There are two sorted arrays A and B of size m and n respectively. Find the median of the two sorted arrays. The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
Thoughts:
Find K/2th index from first array, call it i and K/2th index from the second, call it j. Now consider this:
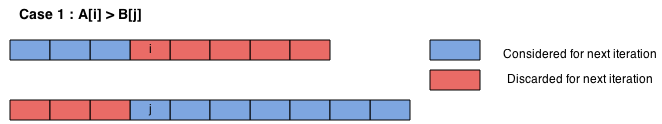
1. If A[i] > B[j], then Kth smallest element will include elements more than K/2 elements from array B and less than K/2 elements from array A. So our area of searching reduces to left part of K/2 index in array A and right part of k/2 index in array B, as shown in figure below.
Again since we have already found j definite smallest elements, we will reduce the search for (k-j)th smallest element in reduced search space.
2. Similarly, if A[i] < B[j], our search space reduces to right part of k/2 index in array A and left of K/2 elements of array B, as shown in figure below. Again since we have already found i definite smallest elements, we will reduce the search for (k-i)th smallest element in reduced search space.
 |
| Find Kth smallest in two sorted arrays |
So what will be the base case:
When K is one, then we return the minimum of A[K-1] and B[K-1] (considering the zero based indexing of array) or if one of the array becomes null then return the other array's Kth smallest element.
Solution 1:
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int A[], int B[]) {
int m = A.length, n = B.length;
if(((m+n)&1) == 1) {//m+n: odd
return findKth(A, 0, m-1, B, 0, n-1, (m+n)/2);
} else {
return (findKth(A,0,m-1,B,0,n-1,(m+n)/2)+findKth(A,0,m-1,B,0,n-1,(m+n)/2-1))/2.0;
}
}
public double findKth(int A[], int aStart, int aEnd, int B[], int bStart, int bEnd, int k) {
int aLen = aEnd - aStart + 1;
int bLen = bEnd - bStart + 1;
if(aLen == 0) return B[bStart+k];
if(bLen == 0) return A[aStart+k];
if(k == 0) return Math.min(A[aStart], B[bStart]);
int aMid = aLen*k/(aLen+bLen);
int bMid = k-aMid-1;
aMid += aStart;
bMid += bStart;
if(A[aMid] > B[bMid]) {
k = k - (bMid - bStart + 1);
aEnd = aMid;
bStart = bMid + 1;
} else {
k = k - (aMid - aStart + 1);
aStart = aMid + 1;
bEnd = bMid;
}
return findKth(A, aStart, aEnd, B, bStart, bEnd, k);
}
Complexity of code to find median of two sorted array with above algorithm is O(log (m+n)).
Soltion 2:
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int A[], int B[]) {
int n = A.length;
int m = B.length;
// the following call is to make sure len(A) <= len(B).
// yes, it calls itself, but at most once, shouldn't be
// consider a recursive solution
if (n > m)
return findMedianSortedArrays(B, A);
// now, do binary search
int k = (n + m - 1) / 2;
int l = 0, r = Math.min(k, n); // r is n, NOT n-1, this is important!!
while (l < r) {
int midA = (l + r) / 2;
int midB = k - midA;
if (A[midA] < B[midB])
l = midA + 1;
else
r = midA;
}
// after binary search, we almost get the median because it must be between
// these 4 numbers: A[l-1], A[l], B[k-l], and B[k-l+1]
// if (n+m) is odd, the median is the larger one between A[l-1] and B[k-l].
// and there are some corner cases we need to take care of.
int a = Math.max(l > 0 ? A[l - 1] : Integer.MIN_VALUE, k - l >= 0 ? B[k - l] : Integer.MIN_VALUE);
if (((n + m) & 1) == 1)
return (double) a;
// if (n+m) is even, the median can be calculated by
// median = (max(A[l-1], B[k-l]) + min(A[l], B[k-l+1]) / 2.0
// also, there are some corner cases to take care of.
