API:
public interface Future<V> {
/**
* Attempts to cancel execution of this task. This attempt will
* fail if the task has already completed, has already been cancelled,
* or could not be cancelled for some other reason. If successful,
* and this task has not started when <tt>cancel</tt> is called,
* this task should never run. If the task has already started,
* then the <tt>mayInterruptIfRunning</tt> parameter determines
* whether the thread executing this task should be interrupted in
* an attempt to stop the task.
*/
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this task was cancelled before it completed
* normally.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this task was cancelled before it completed
*/
boolean isCancelled();
/**
* Returns <tt>true</tt> if this task completed.
*
* Completion may be due to normal termination, an exception, or
* cancellation -- in all of these cases, this method will return
* <tt>true</tt>.
*
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this task completed
*/
boolean isDone();
/**
* Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then
* retrieves its result.
*
* @return the computed result
* @throws CancellationException if the computation was cancelled
* @throws ExecutionException if the computation threw an
* exception
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
*/
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
/**
* Waits if necessary for at most the given time for the computation
* to complete, and then retrieves its result, if available.
*
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument
* @return the computed result
* @throws CancellationException if the computation was cancelled
* @throws ExecutionException if the computation threw an
* exception
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
* @throws TimeoutException if the wait timed out
*/
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
}
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
<T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result);
Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
...
}
public class FutureTask<V> extends Object
implements Future<V>, Runnable {
FutureTask(Callable<V> callable)
//创建一个 FutureTask,一旦运行就执行给定的 Callable。
FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result)
//创建一个 FutureTask,一旦运行就执行给定的 Runnable,并安排成功完成时 get 返回给定的结果 。
}
/*参数:
runnable - 可运行的任务。
result - 成功完成时要返回的结果。
如果不需要特定的结果,则考虑使用下列形式的构造:Future<?> f = new FutureTask<Object>(runnable, null) */
单独使用Runnable时:
无法获得返回值
单独使用Callable时:
无法在新线程中(new Thread(Runnable r))使用,只能使用ExecutorService
Thread类只支持Runnable
FutureTask:
实现了Runnable和Future,所以兼顾两者优点
既可以使用ExecutorService,也可以使用Thread
Callable pAccount = new PrivateAccount(); FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(pAccount); // 使用futureTask创建一个线程 Thread thread = new Thread(futureTask); thread.start();
=================================================================
public interface Future<V> Future 表示异步计算的结果。
Future有个get方法而获取结果只有在计算完成时获取,否则会一直阻塞直到任务转入完成状态,然后会返回结果或者抛出异常。
Future 主要定义了5个方法:
1)boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning):试图取消对此任务的执行。如果任务已完成、或已取消,或者由于某些其他原因而无法取消,则此尝试将失败。当调用 cancel 时,如果调用成功,而此任务尚未启动,则此任务将永不运行。如果任务已经启动,则 mayInterruptIfRunning 参数确定是否应该以试图停止任务的方式来中断执行此任务的线程。此方法返回后,对 isDone() 的后续调用将始终返回 true。如果此方法返回 true,则对 isCancelled() 的后续调用将始终返回 true。
2)boolean isCancelled():如果在任务正常完成前将其取消,则返回 true。
3)boolean isDone():如果任务已完成,则返回 true。 可能由于正常终止、异常或取消而完成,在所有这些情况中,此方法都将返回 true。
4)V get()throws InterruptedException,ExecutionException:如有必要,等待计算完成,然后获取其结果。
5)V get(long timeout,TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException,ExecutionException,TimeoutException:如有必要,最多等待为使计算完成所给定的时间之后,获取其结果(如果结果可用)。
6)finishCompletion()该方法在任务完成(包括异常完成、取消)后调用。删除所有正在get获取等待的节点且唤醒节点的线程。和调用done方法和置空callable.
