В
В

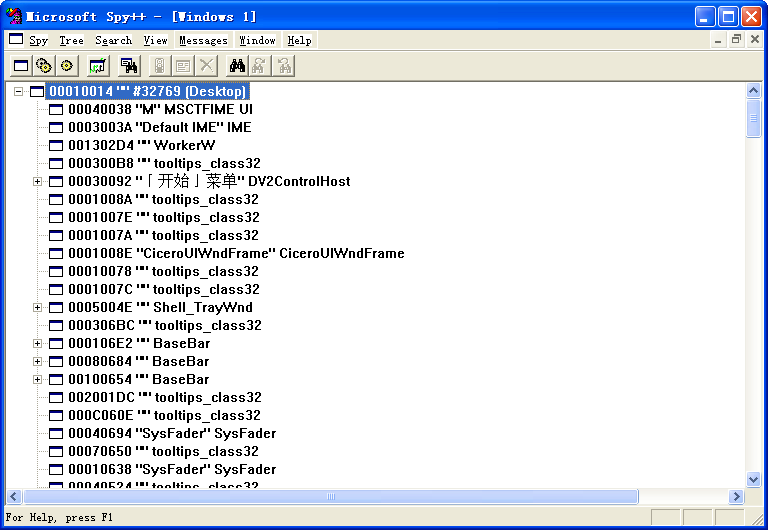
зӘ—еҸЈзұ»
WindowsдёӢзҡ„зӘ—еҸЈжңүдёӘзӘ—еҸЈзұ»гҖӮWindowsдёӢзҡ„зӘ—еҸЈзұ»еҢ…жӢ¬зі»з»ҹзұ»пјҢеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸе…ЁеұҖзұ»д»ҘеҸҠеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸжң¬ең°зұ»дёүзұ»гҖӮзі»з»ҹзұ»жҳҜWindowsжҸҗдҫӣзҡ„еҸҜд»ҘзӣҙжҺҘдҪҝз”ЁпјҢдёҚйңҖиҰҒжіЁеҶҢзҡ„зӘ—еҸЈзұ»гҖӮеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸе…ЁеұҖзұ»д»ҘеҸҠеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸжң¬ең°зұ»жҳҜйңҖиҰҒи°ғз”ЁRegisterClassеҮҪж•°иҝӣиЎҢжіЁеҶҢгҖӮ
В
иҰҒе®һзҺ°дёҖдёӘзӘ—еҸЈпјҢйңҖиҰҒжіЁеҶҢдёҖдёӘзӘ—еҸЈзұ»гҖӮеҲҡејҖе§Ӣзј–еҶҷWindowsзҡ„зӘ—еҸЈз•Ңйқўж—¶пјҢеҰӮжһңдёҚдәҶи§ЈWindowsдёӢзҡ„зӘ—еҸЈжіЁеҶҢпјҢжғіиҰҒе®һзҺ°дёҖдёӘйҖҡеёёж„Ҹд№үдёӢзҡ„зӘ—еҸЈпјҢдёҠйқўзҡ„ж ҮеҮҶзӘ—еҸЈпјҢиҝҷдёӘе·ҘдҪңиҝҳжңүзӮ№йә»зғҰпјҢеӣ дёәйңҖиҰҒиҮӘе·ұжіЁеҶҢдёҖдёӘзӘ—еҸЈзұ»пјҢWindowsзҡ„зі»з»ҹзӘ—еҸЈзұ»е№¶жІЎжңүиҝҷж ·зҡ„зӘ—еҸЈзұ»пјҢеҲ°жҳҜжңүдёӘеҜ№иҜқжЎҶзӘ—еҸЈпјҢзӘ—еҸЈзұ»дёә#32770пјҢеҸҜд»ҘзӣҙжҺҘдҪҝз”ЁпјҢдёҚиҝҮиҝҷжҜ•з«ҹиҝҳжҳҜи·ҹжҷ®йҖҡзҡ„ж ҮеҮҶзӘ—еҸЈиҝҳжҳҜжңүдәӣдёҚеҗҢгҖӮ
еҶҷйҒ“
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/winmsg/about-window-classes?redirectedfrom=MSDN
жіЁеҶҢзӘ—еҸЈзұ»
В
еҲӣе»әзӘ—еҸЈ
и°ғз”ЁCreateWindowжҲ–иҖ…CreateWindowExеҮҪж•°еҲӣе»әзӘ—еҸЈгҖӮ
В
CreateWindow
HWND CreateWindow(
LPCTSTR lpClassName,
LPCTSTR lpWindowName,
DWORD dwStyle,
int x,
int y,
int nWidth,
int nHeight,
HWND hWndParent,
HMENU hMenu,
HANDLE hInstance,
PVOID lpParam
);
CreateWindowEx
HWND CreateWindowEx(
DWORD dwExStyle,
LPCTSTR lpClassName,
LPCTSTR lpWindowName,
DWORD dwStyle,
int x, a
int y,
int nWidth,
int nHeight,
HWND hWndParent,
HMENU hMenu,
HINSTANCE hInstance,
LPVOID lpParam
);
иҝҷдёӨдёӘеҮҪж•°йғҪиҝ”еӣһдёҖдёӘзӘ—еҸЈеҸҘжҹ„гҖӮ
В
зӘ—еҸЈеҸҘжҹ„
еҸҘжҹ„еңЁWin32 APIдёӯжҳҜдёҖдёӘеҫҲйҮҚиҰҒзҡ„жҰӮеҝөгҖӮеҗҺз»ӯжүҖжңүе’ҢзӘ—еҸЈзӣёе…ізҡ„ж“ҚдҪңйғҪйңҖиҰҒиҝҷдёӘзӘ—еҸЈеҸҘжҹ„гҖӮ
В
йҷӨдәҶзӘ—еҸЈеҸҘжҹ„пјҲHWNDпјүпјҢиҝҳжңүHMODULEгҖҒHINSTANCEзӯүгҖӮ
В
зӘ—еҸЈдәӢ件еӨ„зҗҶ
В
зӘ—еҸЈеӨ„зҗҶеҮҪж•°
еҮҪж•°еҺҹеһӢ
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(
HWND hwnd,
UINT uMsg,
WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam
);
В
зҲ¶зӘ—еҸЈ
еӯҗзӘ—еҸЈ
В
зӘ—еҸЈжӢҘжңүиҖ…
В
зӘ—еҸЈиў«жӢҘжңүиҖ…
В
ж ҮеҮҶзӘ—еҸЈ
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include "window.h"
