- жөҸи§Ҳ: 151253 ж¬Ў
- жҖ§еҲ«:

- жқҘиҮӘ: жӯҰжұү
-

ж–Үз« еҲҶзұ»
- е…ЁйғЁеҚҡе®ў (153)
- spring2.5 (22)
- hibernate3 (28)
- struts2 (1)
- javaеҹәзЎҖ (13)
- DOM4J (1)
- log4j (1)
- android (24)
- webservice-XFire1.2 (1)
- webservice-Axis (1)
- sql (11)
- жңҚеҠЎеҷЁ (1)
- linux (3)
- IDEејҖеҸ‘е·Ҙе…· (4)
- зүҲжң¬з®ЎзҗҶ (4)
- js (3)
- struts1 (6)
- ж„ҹжӮҹеҝғжғ… (4)
- jspжқӮи°Ҳ (8)
- ж•ҙеҗҲжҠҖжңҜ (1)
- йқўиҜ• (3)
- Ubuntu (3)
зӨҫеҢәзүҲеқ—
- жҲ‘зҡ„иө„и®Ҝ ( 0)
- жҲ‘зҡ„и®әеқӣ ( 0)
- жҲ‘зҡ„й—®зӯ” ( 0)
еӯҳжЎЈеҲҶзұ»
- 2012-03 ( 11)
- 2011-07 ( 41)
- 2011-04 ( 54)
- жӣҙеӨҡеӯҳжЎЈ...
жңҖж–°иҜ„и®ә
-
flyingcatjjпјҡ
еҫҲйҖӮеҗҲжҲ‘иҝҷз§ҚеҲҡжҺҘи§Ұзҡ„
myeclipse xfire ејҖеҸ‘webserviceе®һдҫӢ -
tangzlboyпјҡ
йқһеёёеҘҪпјҢйқһеёёиҜҰз»ҶпјҢйқһеёёдёӯз”ЁгҖӮ
linuxе…Ҙй—Ё -
yzz9iпјҡ
В жҘјдё»иҜҙзҡ„еҫҲжҳҜиҜҰз»ҶгҖӮ
myeclipse xfire ејҖеҸ‘webserviceе®һдҫӢ -
zqx888191пјҡ
еҫҲеҶҚзҗҶйҳҝпјҒ
иҖҒзЁӢеәҸе‘ҳзҡ„ж•ҷиҜІ -
simplecat123пјҡ
...
SQLiteж•°жҚ®иҜ»еҸ–
еҶҷйҒ“
еӨ§е®¶еҘҪпјҢдёҠдёҖиҠӮжҲ‘и®Іи§ЈдәҶAndroid Activityзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹпјҢиҝҷдёҖиҠӮжҲ‘е°Ҷи®Іи§ЈдёҖдёӢServiceпјҢйҰ–е…ҲжҲ‘们иҰҒзҹҘйҒ“Serviceе…·дҪ“жҳҜе№Ід»Җд№Ҳзҡ„пјҢд»Җд№Ҳж—¶еҖҷз”ЁеҲ°пјҹд»ҘеҸҠе®ғзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹзӯүгҖӮ
ServiceжҰӮеҝөеҸҠз”ЁйҖ”:
Androidдёӯзҡ„жңҚеҠЎпјҢе®ғдёҺActivityдёҚеҗҢпјҢе®ғжҳҜдёҚиғҪдёҺз”ЁжҲ·дәӨдә’зҡ„пјҢдёҚиғҪиҮӘе·ұеҗҜеҠЁзҡ„пјҢиҝҗиЎҢеңЁеҗҺеҸ°зҡ„зЁӢеәҸпјҢеҰӮжһңжҲ‘们йҖҖеҮәеә”з”Ёж—¶пјҢServiceиҝӣзЁӢ并没жңүз»“жқҹпјҢе®ғд»Қ然еңЁеҗҺеҸ°иҝҗиЎҢпјҢйӮЈжҲ‘们д»Җд№Ҳж—¶еҖҷдјҡз”ЁеҲ°Serviceе‘ўпјҹжҜ”еҰӮжҲ‘们ж’ӯж”ҫйҹід№җзҡ„ж—¶еҖҷпјҢжңүеҸҜиғҪжғіиҫ№еҗ¬йҹід№җиҫ№е№Ідәӣе…¶д»–дәӢжғ…пјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们йҖҖеҮәж’ӯж”ҫйҹід№җзҡ„еә”з”ЁпјҢеҰӮжһңдёҚз”ЁServiceпјҢжҲ‘们е°ұеҗ¬дёҚеҲ°жӯҢдәҶпјҢжүҖд»Ҙиҝҷж—¶еҖҷе°ұеҫ—з”ЁеҲ°ServiceдәҶпјҢеҸҲжҜ”еҰӮеҪ“жҲ‘们дёҖдёӘеә”з”Ёзҡ„ж•°жҚ®жҳҜйҖҡиҝҮзҪ‘з»ңиҺ·еҸ–зҡ„пјҢдёҚеҗҢж—¶й—ҙпјҲдёҖж®өж—¶й—ҙпјүзҡ„ж•°жҚ®жҳҜдёҚеҗҢзҡ„иҝҷж—¶еҖҷжҲ‘们еҸҜд»Ҙз”ЁServiceеңЁеҗҺеҸ°е®ҡж—¶жӣҙж–°пјҢиҖҢдёҚз”ЁжҜҸжү“ејҖеә”з”Ёзҡ„ж—¶еҖҷеңЁеҺ»иҺ·еҸ–гҖӮ
Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ :
Android Serviceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ并дёҚеғҸActivityйӮЈд№ҲеӨҚжқӮпјҢе®ғеҸӘ继жүҝдәҶonCreate(),onStart(),onDestroy()дёүдёӘж–№жі•пјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们第дёҖж¬ЎеҗҜеҠЁServiceж—¶пјҢе…ҲеҗҺи°ғз”ЁдәҶonCreate(),onStart()иҝҷдёӨдёӘж–№жі•пјҢеҪ“еҒңжӯўServiceж—¶пјҢеҲҷжү§иЎҢonDestroy()ж–№жі•пјҢиҝҷйҮҢйңҖиҰҒжіЁж„Ҹзҡ„жҳҜпјҢеҰӮжһңServiceе·Із»ҸеҗҜеҠЁдәҶпјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们еҶҚж¬ЎеҗҜеҠЁServiceж—¶пјҢдёҚдјҡеңЁжү§иЎҢonCreate()ж–№жі•пјҢиҖҢжҳҜзӣҙжҺҘжү§иЎҢonStart()ж–№жі•пјҢе…·дҪ“зҡ„еҸҜд»ҘзңӢдёӢйқўзҡ„е®һдҫӢгҖӮ
ServiceдёҺActivityйҖҡдҝЎ:
ServiceеҗҺз«Ҝзҡ„ж•°жҚ®жңҖз»ҲиҝҳжҳҜиҰҒе‘ҲзҺ°еңЁеүҚз«ҜActivityд№ӢдёҠзҡ„пјҢеӣ дёәеҗҜеҠЁServiceж—¶пјҢзі»з»ҹдјҡйҮҚж–°ејҖеҗҜдёҖдёӘж–°зҡ„иҝӣзЁӢпјҢиҝҷе°ұж¶үеҸҠеҲ°дёҚеҗҢиҝӣзЁӢй—ҙйҖҡдҝЎзҡ„й—®йўҳдәҶ(AIDL)иҝҷдёҖиҠӮжҲ‘дёҚдҪңиҝҮеӨҡжҸҸиҝ°пјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们жғіиҺ·еҸ–еҗҜеҠЁзҡ„Serviceе®һдҫӢж—¶пјҢжҲ‘们еҸҜд»Ҙз”ЁеҲ°bindServiceе’ҢonBindServiceж–№жі•пјҢе®ғ们еҲҶеҲ«жү§иЎҢдәҶServiceдёӯIBinder()е’ҢonUnbind()ж–№жі•гҖӮ
дёәдәҶи®©еӨ§е®¶ жӣҙе®№жҳ“зҗҶи§ЈпјҢжҲ‘еҶҷдәҶдёҖдёӘз®ҖеҚ•зҡ„Demo,еӨ§е®¶еҸҜд»ҘжЁЎд»ҝзқҖжҲ‘пјҢдёҖжӯҘдёҖжӯҘзҡ„жқҘгҖӮ
第дёҖжӯҘ:ж–°е»әдёҖдёӘAndroidе·ҘзЁӢпјҢжҲ‘иҝҷйҮҢе‘ҪеҗҚдёәServiceDemo.
第дәҢжӯҘ:дҝ®ж”№main.xmlд»Јз ҒпјҢжҲ‘иҝҷйҮҢеўһеҠ дәҶеӣӣдёӘжҢүй’®,д»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢ:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
01.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
02.<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
03. android:orientation="vertical"
04. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
05. android:layout_height="fill_parent"
06. >
07. <TextView
08. android:id="@+id/text"
09. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
10. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
11. android:text="@string/hello"
12. />
13. <Button
14. android:id="@+id/startservice"
15. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
16. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
17. android:text="startService"
18. />
19. <Button
20. android:id="@+id/stopservice"
21. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
22. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
23. android:text="stopService"
24. />
25. <Button
26. android:id="@+id/bindservice"
27. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
28. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
29. android:text="bindService"
30. />
31. <Button
32. android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
33. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
34. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
35. android:text="unbindService"
36. />
37.</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/startservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="startService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="stopService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="bindService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="unbindService"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第дёүжӯҘ:ж–°е»әдёҖдёӘServiceпјҢе‘ҪеҗҚдёәMyService.javaд»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢ:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
01.package com.tutor.servicedemo;
02.import android.app.Service;
03.import android.content.Intent;
04.import android.os.Binder;
05.import android.os.IBinder;
06.import android.text.format.Time;
07.import android.util.Log;
08.public class MyService extends Service {
09. //е®ҡд№үдёӘдёҖдёӘTagж Үзӯҫ
10. private static final String TAG = "MyService";
11. //иҝҷйҮҢе®ҡд№үеҗ§дёҖдёӘBinderзұ»пјҢз”ЁеңЁonBind()жңүж–№жі•йҮҢпјҢиҝҷж ·ActivityйӮЈиҫ№еҸҜд»ҘиҺ·еҸ–еҲ°
12. private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
13. @Override
14. public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
15. Log.e(TAG, "start IBinder~~~");
16. return mBinder;
17. }
18. @Override
19. public void onCreate() {
20. Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~");
21. super.onCreate();
22. }
23.
24. @Override
25. public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
26. Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~");
27. super.onStart(intent, startId);
28. }
29.
30. @Override
31. public void onDestroy() {
32. Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~");
33. super.onDestroy();
34. }
35.
36.
37. @Override
38. public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
39. Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
40. return super.onUnbind(intent);
41. }
42.
43. //иҝҷйҮҢжҲ‘еҶҷдәҶдёҖдёӘиҺ·еҸ–еҪ“еүҚж—¶й—ҙзҡ„еҮҪж•°пјҢдёҚиҝҮжІЎжңүж јејҸеҢ–е°ұе…Ҳиҝҷд№ҲзқҖеҗ§
44. public String getSystemTime(){
45.
46. Time t = new Time();
47. t.setToNow();
48. return t.toString();
49. }
50.
51. public class MyBinder extends Binder{
52. MyService getService()
53. {
54. return MyService.this;
55. }
56. }
57.}
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.text.format.Time;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
//е®ҡд№үдёӘдёҖдёӘTagж Үзӯҫ
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
//иҝҷйҮҢе®ҡд№үеҗ§дёҖдёӘBinderзұ»пјҢз”ЁеңЁonBind()жңүж–№жі•йҮҢпјҢиҝҷж ·ActivityйӮЈиҫ№еҸҜд»ҘиҺ·еҸ–еҲ°
private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start IBinder~~~");
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
//иҝҷйҮҢжҲ‘еҶҷдәҶдёҖдёӘиҺ·еҸ–еҪ“еүҚж—¶й—ҙзҡ„еҮҪж•°пјҢдёҚиҝҮжІЎжңүж јејҸеҢ–е°ұе…Ҳиҝҷд№ҲзқҖеҗ§
public String getSystemTime(){
Time t = new Time();
t.setToNow();
return t.toString();
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
MyService getService()
{
return MyService.this;
}
}
}
第еӣӣжӯҘ:дҝ®ж”№ServiceDemo.javaпјҢд»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢ:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
01.package com.tutor.servicedemo;
02.import android.app.Activity;
03.import android.content.ComponentName;
04.import android.content.Context;
05.import android.content.Intent;
06.import android.content.ServiceConnection;
07.import android.os.Bundle;
08.import android.os.IBinder;
09.import android.view.View;
10.import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
11.import android.widget.Button;
12.import android.widget.TextView;
13.public class ServiceDemo extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
14.