CompletionService接口能拿到按完成顺序拿到一组线程池中所有线程,依靠的就是FutureTask中的finishCompletion()方法。
/**
该方法在任务完成(包括异常完成、取消)后调用。删除所有正在get获取等待的节点且唤醒节点的线程。和调用done方法和置空callable.
**/
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
public class FutureTask<V> extends Object implements Future<V>, RunnableFuture是一个接口, FutureTask类是Future 的一个实现类,并实现了Runnable,因此FutureTask可以传递到线程对象Thread中新建一个线程执行。所以可通过Excutor(线程池) 来执行,也可传递给Thread对象执行。如果在主线程中需要执行比较耗时的操作时,但又不想阻塞主线程时,可以把这些作业交给Future对象在后台完成,当主线程将来需要时,就可以通过Future对象获得后台作业的计算结果或者执行状态。
FutureTask是为了弥补Thread的不足而设计的,它可以让程序员准确地知道线程什么时候执行完成并获得到线程执行完成后返回的结果(如果有需要)。
FutureTask是一种可以取消的异步的计算任务。它的计算是通过Callable实现的,它等价于可以携带结果的Runnable,并且有三个状态:等待、运行和完成。完成包括所有计算以任意的方式结束,包括正常结束、取消和异常。
Executor框架利用FutureTask来完成异步任务,并可以用来进行任何潜在的耗时的计算。一般FutureTask多用于耗时的计算,主线程可以在完成自己的任务后,再去获取结果。
FutureTask多用于耗时的计算,主线程可以在完成自己的任务后,再去获取结果。
JDK:
此类提供了对 Future 的基本实现。仅在计算完成时才能检索结果;如果计算尚未完成,则阻塞 get 方法。一旦计算完成,就不能再重新开始或取消计算。
可使用 FutureTask 包装 Callable 或 Runnable 对象。因为 FutureTask 实现了 Runnable,所以可将 FutureTask 提交给 Executor 执行。
//构造方法摘要
FutureTask(Callable<V> callable)
//创建一个 FutureTask,一旦运行就执行给定的 Callable。
FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result)
//创建一个 FutureTask,一旦运行就执行给定的 Runnable,并安排成功完成时 get 返回给定的结果 。
//参数:
runnable - 可运行的任务。
result - 成功完成时要返回的结果。
如果不需要特定的结果,则考虑使用下列形式的构造:Future<?> f = new FutureTask<Object>(runnable, null)
Example1:
下面的例子模拟一个会计算账的过程,主线程已经获得其他帐户的总额了,为了不让主线程等待 PrivateAccount类的计算结果的返回而启用新的线程去处理, 并使用 FutureTask对象来监控,这样,主线程还可以继续做其他事情, 最后需要计算总额的时候再尝试去获得privateAccount 的信息。
package test;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
/**
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class FutureTaskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化一个Callable对象和FutureTask对象
Callable pAccount = new PrivateAccount();
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(pAccount);
// 使用futureTask创建一个线程
Thread pAccountThread = new Thread(futureTask);
System.out.println("futureTask线程现在开始启动,启动时间为:" + System.nanoTime());
pAccountThread.start();
System.out.println("主线程开始执行其他任务");
// 从其他账户获取总金额
int totalMoney = new Random().nextInt(100000);
System.out.println("现在你在其他账户中的总金额为" + totalMoney);
System.out.println("等待私有账户总金额统计完毕...");
// 测试后台的计算线程是否完成,如果未完成则等待
while (!futureTask.isDone()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("私有账户计算未完成继续等待...");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("futureTask线程计算完毕,此时时间为" + System.nanoTime());
Integer privateAccountMoney = null;
try {
privateAccountMoney = (Integer) futureTask.get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("您现在的总金额为:" + totalMoney + privateAccountMoney.intValue());
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("all")
class PrivateAccount implements Callable {
Integer totalMoney;
@Override
public Object call() throws Exception {
Thread.sleep(5000);
totalMoney = new Integer(new Random().nextInt(10000));
System.out.println("您当前有" + totalMoney + "在您的私有账户中");
return totalMoney;
}
}
运行结果

- 来源:
public class FutureTaskSample {
static FutureTask<String> future = new FutureTask(new Callable<String>(){
public String call(){
return getPageContent();
}
});
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException{
//Start a thread to let this thread to do the time exhausting thing
new Thread(future).start();
//Main thread can do own required thing first
doOwnThing();
//At the needed time, main thread can get the result
System.out.println(future.get());
}
public static String doOwnThing(){
return "Do Own Thing";
}
public static String getPageContent(){
return "Callable method...";
}
}
结果为:Callable method...不科学啊,为毛??!