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hWnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hDC;
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_CREATE:
{
printf("[WM_CREATE] \n");
break;
}
case WM_COMMAND:
printf("[WM_COMMAND] \n");
break;
case WM_PAINT:
{
printf("[WM_PAINT] \n");
hDC = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
break;
}
case WM_DESTROY:
printf("[WM_DESTROY] \n");
PostQuitMessage(0);
printf("Goodbye!.\n");
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
HMODULE hModule;
LPCTSTR hWndCls;
HWND hWnd;
int nCmdShow = SW_SHOW;
MSG msg;
hModule = GetModuleHandle(NULL);
if (hModule == NULL)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("GetModuleHandle err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
hWndCls = register_window_class(hModule, WindowProc);
hWnd = CreateWindow(hWndCls, TEXT("дё»зӘ—еҸЈ"), 0 /* styles */, 0, 0, 500, 500, NULL, NULL, hModule, NULL);
if (! hWnd)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("CreateWindow err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
ShowWindow(hWnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
printf("exit.\n");
return 0;
}
В В 
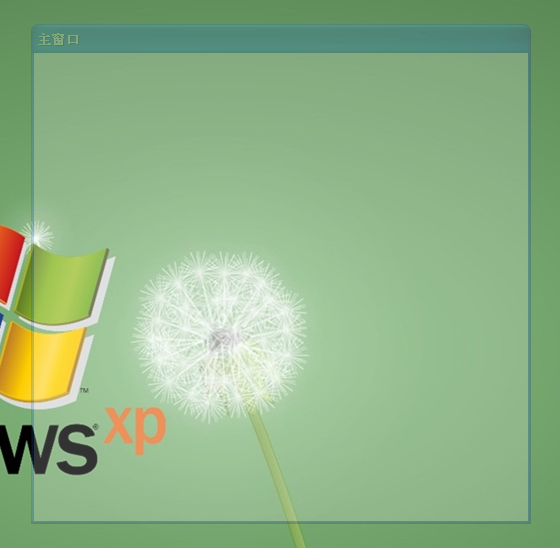
еҰӮжһңйңҖиҰҒе®һзҺ°дёҖдёӘж— ж Үйўҳж ҸгҖҒж— иҫ№жЎҶзҡ„зӘ—еҸЈпјҢдҪҝз”ЁPop-UpзӘ—еҸЈжҳҜжңҖз®ҖеҚ•зҡ„е®һзҺ°ж–№ејҸгҖӮеҪ“然пјҢйҖҡиҝҮдёҠйқўзҡ„ж ҮеҮҶзӘ—еҸЈпјҢд№ҹеҸҜд»Ҙе®һзҺ°гҖӮ
В
йҖҸжҳҺзӘ—еҸЈ

В
Pop-UpзӘ—еҸЈВ
ж— ж Үйўҳж Ҹ
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include "window.h"
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hWnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hDC;
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_CREATE:
{
printf("[WM_CREATE] \n");
break;
}
case WM_COMMAND:
printf("[WM_COMMAND] \n");
break;
case WM_PAINT:
{
printf("[WM_PAINT] \n");
hDC = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
break;
}
case WM_DESTROY:
printf("[WM_DESTROY] \n");
PostQuitMessage(0);
printf("Goodbye!.\n");
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
HMODULE hModule;
LPCTSTR hWndCls;
HWND hWnd;
LONG_PTR style;
int nCmdShow = SW_SHOW;
MSG msg;
hModule = GetModuleHandle(NULL);