15. private MyService mMyService;
16. private TextView mTextView;
17. private Button startServiceButton;
18. private Button stopServiceButton;
19. private Button bindServiceButton;
20. private Button unbindServiceButton;
21. private Context mContext;
22.
23. //иҝҷйҮҢйңҖиҰҒз”ЁеҲ°ServiceConnectionеңЁContext.bindServiceе’Ңcontext.unBindService()йҮҢз”ЁеҲ°
24. private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
25. //еҪ“жҲ‘bindServiceж—¶пјҢи®©TextViewжҳҫзӨәMyServiceйҮҢgetSystemTime()ж–№жі•зҡ„иҝ”еӣһеҖј
26. public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
27. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
28. mMyService = ((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
29. mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
30. }
31.
32. public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
33. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
34.
35. }
36. };
37. public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
38. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
39. setContentView(R.layout.main);
40. setupViews();
41. }
42.
43. public void setupViews(){
44.
45. mContext = ServiceDemo.this;
46. mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text);
47.
48.
49.
50. startServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
51. stopServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
52. bindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
53. unbindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice);
54.
55. startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
56. stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
57. bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
58. unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
59. }
60.
61. public void onClick(View v) {
62. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
63. if(v == startServiceButton){
64. Intent i = new Intent();
65. i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
66. mContext.startService(i);
67. }else if(v == stopServiceButton){
68. Intent i = new Intent();
69. i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
70. mContext.stopService(i);
71. }else if(v == bindServiceButton){
72. Intent i = new Intent();
73. i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
74. mContext.bindService(i, mServiceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
75. }else{
76. mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
77. }
78. }
79.
80.
81.
82.}
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ServiceDemo extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
private MyService mMyService;
private TextView mTextView;
private Button startServiceButton;
private Button stopServiceButton;
private Button bindServiceButton;
private Button unbindServiceButton;
private Context mContext;
//иҝҷйҮҢйңҖиҰҒз”ЁеҲ°ServiceConnectionеңЁContext.bindServiceе’Ңcontext.unBindService()йҮҢз”ЁеҲ°
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
//еҪ“жҲ‘bindServiceж—¶пјҢи®©TextViewжҳҫзӨәMyServiceйҮҢgetSystemTime()ж–№жі•зҡ„иҝ”еӣһеҖј
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mMyService = ((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
setupViews();
}
public void setupViews(){
mContext = ServiceDemo.this;
mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text);
startServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
stopServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
bindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
unbindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice);
startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
}
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(v == startServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.startService(i);
}else if(v == stopServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.stopService(i);
}else if(v == bindServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.bindService(i, mServiceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}else{
mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
}
}
}
