In order to avoid unnecessary query on database it is a common pattern to define a cache in application layer to cache the query result from database. See one example below. Here the application cache is maintained in a custom class CacheContext.
public class AccountService1 {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AccountService1.class);
private CacheContext<Account> accountCacheContext;
public Account getAccountByName(String accountName) {
Account result = accountCacheContext.get(accountName);
if (result != null) {
logger.info("get from cache... {}", accountName);
return result;
}
Optional<Account> accountOptional = getFromDB(accountName);
if (!accountOptional.isPresent()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format("can not find account by account name : [%s]", accountName));
}
Account account = accountOptional.get();
accountCacheContext.addOrUpdateCache(accountName, account);
return account;
}In Spring there is an annotation @Cacheable which can make the cache managed by Spring instead of application developer. See improved version:
public class AccountService2 {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AccountService2.class);
@Cacheable(value="accountCache")
public Account getAccountByName(String accountName) {
logger.info("in method getAccountByName, querying account... {}", accountName);
Optional<Account> accountOptional = getFromDB(accountName);
if (!accountOptional.isPresent()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format("can not find account by account name : [%s]", accountName));
}
return accountOptional.get();
}In this example, there is no more cache evaluation and cache fill logic. All such stuff are taken over by Spring under the hood and completely transparent to application developer, with the help of following bean configuration in xml:
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<property name="caches">
<set>
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean">
<property name="name" value="default" />
</bean>
<bean
class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean">
<property name="name" value="accountCache" />
</bean>
</set>
</property>
</bean>And how to research what magic has been done by Spring to achieve this behavior? We use the following code to research. It is expected that the request sent by line 31 will directly reach database, while the second request in line 34 will be handled by Spring cache handler.
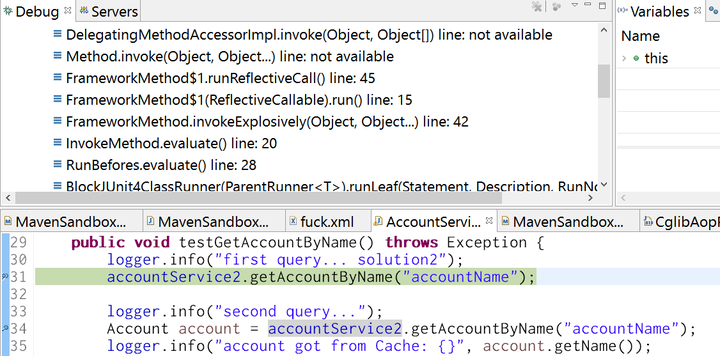
Here in line 31, in debugger we can find that accountService2 is not an instance of application class com.sap.AccountService2, but a dynamic proxy class generated by Spring.
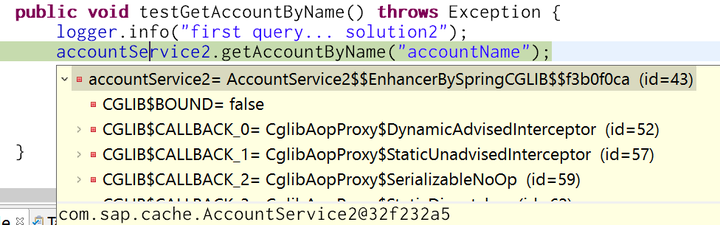
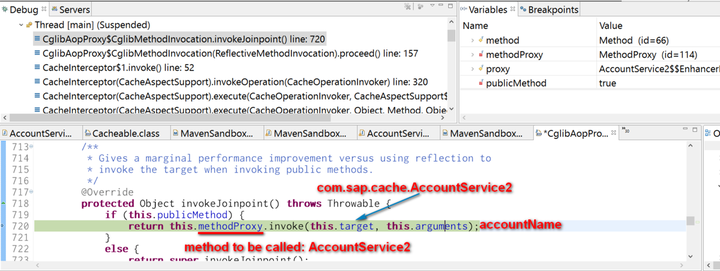
As a result after pressing F5, the intercept method of this dynamic proxy class is called:
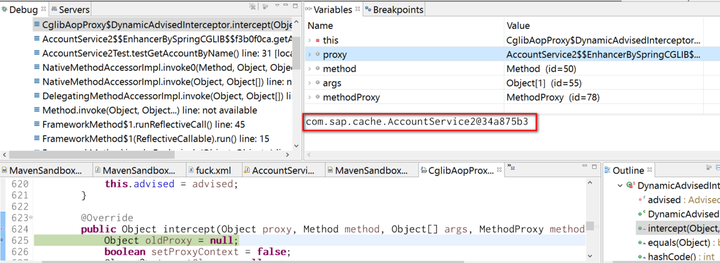
In this method, the execution will be delegated to Spring cache handler class:
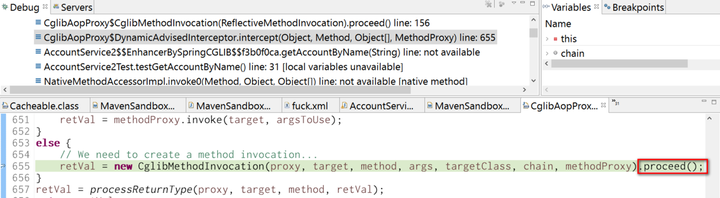
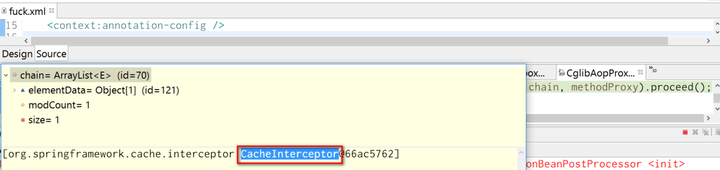
In example 1, the logic of cache evaluation and fill is done by application, and now it is done in method execute below.
