 Java is one of the language which has overhauled it’s underneath technology ground-up. Even though, the basic concept of running inside JVM holds good, the way JVM handles Objects, Memory management has completely been revamped.
Java is one of the language which has overhauled it’s underneath technology ground-up. Even though, the basic concept of running inside JVM holds good, the way JVM handles Objects, Memory management has completely been revamped.
A lot changed over 1.4 to 1.5. There were critical compile-time improvements, Runtime smartness and with Java 6 more performance optimizations; Java 7 – the modularity.
Let’s start discussing each aspect of Java 7 which makes it go Loud -
- Modularization – JSR 294 or Project Jigsaw
- JVM Support for dynamic languages
- More New I/O APIs which are nearly finished, includes true asynchronous I/O and finally a real file system API – JSR 203
- The native language support for XML. (probable)
- Safe rethrow – Allows a broad catch clause, with the compiler being smarter on what you’re allowed to rethrow based on what is thrown from the try block. (I had not seen this before but it looks nice)
- Null dereference expressions – Null checks with ‘?’ syntax similar to Groovy… lettign developers avoid a nest of null checks.
- Better type inference – Example around generics instantiations, but it was not clear how far the inference would be taken (the more the better in my opinion).
- Multi-catch - Allows a comma separated list of disjunctive exception types in catch clause.
- JSR 296 – Swing application framework – It still needs to be easier to create Swing apps.
Update: As per Sun Blogs
The “Small” Sun changes are:
- Upgrade class loader architecture – Work started in Java 5 and continues to evolve. There are some deadlock issues today in classloader delegation that will be addressed.
- XRender pipeline for Java 2D – This was an Open JDK Integrators Challenge project,and is an analog to the OpenGL pipeline but much more portable across x11.
- Swing Updates – JXLayer, DatePicker, CSS styling (maybe) that Ethan Nicholaus (sp?) has been working on
- JavaFX
Update: Few new Small changes of “Project coin” are available here.
The “Fast” changes from Sun (This refers to performance improvements):
Hotspot run-time compiler enhancements
- A couple of concurrency (JSR 166) tweaks (Better support for Multicore)
- G1 Garbage collector- Leads to much smaller pause times and hopes to replace CMS (Concurrent mark sweep) GC
- Compressed pointer 64 bit VM
- MVM-lite – Multiple Virtual Machines will help run isolated applications and allow a kill -9 on a Java application. Mark said it is not clear what problem would be solved, and original project was extremely ambitious, but desire to drag apps out of browser plugin presents a good usage and need for MVM. (This could be moved to a later release)
The Theory and Practical
As far as what changes you’ll see in your day-to-day work, my guess is that the major impact will be stuff like JSR 203 which overhauls the file system API. If JSR 310 is included, then it would also have a major impact on how you interact with any aspect of the date and time APIs. Many of the other JSRs will only impact you if you happen to already do something in that particular area (JMX – JSR 255, concurrency – JSR 166, etc).
The biggest thing most people will notice may be performance. This is my favorite. And that is exactly what I thought about writing, and it expanded the scope to features aswell. As usual, each JDK brings a whole new set of performance optimizations. We’ve already seen some very encouraging results in String performance, array performance, and a new concurrent garbage collector (G1). I suspect many people will find that their existing code will work and run noticeably faster than it did in the past.
Performance
I saw this one about the new features in Java 7:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/java/library/j-jtp03048.html
They use MergeSort as an example of how to exploit multiple CPUs for sorting. Java 7 has the nice feature, that it can now decide at runtime, how many threads should be used to solve a particular problem (see the coInvoke part).
However, there is this tricky constant, SEQUENTIAL_THRESHOLD, which is used to decide whether to enforce sequential processing or not. How do you set this value? Well, you set it at design time, even though the example was meant to show how Java adapts at runtime…
The next thing is that the whole array is passed as parameter. No matter what programming language you use, this is a bad design. If Java doesn’t copy the memory, you may have 2 CPUs looking at the same RAM area. If Java has a runtime optimization that detects that 2 CPUs are looking at the same area, and decides to copy the data, it will copy too much data…
I’m not sure this example would perform better on a 4-CPU machine than on a single-CPU machine with the same CPUs…
The basic problem in all this is, that it is extremely hard to find real world examples of parallelization of algorithms that can be optimized to any kind of parallel hardware. Good multi-threading must be done on a functionality level, not on the algorithm level.
Also, every time we add multi-threading to code, we make it more complex. In other words, it comes at a cost. I predict that some of the future performance gains don’t come from making algorithms more threaded, but from changing data structures, reducing memory footprint and simple optimizations. As the price of more performance increases, efforts will be spent where most speed can be gained at the lowest price.
Benchmarking JDK 7
As per Sun, The JDK 7 delivers quite a speed boost over JDK 6 array accesses. For us, this is huge. It’s like another year and a half of Moore’s law for free. Only in software. And you don’t even have to write multi-threaded code.