if (hModule == NULL)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("GetModuleHandle err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
hWndCls = register_window_class(hModule, WindowProc);
hWnd = CreateWindow(hWndCls, TEXT("дё»зӘ—еҸЈ"), WS_VISIBLE | WS_POPUP | WS_THICKFRAME /* styles */, 0, 0, 500, 500, NULL, NULL, hModule, NULL);
if (! hWnd)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("CreateWindow err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
ShowWindow(hWnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
printf("exit.\n");
return 0;
}
 В ж— ж Үйўҳж Ҹж— иҫ№жЎҶ
В ж— ж Үйўҳж Ҹж— иҫ№жЎҶ
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include "window.h"
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hWnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hDC;
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_CREATE:
{
printf("[WM_CREATE] \n");
break;
}
case WM_COMMAND:
printf("[WM_COMMAND] \n");
break;
case WM_PAINT:
{
printf("[WM_PAINT] \n");
hDC = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
break;
}
case WM_DESTROY:
printf("[WM_DESTROY] \n");
PostQuitMessage(0);
printf("Goodbye!.\n");
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
HMODULE hModule;
LPCTSTR hWndCls;
HWND hWnd;
LONG_PTR style;
int nCmdShow = SW_SHOW;
MSG msg;
hModule = GetModuleHandle(NULL);
if (hModule == NULL)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("GetModuleHandle err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
hWndCls = register_window_class(hModule, WindowProc);
hWnd = CreateWindow(hWndCls, TEXT("дё»зӘ—еҸЈ"), WS_VISIBLE | WS_POPUP/* styles */, 0, 0, 500, 500, NULL, NULL, hModule, NULL);
if (! hWnd)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("CreateWindow err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
ShowWindow(hWnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
printf("exit.\n");
return 0;
}
В 
В
еҜ№иҜқжЎҶ
#include<windows.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "User32.lib")
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
PWSTR pCmdLine,
int nCmdShow)
{
char *wc_name = "#32770";
HWND hwnd;
HACCEL hAccelTable;
MSG msg;
hwnd = CreateWindowEx(
0, // Optional window styles.