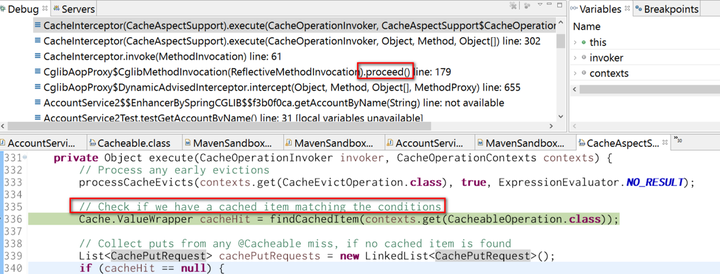
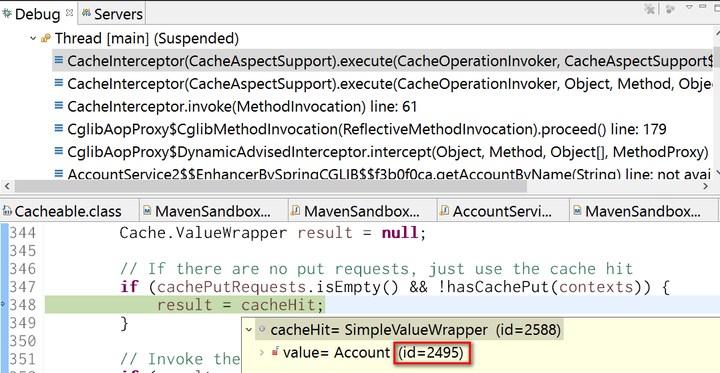
First internal cache managed by Spring is checked in line 336 via method findCachedItem. Due to expected cache miss, our application method will be called as usual via reflection, as demonstrated below:
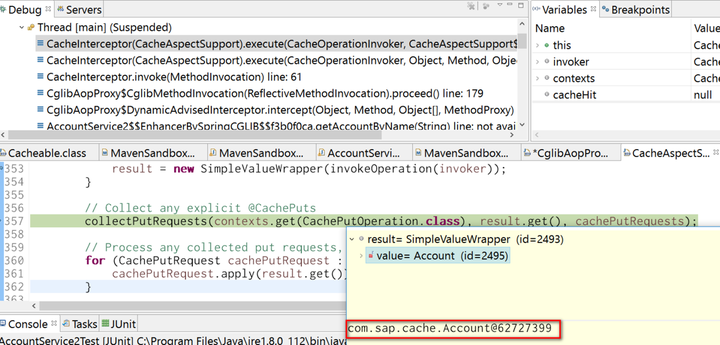
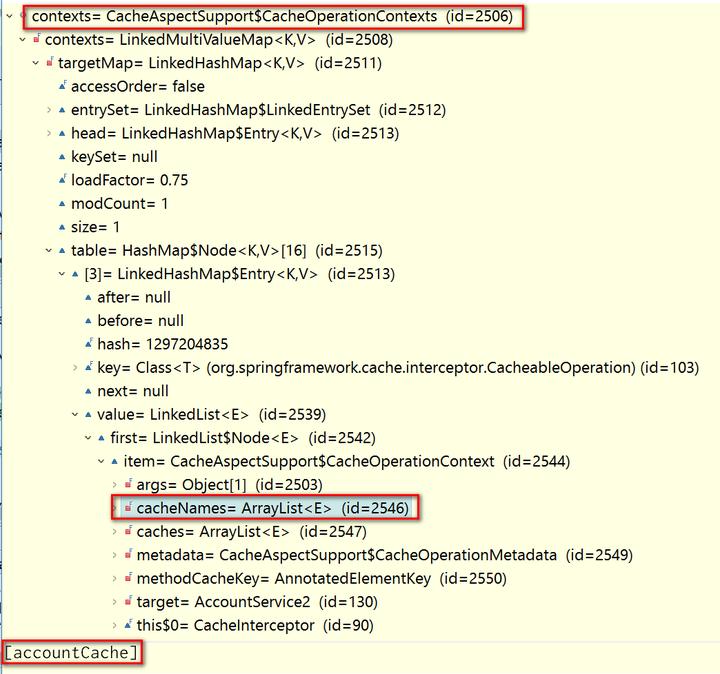
After application method to retrieve account from database is done, the result, Account instance with id 2495 is filled to Spring cache, the variable contexts below.
