- 浏览: 185529 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 北京
-

文章分类
最新评论
在自定义 JToolTip 里面显示组件
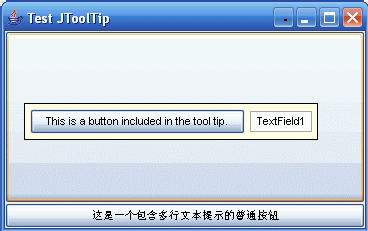
我们经常可以看到很多 Windows 程序显示出各种各样好看的工具栏提示, 不是默认的那种只有文字的提示... 但是 Java Swing 默认的那个, 似乎只有那个一行文字, well, how can we change it? 请参阅: JFC -- Chapter 24 - Building a Custom Component http://mail.phys-iasi.ro/Library/Computing/jfc_unleashed/ch24.htm
笔者基于文中的介绍写出了自己的解决方案. First, 写一个自定义的 ToolTipUI 来显示 JToolTip, 实现下列逻辑:
1. 如果没有在 JToolTip 中包含子组件(还记得嘛, 所有 JComponent 都是容器), 那么按照普通的模式显示 JToolTip, 稍微改进了一点, 就是可以显示多行的文字, 例如 "a\nb" 这样的文字就被显示为两行, 而不是默认的 JToolTip 显示的单行文本.
2. 如果包含了子组件, 就忽略设置的提示文本, 转而显示里面包含的组件, 这样就实现了在 JToolTip 中显示组件的功能. 源代码如下:
import java.awt.*;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.plaf.ComponentUI;
import javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicToolTipUI;
/**
* The ComponentToolTipUI class may be registered with the UIManager
* to replace the ToolTipUI for JToolTip instances. When used, it
* divides the ToolTip into multiple lines, if has child components,
* all child components will be displayed instead of only some tooltip
* text. Each line is divided by
* the '\ n' character.
* <p>
* @author Mike Foley
**/
public class ComponentToolTipUI extends BasicToolTipUI
{
/**
* The single shared UI instance.
**/
static ComponentToolTipUI sharedInstance = new ComponentToolTipUI();
/**
* The margin around the text.
**/
static final int MARGIN = 2;
/**
* The character to use in the StringTokenizer to
* separate lines in the ToolTip. This could be the
* system property end of line character.
**/
static final String lineSeparator = "\n";
/**
* MultiLineToolTipUI, constructor.
* <p>
* Have the constructor be protected so we can be subclassed,
* but not created by client classes.
**/
protected ComponentToolTipUI()
{
super();
}
/**
* Create the UI component for the given component.
* The same UI can be shared for all components, so
* return our shared instance.
* <p>
* @param c The component to create the UI for.
* @return Our shared UI component instance.
**/
public static ComponentUI createUI(JComponent c)
{
return sharedInstance;
}
/**
* Paint the ToolTip. Use the current font and colors
* set for the given component.
* <p>
* @param g The graphics to paint with.
* @param c The component to paint.
**/
public void paint(Graphics g, JComponent c)
{
// Paints each of the components in this container.
if(c.getComponentCount() > 0) {
c.paintComponents(g);
return;
}
// If no components, then paint a muiltiple line tooltip
//
// Determine the size for each row.
//
Font font = c.getFont();
FontMetrics fontMetrics = c.getFontMetrics(font);
int fontHeight = fontMetrics.getHeight();
int fontAscent = fontMetrics.getAscent();
//
// Paint the background in the tip color.
//
g.setColor(c.getBackground());
Dimension size = c.getSize();
g.fillRect(0, 0, size.width, size.height);
//
// Paint each line in the tip using the
// foreground color. Use a StringTokenizer
// to parse the ToolTip. Each line is left
// justified, and the y coordinate is updated
// through the loop.
//
g.setColor(c.getForeground());
int y = 2+fontAscent;
String tipText = ((JToolTip)c).getTipText();
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(tipText, lineSeparator);
int numberOfLines = tokenizer.countTokens();
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfLines; i++)
{
g.drawString(tokenizer.nextToken(), MARGIN, y);
y += fontHeight;
}
}
// paint
/**
* The preferred size for the ToolTip is the width of
* the longest row in the tip, and the height of a
* single row times the number of rows in the tip.
*
* @param c The component whose size is needed.
* @return The preferred size for the component.
**/
public Dimension getPreferredSize(JComponent c)
{
// If has children components
if(c.getComponentCount() > 0) {
return c.getLayout().preferredLayoutSize(c);
}
//
// Determine the size for each row.
//
Font font = c.getFont();
FontMetrics fontMetrics = c.getFontMetrics(font);
int fontHeight = fontMetrics.getHeight();
//
// Get the tip text string.
//
String tipText = ((JToolTip)c).getTipText();
//
// Empty tip, use a default size.
//
if (tipText == null)
return new Dimension(2 * MARGIN, 2 * MARGIN);
//
// Create a StringTokenizer to parse the ToolTip.
