- 浏览: 1413752 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 广州
-

文章分类
最新评论
-
sdgxxtc:
[quo[color=red]te][/color]
C#使用OleDb读取Excel,生成SQL语句 -
zcs302567601:
博主,你好,一直都有个问题没有搞明白,就是 2.x的版本是通过 ...
NGUI所见即所得之UIPanel -
一样的追寻:
感谢楼主!
有向强连通和网络流大讲堂——史无前例求解最大流(最小割)、最小费用最大流 -
cp1993518:
感谢!从你的博客里学到了很多
Unity日志工具——封装,跳转 -
cp1993518:
学习了~,话说现在的版本custom还真的变委托了
NGUI所见即所得之UIGrid & UITable
归并排序(merge sorts)算法大串讲
本文内容框架:
§1 归并排序(Merge Sort)
§2 归并排序算法改进和优化
§3 Strand Sort排序
§4 小结
§1 归并排序(Merge Sort)
归并排序(Merge Sort)算法
归并排序(Merge sort)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法。该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。
归并排序,它采取分而治之(Divide-and-Conquer)的策略,时间复杂度是Θ(nlgn)。归并排序的步骤如下:
1. Divide: 把长度为n的输入序列分成两个长度为n/2的子序列。
2. Conquer: 对这两个子序列分别采用归并排序。
3. Combine: 将两个排序好的子序列合并成一个最终的排序序列。
在描述归并排序的步骤时又调用了归并排序本身,可见这是一个递归的过程。
下面给出归并排序的递归和迭代两个版本实现
递归版本
//将有二个有序数列a[first...mid]和a[mid...last]合并。
void mergearray(int a[], int first, int mid, int last, int temp[])
{
int i = first, j = mid + 1;
int m = mid, n = last;
int k = 0;
while (i <= m && j <= n)
{
if (a[i] < a[j])
temp[k++] = a[i++];
else
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
while (i <= m)
temp[k++] = a[i++];
while (j <= n)
temp[k++] = a[j++];
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
a[first + i] = temp[i];
}
void mergesort(int a[], int first, int last, int temp[])
{
if (first < last)
{
int mid = (first + last) / 2;
mergesort(a, first, mid, temp); //左边有序
mergesort(a, mid + 1, last, temp); //右边有序
mergearray(a, first, mid, last, temp); //再将二个有序数列合并
}
}
bool MergeSort(int a[], int n)
{
int *p = new int[n];
if (p == NULL)
return false;
mergesort(a, 0, n - 1, p);
delete[] p;
return true;
}
不使用递归,使用迭代版本
void merge_sort(int *list, int length){
int i, left_min, left_max, right_min, right_max, next;
int *tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * length);
if (tmp == NULL){
fputs("Error: out of memory\n", stderr);
abort();
}
for (i = 1; i < length; i *= 2)
for (left_min = 0; left_min < length - i; left_min = right_max){
right_min = left_max = left_min + i;
right_max = left_max + i;
if (right_max > length)
right_max = length;
next = 0;
while (left_min < left_max && right_min < right_max)
tmp[next++] = list[left_min] > list[right_min] ? list[right_min++] : list[left_min++];
while (left_min < left_max)
list[--right_min] = list[--left_max];
while (next > 0)
list[--right_min] = tmp[--next];
}
free(tmp);
}
比较操作的次数介于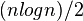 和
和 。 赋值操作的次数是
。 赋值操作的次数是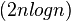 。 归并算法的空间复杂度为:Θ (n)
。 归并算法的空间复杂度为:Θ (n)
§2 归并排序算法改进和优化
归并排序算法改进
1.利用插入排序优化归并排序
在归并中利用插入排序不仅可以减少递归次数,还可以减少内存分配次数(针对于原始版本)。
尽管合并排序最坏情况运行时间为o(nlgn),插入排序的最坏运行时间为o(n^2),但是插入排序的常数因子使得它在n较小时,运行要更快一些。因此,在合并排序算法中,当子问题足够小时,采用插入排序就比较合适了。考虑对合并排序做这样的修改,即采用插入排序策略,对n/k个长度为k的子列表进行排序。然后,再用标准的合并机制将它们合并起来,此处k是一个待定的值。
a) 证明在最坏的情况下,n/k个子列表可以用插入排序在o(nk)的时间内完成排序
解答:每个列表长度为k,因此采用插入排序o(k^2)复杂度。因此k^2*n/k=kn
b) 证明这些子列表可以在o(nlg(n/k))最坏情况内完成合并。
c) 如果已知修改后的合并排序算法的最坏运行时间为o(nk+nlg(n/k)),要使得修改后的算法具有与标准合并算法一样的渐进运行时间,k的最大渐进形式是什么?
