- 浏览: 493694 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 北京
-

文章分类
最新评论
-
cloudfile:
谢谢分享!
MyEclipse配置Tomcat(图解) -
dotjar:
有效没?
治咳嗽秘方 -
jyslb:
设置密码长度大于10位,其中包含%$#&等符号,你这个 ...
奶瓶无线破解介绍 -
廖乐逍遥:
还是不行。。
eclipse里不支持泛型的解决方法 -
cue2008:
http://backtrack.unixheads.org/ ...
Intel 3945ABG无线网卡破解无线路由器密码 BT3
转自:http://www.riyaz.net/sap/xipi-introduction-to-context-handling-in-message-mapping/5/
Context handling is an important technique to map complex scenarios in XI. This article introduces the basics of context handling using a simple example.
Message mapping in XI works by means of queues. A queue contains an entire XML instance of the source message. Depending on the hierarchy in the source message, different nodes and elements can be categorised into different contexts. All the nodes and elements that belong to the same parent node are said to be in the same context. Hence, the nodes and elements that belong to different parent nodes have to be separated by a context change.
XI provides various node functions for context handling during message mapping. Let us understand the concept of contexts using a simple example. Consider the source message shown below:
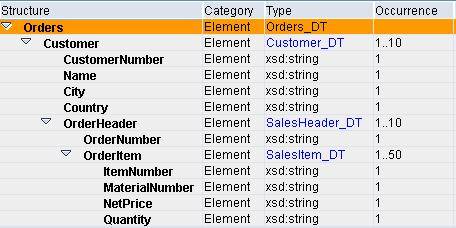
Elements ItemNumber and MaterialNumber belong to the same parent node OrderItem, and hence are in the same context. Also, node OrderItem and element OrderNumber are under the same parent node OrderHeader, and hence are in the same context. Whereas, as elements ItemNumber and OrderNumber belong to different parent nodes, they fall under different contexts.
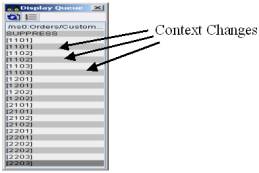
Following figure shows the OrderItem context. Context change is inserted after every occurrence of OrderItem. Grey coloured rows correspond to context changes.
Following figure shows the OrderHeader context. Context change is inserted after every occurrence of OrderHeader.
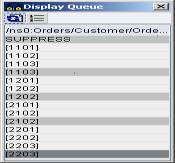
Similarly, using the Customer context, inserts a context change after every occurrence of Customer.
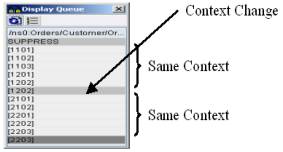
If the Orders context is used, no context changes will be inserted as Orders is at the highest level in the hierarchy.
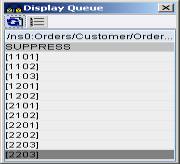
We can use explicit context selection as shown above or use the node functions available in the Graphical Mapping Editor.
Let us take an example where the use of contexts can be emphasised. In the source message shown above OrderNumber appears only once while OrderItem can occur multiple times within the OrderHeader node. Suppose we want to map OrderNumber multiple times in the target message, such that it is available under the target node corresponding to every sales order item. To do this, we can use the node function called useOneAsMany as described below:
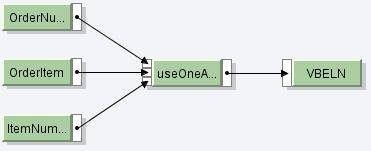
The first input parameter expects the list of values that we want to propagate to the target message.
The second input parameter expects the number of iterations or how many times we want to replicate the value given in the first parameter.
The third input parameter is the list of context changes. Depending on this parameter the source values will be propagated to the target after every context change.
Note: For this function to work as expected, the first two parameters must contain the same number of contexts while the last two parameters must contain the same number of values.
In our case, the first parameter is OrderNumber, since we want to assign value of this element to the field in the target structure. Second parameter is OrderItem as it corresponds to the number of times sales order items would occur in the target structure. Note that both these parameters have the same number of contexts (See figure below). The third parameter is ItemNumber, which indicates the number of context changes. ItemNumber uses OrderItem context by default (since, OrderItem is the immediate parent node of ItemNumber). Hence, the value of first parameter will be assigned to the target every time the context change occurs for ItemNumber. Also note that the second and third parameter has the same number of values (See figure below).
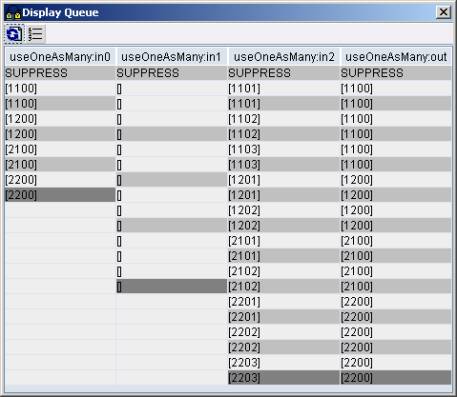
We can see that the value 1100 (first parameter) has been replicated three times (second parameter) at every context change in third parameter.
There are many other node functions available within the Graphical Mapping Editor to aid the context handling in different scenarios. Graphical Mapping Editor also allows you to write your own functions wherein you can use methods of predefined classes to handle contexts.
Context handling is an important technique to map complex scenarios in XI. This article introduces the basics of context handling using a simple example.
Message mapping in XI works by means of queues. A queue contains an entire XML instance of the source message. Depending on the hierarchy in the source message, different nodes and elements can be categorised into different contexts. All the nodes and elements that belong to the same parent node are said to be in the same context. Hence, the nodes and elements that belong to different parent nodes have to be separated by a context change.
XI provides various node functions for context handling during message mapping. Let us understand the concept of contexts using a simple example. Consider the source message shown below:

Elements ItemNumber and MaterialNumber belong to the same parent node OrderItem, and hence are in the same context. Also, node OrderItem and element OrderNumber are under the same parent node OrderHeader, and hence are in the same context. Whereas, as elements ItemNumber and OrderNumber belong to different parent nodes, they fall under different contexts.
Following figure shows the OrderItem context. Context change is inserted after every occurrence of OrderItem. Grey coloured rows correspond to context changes.


Following figure shows the OrderHeader context. Context change is inserted after every occurrence of OrderHeader.


Similarly, using the Customer context, inserts a context change after every occurrence of Customer.


If the Orders context is used, no context changes will be inserted as Orders is at the highest level in the hierarchy.


We can use explicit context selection as shown above or use the node functions available in the Graphical Mapping Editor.
Let us take an example where the use of contexts can be emphasised. In the source message shown above OrderNumber appears only once while OrderItem can occur multiple times within the OrderHeader node. Suppose we want to map OrderNumber multiple times in the target message, such that it is available under the target node corresponding to every sales order item. To do this, we can use the node function called useOneAsMany as described below:

The first input parameter expects the list of values that we want to propagate to the target message.
The second input parameter expects the number of iterations or how many times we want to replicate the value given in the first parameter.
The third input parameter is the list of context changes. Depending on this parameter the source values will be propagated to the target after every context change.
Note: For this function to work as expected, the first two parameters must contain the same number of contexts while the last two parameters must contain the same number of values.
In our case, the first parameter is OrderNumber, since we want to assign value of this element to the field in the target structure. Second parameter is OrderItem as it corresponds to the number of times sales order items would occur in the target structure. Note that both these parameters have the same number of contexts (See figure below). The third parameter is ItemNumber, which indicates the number of context changes. ItemNumber uses OrderItem context by default (since, OrderItem is the immediate parent node of ItemNumber). Hence, the value of first parameter will be assigned to the target every time the context change occurs for ItemNumber. Also note that the second and third parameter has the same number of values (See figure below).

We can see that the value 1100 (first parameter) has been replicated three times (second parameter) at every context change in third parameter.
There are many other node functions available within the Graphical Mapping Editor to aid the context handling in different scenarios. Graphical Mapping Editor also allows you to write your own functions wherein you can use methods of predefined classes to handle contexts.
发表评论
-
Gateway Access Control Lists
2015-10-12 11:34 1223Source:http://wiki.scn.sap.com ... -
SLD_UC registration failes with return code 748
2015-10-12 09:44 2209The managed ABAP systems shoul ... -
SLD Related Gateway Serivces Unavaliable
2015-10-12 09:01 769转自:http://www.sapnew.com/212. ... -
JDBC/JMS driver deployment - now more forceMode=true
2012-11-07 19:36 1254转自:http://scn.sap.com/people ... -
JDBC Receiver Adatper的同步场景设计
2012-10-18 15:15 1111转自:http://scnblogs.techweb. ... -
XML Anonymizer Bean in Communication Channel to remove namespace prefix in XML P
2012-07-24 16:14 1441转:http://www.saptechnical.com/T ... -
Step-by-Step Guides - Connectivity > CIDX Message eStandards
2012-05-29 11:36 1355http://wiki.sdn.sap.com/wiki/di ... -
Chem XML Message eStandards and CIDX Scenario Part III
2012-05-25 00:32 960http://scn.sap.com/people/suraj ... -
Chem XML Message eStandards and CIDX Scenario development – Part II
2012-05-25 00:30 1117http://scn.sap.com/people/suraj ... -
Chem XML Message eStandards and CIDX Scenario – Part I
2012-05-25 00:28 1123http://scn.sap.com/people/suraj ... -
SLDDSUSER in SLD is getting Locked
2012-05-24 17:59 1240******* LOCAL to Solution Manag ... -
How to Start the Visual Administrator
2012-05-22 16:24 978http://help.sap.com/saphelp_nw7 ... -
利用XI同步调用(JDBC)oracle数据库的返回值。
2012-02-13 18:03 1165今天用CCBPM做一串业务操作,具体的操作是:我先异步更 ... -
XI/PI Tables LIST
2012-02-09 15:28 1107ABAP ABAP schema Database Trans ... -
(MID)com.sap.SOA.apt_rfc.0303
2012-02-02 11:51 867MessageID com.sap.SOA.apt_rfc.0 ... -
FAQ XI 3.0/ PI 7.0/ PI 7.1 RFC Adapter
2012-02-01 16:52 2463转自:http://www.saptechies.com/fa ... -
如何排查mapping报错。
2012-01-18 15:50 987XI/PI在开发过程中最容易也是出错最多的地位就是map ... -
RFC Sender to JDBC receiver scenario中值得注意的三个问题
2012-01-17 17:09 1491转自:http://scnblogs.techweb.com. ... -
copyValue用法
2012-01-05 15:24 1194copyValue目的就是实现可以取到一个LIST的任意值。 ... -
PI动态生成字段方法
2011-12-28 18:48 1100今天遇到这样一种情况,PI更新数据库时,有的字段是动态更新 ...