public class FutureTaskSample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException{
//Start a thread to let this thread to do the time exhausting thing
Callable call = new MyCallable();
FutureTask future = new FutureTask(call);
new Thread(future).start();
//Main thread can do own required thing first
//doOwnThing();
System.out.println("Do Own Thing");
//At the needed time, main thread can get the result
System.out.println(future.get());
}
}
class MyCallable implements Callable<String>{
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
return getPageContent();
}
public String getPageContent(){
return "Callable method...";
}
}
结果:
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class Changgong implements Callable<Integer>{
private int hours=12;
private int amount;
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
while(hours>0){
System.out.println("I'm working......");
amount ++;
hours--;
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
return amount;
}
}
public class Dizhu {
public static void main(String args[]){
Changgong worker = new Changgong();
FutureTask<Integer> jiangong = new FutureTask<Integer>(worker);
new Thread(jiangong).start();
while(!jiangong.isDone()){
try {
System.out.println("看长工做完了没...");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
int amount;
try {
amount = jiangong.get();
System.out.println("工作做完了,上交了"+amount);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
I'm working......
看工人做完了没...
工作做完了,上交了12
/**
* Factory and utility methods for {@link Executor}, {@link
* ExecutorService}, {@link ScheduledExecutorService}, {@link
* ThreadFactory}, and {@link Callable} classes defined in this
* package. This class supports the following kinds of methods:
*
* <ul>
* <li> Methods that create and return an {@link ExecutorService}
* set up with commonly useful configuration settings.
* <li> Methods that create and return a {@link ScheduledExecutorService}
* set up with commonly useful configuration settings.
* <li> Methods that create and return a "wrapped" ExecutorService, that
* disables reconfiguration by making implementation-specific methods
* inaccessible.
* <li> Methods that create and return a {@link ThreadFactory}
* that sets newly created threads to a known state.
* <li> Methods that create and return a {@link Callable}
* out of other closure-like forms, so they can be used
* in execution methods requiring <tt>Callable</tt>.
* </ul>
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Doug Lea
*/
public class Executors {
/**
* Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads
* operating off a shared unbounded queue. At any point, at most
* <tt>nThreads</tt> threads will be active processing tasks.
* If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active,
* they will wait in the queue until a thread is available.
* If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution
* prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to
* execute subsequent tasks. The threads in the pool will exist
* until it is explicitly {@link ExecutorService#shutdown shutdown}.
*
* @param nThreads the number of threads in the pool
* @return the newly created thread pool
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if <tt>nThreads <= 0</tt>
*/
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
/**
* Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads
* operating off a shared unbounded queue, using the provided
* ThreadFactory to create new threads when needed. At any point,
* at most <tt>nThreads</tt> threads will be active processing
* tasks. If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are
* active, they will wait in the queue until a thread is
* available. If any thread terminates due to a failure during
* execution prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if
* needed to execute subsequent tasks. The threads in the pool will
* exist until it is explicitly {@link ExecutorService#shutdown
* shutdown}.
