- 浏览: 12376 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 石家庄
-

最新评论
-
lovehong0306:
aswang 写道你的文章不错,说到内部机制上了,赞一个!转载 ...
ScrollView当显示超出当前页面时自动移动到最底端 -
aswang:
你的文章不错,说到内部机制上了,赞一个!
ScrollView当显示超出当前页面时自动移动到最底端
文章出处:http://terryblog.blog.51cto.com/1764499/414884
Android 自定义View 己经不是什么新鲜话题,Android Api提供了一大堆基础组件给我们,需要什么特定功能还需要我们继承它们然后定制更加丰富的功能。前面有篇文章也说过为自定义VIEW添加属性,但只是一笔带过,这里就拿这点来说说吧。
第一种添加属性的方法,之前我也是经常使用这种写法,代码如下:
package com.terry.attrs;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class EditTextExt1 extends LinearLayout {
private String Text = "";
public EditTextExt1(Context context) {
this(context, null);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public EditTextExt1(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
int resouceId = -1;
TextView tv = new TextView(context);
EditText et = new EditText(context);
resouceId = attrs.getAttributeResourceValue(null, "Text", 0);
if (resouceId > 0) {
Text = context.getResources().getText(resouceId).toString();
} else {
Text = "";
}
tv.setText(Text);
addView(tv);
addView(et, new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,
LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT));
this.setGravity(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
}
}
这种写法,简单明了,不需要额外XML的配置,就可以在我们的VIEW文件下使用。 以上代码通过构造函数中引入的AttributeSet 去查找XML布局的属性名称,然后找到它对应引用的资源ID去找值。使用也时分方便。所以一直以来我也是很喜欢这种写法。 如上,自定好VIEW文件就可以在XML布局下如此使用:
<com.terry.attrs.EditTextExt1 android:id="@+id/ss3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
Text="@string/app_name" ></com.terry.attrs.EditTextExt1>
好了,这是第一种为VIEW注册属性的写法,比较简单就不多介绍。
下面是第二为VIEW注册属性的写法,这里也要重点说说第二种注册 属性的写法和使用要点,先看一下JAVA代码要如何编写:
package com.terry.attrs;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class EditTextExt extends LinearLayout {
public EditTextExt(Context context) {
this(context, null);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
public EditTextExt(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
int resouceId = -1;
TypedArray typeArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.EditTextExt);
TextView tv = new TextView(context);
EditText et = new EditText(context);
int N = typeArray.getIndexCount();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
int attr = typeArray.getIndex(i);
switch (attr) {
case R.styleable.EditTextExt_Oriental:
resouceId = typeArray.getInt(R.styleable.EditTextExt_Oriental,
0);
this.setOrientation(resouceId == 1 ? LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL
: LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
break;
case R.styleable.EditTextExt_Text:
resouceId = typeArray.getResourceId(
R.styleable.EditTextExt_Text, 0);
tv.setText(resouceId > 0 ? typeArray.getResources().getText(
resouceId) : typeArray
.getString(R.styleable.EditTextExt_Text));
break;
}
}
addView(tv);
addView(et);
typeArray.recycle();
}
}
如上代码,跟前面代码一样。还是用的一个EDITTEXT和TEXTVIEW做基础组件。下面我们一步步分析上面的代码:
R.styleable.EditTextExt 代码的是一个attrs指向的一个declare-styleable 的标签,如下代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<resources>
<declare-styleable name="EditTextExt">
<attr name="Text" format="reference|string"></attr>
<attr name="Oriental">
<enum name="Horizontal" value="1"></enum>
<enum name="Vertical" value="0"></enum>
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
</resources>
这个文件位于,values下的attrs.xml目录下面,我比较喜欢一个自定义View 对应一个declare-styleable标签。
Tip:一个自定义View 第一部分的代码,
R.styleable.EditTextExt);
指定为一个declare-styleable,而在declare-styleable 下的attr (即各属性)Android 的ADT 将会自动生成为declare-styleable的name 名字加上“_”加上对应attr(即属性名称)的名称,如上(EditTextExt_Text)我们要得到Text 就需要R.styleable.EditTextExt_Text,这一点的话可以看看R.java生成文件:
public static final class styleable {
/** Attributes that can be used with a EditTextExt.
<p>Includes the following attributes:</p>
<table>
<colgroup align="left" />
<colgroup align="left" />
<tr><th>Attribute</th><th>Description</th></tr>
<tr><td><code>{@link #EditTextExt_Oriental com.terry.attrs:Oriental}</code></td><td></td></tr>
<tr><td><code>{@link #EditTextExt_Text com.terry.attrs:Text}</code></td><td></td></tr>
</table>
@see #EditTextExt_Oriental
@see #EditTextExt_Text
*/
public static final int[] EditTextExt = {
0x7f010000, 0x7f010001
};
/**
<p>This symbol is the offset where the {@link com.terry.attrs.R.attr#Oriental}
attribute's value can be found in the {@link #EditTextExt} array.
