转自https://blog.csdn.net/garfier/article/details/12489953#
性能分析工具
软件的性能是软件质量的重要考察点,不论是在线服务程序还是离线程序,甚至是终端应用,性能都是用户体验的关键。这里说的性能重大的范畴来讲包括了性能和稳定性两个方面,我们在做软件测试的时候也是要重点测试版本的性能表现和稳定性的。对于软件测试过程中发现的性能问题,如何定位有很多的方法。基本的方法可能是开发者对代码进行review,或者是使用一些工具对代码进行性能分析。常见的性能分析tuning工具有哪些呢?下面两篇文章做了详细的总结:
- https://computing.llnl.gov/tutorials/performance_tools/#Considerations
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_performance_analysis_tools
Gprof的基本原理
gprof能够让你知道你的代码哪些地方是比较耗时的,哪些函数是被调用次数很多的,并且能够让你一目了然的看到函数与函数之间的调用关系。gprof是gcc/g++编译器支持的一种性能诊断工具。只要在编译时加上-pg选项,编译器就会在编译程序时在每个函数的开头加一个mcount函数调用,在每一个函数调用之前都会先调用这个mcount函数,在mcount中会保存函数的调用关系图和函数的调用时间和被调次数等信息。最终在程序退出时保存在gmon.out文件中,需要注意的是程序必须是正常退出或者通过exit调用退出,因为只要在exit()被调用时才会触发程序写gmon.out文件。
那么,gprof的使用方法主要以下三步:
- 会用-pg参数编译程序
- 运行程序,并正常退出
- 查看gmon.out文件
Gprof使用实例
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a+b;
}
int sub(int a, int b)
{
return a-b;
}
int call ()
{
std::cout << add(1,2) << std::endl;
std::cout << sub(2,4) << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
int a=1, b=2;
cout << add(a,b) << endl;
for (int i=0; i<10000; i++)
call();
return 0;
}
使用g++编译并加上-pg参数:
- g++ -o hello hello_grof.cpp -pg -g
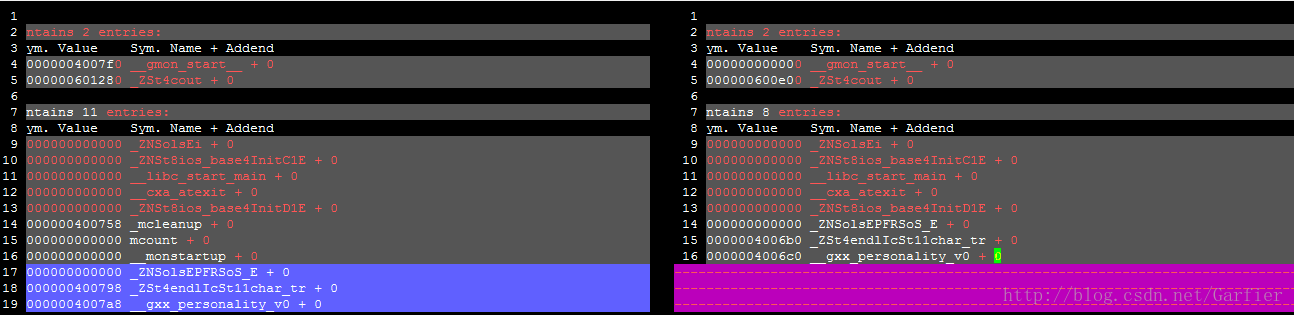
得到可执行文件,我们可以使用readelf查看一下它的符号表里和没有-pg时编译的有啥不同:readelf -r ./hello和readelf -r ./hello_normal得出的结果对比。
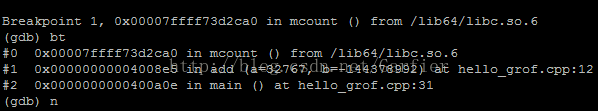
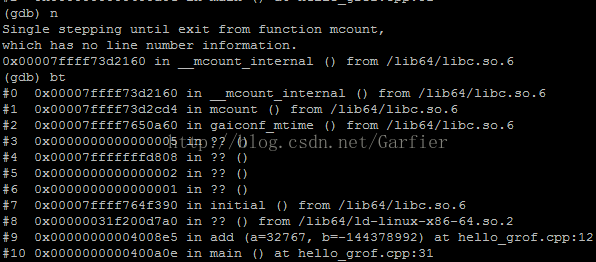
- gprof -b ./hello gmon.out
- Flat profile:
- Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds.
