Service是Android中四大组件之一,在Android开发中起到非常重要的作用,先来看一下官方对Service的定义:
AServiceis
an application component that can perform long-running operations in the background and does not provide a user interface. Another application component can start a service and it will continue to run in the background even if the user switches to another
application. Additionally, a component can bind to a service to interact with it and even perform interprocess communication (IPC). For example, a service might handle network transactions, play music, perform file I/O, or interact with a content provider,
all from the background.
翻译过来就是:Service(服务)是一个没有用户界面的在后台运行执行耗时操作的应用组件。其他应用组件能够启动Service,并且当用户切换到另外的应用场景,Service将持续在后台运行。另外,一个组件能够绑定到一个service与之交互(IPC机制),例如,一个service可能会处理网络操作,播放音乐,操作文件I/O或者与内容提供者(content
provider)交互,所有这些活动都是在后台进行。
Service有两种状态,“启动的”和“绑定”
Started
A service is "started" when an application component (such as an activity) starts it by callingstartService().
Once started, a service can run in the background indefinitely, even if the component that started it is destroyed. Usually, a started service performs a single operation and does not return a result to the caller. For example, it might download or upload
a file over the network. When the operation is done, the service should stop itself.
Bound
A service is "bound" when an application component binds to it by callingbindService().
A bound service offers a client-server interface that allows components to interact with the service, send requests, get results, and even do so across processes with interprocess communication (IPC). A bound service runs only as long as another application
component is bound to it. Multiple components can bind to the service at once, but when all of them unbind, the service is destroyed.
通过startService()启动的服务处于“启动的”状态,一旦启动,service就在后台运行,即使启动它的应用组件已经被销毁了。通常started状态的service执行单任务并且不返回任何结果给启动者。比如当下载或上传一个文件,当这项操作完成时,service应该停止它本身。
还有一种“绑定”状态的service,通过调用bindService()来启动,一个绑定的service提供一个允许组件与service交互的接口,可以发送请求、获取返回结果,还可以通过夸进程通信来交互(IPC)。绑定的service只有当应用组件绑定后才能运行,多个组件可以绑定一个service,当调用unbind()方法时,这个service就会被销毁了。
另外,在官方的说明文档中还有一个警告:
Caution:A service runs in the main thread of its hosting process—the service doesnotcreate its
own thread and doesnotrun in a separate process (unless you specify otherwise). This means that, if your service is going to do any CPU intensive work or blocking operations (such as MP3 playback or networking), you should create a new thread within the
service to do that work. By using a separate thread, you will reduce the risk of Application Not Responding (ANR) errors and the application's main thread can remain dedicated to user interaction with your activities.
意思是service与activity一样都存在与当前进程的主线程中,所以,一些阻塞UI的操作,比如耗时操作不能放在service里进行,比如另外开启一个线程来处理诸如网络请求的耗时操作。如果在service里进行一些耗CPU和耗时操作,可能会引发ANR警告,这时应用会弹出是强制关闭还是等待的对话框。所以,对service的理解就是和activity平级的,只不过是看不见的,在后台运行的一个组件,这也是为什么和activity同被说为Android的基本组件。
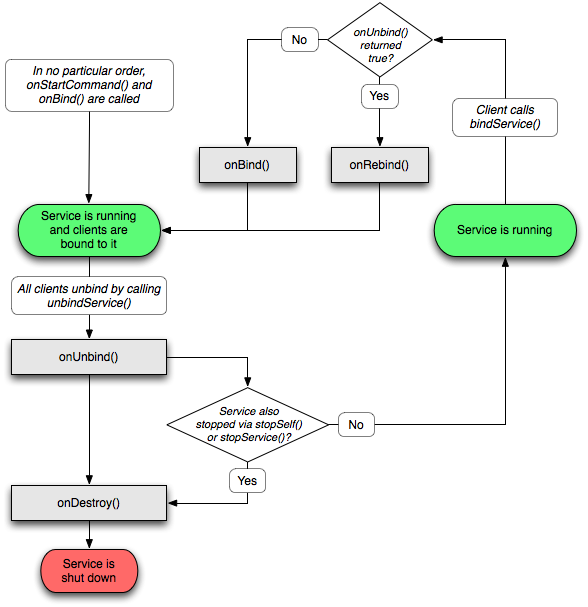
Service生命周期中的一些方法:

通过这个图可以看到,两种启动service的方式以及他们的生命周期,bind service的不同之处在于当绑定的组件销毁后,对应的service也就被kill了。service的声明周期相比与activity的简单了许多,只要好好理解两种启动service方式的异同就行。
service生命周期也涉及一些回调方法,这些方法都不用调用父类方法,具体如下:
public class ExampleService extends Service {
int mStartMode; // indicates how to behave if the service is killed
IBinder mBinder; // interface for clients that bind
boolean mAllowRebind; // indicates whether onRebind should be used
@Override
public void onCreate() {
// The service is being created
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// The service is starting, due to a call to startService()
return mStartMode;
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// A client is binding to the service with bindService()
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
// All clients have unbound with unbindService()
return mAllowRebind;
}
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
// A client is binding to the service with bindService(),
// after onUnbind() has already been called
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// The service is no longer used and is being destroyed
}
}
关于Service生命周期还有一张比较易懂的图(来源于网络)
另外,这里要说明Service的一个子类,IntentService,首先看下官方文档的说明:
IntentService
This is a subclass ofServicethat
uses a worker thread to handle all start requests, one at a time. This is the best option if you don't require that your service handle multiple requests simultaneously. All you need to do is implementonHandleIntent(),
which receives the intent for each start request so you can do the background work.