Below is the screenshot for Spring internal cache to store application data, which is based on ConcurrentHashMap. Our cached Account instance with id 2495 could be found there.

For the second query request issued by application, the cached result will be returned by Spring handler:
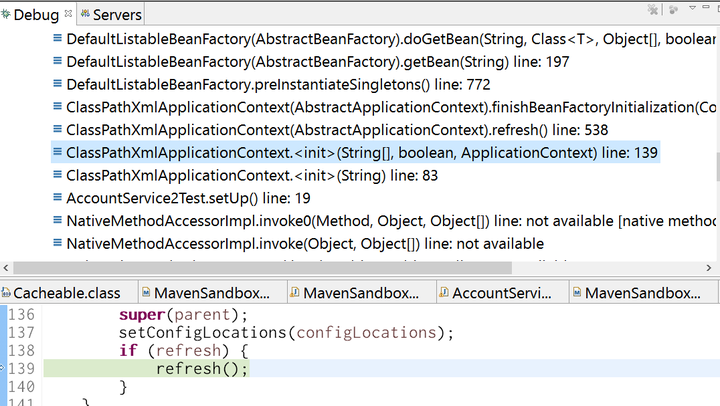
The last question is, how and when the dynamic proxy is generated? Again let’s go to the entry point of Beans initialization:
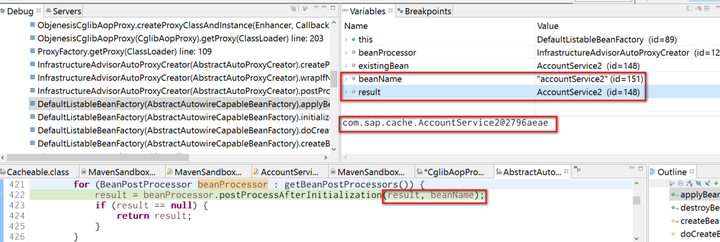
Here the dynamic proxy is created based on configuration defined in xml with the help of CGlibAopProxy. For more detail about CGlibAopProxy, please refer to Spring official document.
要获取更多Jerry的原创文章,请关注公众号"汪子熙":








相关推荐
python学习资源
jfinal-undertow 用于开发、部署由 jfinal 开发的 web 项目
基于Andorid的音乐播放器项目设计(国外开源)实现源码,主要针对计算机相关专业的正在做毕设的学生和需要项目实战练习的学习者,也可作为课程设计、期末大作业。
python学习资源
python学习资源
python学习一些项目和资源
【毕业设计】java-springboot+vue家具销售平台实现源码(完整前后端+mysql+说明文档+LunW).zip
HTML+CSS+JavaScarip开发的前端网页源代码
python学习资源
【毕业设计】java-springboot-vue健身房信息管理系统源码(完整前后端+mysql+说明文档+LunW).zip
成绩管理系统C/Go。大学生期末小作业,指针实现,C语言版本(ANSI C)和Go语言版本
1_基于大数据的智能菜品个性化推荐与点餐系统的设计与实现.docx
【毕业设计】java-springboot-vue交流互动平台实现源码(完整前后端+mysql+说明文档+LunW).zip
内容概要:本文主要探讨了在高并发情况下如何设计并优化火车票秒杀系统,确保系统的高性能与稳定性。通过对比分析三种库存管理模式(下单减库存、支付减库存、预扣库存),强调了预扣库存结合本地缓存及远程Redis统一库存的优势,同时介绍了如何利用Nginx的加权轮询策略、MQ消息队列异步处理等方式降低系统压力,保障交易完整性和数据一致性,防止超卖现象。 适用人群:具有一定互联网应用开发经验的研发人员和技术管理人员。 使用场景及目标:适用于电商、票务等行业需要处理大量瞬时并发请求的业务场景。其目标在于通过合理的架构规划,实现在高峰期保持平台的稳定运行,保证用户体验的同时最大化销售额。 其他说明:文中提及的技术细节如Epoll I/O多路复用模型以及分布式系统中的容错措施等内容,对于深入理解大规模并发系统的构建有着重要指导意义。
基于 OpenCV 和 PyTorch 的深度车牌识别
【毕业设计-java】springboot-vue教学资料管理系统实现源码(完整前后端+mysql+说明文档+LunW).zip
此数据集包含有关出租车行程的详细信息,包括乘客人数、行程距离、付款类型、车费金额和行程时长。它可用于各种数据分析和机器学习应用程序,例如票价预测和乘车模式分析。
把代码放到Word中,通过开发工具——Visual Basic——插入模块,粘贴在里在,把在硅基流动中申请的API放到VBA代码中。在Word中,选择一个问题,运行这个DeepSeekV3的宏就可以实现在线问答
【毕业设计】java-springboot+vue机动车号牌管理系统实现源码(完整前后端+mysql+说明文档+LunW).zip
【毕业设计】java-springboot-vue交通管理在线服务系统的开发源码(完整前后端+mysql+说明文档+LunW).zip