的执行是在不同的节点上。 Shuffle过程的主要目标是: 1. 完整地从map task端拉取数据...
本知识点将详细介绍如何运行Autoware.Universe样例,并验证高精地图的安装过程。 首先,进行Autoware.Universe的运行样例操作之前,需要确保系统已经正确安装了Autoware.Universe。安装过程中需要设置好依赖项,...
4. **编译与安装**:执行`make`进行编译,然后使用`make install`将MapServer安装到指定目录。 5. **配置Web服务器**:配置Apache或其他Web服务器以支持CGI(Common Gateway Interface)或FastCGI,这使得MapServer...
反射允许程序在运行时检查和修改其他类的信息,包括类名、属性、方法等。在转换Map到实体时,我们需要获取实体类的属性信息,然后根据Map中的键值对设置这些属性的值,这就需要用到反射。 下面是一个简单的工具类`...