TEXT(wc_name), // Window class
TEXT("Dialog"), // Window text
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, // Window style
// Size and position
CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT,
NULL, // Parent window
NULL, // Menu
hInstance, // Instance handle
NULL // Additional application data
);
if (hwnd == NULL)
{
return GetLastError();
}
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hwnd);
hAccelTable = LoadAccelerators(hInstance, TEXT(wc_name));
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
if (! TranslateAccelerator(msg.hwnd, hAccelTable, &msg))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
}
return 0;
}
еҜ№иҜқжЎҶзӘ—еҸЈдәӢ件еӨ„зҗҶ
#include<stdio.h>
#include<windows.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "User32.lib")
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(
HWND hwnd,
UINT uMsg,
WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam)
{
switch(uMsg)
{
case WM_COMMAND:
if (LOWORD(wParam) == IDOK || LOWORD(wParam) == IDCANCEL)
{
EndDialog(hwnd, LOWORD(wParam));
return TRUE;
}
break;
default:
return DefDlgProc(hwnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
int WINAPI wWinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance,
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
PWSTR pCmdLine,
int nCmdShow)
{
char *wc_name = "#32770";
HWND hwnd;
HACCEL hAccelTable;
MSG msg;
AllocConsole();
freopen("conout$", "w", stdout);
hwnd = CreateWindowEx(
0, // Optional window styles.
TEXT(wc_name), // Window class
TEXT("Dialog"), // Window text
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, // Window style
// Size and position
CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT,
NULL, // Parent window
NULL, // Menu
hInstance, // Instance handle
NULL // Additional application data
);
if (hwnd == NULL)
{
return GetLastError();
}
ShowWindow(hwnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hwnd);
hAccelTable = LoadAccelerators(hInstance, TEXT(wc_name));
while (GetMessage(&msg, hwnd, 0, 0))
{
if (! TranslateAccelerator(msg.hwnd, hAccelTable, &msg))
{
//TranslateMessage(&msg);
//DispatchMessage(&msg);
//DefWindowProc(msg.hwnd, msg.message, msg.wParam, msg.lParam);
//DefDlgProc(msg.hwnd, msg.message, msg.wParam, msg.lParam);
CallWindowProc(WindowProc, msg.hwnd, msg.message, msg.wParam, msg.lParam);
}
}
return 0;
}
еј№зӘ—
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#include "window.h"
LRESULT CALLBACK WindowProc(HWND hWnd, UINT uMsg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
PAINTSTRUCT ps;
HDC hDC;
switch (uMsg)
{
case WM_CREATE:
{
printf("[WM_CREATE] \n");
break;
}
/*
case WM_ERASEBKGND:
{
printf("[WM_ERASEBKGND] \n");
break;
}
*/
case WM_COMMAND:
printf("[WM_COMMAND] \n");
break;
case WM_PAINT:
{
printf("[WM_PAINT] \n");
hDC = BeginPaint(hWnd, &ps);
EndPaint(hWnd, &ps);
break;
}
case WM_DESTROY:
printf("[WM_DESTROY] \n");
PostQuitMessage(0);
printf("Goodbye!.\n");
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, uMsg, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
HMODULE hModule;
HWND hDesktop;
HWND hWnd;
LPCTSTR hWndCls;
LONG_PTR style;
HBRUSH brush;
int nCmdShow = SW_SHOW;
RECT rect;
MSG msg;
hModule = GetModuleHandle(NULL);
if (hModule == NULL)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("GetModuleHandle err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
hWndCls = register_window_class(hModule, CreateSolidBrush(RGB(0, 0, 255)), WindowProc);
hWnd = CreateWindowEx(WS_EX_TOOLWINDOW, hWndCls, TEXT("еј№зӘ—"),
WS_VISIBLE | WS_POPUP/* styles */,
0, 0, 280, 180, NULL, 0, hModule, NULL);
if (! hWnd)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("CreateWindow err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
hDesktop = GetDesktopWindow();
if (hDesktop == NULL)
{
DWORD error = GetLastError();
printf("GetDesktopWindow err=%d\n", error);
return -1;
}
GetClientRect(hDesktop, &rect);
SetWindowPos(hWnd, HWND_TOP, rect.right - 280, rect.bottom - 180, rect.right, rect.bottom, 0);
ShowWindow(hWnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow(hWnd);
//brush = CreateSolidBrush(RGB(0, 0, 0));
//SetClassLong(hWnd, GCL_HBRBACKGROUND, (long) brush);
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
printf("exit.\n");
return 0;
}
В 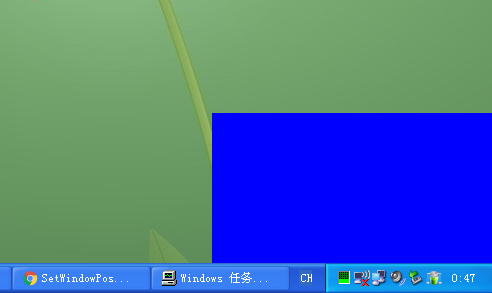
В
В
В







 В ж— ж Үйўҳж Ҹж— иҫ№жЎҶ
В ж— ж Үйўҳж Ҹж— иҫ№жЎҶ




зӣёе…іжҺЁиҚҗ
PyWin32пјҢд№ҹиў«з§°дёәpywin32жҲ–pythonwinпјҢжҳҜPythonзј–зЁӢиҜӯиЁҖдёӯзҡ„дёҖдёӘжү©еұ•жЁЎеқ—пјҢдё»иҰҒз”ЁдәҺдёҺMicrosoft Windowsж“ҚдҪңзі»з»ҹиҝӣиЎҢдәӨдә’гҖӮиҝҷдёӘеҺӢзј©еҢ…вҖңpywin32-221.win32-py2.7-pywin32-221.win64-py3.5.zipвҖқеҢ…еҗ«дәҶй’ҲеҜ№Python ...