d) 实践中,应该如何选取k值。K=o(lgn)
解答:在实践中,k应该是使得插入排序比归并排序快的最大列表长度。
2.不回写+非递归优化归并排序
1)不回写:因为这样可以减少移动的次数,最简单的归并排序,每次对每两个有序表进行合并的时候都要保存到另外一个数组当中比如B【】数组,合并完之后要回写到原来的数组当中比如A【】。优化:我们可以这么做,比如当奇数次合并的时候是从A[]数组到B[]数组,偶数次是从B[]数组到A[]数组。这样可以减少一半的数据移动的次数
2)不递归:大家应该都知道,在进行递归调用的时候,需要对函数调用进行压栈出栈的操作,是非常的耗时间的,所以我们采用迭代法来代替递归对其进行改进,可以提高程序的性能。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int data[10]={8,7,2,6,9,10,3,4,5,1};
int cp[10];
void Merge(int a[],int b[],int first,int mid,int last) //合并两个有序序列
{
int p=first,q=mid+1;
int pos=first;
while(p<=mid&&q<=last)
{
if(a[p]<a[q])
{
b[pos++]=a[p++];
}
else
{
b[pos++]=a[q++];
}
}
if(p>mid)
{
while(q<=last)
{
b[pos++]=a[q++];
}
}
else
{
while(p<=mid)
{
b[pos++]=a[p++];
}
}
}
void MergePass(int a[],int b[],int gap,int n) //以一定的步长对数据进行合并
{
int i=0;
int j;
while(i<=n-2*gap+1)
{
Merge(a,b,i,i+gap-1,i+2*gap-1);
i=i+2*gap;
}
if(i<(n-gap))
Merge(a,b,i,i+gap-1,n-1);
else
for(j=i;j<n;j++)
b[j]=a[j];
}
void Merge_sort(int a[],int b[],int n) //归并排序的非递归 并且不进行回写
{
int gap=1;
while(gap<n)
{
MergePass(a,b,gap,n);
gap=2*gap;
MergePass(b,a,gap,n);
gap=2*gap;
}
}
int main()
{
Merge_sort(data,cp,10);
for(int i=0;i<=9;i++)
cout<<data[i]<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.利用自然合并排序优化归并排序
该排序需要一个叫做pass()的子函数,该函数通过一次扫描,将排序前数组中已经有序的子数组段信息记录在rec[]数组中,然后返回原数组中自然序列的个数。
// 自然归并是归并排序的一个变形,效率更高一些,可以在归并排序非递归实现的基础上进行修改
//对于已经一个已经给定数组a,通常存在多个长度大于1的已经自然排好的子数组段
//因此用一次对数组a的线性扫描就可以找出所有这些排好序的子数组段
//然后再对这些子数组段俩俩合并
//代码的实现如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int SIZE = 100;
int arr[SIZE];
int rec[SIZE];//记录每个子串的起始坐标
//排序数组arr[fir:end]
//合并操作的子函数
void merge(int fir,int end,int mid);
//扫描得到子串的子函数
int pass(int n);
//自然合并函数
void mergeSort3(int n);
/********************************************************************/
void mergeSort3(int n){
int num=pass(n);
while(num!=2){
//num=2说明已经排好序了
//每循环一次,进行一次pass()操作
for(int i=0;i<num;i+=2)
//坐标解释可参加P23页的图示
merge(rec[i],rec[i+2]-1,rec[i+1]-1);
num=pass(n);
}
}
void merge(int fir,int end,int mid){
//合并
int tempArr[SIZE];
int fir1=fir,fir2=mid+1;
for(int i=fir;i<=end;i++){
if(fir1>mid)
tempArr[i]=arr[fir2++];
else if(fir2>end)
tempArr[i]=arr[fir1++];
else if(arr[fir1]>arr[fir2])
tempArr[i]=arr[fir2++];
else
tempArr[i]=arr[fir1++];
}
for(int i=fir;i<=end;i++)
arr[i]=tempArr[i];
}
int pass(int n){
int num=0;
int biger=arr[0];
rec[num++]=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if(arr[i]>=biger)biger=arr[i];
else {
rec[num++]=i;
biger=arr[i];
}
}
//给rec[]加一个尾巴,方便排序
rec[num++]=n;
return num;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(cin>>n){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)cin>>arr[i];
//测试mergeSort函数
/**/mergeSort3(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)cout<<arr[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
//测试pass函数
/*int num = pass(n);
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)cout<<rec[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;*/
}
return 0;
}
4.双向自然合并排序优化归并排序算法
这个算法在上一个优化算法的基础上改进的,就是同时记录逆序的子数组,并进行将其转换为升序来处理。
Strand Sort算法
Strand Sort算法的思想:需要一个空的数组用来存放最终的输出结果,给它取个名字叫"有序数组",然后每次遍历待排数组,得到一个"子有序数组",然后将"子有序数组"与"有序数组"合并排序。
The strand sort algorithm is O(n^2) in the average case. In the best case (a list which is already sorted) the algorithm is linear, or O(n). In the worst case (a list which is sorted in reverse order) the algorithm is O(n^2).
