Before we start to research tail recursion, let’s first have a look at the normal recursion. A simple factorial implementation by recursion:
function factorial(n){
if(n ===1) {
return 1;
}
return n *factorial(n -1);
}
Let N = 5, see how new stack frame is created for each time of recursive call:
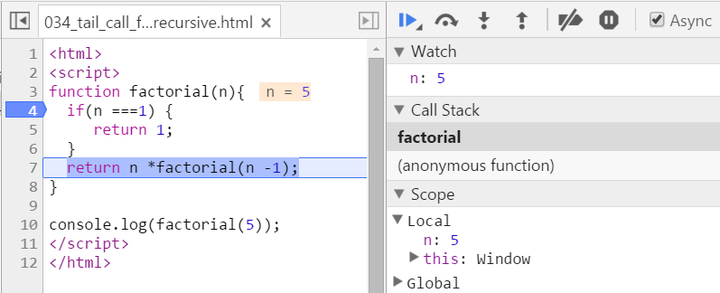
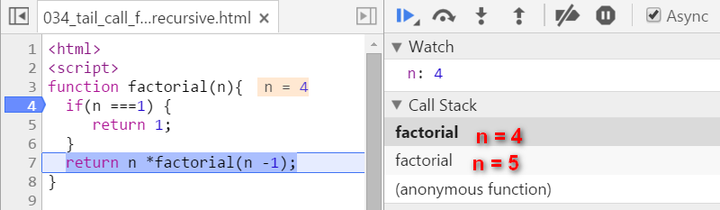
We have two stack frames now, one stores the context when n = 5, and the topmost one for current calculation: n = 4
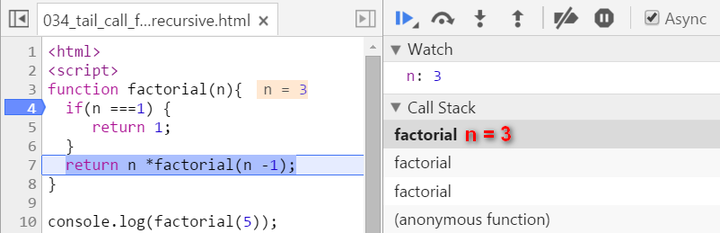
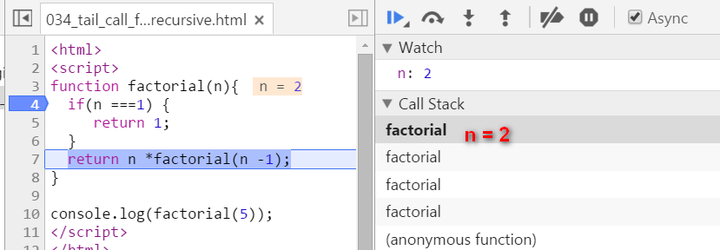
Now since n equals to 1, we stop recursion. The current stack frame ( n = 1 ) will be poped up, the frame under it will be activated and become the topmost frame, with calculated result 1 passed into.
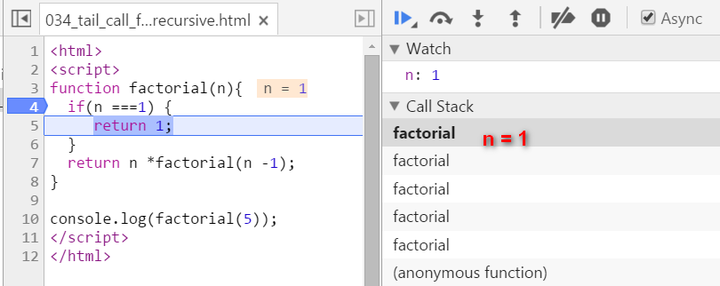
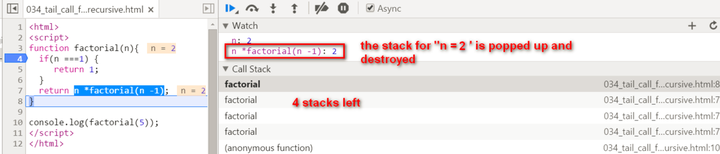
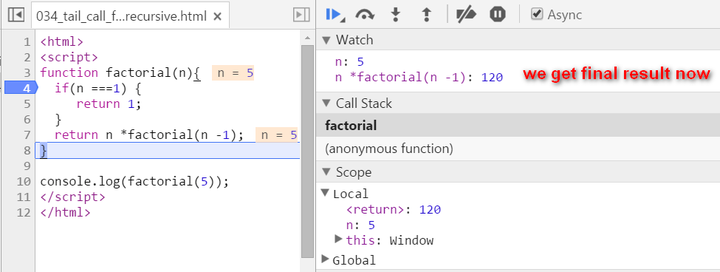
key note for normal recursion: during recursion, every generated stack frame is needed and could not e destroyed until the final result is calculated. The calculation is actually not started until the recursion reaches the end ( the condition n === 1 fulfills ). If N is a big integer, it will lead to huge number of stack frames and finally the “stack overflow” or “out of memory” is inevitable.