相关推荐
This updated bestseller provides an introduction to programming interactive computer graphics, with an emphasis on game development using DirectX 11. The book is divided into three main parts: basic ...
This book presents an introduction to programming interactive computer graphics, with an emphasis on game development, using Direct3D 12. It teaches the fundamentals of Direct3D and shader programming...
本示例“PoMappingDemo”是关于如何在SAP PO中进行消息映射(Message Mapping)的一个具体实践,同时包含了Java编程元素。以下是基于这个主题的详细知识点解释: 1. **SAP PO**: SAP PO是SAP NetWeaver Process ...
This book presents an introduction to programming interactive computer graphics, with an emphasis on game development, using Direct3D 10. It teaches the fundamentals of Direct3D and shader programming...
This book presents an introduction to programming interactive computer graphics, with an emphasis on game development, using Direct3D 10. It teaches the fundamentals of Direct3D and shader programming...
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping for Mobile Robots: Introduction and Methods Simultaneous Localization and Mapping for Mobile Robots: Introduction and Methods
Introduction to 3D Game Programming with DirectX 9.0c Shader Approach 源代码 This book presents an introduction to programming interactive computer graphics, with an emphasis on game development, ...
**目的:** 在SAP PI Mapping过程中,经常需要获取消息的唯一标识MessageID。这有助于在后续处理或故障排除时定位特定的消息。 **实现方式:** ```java java.util.Map map = container....
在《Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots》一书中,作者Roland Siegwart和Illah R. Nourbakhsh介绍了移动机器人的各项技术和理论,并将其划分为不同模块,从低级到高级逐步展开,涵盖了移动机器人的多个关键...
在Microsoft Foundation Classes (MFC)库中,消息映射(Message Mapping)是MFC应用程序框架的核心组成部分,它负责将窗口消息与相应的成员函数关联起来。本示例将深入讲解如何在MFC应用中建立消息映射,从而实现...
《Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots》这本书由Roland Siegwart、Illah R. Nourbakhsh和Davide Scaramuzza合著,是关于自主导航移动机器人的权威著作之一。本书属于Intelligent Robotics and Autonomous ...
在SAP Process Integration (PI) 中,Java Mapping是一种强大的工具,用于处理和转换数据流,以确保不同系统间的数据交换准确无误。标题提到的"com.sap.aii.mapping.api PI MAPPING开发必须jar包"是Java Mapping开发...
This book presents an introduction to programming interactive computer graphics, with an emphasis on game development, using real-time shaders with DirectX 9.0c. It teaches the fundamentals of Direct...
《Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots》第二版是由Davide Scaramuzza教授编著的一本深入探讨自主移动机器人的权威书籍。这本书旨在引导读者理解并掌握移动机器人技术的基础知识,特别是自主导航和同时定位与...
标题“SOLUTIONS MANUAL FOR AN INTRODUCTION TO CRYPTOGRPHY WITH CODING”指的是《一种密码学与编码理论介绍的习题解答手册》。本书为《密码学与编码理论》第二版的配套解答册,而密码学与编码理论是信息安全领域...
Python scripting in the context of Maya is a powerful tool that enables artists and animators to automate tasks, create custom tools, and enhance their workflow within Autodesk's Maya software....
This updated bestseller provides an introduction to programming interactive computer graphics, with an emphasis on game development using DirectX 11. The book is divided into three main parts: basic ...
为了解决更复杂的域偏移问题,目前存在多种方法,主要包括:重要性加权(importance weighting)、子空间映射(subspace mapping)、领域不变空间(domain-invariant spaces)、特征增强(feature augmentation)、...