第дә”жӯҘ:дҝ®ж”№AndroidManifest.xmlд»Јз Ғ(е°ҶжҲ‘们新е»әзҡ„MyServiceжіЁеҶҢиҝӣеҺ»еҰӮдёӢд»Јз Ғ第14иЎҢ:)
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
01.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
02.<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
03. package="com.tutor.servicedemo"
04. android:versionCode="1"
05. android:versionName="1.0">
06. <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
07. <activity android:name=".ServiceDemo"
08. android:label="@string/app_name">
09. <intent-filter>
10. <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
11. <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
12. </intent-filter>
13. </activity>
14. <service android:name=".MyService" android:exported="true"></service>
15. </application>
16. <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
17.</manifest>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.tutor.servicedemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".ServiceDemo"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" android:exported="true"></service>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
</manifest>
第е…ӯжӯҘ:жү§иЎҢдёҠиҝ°е·ҘзЁӢ,ж•ҲжһңеӣҫеҰӮдёӢ:
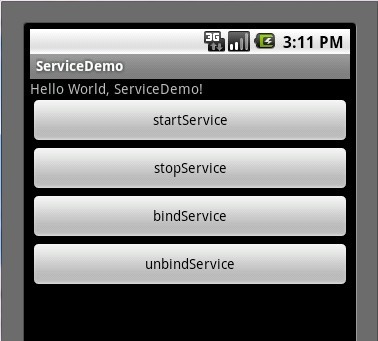
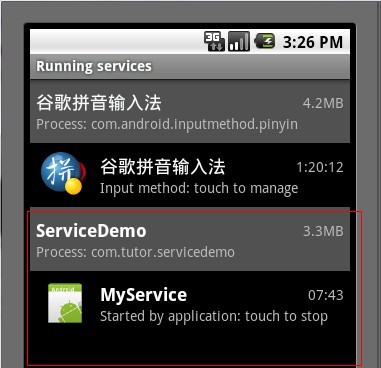
зӮ№еҮ»startServieжҢүй’®ж—¶е…ҲеҗҺжү§иЎҢдәҶServiceдёӯonCreate()->onStart()иҝҷдёӨдёӘж–№жі•пјҢжү“ејҖLogcatи§ҶзӘ—ж•ҲжһңеҰӮдёӢеӣҫ:

жҲ‘们иҝҷж—¶еҸҜд»ҘжҢүHOMEй”®иҝӣе…ҘSettings(и®ҫзҪ®)->Applications(еә”з”Ёпјү->Running Services(жӯЈеңЁиҝҗиЎҢзҡ„жңҚеҠЎпјүзңӢдёҖдёӢжҲ‘们新еҗҜеҠЁдәҶдёҖдёӘжңҚеҠЎпјҢж•ҲжһңеҰӮдёӢ:
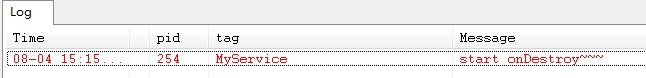
зӮ№еҮ»stopServiceжҢүй’®ж—¶пјҢServiceеҲҷжү§иЎҢдәҶonDestroy()ж–№жі•пјҢж•ҲжһңеӣҫеҰӮдёӢжүҖзӨә:
иҝҷж—¶еҖҷжҲ‘们еҶҚж¬ЎзӮ№еҮ»startServiceжҢүй’®пјҢ然еҗҺзӮ№еҮ»bindServiceжҢүй’®(йҖҡеёёbindServiceйғҪжҳҜbindе·Із»ҸеҗҜеҠЁзҡ„Service)пјҢжҲ‘们зңӢдёҖдёӢServiceжү§иЎҢдәҶIBinder()ж–№жі•пјҢд»ҘеҸҠTextViewзҡ„еҖјд№ҹжңүжүҖеҸҳеҢ–дәҶпјҢеҰӮдёӢдёӨеј еӣҫжүҖзӨә:

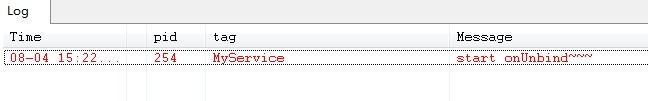
жңҖеҗҺзӮ№еҮ»unbindServiceжҢүй’®пјҢеҲҷServiceжү§иЎҢдәҶonUnbind()ж–№жі•пјҢеҰӮдёӢеӣҫжүҖзӨә:
OkпјҢд»ҠеӨ©е°ұе…Ҳи®ІеҲ°иҝҷйҮҢдәҶпјҢи°ўи°ўеӨ§е®¶е…іжіЁВ
ServiceжҰӮеҝөеҸҠз”ЁйҖ”:
Androidдёӯзҡ„жңҚеҠЎпјҢе®ғдёҺActivityдёҚеҗҢпјҢе®ғжҳҜдёҚиғҪдёҺз”ЁжҲ·дәӨдә’зҡ„пјҢдёҚиғҪиҮӘе·ұеҗҜеҠЁзҡ„пјҢиҝҗиЎҢеңЁеҗҺеҸ°зҡ„зЁӢеәҸпјҢеҰӮжһңжҲ‘们йҖҖеҮәеә”з”Ёж—¶пјҢServiceиҝӣзЁӢ并没жңүз»“жқҹпјҢе®ғд»Қ然еңЁеҗҺеҸ°иҝҗиЎҢпјҢйӮЈжҲ‘们д»Җд№Ҳж—¶еҖҷдјҡз”ЁеҲ°Serviceе‘ўпјҹжҜ”еҰӮжҲ‘们ж’ӯж”ҫйҹід№җзҡ„ж—¶еҖҷпјҢжңүеҸҜиғҪжғіиҫ№еҗ¬йҹід№җиҫ№е№Ідәӣе…¶д»–дәӢжғ…пјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们йҖҖеҮәж’ӯж”ҫйҹід№җзҡ„еә”з”ЁпјҢеҰӮжһңдёҚз”ЁServiceпјҢжҲ‘们е°ұеҗ¬дёҚеҲ°жӯҢдәҶпјҢжүҖд»Ҙиҝҷж—¶еҖҷе°ұеҫ—з”ЁеҲ°ServiceдәҶпјҢеҸҲжҜ”еҰӮеҪ“жҲ‘们дёҖдёӘеә”з”Ёзҡ„ж•°жҚ®жҳҜйҖҡиҝҮзҪ‘з»ңиҺ·еҸ–зҡ„пјҢдёҚеҗҢж—¶й—ҙпјҲдёҖж®өж—¶й—ҙпјүзҡ„ж•°жҚ®жҳҜдёҚеҗҢзҡ„иҝҷж—¶еҖҷжҲ‘们еҸҜд»Ҙз”ЁServiceеңЁеҗҺеҸ°е®ҡж—¶жӣҙж–°пјҢиҖҢдёҚз”ЁжҜҸжү“ејҖеә”з”Ёзҡ„ж—¶еҖҷеңЁеҺ»иҺ·еҸ–гҖӮ
Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ :
Android Serviceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ并дёҚеғҸActivityйӮЈд№ҲеӨҚжқӮпјҢе®ғеҸӘ继жүҝдәҶonCreate(),onStart(),onDestroy()дёүдёӘж–№жі•пјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们第дёҖж¬ЎеҗҜеҠЁServiceж—¶пјҢе…ҲеҗҺи°ғз”ЁдәҶonCreate(),onStart()иҝҷдёӨдёӘж–№жі•пјҢеҪ“еҒңжӯўServiceж—¶пјҢеҲҷжү§иЎҢonDestroy()ж–№жі•пјҢиҝҷйҮҢйңҖиҰҒжіЁж„Ҹзҡ„жҳҜпјҢеҰӮжһңServiceе·Із»ҸеҗҜеҠЁдәҶпјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们еҶҚж¬ЎеҗҜеҠЁServiceж—¶пјҢдёҚдјҡеңЁжү§иЎҢonCreate()ж–№жі•пјҢиҖҢжҳҜзӣҙжҺҘжү§иЎҢonStart()ж–№жі•пјҢе…·дҪ“зҡ„еҸҜд»ҘзңӢдёӢйқўзҡ„е®һдҫӢгҖӮ
ServiceдёҺActivityйҖҡдҝЎ:
ServiceеҗҺз«Ҝзҡ„ж•°жҚ®жңҖз»ҲиҝҳжҳҜиҰҒе‘ҲзҺ°еңЁеүҚз«ҜActivityд№ӢдёҠзҡ„пјҢеӣ дёәеҗҜеҠЁServiceж—¶пјҢзі»з»ҹдјҡйҮҚж–°ејҖеҗҜдёҖдёӘж–°зҡ„иҝӣзЁӢпјҢиҝҷе°ұж¶үеҸҠеҲ°дёҚеҗҢиҝӣзЁӢй—ҙйҖҡдҝЎзҡ„й—®йўҳдәҶ(AIDL)иҝҷдёҖиҠӮжҲ‘дёҚдҪңиҝҮеӨҡжҸҸиҝ°пјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们жғіиҺ·еҸ–еҗҜеҠЁзҡ„Serviceе®һдҫӢж—¶пјҢжҲ‘们еҸҜд»Ҙз”ЁеҲ°bindServiceе’ҢonBindServiceж–№жі•пјҢе®ғ们еҲҶеҲ«жү§иЎҢдәҶServiceдёӯIBinder()е’ҢonUnbind()ж–№жі•гҖӮ
дёәдәҶи®©еӨ§е®¶ жӣҙе®№жҳ“зҗҶи§ЈпјҢжҲ‘еҶҷдәҶдёҖдёӘз®ҖеҚ•зҡ„Demo,еӨ§е®¶еҸҜд»ҘжЁЎд»ҝзқҖжҲ‘пјҢдёҖжӯҘдёҖжӯҘзҡ„жқҘгҖӮ
第дёҖжӯҘ:ж–°е»әдёҖдёӘAndroidе·ҘзЁӢпјҢжҲ‘иҝҷйҮҢе‘ҪеҗҚдёәServiceDemo.