Strand sort is most useful for data which is stored in a linked list, due to the frequent insertions and removals of data. Using another data structure, such as an array, would greatly increase the running time and complexity of the algorithm due to lengthy insertions and deletions. Strand sort is also useful for data which already has large amounts of sorted data, because such data can be removed in a single strand.
§3 Strand Sort排序
Strand Sort算法举例
| 3 1 5 4 2 | ||
| 1 4 2 | 3 5 | |
| 1 4 2 | 3 5 | |
| 2 | 1 4 | 3 5 |
| 2 | 1 3 4 5 | |
| 2 | 1 3 4 5 | |
| 1 2 3 4 5 |
待排数组[ 6 2 4 1 5 9 ]
第一趟遍历得到"子有序数组"[ 6 9],并将其归并排序到有序数组里
待排数组[ 2 4 1 5]
有序数组[ 6 9 ]
第二趟遍历再次得到"子有序数组"[2 4 5],将其归并排序到有序数组里
待排数组[ 1 ]
有序数组[ 2 4 5 6 9 ]
第三趟遍历再次得到"子有序数组"[ 1 ],将其归并排序到有序数组里
待排数组[]
有序数组[ 1 2 4 5 6 9 ]
待排数组为空,排序结束
Strand Sort算法步骤:
1.Parse the unsorted list once, taking out any ascending (sorted) numbers.
2.The (sorted) sublist is, for the first iteration, pushed onto the empty sorted list.
3.Parse the unsorted list again, again taking out relatively sorted numbers.
4.Since the sorted list is now populated, merge the sublist into the sorted list.
5.Repeat steps 3–4 until both the unsorted list and sublist are empty.
Strand Sort算法实现
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void merge(int res[],int resLen,int sublist[],int last)
{
int *temp = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(resLen+last));
int beginRes=0;
int beginSublist=0;
int k;
for(k=0;beginRes<resLen && beginSublist<last;k++)
{
if(res[beginRes]<sublist[beginSublist])
temp[k]=res[beginRes++];
else temp[k]=sublist[beginSublist++];
//cout<<"k:"<<k<<" temp[k]:"<<temp[k]<<endl;
}
if(beginRes<resLen)
memcpy(temp+k,res+beginRes,(resLen-beginRes)*sizeof(int));
else if(beginSublist<last)
memcpy(temp+k,sublist+beginSublist,(last-beginSublist)*sizeof(int));
memcpy(res,temp,(resLen+last)*sizeof(int));
free(temp);
}
void strandSort(int array[],int length)
{
int *sublist=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*length);
int *res=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*length); //sizeof(array)=4
int i;
int resLen=0;
res[0]=array[0];
array[0]=0;
for(i=1;i<length;i++)
{
if(array[i]>res[resLen])
{
resLen++;
res[resLen]=array[i];
array[i]=0;
}
}
resLen++;
int last;
int times=1;
bool finished;
while (true)
{
finished = true;
last = -1;
for(i=times;i<length;i++)
{
//cout<<"This time array[i]: "<<array[i]<<endl;
if(array[i]!=0)
{
//cout<<"This time array[i]: "<<array[i]<<endl;
if (last==-1)
{
sublist[0]=array[i];
array[i]=0;
last=0;
finished = false;
}
else if(array[i]>sublist[last])
{
last++;
sublist[last]=array[i];
array[i]=0;
}
}
}
if(finished) break;
last++;
merge(res,resLen,sublist,last);
resLen=resLen+last;
times++;
}