гҖҗж ҮйўҳгҖ‘"api-ms-win-core-console-l1-1-0_Windowsзј–зЁӢ_" ж¶үеҸҠзҡ„жҳҜWindowsж“ҚдҪңзі»з»ҹдёӯзҡ„ж ёеҝғжҺ§еҲ¶еҸ°жҺҘеҸЈAPIпјҢиҝҷжҳҜWindowsзј–зЁӢдёӯдёҖдёӘе…ій”®зҡ„组件гҖӮиҝҷдёӘж Үйўҳжҡ—зӨәдәҶжҲ‘们е°ҶжҺўи®Ёзҡ„жҳҜеҰӮдҪ•еҲ©з”ЁиҝҷдәӣAPIеңЁWindowsзҺҜеўғдёӢиҝӣиЎҢзі»з»ҹ...
`Win32-GUI`жЁЎеқ—жҳҜPerlзӨҫеҢәдёәWindowsе№іеҸ°ејҖеҸ‘зҡ„дёҖдёӘејҖжәҗеә“пјҢе®ғдҪҝеҫ—PerlзЁӢеәҸе‘ҳиғҪеӨҹиҪ»жқҫең°еҲӣе»әеҗ„з§ҚзӘ—еҸЈгҖҒжҺ§д»¶е’ҢдәӢ件еӨ„зҗҶзЁӢеәҸпјҢиҖҢж— йңҖж·ұе…ҘеӯҰд№ еә•еұӮзҡ„Windowsзј–зЁӢжҠҖжңҜгҖӮ`Win32-GUI`жҸҗдҫӣдәҶеҢ…жӢ¬жҢүй’®гҖҒж–Үжң¬жЎҶгҖҒеҲ—иЎЁи§ҶеӣҫгҖҒ...
еңЁж Үйўҳ"pywin32-221.win-amd64-32-py2.6.rar"дёӯпјҢ"pywin32-221"иЎЁзӨәиҜҘзүҲжң¬жҳҜPyWin32зҡ„221зүҲпјҢ"win-amd64"иЎЁжҳҺиҝҷжҳҜй’ҲеҜ№64дҪҚAMDеӨ„зҗҶеҷЁдјҳеҢ–зҡ„зүҲжң¬пјҢиҖҢ"py2.6"еҲҷж„Ҹе‘ізқҖе®ғжҳҜдёәPython 2.6зј–иҜ‘зҡ„гҖӮжҸҸиҝ°дёӯзҡ„"pywin32-221.win...
8. **зӘ—еҸЈе’ҢжҺ§д»¶ж“ҚдҪң**пјҡйҖҡиҝҮWin32APIеҮҪж•°пјҢеҸҜд»ҘзӣҙжҺҘеҲӣе»әе’Ңж“ҚдҪңWindowsзӘ—еҸЈеҸҠжҺ§д»¶пјҢе®һзҺ°иҮӘе®ҡд№үз•ҢйқўгҖӮ еңЁе®үиЈ…PyWin32ж—¶пјҢйҖҡеёёдјҡйҒҮеҲ°зҡ„ж–Ү件жҳҜ`pywin32-221.win32-py3.4.exe`иҝҷж ·зҡ„еҸҜжү§иЎҢж–Ү件пјҢиҝҷжҳҜдёҖдёӘе®үиЈ…зЁӢеәҸпјҢиҝҗиЎҢ...