tail recursion
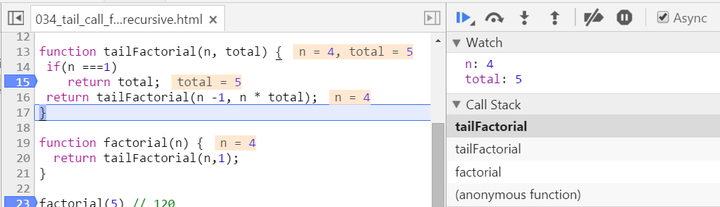
Source code below:
function tailFactorial(n, total) {
if(n ===1)
return total;
return tailFactorial(n -1, n * total);
}
function factorial2(n) {
return tailFactorial(n,1);
}
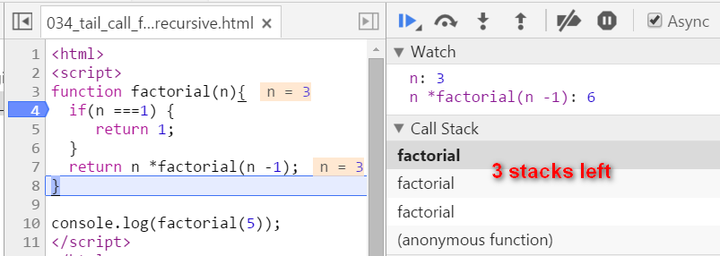
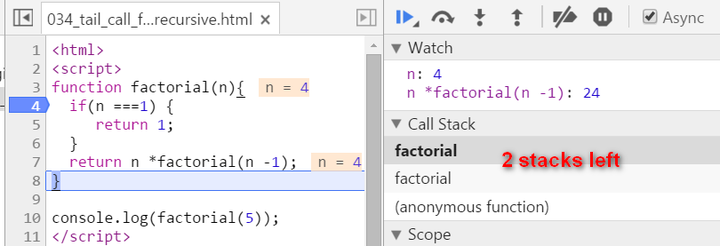
There are two biggest differences compared with normal recursion: (1) A new internal function tailFactorial is introduced here. (2) The calculation is actually now spread within every recursive stack frame. Each frame finishes one part of calculation and pass the current result to the next frame. Once the current stack frame finishes its task, it is actually not needed any more. And thus for example the model browser can then do some optimization on those useless stack frames. Observe the stack frame for tail recursion step by step:
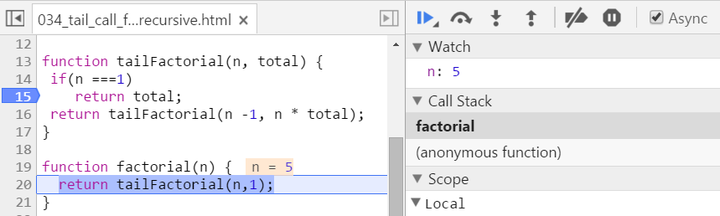
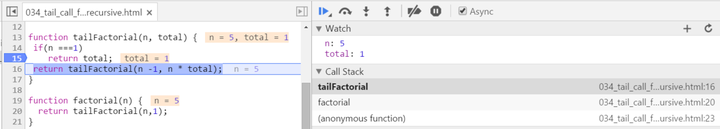
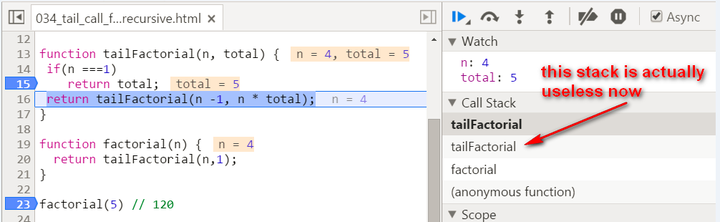
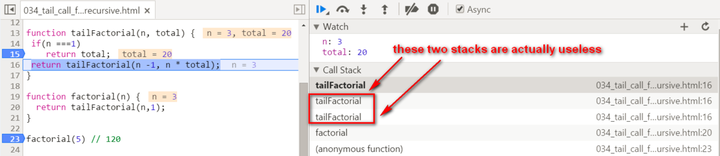
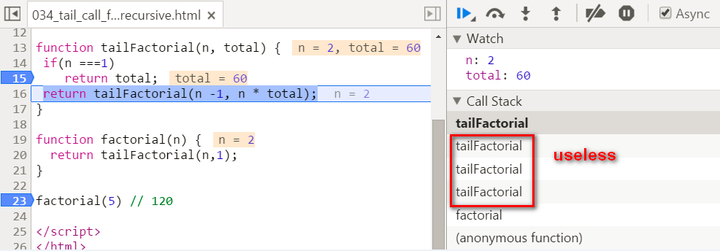
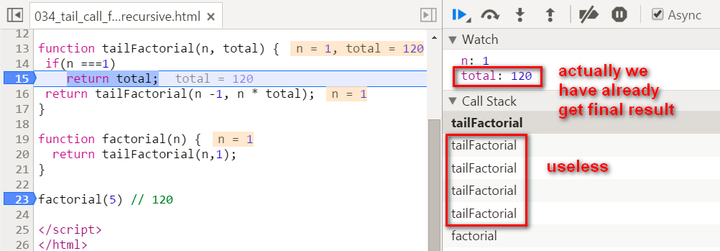
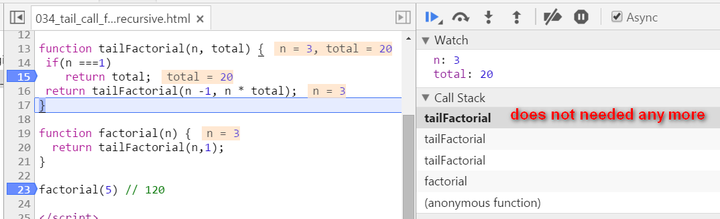
stack popped up:
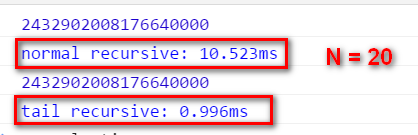
When N = 20, the tail recursion has a far better performance than the normal recursion:
Update 2016-01-11
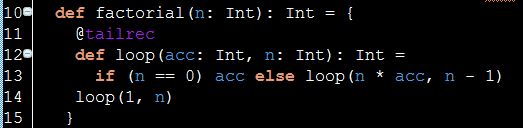
Tail recursion implementation via Scala:
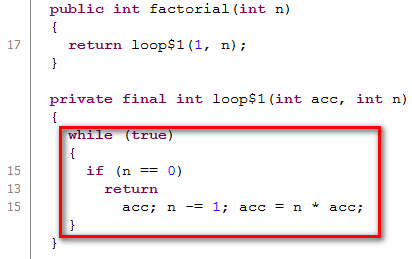
The interesting thing is, after the Scala code is compiled into Java Byte code, compiler will eliminate the recursion automatically:
Tail Recursion in ABAP
First this is the normal recursion:
REPORT zrecursion.
START-OF-SELECTION.
DATA: lv_result TYPE int4.
PERFORM fac USING 6 CHANGING lv_result.
WRITE: / lv_result.
FORM fac USING iv_n TYPE int4 CHANGING cv_result TYPE int4.
DATA: lv_n TYPE i.
cv_result = lv_n = iv_n.
lv_n = lv_n - 1.
IF lv_n > 1.
PERFORM fac USING lv_n CHANGING cv_result.
ENDIF.
IF lv_n = 1.
cv_result = cv_result * lv_n.
ELSE.
cv_result = cv_result * iv_n.
ENDIF.
ENDFORM.And here comes tail recursion version:
REPORT ztail.
START-OF-SELECTION.
DATA: lv_result TYPE int4.
PERFORM fac USING 5 1 CHANGING lv_result.
WRITE: / lv_result.
FORM fac USING iv_n TYPE int4 iv_acc TYPE int4 CHANGING cv_result TYPE int4.
DATA: lv_n TYPE i,
lv_accumulate TYPE i.
IF iv_n < 1.
cv_result = 1.
ELSEIF iv_n = 1.
cv_result = iv_acc * iv_n.
ELSEIF iv_n > 1.
lv_n = iv_n - 1.
lv_accumulate = iv_acc * iv_n.
PERFORM fac USING lv_n lv_accumulate CHANGING cv_result.
ENDIF.