It’s basically a stress test that I used for ArrayLists, HashMaps, gets, array sets, and simple multiply-add-subtract, arithmetic, and concurrency APIs, Threads.
I installed the following beta release of JDK 7:
> java -version java version "1.7.0-ea" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0-ea-b66) Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM (build 16.0-b06, mixed mode, sharing)
Java has always suffered relative to C/C++ in matrix multiplication because Java does range checks on every array access (set or get). With some clever static and run-time analysis, we are able to eliminate most of the array bounds checks. They show on matrix benchmarks that this one improvement doubles the speed of the LU matrix factorization benchmark in the U.S. National Institute of Standards (NIST) benchmark suite SciMark 2, which like our clustering algorithm, is basically just a stress test for array access and arithmetic.
I’m pretty excited about the new fork-join concurrency, too, as it’s just what we’ll need to parallelize the inner loops without too much work for us or the operating system.
I decided to take my on Test-check for performance for Java 7 and then compare it with 5, 6.
My tests have been on a Dell D630 Notebook running Windows 7 RTM (32 bit) with an Intel Core 2 CPU (2.4GHz), and 3GB of RAM.
Here are the Benchmark Tests -
Test 1. Add 5 Million String values (each calculated with some complex Math arithmetic)
Test 2. ArrayList <String> with 5 Million insertions (with values from Test1). Insertions are conditional and have additional computation before adding to array.
Test 3. HashMap <String, Integer> with 5 million keys, values. Each key, value pair is being calculated via concurrent thread. (This tread tests both Arithmetic and concurrency capabilities)
Test 4. Printing 5 million items of ArrayList <String> to number of Files (1000) and Reading back again. (Tests multicore concurrency to the edge) My CPU, HDD, RAM all went to Max.
All of these tests were very memory intensive. Heap size varied between 1 – 2 GB during tests, due to large no. of objects. CPU Utilization was sometimes 50% (1 core’s max) and most of the time >70% and in Test3, Test4; CPU touched 100% most of the times.
The Result is mind blowing!
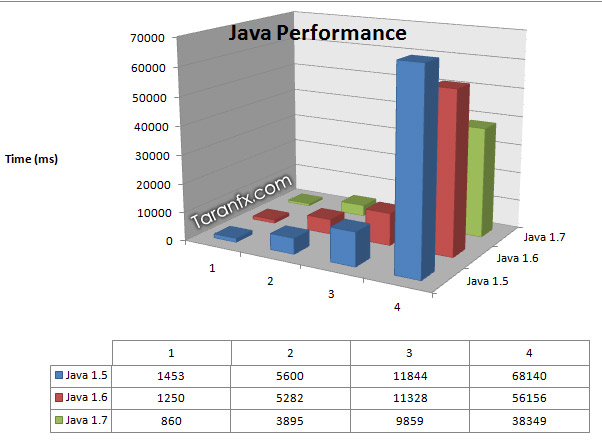
And the Result The Winner is … Java 7
Java 5 <=== 18% faster=== < Java 6 < ===46% faster===< Java 7
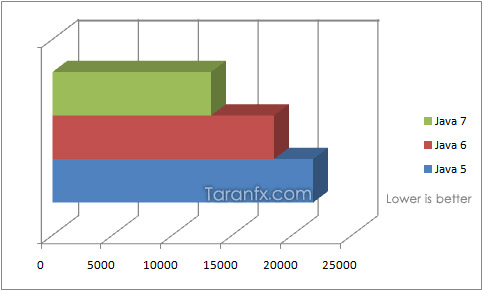 Note – This was totally based upon my tests, doesn’t necessarily means it’s for overall Java. The results may vary for different kinds of computations.
Note – This was totally based upon my tests, doesn’t necessarily means it’s for overall Java. The results may vary for different kinds of computations.







相关推荐
JDK updates often include bug fixes, performance improvements, and security enhancements to ensure developers have a stable and secure environment. **主要内容** 1. **Java Virtual Machine (JVM)**: ...
- JDK 1.8 includes various security updates and improvements to ensure better protection against vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security of Java applications. 10. **Modularization (Project ...
With JDK 1.8 installed, developers can start building Java applications using the latest features and improvements. The JDK includes the Java compiler (`javac`) for translating source code into ...
This version, Update 80, brings several enhancements, bug fixes, and performance improvements over previous releases in the JDK 7 series. **主要内容:** 1. **JVM (Java Virtual Machine):** - JDK 1.7...
10. 性能提升(Performance Improvements): JDK 1.5对垃圾回收、内存管理等方面进行了优化,提高了程序的运行效率。 UUCall3.exe可能是一个与JDK 1.5相关的应用程序或者工具,但具体信息不足,无法在此详细讨论...
7. **Parallel Collectors**: The Collections Framework was enhanced with parallel processing capabilities, enabling faster execution of collection operations using multiple threads. These collectors ...
5.0.2 comes with significant tightening-up across the framework, including performance improvements and fine-tuned configuration variants. Many of those changes have been backported to 4.3.13 for ...