жҖ»д№ӢпјҢPyWin32-219.win32-py3.4.zipжҳҜPython 3.4ејҖеҸ‘иҖ…еңЁWindowsе№іеҸ°дёҠиҝӣиЎҢзі»з»ҹзә§зј–зЁӢдёҚеҸҜжҲ–зјәзҡ„е·Ҙе…·гҖӮиҷҪ然pypiе®ҳж–№д»“еә“дёҚеҶҚж”ҜжҢҒиҝҷдёӘзүҲжң¬пјҢдҪҶиҝҷдёӘеҲҶдә«зЎ®дҝқдәҶйӮЈдәӣд»ҚеңЁдҪҝз”ЁPython 3.4зҡ„йЎ№зӣ®иғҪеӨҹ继з»ӯдә«еҸ—PyWin32еёҰжқҘзҡ„...
ж Үйўҳ"wxPython2.8-win32-unicode-2.8.12.1-py27"д»ҘеҸҠжҸҸиҝ°дёӯзҡ„"wxPython2.8-win32-unicode-2.8.12.1-py27.exe"жҢҮеҗ‘зҡ„жҳҜдёҖдёӘзү№е®ҡзүҲжң¬зҡ„wxPythonеә“зҡ„е®үиЈ…зЁӢеәҸпјҢз”ЁдәҺWindows 32дҪҚзі»з»ҹпјҢж”ҜжҢҒUnicodeзј–з ҒпјҢ并且жҳҜй’ҲеҜ№...
ж Үйўҳ"swt-4.2.2-win32-win32-x86"иЎЁжҳҺиҝҷжҳҜдёҖдёӘй’ҲеҜ№Windows 32дҪҚзі»з»ҹзҡ„SWTзүҲжң¬пјҢзүҲжң¬еҸ·дёә4.2.2пјҢйҖӮз”ЁдәҺејҖеҸ‘Eclipse 4.2зүҲжң¬зҡ„еә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸгҖӮ EclipseжҳҜдёҖж¬ҫи‘—еҗҚзҡ„ејҖжәҗйӣҶжҲҗејҖеҸ‘зҺҜеўғпјҲIDEпјүпјҢе№ҝжіӣз”ЁдәҺJavaеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸзҡ„ејҖеҸ‘гҖӮ...
Win32 GUIпјҲеӣҫеҪўз”ЁжҲ·з•Ңйқўпјүзј–зЁӢжҳҜWindowsе№іеҸ°дёҠжһ„е»әеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸзҡ„йҮҚиҰҒжҠҖжңҜпјҢе°Өе…¶еҜ№дәҺеҲқеӯҰиҖ…жқҘиҜҙпјҢе®ғжҸҗдҫӣдәҶдёҖз§Қзӣҙи§Ӯдё”жҳ“дәҺдёҠжүӢзҡ„ж–№ејҸеҺ»еҲӣе»әз”ЁжҲ·з•ҢйқўгҖӮжң¬зҜҮж–Үз« е°Ҷж·ұе…ҘжҺўи®ЁWin32 GUIзј–зЁӢзҡ„еҹәзЎҖзҹҘиҜҶпјҢеҢ…жӢ¬ж ёеҝғжҰӮеҝөгҖҒе…ій”®...
ж Үйўҳдёӯзҡ„"swt-3.6M3-win32-win32-x86.jar"жҳҜSWTй’ҲеҜ№Windows 32дҪҚзі»з»ҹзҡ„зү№е®ҡзүҲжң¬гҖӮ иҝҷдёӘjarеҢ…жҳҜSWTеә“зҡ„дёҖдёӘеҸ‘иЎҢзүҲпјҢзүҲжң¬еҸ·дёә3.6M3пјҲM3д»ЈиЎЁ Milestone 3пјҢж„Ҹе‘ізқҖиҝҷжҳҜдёҖдёӘеңЁжӯЈејҸеҸ‘еёғеүҚзҡ„дёӯй—ҙејҖеҸ‘зүҲжң¬пјүгҖӮејҖеҸ‘иҖ…еҸҜд»Ҙе°Ҷ...