第дәҢжӯҘ:дҝ®ж”№main.xmlд»Јз ҒпјҢжҲ‘иҝҷйҮҢеўһеҠ дәҶеӣӣдёӘжҢүй’®,д»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢ:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
01.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
02.<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
03. android:orientation="vertical"
04. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
05. android:layout_height="fill_parent"
06. >
07. <TextView
08. android:id="@+id/text"
09. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
10. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
11. android:text="@string/hello"
12. />
13. <Button
14. android:id="@+id/startservice"
15. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
16. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
17. android:text="startService"
18. />
19. <Button
20. android:id="@+id/stopservice"
21. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
22. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
23. android:text="stopService"
24. />
25. <Button
26. android:id="@+id/bindservice"
27. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
28. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
29. android:text="bindService"
30. />
31. <Button
32. android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
33. android:layout_width="fill_parent"
34. android:layout_height="wrap_content"
35. android:text="unbindService"
36. />
37.</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/startservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="startService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/stopservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="stopService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/bindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="bindService"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/unbindservice"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="unbindService"
/>
</LinearLayout>
第дёүжӯҘ:ж–°е»әдёҖдёӘServiceпјҢе‘ҪеҗҚдёәMyService.javaд»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢ:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
01.package com.tutor.servicedemo;
02.import android.app.Service;
03.import android.content.Intent;
04.import android.os.Binder;
05.import android.os.IBinder;
06.import android.text.format.Time;
07.import android.util.Log;
08.public class MyService extends Service {
09. //е®ҡд№үдёӘдёҖдёӘTagж Үзӯҫ
10. private static final String TAG = "MyService";
11. //иҝҷйҮҢе®ҡд№үеҗ§дёҖдёӘBinderзұ»пјҢз”ЁеңЁonBind()жңүж–№жі•йҮҢпјҢиҝҷж ·ActivityйӮЈиҫ№еҸҜд»ҘиҺ·еҸ–еҲ°
12. private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
13. @Override
14. public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
15. Log.e(TAG, "start IBinder~~~");
16. return mBinder;
17. }
18. @Override
19. public void onCreate() {
20. Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~");
21. super.onCreate();
22. }
23.
24. @Override
25. public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
26. Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~");
27. super.onStart(intent, startId);
28. }
29.
30. @Override
31. public void onDestroy() {
32. Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~");
33. super.onDestroy();
34. }
35.
36.
37. @Override
38. public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
39. Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
40. return super.onUnbind(intent);
41. }
42.
43. //иҝҷйҮҢжҲ‘еҶҷдәҶдёҖдёӘиҺ·еҸ–еҪ“еүҚж—¶й—ҙзҡ„еҮҪж•°пјҢдёҚиҝҮжІЎжңүж јејҸеҢ–е°ұе…Ҳиҝҷд№ҲзқҖеҗ§
44. public String getSystemTime(){
45.
46. Time t = new Time();
47. t.setToNow();
48. return t.toString();
49. }
50.
51. public class MyBinder extends Binder{
52. MyService getService()
53. {
54. return MyService.this;
55. }
56. }
57.}
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.text.format.Time;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
//е®ҡд№үдёӘдёҖдёӘTagж Үзӯҫ
private static final String TAG = "MyService";
//иҝҷйҮҢе®ҡд№үеҗ§дёҖдёӘBinderзұ»пјҢз”ЁеңЁonBind()жңүж–№жі•йҮҢпјҢиҝҷж ·ActivityйӮЈиҫ№еҸҜд»ҘиҺ·еҸ–еҲ°
private MyBinder mBinder = new MyBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start IBinder~~~");
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.e(TAG, "start onUnbind~~~");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
//иҝҷйҮҢжҲ‘еҶҷдәҶдёҖдёӘиҺ·еҸ–еҪ“еүҚж—¶й—ҙзҡ„еҮҪж•°пјҢдёҚиҝҮжІЎжңүж јејҸеҢ–е°ұе…Ҳиҝҷд№ҲзқҖеҗ§
public String getSystemTime(){
Time t = new Time();
t.setToNow();
return t.toString();
}
public class MyBinder extends Binder{
MyService getService()
{
return MyService.this;
}
}
}
第еӣӣжӯҘ:дҝ®ж”№ServiceDemo.javaпјҢд»Јз ҒеҰӮдёӢ:
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
01.package com.tutor.servicedemo;
02.import android.app.Activity;
03.import android.content.ComponentName;
04.import android.content.Context;
05.import android.content.Intent;
06.import android.content.ServiceConnection;
07.import android.os.Bundle;
08.import android.os.IBinder;
09.import android.view.View;
10.import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
11.import android.widget.Button;
12.import android.widget.TextView;
13.public class ServiceDemo extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
14.
15. private MyService mMyService;
16. private TextView mTextView;
17. private Button startServiceButton;
18. private Button stopServiceButton;
19. private Button bindServiceButton;
20. private Button unbindServiceButton;
21. private Context mContext;
22.
23. //иҝҷйҮҢйңҖиҰҒз”ЁеҲ°ServiceConnectionеңЁContext.bindServiceе’Ңcontext.unBindService()йҮҢз”ЁеҲ°
24. private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
25. //еҪ“жҲ‘bindServiceж—¶пјҢи®©TextViewжҳҫзӨәMyServiceйҮҢgetSystemTime()ж–№жі•зҡ„иҝ”еӣһеҖј
26. public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
27. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
28. mMyService = ((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
29. mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
30. }
31.
