转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/qinjuning
关于PackageManager和ActivityManager的使用 ,自己也写了一些DEMO 了,基本上写的线路参考了Settings模块下的
应用程序,大家如果真正的有所兴趣,建议大家看看源码,不过丑化说在前面,我自己也没怎么看过这方面的源码,只在
需要的时候,才跑过去翻翻。
今天,在耐着最后一点性子,写下了这篇博文,基本上完成了整个应用程序功能模块的介绍,大家也在此系列上慢慢拓展。
ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo类:封装了正在运行的服务信息
获取系统里所有真正运行的服务是通过调用ActivityManager方法来得到的,具体方法如下:
List<ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo>getRunningServices(int
maxNum)
功能:返回所有正在运行的服务
参数: maxNum 代表我们希望返回的服务数目大小,一般给个稍大的值即可, 例如,50 。
ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo 类
常用字段:
long activeSince服务第一次被激活的时间, 包括启动和绑定方式
int clientCount如果该Service是通过Bind方法方式连接,则clientCount代表了service连接客户端的数目
int crashCount 服务运行期间,出现死机的次数
boolean foreground若为true,则该服务在后台执行
int pid如果不为0,表示该service所在的进程ID号( PS:为0的话我也不清楚 - - 求指点)
int uid用户ID 类似于Linux的用户权限,例如root等
String process 进程名,默认是包名或者由属性android:process指定
ComponentName service获得该Service的组件信息 包含了pkgname
/ servicename信息
PackageManger类
说明: 封装了对应用程序信息的操作
获得应用程序信息的的方法如下:
public abstractApplicationInfogetApplicationInfo(String
packageName, int flags)
参数:packagename 包名
flags 该ApplicationInfo是此flags标记,通常可以直接赋予常数0即可
功能:返回ApplicationInfo对象
关于PackageManger更多信息,请查看<Android中获取应用程序(包)的信息-----PackageManager的使用(一)>
Task任务的使用,我也就不在赘述了,大家可以仔细看下SDK,在此推荐一篇博客来帮助大家理解。
《Android系统的进程,任务,服务的信息》
Demo说明:
我们获取了系统里正在运行的服务信息,包括包名,图标,service类名等。为了达到Settings下应用程序模块中的
正在运行服务的效果,我们点击某一服务后,理论上来说是可以停止该服务的,但是由于权限permissions不够,可能报
SecurityException异常,导致应用程序发生异常。
关于权限不够的问题,可以分为两种:
1、 在AndroidManifest.xml文件中,为<activity/>或<service/>节点指定android:permission属性时,在其他进程中操作时,
需要声明该permission权限 。 具体可以参考下面这篇文章:
《android 自定义权限 permission》
2、系统权限,这个咱就没什么话说了。 可以参考下面这篇文章。
《android.uid.system获取系统权限 》
截图如下:(加上了水印,请谅解)
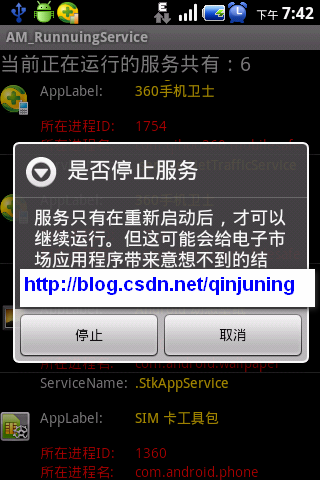
老规矩,资源文件不在贴了。 主工程逻辑如下:
package com.qin.runservice;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.ActivityManager;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.app.Dialog;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.ApplicationInfo;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager.NameNotFoundException;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Debug;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.ContextMenu;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
public class BrowseRunningServiceActivity extends Activity implements
OnItemClickListener {
private static String TAG = "RunServiceInfo";
private ActivityManager mActivityManager = null;
// ProcessInfo Model类 用来保存所有进程信息
private List<RunSericeModel> serviceInfoList = null;
private ListView listviewService;
private TextView tvTotalServiceNo;
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.browse_service_list);
listviewService = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listviewService);
listviewService.setOnItemClickListener(this);
tvTotalServiceNo = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tvTotalServiceNo);
// 获得ActivityManager服务的对象
mActivityManager = (ActivityManager) getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
// 获得正在运行的Service信息
getRunningServiceInfo();
// 对集合排序
Collections.sort(serviceInfoList, new comparatorServiceLable());
System.out.println(serviceInfoList.size() + "-------------");
// 为ListView构建适配器对象
BrowseRunningServiceAdapter mServiceInfoAdapter = new
BrowseRunningServiceAdapter(BrowseRunningServiceActivity.this, serviceInfoList);
listviewService.setAdapter(mServiceInfoAdapter);
tvTotalServiceNo.setText("当前正在运行的服务共有:" + serviceInfoList.size());
}
// 获得系统正在运行的进程信息
private void getRunningServiceInfo() {
// 设置一个默认Service的数量大小
int defaultNum = 20;
// 通过调用ActivityManager的getRunningAppServicees()方法获得系统里所有正在运行的进程
List<ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo> runServiceList = mActivityManager
.getRunningServices(defaultNum);
System.out.println(runServiceList.size());