IntentService使用队列的方式将请求的Intent加入队列,然后开启一个worker thread(线程)来处理队列中的Intent,对于异步的startService请求,IntentService会处理完成一个之后再处理第二个,每一个请求都会在一个单独的worker
thread中处理,不会阻塞应用程序的主线程,这里就给我们提供了一个思路,如果有耗时的操作与其在Service里面开启新线程还不如使用IntentService来处理耗时操作。而在一般的继承Service里面如果要进行耗时操作就必须另开线程,但是使用IntentService就可以直接在里面进行耗时操作,因为默认实现了一个worker thread。对于异步的startService请求,IntentService会处理完成一个之后再处理第二个。
看下IntentService的具体实现:
public class HelloIntentService extends IntentService {
/**
* A constructor is required, and must call the super IntentService(String)
* constructor with a name for the worker thread.
*/
public HelloIntentService() {
super("HelloIntentService");
}
/**
* The IntentService calls this method from the default worker thread with
* the intent that started the service. When this method returns, IntentService
* stops the service, as appropriate.
*/
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
// Normally we would do some work here, like download a file.
// For our sample, we just sleep for 5 seconds.
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + 5*1000;
while (System.currentTimeMillis() < endTime) {
synchronized (this) {
try {
wait(endTime - System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
}
}
关于停止Service,如果service是非绑定的,最终当任务完成时,为了节省系统资源,一定要停止service,可以通过stopSelf()来停止,也可以在其他组件中通过stopService()来停止,绑定的service可以通过onUnBind()来停止service。
关于Service还有很多知识,这里就不再一一列举,可以参考http://developer.android.com/guide/components/services.html
欢迎关注我的新浪微博和我沟通:唐韧_Ryan
分享到:











相关推荐
在Android应用开发中,Service是四大组件之一,用于在后台执行长时间运行的操作,不与用户界面直接交互。在本篇文章中,我们将深入探讨Service的绑定服务(Bound Service)及其相关使用技巧。 首先,绑定服务是一种...
Android服务(Service)是Android操作系统中四个核心应用程序组件之一,其他三个分别是Activity、BroadcastReceiver和ContentProvider,它们在Android应用开发中的作用和使用场景各不相同。Service的作用主要体现在...
本文详细分析了Android中Service服务。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 一、Service简介 Service是Android中实现程序后台运行的解决方案,适用于去执行那些不需要和用户交互而且还要求长期运行的任务。Service是...
## Android服务Service详解 ### 8.1 Service起步 Service是Android应用程序组件的重要组成部分,它主要用于在后台执行任务,不依赖于用户界面。Service通常用于执行长时间运行的操作,如下载数据、播放音乐或处理...
【Android服务Service详解】 在Android应用开发中,Service是四大组件之一,用于执行长时间运行的任务,如后台音乐播放、网络数据下载等。Service不同于Activity,它没有用户界面,但可以在后台持续运行,即使用户...
《Android服务Service详解》 Android服务(Service)是Android应用程序四大组件之一,它主要负责在后台执行长时间运行的操作,而不显示用户界面。Service的使用场景广泛,如在后台下载文件、播放音乐等。本章将深入...
Android服务Service是一种在Android操作系统中应用广泛的服务组件,用于执行后台任务而不提供用户界面。Service作为Android四大组件之一(其他包括Activity、BroadcastReceiver和ContentProvider),在应用程序中...
在Android应用开发中,`Service`...理解并熟练使用`Service`是Android开发中的关键技能,正确使用服务可以提升应用性能和用户体验。在设计服务时,应充分考虑其生命周期、并发处理和资源管理,以实现高效、稳定的应用。
在Android开发中,Service是四大组件之一,它用于在后台执行长时间运行的操作,即使用户界面已经关闭。Service并不提供用户界面,而是专注于处理任务、播放音乐、与其他应用交互等。本篇文章将深入探讨如何在Android...
掌握Service的生命周期、服务的启动和绑定、IPC以及如何在Service中进行线程管理和GUI组件的更新等,是Android开发者必须具备的技能。通过这些知识点的学习和实践,开发者可以更好地构建高效、稳定并且能够满足用户...
Android系统提供了一系列系统服务,如LocationManager、PowerManager等,可以通过`Context.getSystemService()`方法获取这些服务,以便在Service中使用。 **8.2.2 在模拟器上模拟重力感应** 为了在没有物理传感器...
10.1 Service简介 374 10.1.1 创建、配置Service 374 10.1.2 启动和停止Service 376 10.1.3 绑定本地Service并与之 通信 377 10.1.4 Service的生命周期 381 10.2 跨进程调用Service (AIDL服务) ...
### Android各组件详解——Service深度解析 在深入探讨Service组件之前,我们首先简要回顾一下Android框架中的其他关键组件,尤其是ContentProvider。ContentProvider作为数据访问层,它提供了跨应用共享数据的能力...
在Android开发中,Service是一个至关重要的组件,它被设计用于在后台执行长时间运行的操作,即使用户与应用的其他部分(如Activity)交互时也是如此。Service不受用户界面的直接影响,这使得它成为处理音乐播放、...