In earlier blog on Kubernetes networking we have seen how Kubernetes is non-prescriptive of how the network should be designed for running pods. There can be multiple way to design the network that meets Kubernetes networking requirements with varying degree of complexity, flexibility. In this blog we will see how Kube-router implements a pure L3 solution for cross node pod-to-pod networking using BGP and see how use of BGP gives unique advantage which enables pod IP and Kubernetes service cluster IP to be routable from out side of the cluster.
host routing based L3 solution
As we have seen previous blog Kubernetes networking, we can have solution based on either L2 or L3 approach or based on the overly solutions. Kube-router choose to implement a solution based on L3 routing solution. Kube-router does not perform subnet management and relies upon Kubernetes controll manager to do the subnet allocation for each node. Each node in the cluster is allocated unique subnet from the cluster CIDR range for allocation of IP’s to the pods running on the node. For cross node pod-to-pod networking we can build a L3 solution either by gateway based routing or host based routing as seen in the blog.
Lets see how host based routing achives cross-node pod-to-pod networking with below example. Lets assume Node1 and Node2 are allocated subnets 10.1.1.0/24 and 10.1.2.0/24 respectivley. So its just matter of installing route on each node to route the subnet to the node to which subnet is allocated as shown below.
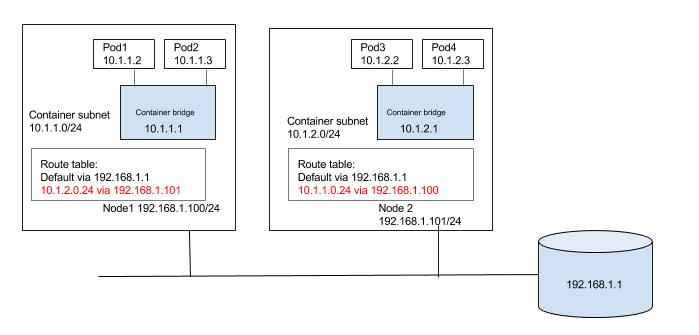
A simplest approach Kube-router could have taken is to learn the subnets assinged to each node and install the routes accordingly on each of the nodes. There are two reasons this approach was not taken. First Kubernetes has a clean approach w.r.t networking for the green field cloud native applications. But its possible in the near future (there is huge community push for the multi-networks ) Kubernetes might have multiple networks and isolated network spanning multiple nodes much like network in IAAS clouds. Second if we want pod ip’s routable from outside the cluster this approach wont work.
Kube-router has taken the approach of running a standard BGP routing protocol on each node which can advertise pod CIDR’s to the peers and configured BGP peers. There are other solutions like Calico, Contiv which similarly use BGP for Kubernetes networking. But Kube-router with ability to act as service proxy as well puts in unique situation to enable new use cases. Kube-router along with advertising pod CIDR of each nodes to peers, can also advertise service cluster IP’s to external routing infrastructure. We will go over the deails how BGP enables these scenarios in below section.
Why BGP?
First natural question is why use BGP? Is it not overkill for the protocol that runs the internet to be used for simple use-cases? As it turns out BGP core is a relatively simple protocol for routes exchange. As we will see in next section use of BGP is really transparent and no configuration is required for basic pod-to-pod connectivity. In case where you want pod IP’s to be routable we just need to peer with BGP router outside the cluster. Use of BGP in the datacenters is quite common and is in fact an approach taken by SDN controllers like Contrail, Nuage for overlay networks in IAAS clouds.
Pod-to-pod cross node networking with BGP
Kube-router runs iBGP on each cluster nodes, and automatically peers with all the nodes in the cluster in full-mesh at this point (can be easily changed to use route reflector for scaling). All the nodes in the cluster will be put in configurable priavate ASN. Kube-router will advertise the pod CIDR allocated for the node to the peers and install the learned routes from the peers in the node host namespace.
Please see the demo to get the feel for how Kube-router runs iBGP on each node to advertise the route and pod-to-pod networking established.
In this simple setup each node is running BGP is in isolation to the cluster and there are no concerns of routes getting leaked or interfering with underlay so pod IP’s remains routable only inside the cluster.
Routable pods and service IP
We can also peer with existing routers outside the cluster so that pod IP’s will be routable from outside the cluster. Also, Kube-router advertises the cluster IP when service is created. A service can be accessed from outside the cluster using single cluster IP and standard ports.