*
* @param nThreads the number of threads in the pool
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when creating new threads
* @return the newly created thread pool
* @throws NullPointerException if threadFactory is null
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if <tt>nThreads <= 0</tt>
*/
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}
/**
* Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread operating
* off an unbounded queue. (Note however that if this single
* thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to
* shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute
* subsequent tasks.) Tasks are guaranteed to execute
* sequentially, and no more than one task will be active at any
* given time. Unlike the otherwise equivalent
* <tt>newFixedThreadPool(1)</tt> the returned executor is
* guaranteed not to be reconfigurable to use additional threads.
*
* @return the newly created single-threaded Executor
*/
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
/**
* Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread operating
* off an unbounded queue, and uses the provided ThreadFactory to
* create a new thread when needed. Unlike the otherwise
* equivalent <tt>newFixedThreadPool(1, threadFactory)</tt> the
* returned executor is guaranteed not to be reconfigurable to use
* additional threads.
*
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when creating new
* threads
*
* @return the newly created single-threaded Executor
* @throws NullPointerException if threadFactory is null
*/
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory));
}
/**
* Creates a thread pool that creates new threads as needed, but
* will reuse previously constructed threads when they are
* available. These pools will typically improve the performance
* of programs that execute many short-lived asynchronous tasks.
* Calls to <tt>execute</tt> will reuse previously constructed
* threads if available. If no existing thread is available, a new
* thread will be created and added to the pool. Threads that have
* not been used for sixty seconds are terminated and removed from
* the cache. Thus, a pool that remains idle for long enough will
* not consume any resources. Note that pools with similar
* properties but different details (for example, timeout parameters)
* may be created using {@link ThreadPoolExecutor} constructors.
*
* @return the newly created thread pool
*/
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
/**
* Creates a thread pool that creates new threads as needed, but
* will reuse previously constructed threads when they are
* available, and uses the provided
* ThreadFactory to create new threads when needed.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when creating new threads
* @return the newly created thread pool
* @throws NullPointerException if threadFactory is null
*/
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(),
threadFactory);
}
/**
* Creates a single-threaded executor that can schedule commands
* to run after a given delay, or to execute periodically.
* (Note however that if this single
* thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to
* shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute
* subsequent tasks.) Tasks are guaranteed to execute
* sequentially, and no more than one task will be active at any
* given time. Unlike the otherwise equivalent
* <tt>newScheduledThreadPool(1)</tt> the returned executor is
* guaranteed not to be reconfigurable to use additional threads.
* @return the newly created scheduled executor
*/
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService
(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1));
}
/**
* Creates a single-threaded executor that can schedule commands
* to run after a given delay, or to execute periodically. (Note
* however that if this single thread terminates due to a failure
* during execution prior to shutdown, a new one will take its
* place if needed to execute subsequent tasks.) Tasks are
* guaranteed to execute sequentially, and no more than one task
* will be active at any given time. Unlike the otherwise
* equivalent <tt>newScheduledThreadPool(1, threadFactory)</tt>
* the returned executor is guaranteed not to be reconfigurable to
* use additional threads.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when creating new
* threads
* @return a newly created scheduled executor
* @throws NullPointerException if threadFactory is null
*/
public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new DelegatedScheduledExecutorService
(new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, threadFactory));
}
/**
* Creates a thread pool that can schedule commands to run after a
* given delay, or to execute periodically.
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool,
* even if they are idle.
* @return a newly created scheduled thread pool
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if <tt>corePoolSize < 0</tt>
*/
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
/**
* Creates a thread pool that can schedule commands to run after a
* given delay, or to execute periodically.
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool,
* even if they are idle.
* @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor
* creates a new thread.
* @return a newly created scheduled thread pool
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if <tt>corePoolSize < 0</tt>
* @throws NullPointerException if threadFactory is null
*/
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(
int corePoolSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, threadFactory);
}
........