memcpy(array,res,length*sizeof(int));
}
int main()
{
//int array[]={15,9,8,1,4,11,7,2,13,16,5,3,6,2,10,14};
int array[]={13,14,94,33,82,25,59,94,65,23,45,27,73,25,39,10,35,54,90,58};
int i;
int length=sizeof(array)/sizeof(int); //在这里 sizeof(array)=80
strandSort(array,length);
//int *arr = array;
//cout<<arr[2]<<endl;
for(i=0;i<length;i++)
{
cout<<array[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
§4 小结
这篇博文列举了主要讲解了归并排序算法及其改进,基本可以掌握其中概要,管中窥豹,不求甚解。如果你有任何建议或者批评和补充,请留言指出,不胜感激,更多参考请移步互联网。
参考:
①MoreWindows: http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6678165
②hzami: http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-27149258-id-3377329.html
③fangxia7: http://fangxia722.blog.163.com/blog/static/317290122009112831244671/
④icyfire0105: http://blog.csdn.net/icyfire0105/article/details/2066602
⑤glose: http://www.cnblogs.com/dlutxm/archive/2011/11/04/2236594.html
⑥六维空间: http://www.cnblogs.com/liushang0419/archive/2011/09/19/2181476.html
⑦tiantangrenjian: http://blog.csdn.net/tiantangrenjian/article/details/7172942
⑧更多参考来着维基百科
发表评论
-
C# 调用Delegate.CreateDelegate方法出现“未处理ArgumentException”错误解决
2013-05-31 12:24 3591在C# 调用Delegate.Create ... -
数组问题集结号
2012-12-06 22:01 0数组是最简单的数据结构,数组问题作为公司招聘的笔试和面试题目 ... -
算法问题分析笔记
2012-12-05 11:59 01.Crash Balloon Zhejiang Univer ... -
Java基础进阶整理
2012-11-26 09:59 2340Java学习笔记整理 ... -
Java学习笔记整理
2012-11-24 23:43 211Java学习笔记整理 本文档是我个人 ... -
《C++必知必会》学习笔记
2012-11-24 23:40 2662《C++必知必会》学� ... -
《C++必知必会》学习笔记
2012-11-24 23:34 1《C++必知必会》学习笔� ... -
C语言名题精选百则——排序
2012-11-04 23:29 128第5章排 序 问题5.1 二分插入法(BIN ... -
C语言名题精选百则——查找
2012-11-04 23:29 4178尊重他人的劳动,支持原创 本篇博文,D.S.Q ... -
基本技术——贪心法、分治法、动态规划三大神兵
2012-11-03 19:30 0基本技术——贪心法、分治法、动态规划三大神兵 -
优先队列三大利器——二项堆、斐波那契堆、Pairing 堆
2012-11-03 13:12 35683优先队列三大利器——二项堆、斐波那契堆、Pairing ... -
优先队列三大利器——二项堆、斐波那契堆、Pairing 堆
2012-11-03 13:01 3优先队列三大利器——二项堆、斐波那契堆、Pairing 堆 ... -
排序算法群星豪华大汇演
2012-10-30 00:09 3169排序算法群星豪华大汇演 排序算法相对简单些,但是由于 ... -
分布排序(distribution sorts)算法大串讲
2012-10-29 15:33 4687分布排序(distribution sorts)算法大串讲 ... -
交换排序(exchange sorts)算法大串讲
2012-10-29 00:22 4435交换排序(exchange sorts)算法大串讲 本 ... -
选择排序(selection sorts)算法大串讲
2012-10-28 12:55 3747选择排序(selection sorts)算法大串讲 本文内 ... -
插入排序(insertion sorts)算法大串讲
2012-10-28 11:30 2768插入排序(insertion sorts� ... -
伸展树(Splay Tree)尽收眼底
2012-10-27 15:11 5594伸展树(Splay Tree)尽收眼底 本文内容 ... -
红黑树(Red-Black Tree)不在话下
2012-10-26 20:54 2257红黑树(Red-Black Tree) 红黑树定义 红黑树 ... -
平衡二叉树(AVL)原理透析和编码解密
2012-10-26 10:22 3033平衡二叉树(AVL)原理透析和编码解密 本文内容 ...








相关推荐
归并排序(Merge Sort)是一种基于分治策略的高效排序算法,由计算机科学家John W. Backus于1945年提出。它的工作原理可以分为三个主要步骤:分解、解决和合并。 1. 分解:将原始数据序列分成两个相等(或接近相等...
归并排序(Merge Sort)是一种高效的、稳定的排序算法,它采用了分治法(Divide and Conquer)的设计理念。在Python中实现归并排序,我们可以将一个大问题分解为两个或多个相同或相似的小问题,然后分别解决这些小...