Please see below demo how Kube-router advertises pod CIDR and service Cluster IP to the external routers.
conclusion
A pure L3 routing based solution is possibly a best solution in terms of performance, simplicity. We can use standard tools like traceroute, ip route to troubleshoot connectivity issues. Combined with BGP ability to advertise routes to external BGP peers we can have a flexible solution with Kube-router.









相关推荐
本书《Diving Deep Into Kubernetes Networking》旨在深入讲解Kubernetes网络的工作原理和不同组件的功能,为读者提供对Kubernetes网络的全面理解,帮助读者为不同环境选择合适的网络解决方案。
Azure Kubernetes网络基础(Azure Kubernetes Networking 101)是为那些希望理解和掌握Azure Kubernetes服务(AKS)网络配置的核心概念和实践的开发者与运维人员所准备的。本课程从Kubernetes的基本概念出发,深入...
这份"Kubernetes networking links"资源清单提供了深入理解Kubernetes网络模型、Container Networking Interface (CNI)以及相关工具的重要参考资料,旨在帮助你掌握这个领域的核心概念。 1. **Kubernetes网络基础**...
《Networking and Kubernetes: A Layered Approach》这本书由James Strong和Vallery Lancey合著,旨在为读者提供一套全面理解Kubernetes网络体系结构的方法。 #### 二、Kubernetes网络基础知识 在深入探讨本书内容...
Container-Networking 中文版... Kubernetes网络7.1 Kubernetes简介7.2 Kubernetes网络概述7.3 Pod内网络7.4 Pod间网络7.5 Kubernetes中的服务发现7.6 Ingress与Egress7.7 Kubernetes 中网络的高级主题7.8 本章小结附录
`kubernetes` 包包含了与 Kubernetes API 对应的各种类和方法,例如 Core V1 API、Networking V1 API 等。 - **Core V1 API**: 提供对 Pod、Service、Node 等核心 Kubernetes 资源的操作。 - **Networking V1 API**...
You will discover how to run complex stateful microservices on Kubernetes including advanced features as horizontal pod autoscaling, rolling updates, resource quotas, and persistent storage back ends....
You will discover how to run complex stateful microservices on Kubernetes including advanced features as horizontal pod autoscaling, rolling updates, resource quotas, and persistent storage back ends....
The atomic unit of modular container service in Kubernetes is a Pod, which is a group of containers with a common filesystem and networking. The Kubernetes Pod abstraction enables design patterns for...
The atomic unit of modular container service in Kubernetes is a Pod, which is a group of containers with a common filesystem and networking. The Kubernetes Pod abstraction enables design patterns for ...
6. **containernetworking-cni-0.6.0-3.el7.x86_64.rpm**:CNI(Container Network Interface)是Kubernetes的网络插件接口标准,这个包提供了CNI的实现,使得Kubernetes能够支持多种不同的网络策略和解决方案,如...
Kubernetes Networking Kubernetes 提供了多种网络模式,包括 ClusterIP、NodePort 和 LoadBalancer 等。这些网络模式可以满足不同的应用场景,例如 ClusterIP 用于集群内部的服务发现,而 NodePort 和 Load...
Container Orchestration Ecosystem Configuration Management ...POD Management Service Controller Multi-host Networking Replication Controller/Deployment Persistent Storage Kubernetes Security
6. **网络(Networking)**:每个 Pod 都有自己的 IP 地址,可以与其他 Pod 直接通信,无需额外配置。 **部署应用** 1. **Docker 容器化**:首先将应用打包成 Docker 映像,便于在任何支持 Docker 的平台上运行。 ...
适合人群:对于想要深入了解Kubernetes网络机制、尤其是关注Pod间通信方案的技术爱好者,运维工程师,或有意向构建和管理自己的Kubernetes集群的专业人士而言极具价值。 使用场景及目标:通过本篇文章的学习,可以...
Kubernetes Cluster Networking是Kubernetes集群中的核心组件,它负责在不同工作负载之间提供网络连接。Kubernetes定义了三种基本的连接场景:External-to-Service(外部到服务)、Pod-to-Service(Pod到服务)和Pod...
8. **Ingress控制器API变动**:Ingress资源的API也进行了调整,从apis/extensions/v1beta1迁移到了apis/networking/v1,这要求使用Ingress的用户进行适配,以保持功能的正常运行。 9. **Kubernetes Dashboard**:...
Kubernetes的核心概念包括节点(Node)、工作负载(Workloads)、服务(Services)、存储(Storage)和网络(Networking)等。在1.20.0版本中,我们关注以下几个关键知识点: 1. **新特性与改进**:每个新版本都带来了一些新...