/** Cannot instantiate. */
private Executors() {}
}
================================================================================- 类继承结构
- 核心成员变量
- 内部状态转换
- 核心方法解析
1 类继承结构
首先我们看一下FutureTask的继承结构:


FutureTask实现了RunnableFuture接口,而RunnableFuture继承了Runnable和Future,也就是说FutureTask既是Runnable,也是Future。
2 核心成员变量
FutureTask内部定义了以下变量,以及它们的含义如下
- volatile int state:表示对象状态,volatile关键字保证了内存可见性。futureTask中定义了7种状态,代表了7种不同的执行状态
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
private static final int NEW = 0; //任务新建和执行中
private static final int COMPLETING = 1; //任务将要执行完毕
private static final int NORMAL = 2; //任务正常执行结束
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3; //任务异常
private static final int CANCELLED = 4; //任务取消
private static final int INTERRUPTING = 5; //任务线程即将被中断
private static final int INTERRUPTED = 6; //任务线程已中断
|
- Callable<V> callable:被提交的任务
- Object outcome:任务执行结果或者任务异常
- volatile Thread runner:执行任务的线程
- volatile WaitNode waiters:等待节点,关联等待线程
- long stateOffset:state字段的内存偏移量
- long runnerOffset:runner字段的内存偏移量
- long waitersOffset:waiters字段的内存偏移量
后三个字段是配合Unsafe类做CAS操作使用的。
3 内部状态转换
FutureTask中使用state表示任务状态,state值变更的由CAS操作保证原子性。
FutureTask对象初始化时,在构造器中把state置为为NEW,之后状态的变更依据具体执行情况来定。
例如任务执行正常结束前,state会被设置成COMPLETING,代表任务即将完成,接下来很快就会被设置为NARMAL或者EXCEPTIONAL,这取决于调用Runnable中的call()方法是否抛出了异常。有异常则后者,反之前者。
任务提交后、任务结束前取消任务,那么有可能变为CANCELLED或者INTERRUPTED。在调用cancel方法时,如果传入false表示不中断线程,state会被置为CANCELLED,反之state先被变为INTERRUPTING,后变为INTERRUPTED。
总结下,FutureTask的状态流转过程,可以出现以下四种情况:
1. 任务正常执行并返回。 NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL
2. 执行中出现异常。NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL
3. 任务执行过程中被取消,并且不响应中断。NEW -> CANCELLED
4. 任务执行过程中被取消,并且响应中断。 NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED
4 核心方法解析
接下来我们一起扒一扒FutureTask的源码。我们先看一下任务线程是怎么执行的。当任务被提交到线程池后,会执行futureTask的run()方法。
1 public void run()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public void run() {<br> // 校验任务状态
if (state != NEW || !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;<br> // double check
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;
boolean ran;
try {<br> //执行业务代码
result = c.call();
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);
}
if (ran)
set(result);
}
} finally {<br> // 重置runner
runner = null;
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
|
翻译一下,这个方法经历了以下几步
- 校验当前任务状态是否为NEW以及runner是否已赋值。这一步是防止任务被取消。
- double-check任务状态state
- 执行业务逻辑,也就是c.call()方法被执行
- 如果业务逻辑异常,则调用setException方法将异常对象赋给outcome,并且更新state值
- 如果业务正常,则调用set方法将执行结果赋给outcome,并且更新state值
我们继续往下看,setException(Throwable t)和set(V v) 具体是怎么做的
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
protected void set(V v) {
// state状态 NEW->COMPLETING
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
// COMPLETING -> NORMAL 到达稳定状态
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL);
// 一些结束工作