- no time accumulated
- % cumulative self self total
- time seconds seconds calls Ts/call Ts/call name
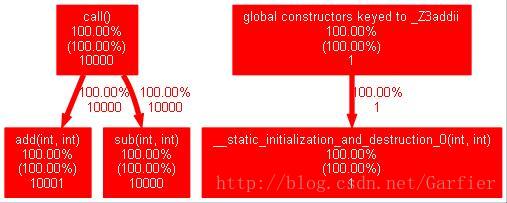
- 0.00 0.00 0.00 10001 0.00 0.00 add(int, int)
- 0.00 0.00 0.00 10000 0.00 0.00 sub(int, int)
- 0.00 0.00 0.00 10000 0.00 0.00 call()
- 0.00 0.00 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 global constructors keyed to _Z3addii
- 0.00 0.00 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 __static_initialization_and_destruction_0(int, int)
- Call graph
- granularity: each sample hit covers 2 byte(s) no time propagated
- index % time self children called name
- 0.00 0.00 1/10001 main [7]
- 0.00 0.00 10000/10001 call() [10]
- [8] 0.0 0.00 0.00 10001 add(int, int) [8]
- -----------------------------------------------
- 0.00 0.00 10000/10000 call() [10]
- [9] 0.0 0.00 0.00 10000 sub(int, int) [9]
- -----------------------------------------------
- 0.00 0.00 10000/10000 main [7]
- [10] 0.0 0.00 0.00 10000 call() [10]
- 0.00 0.00 10000/10001 add(int, int) [8]
- 0.00 0.00 10000/10000 sub(int, int) [9]
- -----------------------------------------------
- 0.00 0.00 1/1 __do_global_ctors_aux [13]
- [11] 0.0 0.00 0.00 1 global constructors keyed to _Z3addii [11]
- 0.00 0.00 1/1 __static_initialization_and_destruction_0(int, int) [12]
- -----------------------------------------------
- 0.00 0.00 1/1 global constructors keyed to _Z3addii [11]
- [12] 0.0 0.00 0.00 1 __static_initialization_and_destruction_0(int, int) [12]
- -----------------------------------------------
- Index by function name
- [11] global constructors keyed to _Z3addii (hello_grof.cpp) [9] sub(int, int) [10] call()
- [8] add(int, int) [12] __static_initialization_and_destruction_0(int, int) (hello_grof.cpp)
可以使用运行命令:
- gprof -b ./hello gmon.out | gprof2doc.py > ~WWW/hello.dot
生成dot格式的调用关系图文件,可以使用windows版的GVEdit for Graphviz软件查看调用关系图:
Gprof输出解读
这部分内容可将gprof -b ./hello中的-b参数去掉,可以显示字段的详细含义描述:
- 14 % the percentage of the total running time of the
- 15 time program used by this function.
- 16
- 17 cumulative a running sum of the number of seconds accounted
- 18 seconds for by this function and those listed above it.
- 19
- 20 self the number of seconds accounted for by this
- 21 seconds function alone. This is the major sort for this
- 22 listing.
- 23
- 24 calls the number of times this function was invoked, if
- 25 this function is profiled, else blank.
- 26
- 27 self the average number of milliseconds spent in this
- 28 ms/call function per call, if this function is profiled,
- 29 else blank.
- 30
- 31 total the average number of milliseconds spent in this
- 32 ms/call function and its descendents per call, if this
- 33 function is profiled, else blank.
- 34
- 35 name the name of the function. This is the minor sort
- 36 for this listing. The index shows the location of
- 37 the function in the gprof listing. If the index is
- 38 in parenthesis it shows where it would appear in
- 39 the gprof listing if it were to be printed.
总结
gprof是常见的性能分析工具,在此罗列一下它的一些不足,也是从网上看的:
- 1、对多线程支持不好,不准确
- 2、必须退出exit()才行
- 3、它只能分析应用程序在运行过程中所消耗掉的用户时间,无法得到程序内核空间的运行时间。对内核态的调用分析无能为力。如果程序系统调用比率比较大,就不适合。







相关推荐
- **-pg**: 生成剖析信息,便于使用gprof等工具进行性能分析。 #### 结论 本文介绍了Linux环境下C/C++开发的基础知识,重点讲解了GCC的使用方法及常见选项。掌握这些基本技能对于初学者来说至关重要,能够帮助他们...