//
StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(tipText, lineSeparator);
int numberOfLines = tokenizer.countTokens();
//
// Height is number of lines times height of a single line.
//
int height = numberOfLines * fontHeight;
//
// Width is width of longest single line.
//
int width = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfLines; i++)
{
int thisWidth = fontMetrics.stringWidth(tokenizer.nextToken());
width = Math.max(width, thisWidth);
}
//
// Add the margin to the size, and return.
//
return (new Dimension(width + 2 * MARGIN, height + 2 * MARGIN));
}
// getPreferredSize
}
// ComponentToolTipUI
接着, 我们定义一个包含了其它组件的 JToolTip:
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class MyTooltip extends javax.swing.JToolTip
{
JButton jButton1 = new JButton();
FlowLayout flowLayout1 = new FlowLayout();
JTextField jTextField1 = new JTextField();
public MyTooltip()
{
try {
jbInit();
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void setTipText(String tipText) {
super.setTipText(tipText);
// button.setText(tipText);
}
private void jbInit() throws Exception {
// jLabel1.setMaximumSize(new Dimension(400, 300));
// jLabel1.setMinimumSize(new Dimension(400, 300));
// jLabel1.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(400, 300));
jButton1.setText("This is a button included in the tool tip.");
this.setLayout(flowLayout1);
this.setOpaque(true);
jTextField1.setText("jTextField1");
this.add(jButton1, null);
this.add(jTextField1, null);
}
}
最后, 我们编写一个测试类来测试这个 JToolTip:
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class MyButton extends javax.swing.JButton
{
public MyButton()
{
}
public JToolTip createToolTip() {
JToolTip tip = new MyTooltip();
tip.setComponent(this);
tip.setTipText(getToolTipText());
return tip;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(UIManager.getSystemLookAndFeelClassName());
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try
{
String multiLineToolTipUIClassName =
"ComponentToolTipUI";
// System.out.println(multiLineToolTipUIClassName);
UIManager.put( "ToolTipUI", multiLineToolTipUIClassName );
UIManager.put( multiLineToolTipUIClassName,
Class.forName( multiLineToolTipUIClassName ) );
}
catch( ClassNotFoundException cnfe )
{
System.err.println( "MultiLine ToolTip UI class not found" );
System.err.println( cnfe );
}
final JFrame frame = new JFrame("Test JToolTip");
frame.addWindowListener(new java.awt.event.WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
frame.dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
MyButton button = new MyButton();
button.setText("这个按钮显示一个包含组件的工具提示");
button.setToolTipText("提示");
frame.getContentPane().add(button);
JButton buttonPlain = new JButton("这是一个包含多行文本提示的普通按钮");
buttonPlain.setToolTipText("Line 1\nLine 2\n");
frame.getContentPane().add(java.awt.BorderLayout.SOUTH, buttonPlain);
// frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.pack();
frame.show();
}
}
编译并运行最后一个类: MyButton, 就可以看到包含了可以交互的按钮和文本框, 以及一个显示两行文本的工具栏提示。
发表评论
-
人民币转换数字
2012-11-07 15:14 1153该贴原因: ... -
个人收集的java精品网站
2012-05-30 08:19 0java进阶网 http://www.javady.com ... -
JVM(java 虚拟机)内存设置
2011-06-02 16:37 15223JVM(java 虚拟机)内存� ... -
汉字全半角转化程序
2011-02-25 08:52 1495转载一个牛人的。方便以后查看使用: 也许. 这个代码对很多人 ... -
md5JAVA实现
2010-06-07 22:43 1222MD5算法研究 MD5的� ... -
在Java中操作串口实现短信收发2
2010-06-07 22:08 14264.发送数据成功进行初� ... -
在Java中操作串口实现短信收发1
2010-06-07 22:06 1625在Java中操作串口实现短信收发 采用串口操作进行短信收发 ... -
JVM内存参数调优
2010-06-07 22:03 2007JVM内存参数调优 我们前面所提到的堆内存(heap)是由 ... -
多线程程序设计的要点
2010-06-07 22:00 872多线程中有主内存和工� ... -
Java 处理事务精要
2010-06-07 21:58 1007简单事务的概念 我 ... -
如何开公司及手续过程
2010-06-07 21:55 1237注册一个公司,首先想好经营什么,怎样经营好,再来注册。要不,注 ... -
运用加密技术保护Java源代码
2010-06-07 21:52 960Java程序的源代码很容易被别人偷看,只要有一个反编译器,任何 ... -
连接池的基本工作原理
2010-06-07 21:39 862连接池的基本工作原理 1、基本概念及原理 由上面的分析可以 ... -
高效的Java音乐播放类
2010-06-07 21:34 1553/** *//** * 自动播放,循环停止后结束。 ... -
高效的Java音乐播放类 2
2010-06-07 21:32 1217/** *//** * 直接播放url文件 * ... -
高效的Java音乐播放类
2010-06-07 21:26 1392Java音频播放,因为必须依赖到本地环境,所以JAVA在音频处 ... -
用开源的 InnoSetup 为 Java 应用制作 Windows 安装程序
2010-04-24 11:30 1703在这个例子里, 我将给大家展示如何使用 InnoSetup 自 ... -
Swing: 用 GlassPane 显示一个透明的正在操作框
2010-04-24 10:25 2047这个组件可以让用户看到界面里的显示但是无法操作. 需要的图: ... -
文本放大器
2010-04-24 10:06 1303/** * @(#)Text2Image.java 1.0 D ... -
JIDE的开源Swing组件
2010-04-24 09:57 9652虽然它们早就开源了(去年吧),我也是今天才看到,虽然目前也用不 ...