32. public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
33. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
34.
35. }
36. };
37. public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
38. super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
39. setContentView(R.layout.main);
40. setupViews();
41. }
42.
43. public void setupViews(){
44.
45. mContext = ServiceDemo.this;
46. mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text);
47.
48.
49.
50. startServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
51. stopServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
52. bindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
53. unbindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice);
54.
55. startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
56. stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
57. bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
58. unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
59. }
60.
61. public void onClick(View v) {
62. // TODO Auto-generated method stub
63. if(v == startServiceButton){
64. Intent i = new Intent();
65. i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
66. mContext.startService(i);
67. }else if(v == stopServiceButton){
68. Intent i = new Intent();
69. i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
70. mContext.stopService(i);
71. }else if(v == bindServiceButton){
72. Intent i = new Intent();
73. i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
74. mContext.bindService(i, mServiceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
75. }else{
76. mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
77. }
78. }
79.
80.
81.
82.}
package com.tutor.servicedemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class ServiceDemo extends Activity implements OnClickListener{
private MyService mMyService;
private TextView mTextView;
private Button startServiceButton;
private Button stopServiceButton;
private Button bindServiceButton;
private Button unbindServiceButton;
private Context mContext;
//иҝҷйҮҢйңҖиҰҒз”ЁеҲ°ServiceConnectionеңЁContext.bindServiceе’Ңcontext.unBindService()йҮҢз”ЁеҲ°
private ServiceConnection mServiceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
//еҪ“жҲ‘bindServiceж—¶пјҢи®©TextViewжҳҫзӨәMyServiceйҮҢgetSystemTime()ж–№жі•зҡ„иҝ”еӣһеҖј
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
mMyService = ((MyService.MyBinder)service).getService();
mTextView.setText("I am frome Service :" + mMyService.getSystemTime());
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
};
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
setupViews();
}
public void setupViews(){
mContext = ServiceDemo.this;
mTextView = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text);
startServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startservice);
stopServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.stopservice);
bindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.bindservice);
unbindServiceButton = (Button)findViewById(R.id.unbindservice);
startServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
stopServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
bindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
unbindServiceButton.setOnClickListener(this);
}
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(v == startServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.startService(i);
}else if(v == stopServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.stopService(i);
}else if(v == bindServiceButton){
Intent i = new Intent();
i.setClass(ServiceDemo.this, MyService.class);
mContext.bindService(i, mServiceConnection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}else{
mContext.unbindService(mServiceConnection);
}
}
}
第дә”жӯҘ:дҝ®ж”№AndroidManifest.xmlд»Јз Ғ(е°ҶжҲ‘们新е»әзҡ„MyServiceжіЁеҶҢиҝӣеҺ»еҰӮдёӢд»Јз Ғ第14иЎҢ:)
view plaincopy to clipboardprint?
01.<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
02.<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
03. package="com.tutor.servicedemo"
04. android:versionCode="1"
05. android:versionName="1.0">
06. <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
07. <activity android:name=".ServiceDemo"
08. android:label="@string/app_name">
09. <intent-filter>
10. <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
11. <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