9. **调试与测试**:学会使用GDB进行远程调试,理解日志系统如syslog,以及性能分析工具如gprof,进行代码优化和问题定位。 10. **硬件接口编程**:学习如何与硬件接口,如GPIO、SPI、I2C、UART等通信协议,以及ADC...
性能分析工具如gprof和strace则可以帮助优化代码,提高系统效率。 总的来说,嵌入式Linux应用程序开发需要开发者具备广泛的知识,包括操作系统原理、编程语言、硬件接口以及各种工具的使用。通过深入学习和实践,...
13. **调试技巧**:学会使用GDB进行远程调试,以及日志系统(如syslog)和性能分析工具(如gprof)的应用。 14. **应用程序框架**:理解如何使用Qt、GTK+等图形用户界面框架,以及如何在嵌入式环境中部署和运行服务...
- 如`xxgdb`、`calls`、`calltree`、`indent`和`gprof`等,这些工具在不同的场景下提供了额外的辅助功能,如代码格式化、性能剖析等。 总之,Linux下的C语言编程是一个广阔而深邃的领域,从基础的编译、链接,到...
13. **性能分析与优化**:了解如何使用`gprof`、`strace`、`valgrind`等工具分析程序性能,以及如何优化代码以提高效率。 14. **嵌入式Linux**:如果书籍涉及嵌入式领域,那么你还需要学习硬件接口、设备驱动、实时...
学习使用GDB进行程序调试,理解性能分析工具如gprof和strace,掌握优化技巧,提升程序运行效率。同时,了解嵌入式系统的电源管理和功耗优化,以适应低功耗场景。 通过这七步曲的学习,可以从零基础逐步成长为一名...
2. 性能分析:`gprof`可以分析程序的性能,找出耗时较多的函数。 七、文件系统与I/O操作 在Linux中,一切皆为文件,包括硬件设备。C语言通过标准I/O库和文件操作函数(如fopen、fclose、fread、fwrite等)进行文件...
- **gprof**:是一个性能分析工具,可以用来分析程序运行时的时间消耗情况,帮助开发者找到性能瓶颈。 #### 五、总结 在Linux环境下进行C语言编程需要掌握一系列工具和技术,尤其是GCC编译器的使用及其各种编译选项...
"嵌入式Linux编程入门与开发实例PPT学习教案" 本PPT学习教案主要介绍了嵌入式Linux编程的入门知识和开发实例,涵盖了嵌入式Linux开发环境的构建、U-boot的移植、嵌入式Linux操作系统内核编译等方面的内容。 1. ...
- **建议**:学会使用分析工具(如 gprof、Valgrind 等)来检测程序的运行情况,并针对瓶颈进行优化。同时,也要注意避免过度优化导致代码可读性降低。 #### 35. 学会使用并发编程 - **重要性**:并发编程能够充分...
- **-pg**:生成可用于 gprof 工具分析程序性能的信息。 #### 4. 示例程序:Hello World 下面是一个简单的 "Hello World" 程序示例: ```c #include int main() { printf("Hello World\n"); return 0; } ``` ...
- **-pg**:在程序中添加额外的代码以生成gprof性能分析信息。 #### 三、GDB调试器 **3.1 GDB简介** GDB(GNU Debugger)是一个功能强大的调试工具,主要用于调试C和C++程序。它可以帮助开发者进行一系列的调试...
学会使用断点、变量查看、内存检查等功能进行问题定位,同时,理解软件性能分析工具,如gprof或OProfile,可以帮助优化代码性能。 最后,文档阅读能力至关重要,无论是ARM的官方技术参考手册,还是特定芯片的数据...
9. 性能分析与调优:通过性能分析工具(如gprof、perf等)进行性能瓶颈定位,学习如何进行代码优化,提升鲲鹏平台上的应用性能。 10. 安全性与可靠性:涵盖鲲鹏平台的安全机制,如访问控制、加密技术、数据保护等,...