finishCompletion();
}
}
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
// state状态 NEW->COMPLETING
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = t;
// COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL 到达稳定状态
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL);
// 一些结束工作
finishCompletion();
}
} |
code中的注释已经写的很清楚,故不翻译了。状态变更的原子性由unsafe对象提供的CAS操作保证。FutureTask的outcome变量存储执行结果或者异常对象,会由主线程返回。
2 get()和get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
任务由线程池提供的线程执行,那么这时候主线程则会阻塞,直到任务线程唤醒它们。我们通过get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)方法看看是怎么做的
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}
|
get的源码很简洁,首先校验参数,然后根据state状态判断是否超时,如果超时则异常,不超时则调用report(s)去获取最终结果。
当 s<= COMPLETING时,表明任务仍然在执行且没有被取消。如果它为true,那么走到awaitDone方法。
awaitDone是futureTask实现阻塞的关键方法,我们重点关注一下它的实现原理。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
/** * 等待任务执行完毕,如果任务取消或者超时则停止
* @param timed 为true表示设置超时时间
* @param nanos 超时时间
* @return 任务完成时的状态
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
// 任务截止时间
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
// 自旋
for (;;) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
//线程中断则移除等待线程,并抛出异常
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) {
// 任务可能已经完成或者被取消了
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
}
else if (s == COMPLETING)
// 可能任务线程被阻塞了,主线程让出CPU
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
// 等待线程节点为空,则初始化新节点并关联当前线程
q = new WaitNode();
else if (!queued)
// 等待线程入队列,成功则queued=true
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);
else if (timed) {
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) {
//已经超时的话,移除等待节点
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
// 未超时,将当前线程挂起指定时间
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos);
}
else
// timed=false时会走到这里,挂起当前线程
LockSupport.park(this);
}
} |
注释里也很清楚的写明了每一步的作用,我们以设置超时时间为例,总结一下过程
- 计算deadline,也就是到某个时间点后如果还没有返回结果,那么就超时了。
- 进入自旋,也就是死循环。
- 首先判断是否响应线程中断。对于线程中断的响应往往会放在线程进入阻塞之前,这里也印证了这一点。
- 判断state值,如果>COMPLETING表明任务已经取消或者已经执行完毕,就可以直接返回了。
- 如果任务还在执行,则为当前线程初始化一个等待节点WaitNode,入等待队列。这里和AQS的等待队列类似,只不过Node只关联线程,而没有状态。AQS里面的等待节点是有状态的。
- 计算nanos,判断是否已经超时。如果已经超时,则移除所有等待节点,直接返回state。超时的话,state的值仍然还是COMPLETING。
- 如果还未超时,就通过LockSupprot类提供的方法在指定时间内挂起当前线程,等待任务线程唤醒或者超时唤醒。
当线程被挂起之后,如果任务线程执行完毕,就会唤醒等待线程哦。这一步就是在finishCompletion里面做的,前面已经提到这个方法。我们再看看这个方法具体做了哪些事吧~
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
/** * 移除并唤醒所有等待线程,执行done,置空callable
* nulls out callable.
*/
private void finishCompletion() {
//遍历等待节点
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (;;) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
//唤醒等待线程
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
// unlink to help gc
q.next = null;
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
//模板方法,可以被覆盖
done();
//清空callable
callable = null;
} |