12. </intent-filter>
13. </activity>
14. <service android:name=".MyService" android:exported="true"></service>
15. </application>
16. <uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
17.</manifest>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.tutor.servicedemo"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".ServiceDemo"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" android:exported="true"></service>
</application>
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="7" />
</manifest>
第е…ӯжӯҘ:жү§иЎҢдёҠиҝ°е·ҘзЁӢ,ж•ҲжһңеӣҫеҰӮдёӢ:

зӮ№еҮ»startServieжҢүй’®ж—¶е…ҲеҗҺжү§иЎҢдәҶServiceдёӯonCreate()->onStart()иҝҷдёӨдёӘж–№жі•пјҢжү“ејҖLogcatи§ҶзӘ—ж•ҲжһңеҰӮдёӢеӣҫ:

жҲ‘们иҝҷж—¶еҸҜд»ҘжҢүHOMEй”®иҝӣе…ҘSettings(и®ҫзҪ®)->Applications(еә”з”Ёпјү->Running Services(жӯЈеңЁиҝҗиЎҢзҡ„жңҚеҠЎпјүзңӢдёҖдёӢжҲ‘们新еҗҜеҠЁдәҶдёҖдёӘжңҚеҠЎпјҢж•ҲжһңеҰӮдёӢ:

зӮ№еҮ»stopServiceжҢүй’®ж—¶пјҢServiceеҲҷжү§иЎҢдәҶonDestroy()ж–№жі•пјҢж•ҲжһңеӣҫеҰӮдёӢжүҖзӨә:

иҝҷж—¶еҖҷжҲ‘们еҶҚж¬ЎзӮ№еҮ»startServiceжҢүй’®пјҢ然еҗҺзӮ№еҮ»bindServiceжҢүй’®(йҖҡеёёbindServiceйғҪжҳҜbindе·Із»ҸеҗҜеҠЁзҡ„Service)пјҢжҲ‘们зңӢдёҖдёӢServiceжү§иЎҢдәҶIBinder()ж–№жі•пјҢд»ҘеҸҠTextViewзҡ„еҖјд№ҹжңүжүҖеҸҳеҢ–дәҶпјҢеҰӮдёӢдёӨеј еӣҫжүҖзӨә:

жңҖеҗҺзӮ№еҮ»unbindServiceжҢүй’®пјҢеҲҷServiceжү§иЎҢдәҶonUnbind()ж–№жі•пјҢеҰӮдёӢеӣҫжүҖзӨә:

OkпјҢд»ҠеӨ©е°ұе…Ҳи®ІеҲ°иҝҷйҮҢдәҶпјҢи°ўи°ўеӨ§е®¶е…іжіЁВ
В
- 2011-03-28 13:03
- жөҸи§Ҳ 670
- иҜ„и®ә(0)
- еҲҶзұ»:移еҠЁејҖеҸ‘
- жҹҘзңӢжӣҙеӨҡ
еҸ‘иЎЁиҜ„и®ә
-
Bitmap Drawable byte[] дёүиҖ…д№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„иҪ¬жҚўд»ҘеҸҠжҠҠж•°з»„еӯҳе…Ҙж•°жҚ®еә“еҸҠжҸҗеҸ–ж•°жҚ®йҮҚж–°з»„еҗҲ
2012-03-06 11:21 814Bitmap Drawable byte[] дёүиҖ…д№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„иҪ¬жҚўд»Ҙ ... -
Android Activityз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ
2011-03-28 11:41 830еӨ§е®¶еҘҪпјҢд»ҠеӨ©з»ҷеӨ§е®¶иҜҰи§ЈдёҖдёӢAndroidдёӯActivityзҡ„з”ҹ ... -
DrawableдҪҝз”Ёе…Ҙй—Ё
2011-03-25 16:03 1178дёҖдёӘи®©дәәиөҸеҝғжӮҰзӣ®зҡ„з•ҢйқўеҜ№иҪҜ件жқҘиҜҙйқһеёёйҮҚиҰҒпјҢеӣ жӯӨеӣҫеҪўеӣҫеғҸиө„жәҗд№ҹжҳҫ ... -
Android дёӯзҡ„еҮ дёӘеёёз”ЁжҺ§д»¶
2011-03-24 14:43 1056еҶҷйҒ“ 1гҖҒRadioButton гҖҖгҖҖRadioButton ... -
androidе‘Ҫд»Ө
2011-03-03 14:44 966еҶҷйҒ“ еӨ§е®¶еҘҪпјҢд»ҠеӨ©жҲ‘д ... -
androidеӯҰд№ зҡ„еҘҪзҪ‘еқҖ
2011-02-22 10:10 963http://www.droidnova.com/and ... -
linuxдёӢж“ҚдҪңandroidжЁЎжӢҹеҷЁе‘Ҫд»Ө
2011-02-14 17:14 2154еҶҷйҒ“ 1пјҡеҲ—еҮәжЁЎжӢҹеҷЁзұ»еһӢ android list ... -
Activityз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ
2011-02-08 19:59 892еӨ§е®¶еҘҪпјҢд»ҠеӨ©з»ҷеӨ§е®¶иҜҰи§ЈдёҖдёӢAndroidдёӯActivit ... -
IntentеҜ№иұЎзҡ„з®ҖеҚ•дҪҝз”Ё
2011-02-08 00:38 661еҰӮжһңиҰҒиҪ¬жҚўзҡ„йЎөйқўдёҚеҸӘжҳҜиғҢжҷҜпјҢйўңиүІжҲ–ж–Үеӯ—еҶ…е®№зҡ„дёҚеҗҢпјҢиҖҢжҳҜA ... -
setContentViewзҡ„еә”з”Ё
2011-02-08 00:34 1529В жүӢжңәйЎөйқўзҡ„иҪ¬жҚўset ... -
еӨҡдёӘActivityд№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„йҖҡдҝЎдёҺж•°жҚ®дј йҖ’зҡ„BundleеҜ№иұЎзҡ„дҪҝз”Ё
2011-02-08 00:18 1180еңЁActivity дёӯи°ғз”ЁеҸҰдёҖдёӘActivity ,дҪҶиӢҘ ... -
еӨҡдёӘActivityд№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„йҖҡдҝЎ
2011-02-07 22:38 2099第дёҖжӯҘпјҡж–°е»әдёҖдёӘ继жүҝActivityзҡ„зұ»пјҢеҰӮпјҡNewActiv ... -
е…ұдә«ж•°жҚ®еҠҹиғҪдҪҝз”Ё-ContentProvider
2011-01-26 11:03 1246package it.date; import it ... -
еӨ–йғЁеә”з”Ёи®ҝй—®
2011-01-11 16:29 1979В дҪҝз”Ёcontextдёӯзҡ„ж–Ү件иҫ“еҮәжөҒе®ғжңүеӣӣз§ҚжЁЎејҸпјҡВ В *В ... -
дҪҝз”ЁSharedPreferencesиҝӣиЎҢж•°жҚ®еӯҳеӮЁ-
2011-01-11 11:07 1040еҫҲеӨҡж—¶еҖҷжҲ‘们ејҖеҸ‘зҡ„иҪҜ件йңҖиҰҒеҗ‘з”ЁжҲ·жҸҗдҫӣиҪҜ件еҸӮж•°и®ҫзҪ®еҠҹиғҪпјҢдҫӢеҰӮжҲ‘们 ... -
pullиҜ»еҸ–xml--android
2011-01-09 22:54 1980pullи§Јжһҗxmlж–Ү件,е’Ңsaxе’ҢdomдёҖж · йғҪеҸҜд»Ҙи„ұзҰ»and ... -
domиҜ»еҸ–xmlж–ҮжЎЈ---android
2011-01-09 22:26 1323йҷӨдәҶеҸҜд»ҘдҪҝз”Ё SAXи§ЈжһҗXMLж–Ү件пјҢеӨ§е®¶д№ҹеҸҜд»ҘдҪҝз”ЁзҶҹжӮүзҡ„DOM ... -
ж•°жҚ®дҝқеӯҳеҲ°sdеҚЎдёҠ
2011-01-05 17:22 9781 е…ій”®д»Јз Ғ В package cn.lee.data; ... -
androidиҜ»еҸ–еҠҹиғҪ
2011-01-05 16:03 9651 и®ҫи®Ўз•Ңйқў <?xml version=" ... -
androidзҡ„ж—Ҙеҝ—иҫ“еҮәе’ҢеҚ•е…ғжөӢиҜ•
2010-12-31 17:52 1556В В ж—Ҙеҝ—иҫ“еҮәВ д»ЈжӣҝSyste ...







зӣёе…іжҺЁиҚҗ
`onDestroy()`еҲҷеңЁServiceиў«еҒңжӯўж—¶и°ғз”ЁпјҢж Үеҝ—зқҖServiceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹзҡ„з»“жқҹгҖӮеҖјеҫ—жіЁж„Ҹзҡ„жҳҜпјҢServiceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹз®ЎзҗҶйңҖиҰҒи°Ёж…ҺеӨ„зҗҶпјҢд»ҘйҒҝе…ҚеҶ…еӯҳжі„жјҸе’ҢдёҚеҝ…иҰҒзҡ„иө„жәҗж¶ҲиҖ—гҖӮ ServiceдёҺActivityд№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„йҖҡдҝЎжҳҜйҖҡиҝҮBinderжңәеҲ¶е®һзҺ°...