<p>Must be one of the following constant values.</p>
<table>
<colgroup align="left" />
<colgroup align="left" />
<colgroup align="left" />
<tr><th>Constant</th><th>Value</th><th>Description</th></tr>
<tr><td><code>Horizontal</code></td><td>1</td><td></td></tr>
<tr><td><code>Vertical</code></td><td>0</td><td></td></tr>
</table>
@attr name android:Oriental
*/
public static final int EditTextExt_Oriental = 1;
/**
<p>This symbol is the offset where the {@link com.terry.attrs.R.attr#Text}
attribute's value can be found in the {@link #EditTextExt} array.
<p>May be a reference to another resource, in the form "<code>@[+][<i>package</i>:]<i>type</i>:<i>name</i></code>"
or to a theme attribute in the form "<code>?[<i>package</i>:][<i>type</i>:]<i>name</i></code>".
<p>May be a string value, using '\\;' to escape characters such as '\\n' or '\\uxxxx' for a unicode character.
@attr name android:Text
*/
public static final int EditTextExt_Text = 0;
};
好了,上述的代码写完,我们要在XML布局如何使用呢?这个会跟Android 提供的基础组件的使用方法是一致的。首先,我们要为其提供一个引用包名如下:
xmlns:terry="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.terry.attrs"
上面提供的是android 基础组件的包名,和我们自己组件的包名。
写好了包名。就可以像使用andriod 基础组件一样使用了,如下全部XML布局源码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:terry="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/com.terry.attrs"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" />
<com.terry.attrs.EditTextExt android:id="@+id/ss"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
terry:Text="fdsafda" terry:Oriental="Vertical"></com.terry.attrs.EditTextExt>
<com.terry.attrs.EditTextExt1 android:id="@+id/ss3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"
Text="@string/app_name" ></com.terry.attrs.EditTextExt1>
</LinearLayout>
运行效果如下:
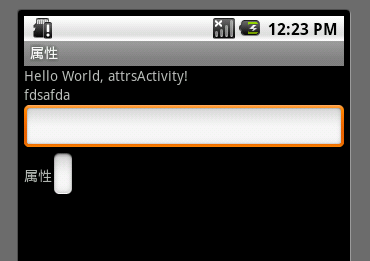
这是这两种为Android 注册 属性的使用方法,那么两者有什么区别呢?
在这里我认为起码有五点,大家可以找找看还有什么区别:
- 第二种可以编译时报错,如果编程人员随便输入什么第一种是不会报错的,第二种可以支持代码检测功能。
- 第二种写法,跟Android 属性标准写法是一致的,而且可以统一书法规则。
- 第二种写法,可以支持数据格式的验证,比如我们在attrs上注明只支持integer 那么就不可以使用字符串,这是第一种达不到的。
- 第二种写法,可以为VIEW提供选择操作,比如如上我们使用的ENUM让VIEW对应的属性支持ENUM列表,或者为其提供BOOL等只有双项选择的操作。
- 第一种写法,所有的属性必须是引用自资源(不大确定,如果朋友有什么好的DEMO麻烦共享),第二种写法,可以即支持引用资源又可以直接输入做操作,为编程带来更多的方便性。
种种都说明,第二种写法更具规范性,功能更性,代码编写 也更优雅,但个人有个人的使用习惯,我两种都喜欢用,具体看需求吧。呵呵。。。
源码下载:属性DEMO
由于自己见解可能有误,而且太久没写BLOG了,编排和中文语法都落步了,晕死。。都是IPAD搞的。。呵呵。需要看者要抱有评判的心来批判一下我。多多给我提意见。谢谢。
发表评论
-
自定义图文并茂的Button
2011-12-31 21:43 1264文章出处:http://gundumw100.iteye.co ... -
ScrollView当显示超出当前页面时自动移动到最底端
2011-12-30 11:25 1409文章出处:http://gundumw100.iteye.co ... -
用getIdentifier()获取资源Id
2011-12-30 11:25 1016文章出处:http://gundumw100.iteye.co ... -
取得当前屏幕的截图
2011-12-28 11:41 762文章出处:http://gundumw100.iteye.co ... -
观察者模式Observable与Observer的运用(单指拖放)
2011-12-28 11:40 867文章出处:http://gundumw100.iteye.co ... -
异步获取已安装程序列表(PackageManager+AsyncTask)
2011-12-28 11:34 1069文章出处:http://gundumw100.iteye.co ... -
Android中实现应用切换主题机制
2011-12-28 11:25 1526文章出处:http://gundumw100.iteye.co ... -
Android流量统计TrafficStats类的使用
2011-12-28 11:14 1240文章出处:http://gundumw100. ...