int b = Math.min(l < n ? A[l] : Integer.MAX_VALUE, k - l + 1 < m ? B[k - l + 1] : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
return (a + b) / 2.0;
}
Solution 3:
int min(int a, int b) {
return a > b ? b : a;
}
int find_kth(int a[], int b[], int size_a, int size_b, int k){
/* to maintain uniformaty, we will assume that size_a is smaller than size_b
else we will swap array in call :) */
if(size_a > size_b) return find_kth(b, a, size_b, size_a, k);
/* Now case when size of smaller array is 0 i.e there is no elemt in one array*/
if(size_a == 0) return b[k-1]; // due to zero based index
/* case where K ==1 that means we have hit limit */
if(k == 1) return min(a[0], b[0]);
/* Now the divide and conquer part */
int i = min(size_a, k/2) ; // K should be less than the size of array
int j = min(size_b, k/2) ; // K should be less than the size of array
if(a[i-1] > b[j-1])
// Now we need to find only K-j th element
return find_kth(a, b+j, size_a, size_b-j, k-j);
else
return find_kth(a+i, b, size_a-i, size_b, k-i);
return -1;
}
double findMedianSortedArrays(int a[], int size_a, int b[], int size_b) {
int left = (size_a + size_b + 1) >>1;
int right = (size_a + size_b + 2) >>1;
return ( find_kth(a,b, size_a,size_b, left) + find_kth(a,b, size_a,size_b, right) )/2.0;
}
References:
http://www.algorithmsandme.com/2014/12/find-median-of-two-sorted-arrays-of.html
http://www.algorithmsandme.com/2014/12/fins-kth-smallest-element-in-two-sorted.html
https://oj.leetcode.com/discuss/11174/share-my-iterative-solution-with-o-log-min-n-m




.png)



相关推荐
java java_leetcode题解之Median of Two Sorted Arrays.java
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively. ...Find the median of the two sorted arrays. The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)). Java AC版本
c语言入门 c语言_leetcode题解04-median-of-two-sorted-arrays.c
js js_leetcode题解之4-median-of-two-sorted-arrays.js
java入门 java_leetcode题解之004_Median_of_Two_Sorted_Arrays
在LeetCode上,题目4(Median of Two Sorted Arrays)是一个经典的算法问题,旨在寻找两个已排序数组的中位数。中位数是将一组数值从小到大排列后处于中间位置的数,在奇数个数的情况下是中间的那个数,而在偶数个数...
leetcode 无法登录两个有序数组的中位数 问题 有两个大小分别为 m 和 n 的排序数组 nums1 和 nums2。求两个排序数组的中位数。 整体运行时间复杂度应该是 O(log (m+n))。 您可以假设 nums1 和 nums2 不能都为空。 ...
leetcode 接口 该项目可帮助您使用首选的 IDE 或带有命令行界面 (CLI) 的编辑器来执行 leetcode。 入门 ...leetcode ...leetcode ...two-sum leetcode ...median-of-two-sorted-arrays 然后问题描述和启动代码将自动
7. Median of Two Sorted Arrays in Java 两个排序数组的中位数是一个经典的数组问题,要求找到两个排序数组的中位数。可以使用归并排序或二分搜索来解决该问题。 8. Regular Expression Matching in Java 正则...
leetcode Python 001 力码 ├── Algorithms │ ├── cpp │ │ ├── 001 - Two Sum.cpp │ │ ├── 002 - Add Two Numbers.cpp │ │ ├── 003 - Longest Substring Without Repeating ...
leetcode题库 LeetCode-Go 理论基础 见Note 脑图 TODO 待填充 算法题 面试高频出现,以及一些非常经典重要的算法题优先 题目列表 No Title Link Solution Acceptance Difficulty Topics Solution 0001 Two Sum 46.1%...
5. 题目4:寻找两个有序数组的中位数 (Median of Two Sorted Arrays) 这是一个经典的二分查找问题,通过比较两个有序数组的大小,找到中间元素,可以采用分治法或者双指针法来解决。 6. 题目30:连接所有路径中的...
4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays 7. Reverse Integer 9. Palindrome Number 11. Container With Most Water 13. Roman to Integer 15. 3Sum 16. 3Sum Closest 17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number 18. 4Sum ...
#4:Median of Two Sorted Arrays 地图 #1:Two Sum #3:Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters #5:Longest Palindromic Substring 链表 #2:Add Two Numbers 分而治之 #53:Maximum Subarray 队列/集 #3:...
4.Median of Two Sorted Arrays 5.Longest Palindromic Substring (Manacher算法待完成) 6.ZigZag Conversion 7.Reverse Integer 8.String to Integer (atoi) 9.Palindrome Number 10.Regular Expression Matching ...
leetcode 2 Leetcode答案集 关于项目: 本项目包含本人LeetCode解题的答案,全部将由JavaScript语言进行解答。并会在每个题目的文件夹中添加相关的思路解析。 详情 # Title Solution Time Space Difficulty 1 Two ...
leetcode中国 LeetCode-Swift LeetCode算法题Swift实现 从2020年6月10日开始挑战每日刷算法,至少完成一道,让我们拭目以待! No. Title Chinese Difficulty Router 0001 Two Sum Easy 0002 Add Two Numbers Medium ...
leetcode分类LeetCodeSourceCodes###LeetCode1TowSum如果数组是有序的,O(n)的时间复杂度就可以解决了,现在是无序的,一开始要排一下序###LeetCode2MedianofTwoSortedArrays让用logn的时间复杂度,用了两个二分,...
leetcode 跳跃 LeetCode Solved by Python easy/middle/hard:15/36/5 1. Two Sum 两数之和 2. Add Two Numbers 两数相加 3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters 无重复字符的最长子串 4. Median of ...
文档内容目录显示了一系列问题编号和对应的题目,例如“Two Sum”,“Add Two Numbers”,“Median of Two Sorted Arrays”等,这些都是典型的算法和数据结构问题。这些问题涵盖了数组操作、字符串处理、递归、动态...