在本资源中,我们主要关注的是使用MATLAB编程语言实现三种经典的排序算法:插入排序、二分归并排序以及归并排序。这些算法是计算机科学基础中的重要组成部分,特别是在算法设计与分析领域。MATLAB是一种强大的数值...
**快速排序与归并排序算法比较实验报告** 在计算机科学中,排序算法是处理大量数据时不可或缺的一部分。这篇实验报告将深入探讨两种经典的排序算法——快速排序和归并排序,通过对它们在Java环境中的实现和性能测试...
归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段...
### 归并排序算法实现详解 #### 一、引言 归并排序是一种经典的排序算法,采用分治法的思想,将待排序数组分为若干个子序列,这些子序列是已排序的,然后再按照一定的方式合并这些子序列得到最终排序后的数组。...
归并排序(Merge Sort)是一种基于分治策略的高效排序算法,它的主要思想是将大问题分解成小问题,然后逐个解决小问题,最后再将解决好的小问题合并成解决大问题的答案。这种算法在计算机科学中有着广泛的应用,尤其...
### C语言二路归并排序算法 #### 概述 归并排序是一种高效的排序算法,其基本思想是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer),将一个数组分成两个子数组,然后递归地对这两个子数组进行排序,最后将两个有序的子数组合并...
首先,我们来讨论归并排序(Merge Sort)。这是一种基于分治策略的排序算法。归并排序将大问题分解为小问题,然后逐步合并这些小问题的解以得到最终解决方案。它的主要步骤包括: 1. 分解:将待排序的序列分为两半...
### 归并排序算法 归并排序是一种稳定的排序算法,同样基于分治法。它将数组分成两半,递归地排序每一半,然后将两个已排序的半数组合并成一个有序数组。 #### Java 实现代码分析 `Project17_Merge` 类展示了归并...
归并排序的稳定性和其O(n log n)的时间复杂度使其在处理大数据集时表现优秀,但其需要额外的存储空间,这是相对于原地排序算法的一个缺点。 在C语言中实现这些排序算法,我们需要了解基本的数据结构如数组,以及...
本实验旨在通过对两种经典排序算法——快速排序和归并排序的研究与实现,深入理解它们的基本原理、时间复杂度,并通过编程实践比较这两种算法在不同数据规模下的性能表现。 #### 二、快速排序 **1. 基本思想** ...
**实验报告:分治法实现归并排序算法** 实验名称:分治法实现归并排序算法 实验日期:年月日 姓名: 学号: 专业班级: ### 一、实验要求 1. **理解分治法**:分治法是一种解决问题的策略,适用于将大问题分解成...
### 归并排序算法原理 归并排序的基本步骤可以概括为以下几点: 1. **分解**:将待排序的序列分解成尽可能小的子序列,直至每个子序列只有一个元素。由于单个元素的序列自然就是有序的,因此这一步实际上是在准备...
归并排序和基数排序是两种不同的排序算法,它们在实现方式和效率特点上存在显著差异。 **归并排序**是一种基于分治策略的排序算法。它的基本思想是将待排序的序列分成两个长度相等(或近似相等)的部分,分别对这两...
然而,题目中提到的“改进的归并排序算法”探讨了两种不同的实现方式:不回写和非递归。 1. **不回写方式**: 在传统的归并排序中,排序过程中会涉及到数组元素的来回移动。不回写是指在排序过程中避免对原始数组...
归并排序可以有效地处理大规模数据,并且具有稳定性和O(n log n)的时间复杂度。 **归并排序的算法设计:** 归并排序的基本步骤包括分割和合并。首先,将数组递归地分割成越来越小的子数组,直到每个子数组只包含一...
归并排序(Merge Sort)是一种基于分治策略的高效排序算法。它的基本思想是将待排序的序列分为两部分,分别对这两部分进行排序,然后将排好序的子序列合并成一个完整的有序序列。这一过程可以递归地进行,直到每个子...
综上所述,归并排序是一种非常有效的排序算法,尤其是在处理大规模数据集时表现出色。尽管它可能不如其他算法(如快速排序)在某些方面更高效,但其稳定性和可预测的时间复杂度使其成为许多实际应用场景中的优选算法...
二路归并算法排序是归并排序的一种实现方式,通过将两个有序表合并成为一个更大的有序表来实现排序。该算法的基本思想是将原始数组分成两个小数组,分别对这两个小数组进行排序,然后将两个有序表合并成为一个更大的...