ж•ҙдҪ“жқҘиҜҙпјҢ"electron-v32.2.5-win32-x64иө„жәҗеҢ…"дёӯзҡ„еҗ„дёӘж–Ү件е…ұеҗҢжһ„жҲҗдәҶдёҖдёӘеңЁWindows 64дҪҚзі»з»ҹдёҠиҝҗиЎҢElectronеә”з”ЁжүҖеҝ…йңҖзҡ„зҺҜеўғгҖӮжү“еҢ…иҝҷдәӣж–Ү件ж„Ҹе‘ізқҖдҪ иғҪеӨҹе°ҶElectronеә”з”ЁеҸҠе…¶иҝҗиЎҢзҺҜеўғдёҖиө·еҲҶеҸ‘пјҢдҪҝеҫ—е…¶д»–з”ЁжҲ·ж— йЎ»йўқеӨ–...
еңЁWindowsж“ҚдҪңзі»з»ҹдёӯпјҢWin32зЁӢеәҸжҳҜдёҖз§ҚеҹәдәҺAPIпјҲеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸжҺҘеҸЈпјүзҡ„зј–зЁӢжЁЎеһӢпјҢе®ғе…Ғи®ёејҖеҸ‘иҖ…еҲӣе»әиғҪеңЁWindowsзҺҜеўғдёӢиҝҗиЎҢзҡ„еә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸгҖӮиҝҷйҮҢзҡ„"WindowsзӘ—еҸЈеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸ"пјҢжӣҙе…·дҪ“ең°жҢҮзҡ„жҳҜдҪҝз”ЁWin32 APIжқҘжһ„е»әе…·жңүеӣҫеҪўз”ЁжҲ·з•Ңйқў...
6. **win32gui**пјҡжҸҗдҫӣеӣҫеҪўз”ЁжҲ·з•ҢйқўпјҲGUIпјүзҡ„ж”ҜжҢҒпјҢеҸҜд»ҘеҲӣе»әе’ҢжҺ§еҲ¶зӘ—еҸЈгҖҒиҸңеҚ•гҖҒеҜ№иҜқжЎҶзӯүпјҢжҳҜзј–еҶҷWindowsжЎҢйқўеә”з”Ёзҡ„еҘҪеё®жүӢгҖӮ 然иҖҢпјҢеҖјеҫ—жіЁж„Ҹзҡ„жҳҜпјҢwin32allд»…ж”ҜжҢҒPython2.xзүҲжң¬пјҢзү№еҲ«жҳҜиҝҷйҮҢжҸҗеҲ°зҡ„"pythonWin_win32...
еңЁWindowsзј–зЁӢйўҶеҹҹпјҢWin32 APIпјҲеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸжҺҘеҸЈпјүжҳҜдёҖдёӘиҮіе…ійҮҚиҰҒзҡ„е·Ҙе…·йӣҶпјҢе®ғе…Ғи®ёејҖеҸ‘иҖ…еҲӣе»әеҺҹз”ҹзҡ„Windowsеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸгҖӮиҝҷдёӘеҺӢзј©еҢ…"е•Ҷдёҡзј–зЁӢ-жәҗз Ғ-Win32 зј–зЁӢдёӯеӯ—дҪ“зҡ„еә”з”Ё.zip"еҢ…еҗ«дәҶе…ідәҺеҰӮдҪ•еңЁWin32зј–зЁӢдёӯеӨ„зҗҶеӯ—дҪ“зҡ„еә”з”Ё...
гҖҠWIN32зј–зЁӢз”өеӯҗд№ҰгҖӢжҳҜдёҖд»Ҫдё“жіЁдәҺд»Ӣз»ҚWindowsж“ҚдҪңзі»з»ҹдёӢWIN32 APIзј–зЁӢжҠҖжңҜзҡ„иө„ж–ҷгҖӮиҝҷд»Ҫз”өеӯҗд№ҰиҜҰз»Ҷйҳҗиҝ°дәҶеҰӮдҪ•еңЁWindowsзҺҜеўғдёӢиҝӣиЎҢзі»з»ҹзә§еҲ«зҡ„зј–зЁӢпјҢж¶өзӣ–дәҶд»ҺеҹәзЎҖжҰӮеҝөеҲ°й«ҳзә§еә”з”Ёзҡ„е№ҝжіӣеҶ…е®№гҖӮй’ҲеҜ№еҲқеӯҰиҖ…е’Ңжңүз»ҸйӘҢзҡ„ејҖеҸ‘иҖ…...