ENDFORM.要获取更多Jerry的原创文章,请关注公众号"汪子熙":







相关推荐
### ABAP简单递归算法解析 #### 一、引言 ABAP(Advanced Business ...通过上述分析,我们不仅了解了递归算法的工作机制,也熟悉了ABAP中递归函数的实现方法,这对于进一步学习和应用ABAP编程具有重要意义。
本主题聚焦于“ABAP编程”与“JavaScript”的结合,探讨如何在SAP环境中集成这两种技术以构建更丰富的用户界面和交互体验。 一、ABAP基础 ABAP是SAP的核心编程语言,用于开发SAP模块,如财务、人力资源、供应链管理...
sap press doc 解压密码:abap_developer
ABAP 4.7引入了类和对象的概念,支持继承、封装和多态性,这使得代码可维护性和复用性大大提升。 5. 功能模块和库: 功能模块是预定义的程序单元,可以被其他程序调用。ABAP库则包含一组相关功能模块,用于特定的...
2. **生成Proxy代码**:在目标系统中,使用SE80事务码,通过“生成ABAP Proxy”功能,输入源系统的服务接口信息,自动生成对应的ABAP Proxy类和相关代码。 3. **编译与激活**:生成的Proxy代码需要在目标系统中进行...
在ABAP编程中,加密和解密是两个关键的安全操作,用于保护敏感数据不被未经授权的用户访问。本文将深入探讨ABAP环境下的加密和解密技术,以及如何在实际应用中实施这些技术。 首先,我们需要理解加密的基本原理。...
1. **递归查询**:通过在数据库层面使用递归SQL查询,逐级获取BOM的子组件,然后在ABAP代码中进行逻辑处理和展示。这种方法简单直接,但可能对数据库性能有影响。 2. **选择屏幕与用户输入**:用户可以选择要展开的...
作为ABAP的学习资料,"ABAP学习资料abap"包含了针对初学者和进阶者的全面教程,旨在帮助用户在三个月内掌握ABAP的基础到高级知识。 文档“ABAP三月通.doc”很可能包含以下关键知识点: 1. **ABAP概述**:介绍ABAP...
本手册旨在为初级学员提供SAP ABAP的基本知识和实践经验,帮助他们快速掌握ABAP语言的基本语法和开发技术。以下是本手册的知识点概要: 一、ABAP基础语法 * ABAP语言的基本结构和组成 * 变量声明和赋值 * 数据类型...
ABAP(Advanced Business Application Programming)是SAP公司开发的一种编程语言,主要用于开发和扩展SAP系统。Git是一种分布式版本控制系统,广泛用于软件开发中的代码管理。在这个“ABAP GIT 项目 AI SDK FOR ...
ABAP - Keyword Documentation This documentation describes the syntax and meaning of the keywords of the ABAP language and its object-oriented part ABAP Objects. Alongside this, language frameworks ...
在ABAP中,ALV(ABAP List Viewer)是一种强大的工具,用于显示和处理数据表。ALV提供了一种标准化的方式来展示表格数据,包括排序、过滤、分组和自定义列等功能,极大地简化了用户界面的开发。 标题“abap-ALV.rar...
abap tips abap tips abap tips abap tips abap tips
随着学习的深入,会涉及ABAP的数据存储,如数据库表(内部表和透明表)的创建和操作,以及如何使用ABAP的数据访问语法来与数据库交互。接着,将学习到ABAP报表编程,包括编写动态SQL和使用ABAP的Report程序来生成...
SAP ABAP 开发环境和开发工具介绍 SAP ABAP 开发环境和开发工具是 SAP 系统中最重要的组件之一,它提供了一个强大的开发平台,允许开发者创建、测试和部署 ABAP 程序。ABAP 是 SAP 系统中的主要编程语言,用于开发...
ABAP开发规范和命名规则是IBM提供的一套开发标准和命名惯例,为ABAP开发者提供了详细的开发指南和命名规则,以确保开发的程序代码质量和可读性。本文将对ABAP开发规范和命名规则进行详细的解释和说明。 一、文档...
它提供了可视化设计工具和组件模型,让开发者能快速构建用户界面,且无需深入HTML和JavaScript。 **ABAP Workbench** ABAP Workbench是SAP开发环境中的一组工具,用于创建、测试和调试ABAP程序。它包括SE38(用于...
- ABAP与数据库交互:学习使用ABAP SQL(Open SQL和Native SQL)与数据库进行高效交互。 - RFC(Remote Function Call):理解如何通过RFC调用其他系统的服务或函数。 通过这些文档的学习,你可以逐步建立起对...
标题和描述所涉及的知识点主要集中在ABAP语言在SAP系统中对数据库的操作和管理。由于这部分内容比较专业,我将尽量详细地阐述ABAP(Advanced Business Application Programming)逻辑数据库和数据库操作的概念和用法...
这个“ABAP中文帮助文档”包含了对ABAP基础、报表编写以及事务处理的详细指南,对于学习和理解ABAP编程至关重要。 在第一部分“ABAP/4基础”中,你将学习到: 1. **ABAP简介**:了解ABAP的历史、作用以及它在SAP...