相关推荐
在Android SDK中,TimePicker分为两种模式:数字时钟(digital)和模拟时钟(analog)。默认情况下,TimePicker会根据系统的主题自动选择显示模式。通过XML布局文件,我们可以轻松地添加TimePicker到视图中: ```...
在Android开发中,自定义组件是非常常见且重要的技术,它允许开发者根据项目需求创造出具有独特功能和视觉效果的UI元素。本篇文章将详细介绍如何在Android中实现自定义组件,主要分为以下几个方面: 首先,自定义...
Android提供了两种方式来定义自定义属性: 1. **使用 attrs.xml 文件**:在res/values目录下创建一个attrs.xml文件,声明自定义属性,包括属性名、类型、默认值等。 2. **使用styleable**:在 attrs.xml 中定义的...
6. **在布局文件中使用**:将自定义组件添加到项目的res/layout目录下的XML布局文件中,并设置相应的属性。 7. **在Activity中使用**:在Activity的onCreate()方法中,通过findViewById()找到自定义组件,并可以...
ProgressBar是Android系统提供的一个用于显示进度的视图组件,它有两种模式:indeterminate(不确定进度)和determinate(确定进度)。在indeterminate模式下,进度条会持续循环显示,通常用作加载数据时的等待指示...
在Android开发中,自定义属性是一种非常常见的技术,它允许开发者扩展系统提供的组件特性,创建具有独特功能和外观的自定义视图或者组件。通过自定义属性,开发者可以更好地控制UI设计,提升应用的用户体验。以下是...
在Android应用开发中,自定义组件是提升用户体验和实现独特功能的重要手段。本项目"Android应用源码之自定义组件实现可滑动的ToggleButton的功能"是针对毕业设计的学习资源,旨在帮助开发者掌握如何通过源码分析和...
在Android开发中,自定义按钮效果是提升...通过以上两种方法,你可以轻松地在Android应用中实现自定义按钮效果,提升应用的交互性和视觉吸引力。每种方法都有其适用场景,选择最合适的一种,让应用设计更加完善和专业。
本文将深入探讨如何在Android中实现自定义滑动开关,并通过两种不同的方式讲解自定义属性的使用。 首先,我们来看第一种实现方式:基于 SeekBar 的改造。SeekBar 是 Android 提供的进度条组件,其本质是一个可滑动...
在.NET框架中,自定义属性(Custom Attributes)是一种元数据,可以附加到代码的各种元素上,如类、方法、字段等,提供额外的信息用于运行时的处理或代码分析。自定义属性增强了代码的可扩展性和灵活性,使得我们...
总结,本项目“android自定义View-手绘地图”涵盖了Android自定义组件的核心技术,包括自定义View和自定义ViewGroup的使用,通过它们可以构建出一个可定制、可交互的地图视图。开发者可以根据实际需求调整绘制逻辑,...
在Android开发中,自定义视图(Custom View)是一种常见的技术,它允许开发者根据特定需求创建独特的用户界面元素。在这个实例中,我们将深入探讨如何实现“自定义流星”和“自定义顶部导航”。这两个特性可以极大地...
首先,要在需要使用自定义权限的组件上添加`android:permission`属性,指示该组件需要此权限才能运行。然后,调用`checkSelfPermission()`方法检查是否已获得权限,如果未获得,需通过`requestPermissions()`方法向...
在Android开发中,自定义控件是提升...自定义属性允许我们为控件增加更多的可配置选项,而组合控件则让我们能够利用已有组件构建更复杂的视图。理解并熟练运用这些技术,对于提升应用的专业性和用户体验具有重要意义。
在Android开发中,自定义控件是提升应用用户体验和界面美观度的重要手段。本文将详细介绍如何实现三种常用的方法来创建...在实际应用中,可以结合Android的属性动画和事件监听,为进度条增加更多交互性和视觉效果。
自定义属性是自定义View的重要组成部分,它能让开发者更灵活地配置和控制自定义组件的行为。在这个案例中,我们将深入探讨如何在自定义View中使用自定义属性。 首先,我们需要了解自定义属性是如何声明的。在...
在Android开发中,`ToggleButton`是一个非常常用的控件,它结合了`Switch`和`Button`的功能,可以方便地在两种状态之间切换。本篇将详细介绍如何在Android中自定义`ToggleButton`,并提供一个实用的示例。 一、`...
在Android开发中,TabLayout是谷歌Material Design设计规范中的一个重要组件,用于展示多个标签页,...这两种方法都需要对Android的自定义视图和事件监听有深入的理解,但能提供更大的灵活性,以实现独特的界面效果。
为了保持状态在配置更改或屏幕旋转时的持久性,自定义控件可能需要覆盖这两个方法,以便保存和恢复自定义属性的状态。 6. **使用Shape Drawable**: 另一种实现圆角效果的方法是使用`Shape Drawable`,它可以定义...