"win64"жҢҮзҡ„жҳҜйҖӮз”ЁдәҺ64дҪҚWindowsзі»з»ҹзҡ„зүҲжң¬пјҢиҖҢ"win32"еҲҷеҜ№еә”32дҪҚWindowsзі»з»ҹгҖӮиҝҷйҮҢзҡ„"2.8.12.1"жҳҜwxPythonзҡ„зүҲжң¬еҸ·пјҢжҜҸдёӘзүҲжң¬еҸҜиғҪеҢ…еҗ«жҖ§иғҪдјҳеҢ–гҖҒж–°еҠҹиғҪжҲ–дҝ®еӨҚзҡ„й”ҷиҜҜгҖӮ"py27"иЎЁзӨәиҝҷдәӣзүҲжң¬жҳҜдёәPython 2.7и§ЈйҮҠеҷЁзј–иҜ‘зҡ„...
1. **Windows API**пјҡиҝҷжҳҜWin32зј–зЁӢзҡ„ж ёеҝғпјҢжҸҗдҫӣдәҶеӨ§йҮҸзҡ„еҮҪж•°гҖҒз»“жһ„дҪ“е’ҢеёёйҮҸпјҢз”ЁдәҺеҲӣе»әзӘ—еҸЈгҖҒеӨ„зҗҶж¶ҲжҒҜгҖҒз»ҳеӣҫгҖҒиҫ“е…Ҙиҫ“еҮәгҖҒеҶ…еӯҳз®ЎзҗҶзӯүгҖӮдҫӢеҰӮпјҢ`CreateWindowEx`з”ЁдәҺеҲӣе»әзӘ—еҸЈпјҢ`GetMessage`е’Ң`DispatchMessage`з”ЁдәҺеӨ„зҗҶ...
2. **win32con**пјҡжӯӨжЁЎеқ—еҢ…еҗ«дәҶеёёйҮҸе®ҡд№үпјҢиҝҷдәӣеёёйҮҸеҜ№еә”дәҺWindows APIдёӯзҡ„еҗ„з§Қж ҮиҜҶз¬ҰпјҢжҜ”еҰӮзӘ—еҸЈж ·ејҸгҖҒж¶ҲжҒҜзұ»еһӢгҖҒй”ҷиҜҜд»Јз ҒзӯүпјҢдҪҝеҫ—Pythonд»Јз ҒиғҪжӣҙзӣҙи§Ӯең°дёҺWindows APIдәӨдә’гҖӮ 3. **win32com**пјҡиҝҷжҳҜдёҺWindows COM...
### Windows-win32-APIindexжҰӮи§Ҳ #### дёҖгҖҒеј•иЁҖ Windows-win32-APIindexжҳҜй’ҲеҜ№WindowsжЎҢйқўеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸејҖеҸ‘иҖ…зҡ„е…Ёйқўиө„жәҗпјҢж—ЁеңЁжҸҗдҫӣдёҖдёӘиҜҰз»ҶгҖҒз»“жһ„еҢ–зҡ„жҢҮеҚ—пјҢеё®еҠ©ејҖеҸ‘иҖ…зҗҶи§Је’Ңиҝҗз”ЁWin32 APIпјҲWindows APIпјүгҖӮиҜҘAPIindex...
"pywin32-221.win-amd64-py3.7"жҳҜдёҖдёӘй’ҲеҜ№Python 3.7зҡ„Windowsе№іеҸ°жү©еұ•еә“пјҢе®ғжҸҗдҫӣдәҶеҜ№Windows APIзҡ„е…Ёйқўи®ҝй—®пјҢдҪҝеҫ—PythonзЁӢеәҸе‘ҳеҸҜд»ҘеҲ©з”ЁWindowsзі»з»ҹзҡ„еҠҹиғҪиҝӣиЎҢејҖеҸ‘гҖӮиҝҷдёӘеә“д№ҹиў«з§°дёәвҖңpywin32вҖқпјҢз”ұMark HammondеҲӣе»ә...