由代码和注释可以看出来,这个方法的作用主要在于唤醒等待线程。由前文可知,当任务正常结束或者异常时,都会调用finishCompletion去唤醒等待线程。这个时候,等待线程就可以醒来,开开心心的获得结果啦。
最后我们看一下任务取消
3 public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning)
注意,取消操作不一定会起作用,这里我们先贴个demo
1 public class FutureDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ThreadPoolExecutor executorService = (ThreadPoolExecutor) Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1); 4 // 预创建线程 5 executorService.prestartCoreThread(); 6 7 Future future = executorService.submit(new Callable<Object>() { 8 @Override 9 public Object call() { 10 System.out.println("start to run callable"); 11 Long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); 12 while (true) { 13 Long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); 14 if ((current - start) > 1000) { 15 System.out.println("当前任务执行已经超过1s"); 16 return 1; 17 } 18 } 19 } 20 }); 21 22 System.out.println(future.cancel(false)); 23 24 try { 25 Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000); 26 executorService.shutdown(); 27 } catch (Exception e) { 28 //NO OP 29 } 30 } 31 }
我们多次测试后发现,出现了2种打印结果,如图
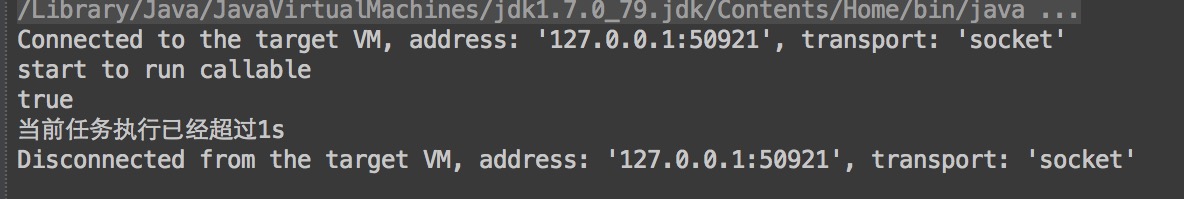
结果1

结果2
第一种是任务压根没取消,第二种则是任务压根没提交成功。
方法签名注释告诉我们,取消操作是可能会失败的,如果当前任务已经结束或者已经取消,则当前取消操作会失败。如果任务尚未开始,那么任务不会被执行。这就解释了出现上图结果2的情况。我们还是从源码去分析cancel()究竟做了哪些事。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (state != NEW)
return false;
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, INTERRUPTING))
return false;
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED); // final state
}
else if (!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, CANCELLED))
return false;
finishCompletion();
return true;
}
|
执行逻辑如下
- state不为NEW时,任务即将进入终态,直接返回false表明取消操作失败。
- state状态为NEW,任务可能已经开始执行,也可能还未开始。
- mayInterruptIfRunning表明是否中断线程。若是,则尝试将state设置为INTERRUPTING,并且中断线程,之后将state设置为终态INTERRUPTED。
- 如果mayInterruptIfRunning=false,则不中断线程,把state设置为CANCELLED
- 移除等待线程并唤醒。
- 返回true
可见,cancel()方法改变了futureTask的状态位,如果传入的是false并且业务逻辑已经开始执行,当前任务是不会被终止的,而是会继续执行,直到异常或者执行完毕。如果传入的是true,会调用当前线程的interrupt()方法,把中断标志位设为true。
事实上,除非线程自己停止自己的任务,或者退出JVM,是没有其他方法完全终止一个线程的任务的。mayInterruptIfRunning=true,通过希望当前线程可以响应中断的方式来结束任务。当任务被取消后,会被封装为CancellationException抛出。
总结
总结一下,futureTask中的任务状态由变量state表示,任务状态都基于state判断。而futureTask的阻塞则是通过自旋+挂起线程实现。理解FutureTask的内部实现机制,我们使用Future时才能更加得心应手。文中掺杂着笔者的个人理解,如果有不正之处,还望读者多多指正









相关推荐
Java中的Runnable、Callable、Future和FutureTask是Java多线程编程中的核心概念,它们各自扮演着不同的角色,共同协作以实现并发任务的管理和执行。 1. **Runnable**: Runnable是最基本的多线程接口,它只有一个`...
4. 使用FutureTask时,可以传入Callable的实现类或Runnable的实现类,获取线程执行的结果。 四、使用与分析 1. 使用Future时,需要实现Callable接口,并通过ExecutorService接口的submit方法获取返回的Future对象...
`Future`、`FutureTask`、`Callable`和`Runnable`是Java并发编程中的核心接口和类,它们在Android开发中同样有着广泛的应用。下面将详细介绍这些概念以及它们如何协同工作。 1. `Runnable`: 这是Java中最基础的多...
`Future`接口提供了对异步计算结果的访问和控制,而`FutureTask`是`Future`的一个具体实现,它还同时实现了`Runnable`接口,因此可以直接提交给`Executor`执行。 `Future`接口提供了以下方法: 1. `boolean cancel...