// ServiceInfo Model类 用来保存所有进程信息
serviceInfoList = new ArrayList<RunSericeModel>();
for (ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo runServiceInfo : runServiceList) {
// 获得Service所在的进程的信息
int pid = runServiceInfo.pid; // service所在的进程ID号
int uid = runServiceInfo.uid; // 用户ID 类似于Linux的权限不同,ID也就不同 比如 root等
// 进程名,默认是包名或者由属性android:process指定
String processName = runServiceInfo.process;
// 该Service启动时的时间值
long activeSince = runServiceInfo.activeSince;
// 如果该Service是通过Bind方法方式连接,则clientCount代表了service连接客户端的数目
int clientCount = runServiceInfo.clientCount;
// 获得该Service的组件信息 可能是pkgname/servicename
ComponentName serviceCMP = runServiceInfo.service;
String serviceName = serviceCMP.getShortClassName(); // service 的类名
String pkgName = serviceCMP.getPackageName(); // 包名
// 打印Log
Log.i(TAG, "所在进程id :" + pid + " 所在进程名:" + processName + " 所在进程uid:"
+ uid + "\n" + " service启动的时间值:" + activeSince
+ " 客户端绑定数目:" + clientCount + "\n" + "该service的组件信息:"
+ serviceName + " and " + pkgName);
// 这儿我们通过service的组件信息,利用PackageManager获取该service所在应用程序的包名 ,图标等
PackageManager mPackageManager = this.getPackageManager(); // 获取PackagerManager对象;
try {
// 获取该pkgName的信息
ApplicationInfo appInfo = mPackageManager.getApplicationInfo(
pkgName, 0);
RunSericeModel runService = new RunSericeModel();
runService.setAppIcon(appInfo.loadIcon(mPackageManager));
runService.setAppLabel(appInfo.loadLabel(mPackageManager) + "");
runService.setServiceName(serviceName);
runService.setPkgName(pkgName);
// 设置该service的组件信息
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(serviceCMP);
runService.setIntent(intent);
runService.setPid(pid);
runService.setProcessName(processName);
// 添加至集合中
serviceInfoList.add(runService);
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
System.out.println("--------------------- error -------------");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// 触摸可停止
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int position,
long arg3) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
final Intent stopserviceIntent = serviceInfoList.get(position)
.getIntent();
new AlertDialog.Builder(BrowseRunningServiceActivity.this).setTitle(
"是否停止服务").setMessage(
"服务只有在重新启动后,才可以继续运行。但这可能会给电子市场应用程序带来意想不到的结果。")
.setPositiveButton("停止", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 停止该Service
//由于权限不够的问题,为了避免应用程序出现异常,捕获该SecurityException ,并弹出对话框
try {
stopService(stopserviceIntent);
} catch (SecurityException sEx) {
//发生异常 说明权限不够
System.out.println(" deny the permission");
new AlertDialog.Builder(BrowseRunningServiceActivity.this).setTitle(
"权限不够").setMessage("对不起,您的权限不够,无法停止该Service").create().show();
}
// 刷新界面
// 获得正在运行的Service信息
getRunningServiceInfo();
// 对集合排序
Collections.sort(serviceInfoList, new comparatorServiceLable());
// 为ListView构建适配器对象
BrowseRunningServiceAdapter mServiceInfoAdapter = new BrowseRunningServiceAdapter(
BrowseRunningServiceActivity.this,
serviceInfoList);
listviewService.setAdapter(mServiceInfoAdapter);
tvTotalServiceNo.setText("当前正在运行的服务共有:"
+ serviceInfoList.size());
}
}).setNegativeButton("取消",
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,
int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
dialog.dismiss(); // 取消对话框
}
}).create().show();
}
// 自定义排序 根据AppLabel排序
private class comparatorServiceLable implements Comparator<RunSericeModel> {
@Override
public int compare(RunSericeModel object1, RunSericeModel object2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return object1.getAppLabel().compareTo(object2.getAppLabel());
}
}
}
代码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/qinjuning/3846097
终于完成了这几块功能的介绍,这些功能的具体使用都挺类似的,最重要的是看你有没有耐心去把他们做出来。
作为一个小小程序员,我还是一步一步来做吧。。
分享到:





相关推荐
本篇文章将详细阐述如何使用`ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo`来获取Android设备上当前正在运行的服务信息。 `ActivityManager`是Android SDK提供的一个系统服务,它提供了对应用活动生命周期管理的功能,其中...