相关推荐
JToolTip 是 Java Swing 库提供的一个工具提示组件,用于在鼠标悬停或其他交互事件发生时显示文本提示信息。
#### (一)基本交互组件:获取用户的输入或者显示状态的简单组件 1. **按钮(JButton)**:这是一种常用的UI元素,允许用户通过点击来触发事件。它可以包含文本、图标或是两者结合,并支持快捷键的设置。开发人员...
- JToolTip:提供组件上的提示信息。 8. Swing的外观和感觉(LookAndFeel): Swing允许开发者改变应用程序的视觉风格,可以设置系统默认的LookAndFeel,也可以自定义LookAndFeel。 9. Swing应用实例: 通过...
6. 其他组件:如JOptionPane用于显示对话框,JProgressBar显示进度,JToolTip显示提示信息,JSlider控制滑块,JTable和JTree显示表格和树状数据。 Java GUI设计允许开发者构建复杂的交互式界面,结合事件处理,可以...
在Swing中,我们可以使用`JToolTip`类来实现,它会在鼠标停留在一个组件上一段时间后显示文本信息。JavaFX中,`Tooltip`类提供了类似的功能,允许设置延迟时间、显示时间和自定义样式。 `ProgressBar`是进度条,...
- `JToolTip` 显示鼠标悬停时的提示信息。 - `JProgressBar` 显示任务进度。 - `JSlider` 和 `JSpinner` 提供数值选择或调整。 - `JFileChooser` 和 `JColorChooser` 分别用于打开文件对话框和颜色选择对话框。 ...
它通常与其他组件关联,例如按钮或文本框,当鼠标悬停在这些组件上时,会显示额外的帮助信息。创建和设置`JToolTip`非常简单,可以使用`JComponent.setToolTipText(String text)`方法为组件添加提示文本。 2. JList...
我们可以创建一个自定义组件,如`JPanel`,并在其中实现绘图逻辑。 3. **JIamge.java**:这个文件可能包含了自定义的图像处理类,比如将生成的饼图保存为图像文件。在Java中,我们可以使用`java.awt.image....
此外,Swing还提供了一些不可编辑的显示组件,如JLabel、JProgressBar和JToolTip,以及可编辑的组件,如JColorChooser、JFileChooser、JTable和JTextArea。 Swing的一个显著特性是其可插拔的外观和感觉(Pluggable ...
- 显示组件:JLabel(标签)、JList(列表)、JComboBox(组合框)等,用于展示信息。 - 文本组件:JTextField(单行文本输入框)、JPasswordField(密码输入框)、JTextArea(多行文本区域)等,用于用户输入。 ...
5. **Uneditable Information Displays**:不可编辑的信息显示,如标签 (`JLabel`)、进度条 (`JProgressBar`) 和工具提示 (`JToolTip`)。 6. **Editable Displays of Formatted Information**:可编辑的信息显示,如...
在本文档中,我们将详细介绍 Swing 中的一些关键组件,包括 JTable、JTree、JList、JToolTip、JComboBox、JMenu、JTabbedPane、Border、JSlider 等,并通过具体的示例来展示它们的应用场景。 #### 二、JTable 示例...
这些导入语句引入了GUI组件所需的类库,如`Frame`用于创建主窗口,`TextField`用于输入和显示数据,`Button`用于创建按钮等。 3. **类定义**: ```java public class computer extends Frame { // 类体... } ...
Java Swing实例源码包,包括了JComboBox 、Border、JList、JMenu、JSlider、JTabbedPane、JTable、JToolTip、JTree等常用Swing组件的用法示例,对Java编写界面来说,Swing确实是个不错的选择,希望这些示例能让你更...
在网页开发中,提示框(Tooltips)是一种常见的交互元素,用于显示额外的信息,通常在用户鼠标悬停在某个元素上时出现。jQuery库提供了许多插件,使得创建具有箭头指示方向的提示框变得简单且高效。以下是一些优秀的...
SUN官方出的有关swing设计的样例,其中包括JTable的34个例子、JList的15个例子、JToolTip的4个例子、JComboBox的5个例子、JComboBox的6个例子、Border的3个例子、JSlider的4个例子。 都含源码,需要自己编译。