Runnable、Callable、Future、FutureTask有什么关联.docx
2 如何使用FutureTask 、Future、Callable、线程池实现线程2.1 FutureTask + Callable实现多线程2.2 线程池+Future+Callable 实现多线程3 Runnable、Callable、Future和FutureTask之间的关系3.1 整体关系介绍3.2 ...
FutureTask类实现了RunnableFuture接口,RunnableFuture接口是Runnable和Future的综合体。 FutureTask类提供了一个runAndReset方法,该方法可以运行任务并重置Future的状态。 Callable和Runnable的转换可以使用...
Java使用Callable和Future创建线程操作示例主要介绍了Java使用Callable和Future创建线程操作,结合实例形式分析了java使用Callable接口和Future类创建线程的相关操作技巧与注意事项。 首先,Java 5开始,Java提供了...
2. 创建FutureTask实例:FutureTask是Java并发包(java.util.concurrent)中的一个类,它是一个可以被取消的任务,同时也是一个实现了Runnable接口的Future。FutureTask提供了对Callable结果的访问和管理,包括获取...
这个类结合了`Runnable`或`Callable`接口的特性,并提供了异步执行的能力,同时允许你在任务完成后获取结果。在深入探讨`FutureTask`之前,我们先来理解`Runnable`和`Callable`的区别。 `Runnable`接口是Java早期...
FutureTask继承自RunnableFuture接口,这是一个复合接口,由Future和Runnable组成。这意味着FutureTask既是可执行的任务,又可以等待其结果。这种设计允许FutureTask既可以直接提交给Thread执行,也可以通过...
在 JDK 中,FutureTask 类是 Future 模式的实现,它实现了 Runnable 接口,作为单独的线程运行。在其 run() 方法中,通过 Sync 内部类调用 Callable 接口,并维护 Callable 接口的返回对象。当使用 FutureTask.get()...
总结来说,`Future` 是一个接口,用于管理异步任务的结果和状态,而`FutureTask`是一个具体的实现,它同时实现了`Runnable`和`Future`接口,可以直接提交给`ExecutorService`执行。在多线程编程中,正确地使用`...
为了更好地理解FutureTask的实现原理,我们需要了解一些重要的接口和类的结构。ThreadPoolExecutor提供了submit接口用于提交任务,submit支持Runnable和Callable两种不同的接口。为了提供统一的对外接口,jdk在内部...
解决线程的死掉问题和超时问题特别好使,在Java中,如果需要设定代码执行的最长时间,即超时,可以用Java线程池ExecutorService类配合Future接口来实现。 Future接口是Java标准API的一部分,在java.util.concurrent...
* 异步计算的结果:包括Future接口和实现Future接口的FutureTask类,代表异步计算的结果。 4. Executor框架的使用 使用Executor框架可以分为三步: 1. 主线程首先要创建实现Runnable接口或者Callable接口的任务...
FutureTask是Future接口的一个实现,它同时实现了Runnable接口,这意味着FutureTask可以被Thread直接执行。FutureTask包含了Callable任务和对其结果的封装,当我们调用FutureTask的start()方法时,它会在新的线程上...
继承 Thread 类可以更好地控制线程的生命周期,而实现 Runnable 接口可以更好地分离线程的业务逻辑和线程的创建过程。 在实际开发中,我们需要根据具体情况选择合适的线程创建方式,以便更好地控制线程的行为和生命...
- `FutureTask<V>`是`Future`接口的一个常见实现,同时也实现了`Runnable`接口,因此可以直接提交给`ExecutorService`执行。 - `SwingWorker, V>`是Java Swing库中用于在事件调度线程外执行耗时操作的`Future`实现...
`FutureTask`实现了`RunnableFuture`接口,该接口继承了`Runnable`和`Future`两个接口。这意味着`FutureTask`既可以作为`Runnable`接口实现被线程直接执行,也可以作为`Future`来获取`Callable`的计算结果。 #### ...