不过,自Android 3.1(API级别16)起,这个方法对非系统应用的访问被严重限制,因此不推荐在实际应用中使用。 2. `getRunningAppProcesses()`:此方法提供了一个列表,包含了系统中当前运行的所有应用进程的信息。`...
此外,我们还可以通过`getRunningServices(int maxNum)`方法获取正在运行的服务信息,这将返回一个`List<ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo>`,其中包含了服务的状态、启动次数等详细信息。 在实际开发中,这些...
一种可能的方法是利用`ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo`获取正在运行的服务信息,或者使用`ActivityManager.RunningTaskInfo`获取前台任务的信息。这些方法虽然不能提供完整的进程列表,但可以帮助开发者了解其...
1. 使用ActivityManager类:Android SDK提供了ActivityManager类,可以获取系统中运行的服务信息。首先需要在AndroidManifest.xml中添加读取运行服务权限: ```xml <uses-permission android:name="android....
在这个DEMO中,`ActivityManager`被用来获取运行中的服务列表,这是了解设备状态的关键。 3. **获取服务信息**: 要获取正在运行的服务信息,首先需要获得`ActivityManager`的实例,通常通过`Context....
`ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo`可能只显示正在运行服务的应用,而`UsageStatsManager`则依赖于用户对应用的使用记录,可能不包含所有后台运行的应用。 在提供的压缩包文件"GetRunApp"中,很可能包含了实现...
2. **获取运行服务**:同样地,`ActivityManager`的`getRunningServices()`方法可以用来获取正在运行的服务列表。每个`RunningServiceInfo`对象包含了服务的包名、类名、启动次数等信息。 3. **获取应用进程**:`...
在这个方法中,我们比较`RunningServiceInfo`中的服务类名与传入的`className`,如果匹配则返回`true`,表示服务正在运行。 最后,如果我们想要获取所有正在运行服务的名称,可以创建一个方法,遍历`serviceList`并...
- 使用`ActivityManager`中的`getRunningServices()`方法来获取当前正在运行的服务列表。 - 参数`100`表示返回最多100个服务的信息。 3. **遍历服务列表**: - 遍历获取到的服务列表,对于每一个`...
6. **ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo**: 包含运行中的服务详细信息,如服务名、服务是否前台服务、服务运行时间等。`ActivityManager.getRunningServices()`方法用于获取这些信息。 7. **ActivityManager....
要获取正在运行的服务,可以使用Android的`ActivityManager`类,它提供了获取系统服务状态的方法。例如,`getRunningServices(int maxNum)`方法可以返回一个`RunningServiceInfo`数组,包含了系统中所有正在运行的...
- **运行中的服务信息** (`ActivityManager.RunningServiceInfo`):展示当前系统中运行的所有服务的详细信息。 - **运行中的任务信息** (`ActivityManager.RunningTaskInfo`):提供关于当前运行的任务的信息。 ####...
这有助于了解设备上哪些服务正在消耗资源,从而可能影响用户体验或电池寿命。本文将详细介绍如何通过Android API来获取这些信息。 首先,我们需要知道在Android中,服务(Service)是一种可以在后台长时间运行的...
需要注意的是,从Android 6.0(API级别23)开始,获取运行服务和任务需要在运行时请求`GET_TASKS`权限。此外,由于安全和隐私原因,从Android 8.0(API级别26)开始,系统对`getRunningTasks()`和`...