жң¬ж–ҮжЎЈдё»иҰҒи®Іиҝ°зҡ„жҳҜ Android Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹеҸҠз”Ёжі•пјӣAndroid Serviceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ并дёҚеғҸActivityйӮЈд№ҲеӨҚжқӮпјҢе®ғеҸӘ继жүҝдәҶonCreate(),onStart(),onDestroy()дёүдёӘж–№жі•пјҢеҪ“жҲ‘们第дёҖж¬ЎеҗҜеҠЁServiceж—¶пјҢе…ҲеҗҺи°ғз”ЁдәҶonCreate(),...
дҪҝз”Ё`startService()`ж–№жі•еҗҜеҠЁServiceпјҢиҝҷдјҡеҜјиҮҙServiceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹдёӯзҡ„`onStartCommand()`иў«и°ғз”ЁгҖӮиӢҘиҰҒеҒңжӯўServiceпјҢеҸҜд»Ҙи°ғз”Ё`stopService()`гҖӮйңҖиҰҒжіЁж„Ҹзҡ„жҳҜпјҢеҚідҪҝи°ғз”ЁдәҶ`stopService()`пјҢServiceеҸҜиғҪ并дёҚдјҡз«ӢеҚіеҒңжӯўпјҢ...
жҖ»зҡ„жқҘиҜҙпјҢAndroid Serviceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹз®ЎзҗҶжҳҜејҖеҸ‘иҖ…еҝ…йЎ»жҺҢжҸЎзҡ„е…ій”®жҠҖиғҪпјҢжӯЈзЎ®зҗҶи§Је’ҢдҪҝз”ЁServiceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹиғҪеӨҹзЎ®дҝқеә”з”Ёзҡ„зЁіе®ҡжҖ§е’Ңж•ҲзҺҮпјҢйҒҝе…ҚдёҚеҝ…иҰҒзҡ„иө„жәҗж¶ҲиҖ—гҖӮеңЁејҖеҸ‘иҝҮзЁӢдёӯпјҢжҲ‘们иҝҳйңҖиҰҒжіЁж„ҸServiceзҡ„жқғйҷҗз®ЎзҗҶпјҢд»ҘеҸҠеңЁ...
жң¬зҜҮе°Ҷж·ұе…ҘжҺўи®ЁActivityе’ҢServiceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹд»ҘеҸҠеҰӮдҪ•еҲ©з”ЁAndroid Interface Definition Language (AIDL)иҝӣиЎҢиҝӣзЁӢй—ҙйҖҡдҝЎгҖӮ ActivityжҳҜAndroidеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸзҡ„з”ЁжҲ·з•ҢйқўпјҢе®ғиҙҹиҙЈдёҺз”ЁжҲ·дәӨдә’гҖӮActivityзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹеҲҶдёәеҮ дёӘе…ій”®...
д»ҘдёӢжҳҜдёҖдёӘе…ідәҺServiceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹзҡ„иҜҰз»Ҷи§ЈжһҗпјҢз»“еҗҲд»Јз ҒзӨәдҫӢжқҘйҳҗиҝ°еҰӮдҪ•еңЁAndroidдёӯж“ҚдҪңServiceгҖӮ 1. **Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹжҰӮиҝ°** Serviceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹдё»иҰҒеҢ…еҗ«д»ҘдёӢеҮ дёӘйҳ¶ж®өпјҡonCreate()гҖҒonStartCommand()гҖҒonBind()гҖҒ...
startServiceеҗҜеҠЁж–№ејҸпјҢеҸӘеңЁactivityдёӯеҗҜеҠЁе’Ңй”ҖжҜҒпјҢе’Ңactivityе…ізі»дёҚеӨ§пјҢеҚідҪҝantivityйҖҖеҮәпјҢжңҚеҠЎд»»з„¶иҝҗиЎҢпјҢжҜ”еҰӮеҗҺеҸ°ж”ҫйҹід№җпјҢеҜ№еә”з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹпјҡ bindServiceеҗҜеҠЁж–№ејҸпјҢе’Ңactivityз»‘е®ҡеҗҺпјҢе’Ңactivityе…ұеӯҳдәЎпјҢactivity...
йҖҡиҝҮеңЁиҝҷдәӣж–№жі•дёӯж·»еҠ LogиҜӯеҸҘжҲ–иҖ…дҪҝз”ЁAndroid Studioзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹжҸ’件пјҢеҸҜд»Ҙжё…жҷ°ең°и§ӮеҜҹеҲ°ActivityзҠ¶жҖҒзҡ„иҪ¬жҚўпјҢд»ҺиҖҢжӣҙеҘҪең°зҗҶи§ЈжҜҸдёӘж–№жі•зҡ„дҪңз”Ёе’Ңжү§иЎҢж—¶жңәгҖӮ жҖ»зҡ„жқҘиҜҙпјҢиҝҷдёӘвҖңAndroidз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹDemoвҖқйЎ№зӣ®жҸҗдҫӣдәҶдёҖдёӘе®һи·ө...
жҖ»зҡ„жқҘиҜҙпјҢAndroid Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹз®ЎзҗҶж¶үеҸҠеҲ°дёҖзі»еҲ—зҡ„еӣһи°ғж–№жі•пјҢйҖҡиҝҮиҝҷдәӣж–№жі•пјҢејҖеҸ‘иҖ…иғҪеӨҹзІҫзЎ®жҺ§еҲ¶жңҚеҠЎзҡ„еҗҜеҠЁгҖҒиҝҗиЎҢе’Ңз»ҲжӯўпјҢеҗҢж—¶зЎ®дҝқжңҚеҠЎеңЁжӯЈзЎ®зҡ„ж—¶й—ҙйҮҠж”ҫиө„жәҗгҖӮеҗҲзҗҶең°дҪҝз”ЁжңҚеҠЎиғҪжҸҗй«ҳеә”з”Ёзҡ„ж•ҲзҺҮе’Ңз”ЁжҲ·дҪ“йӘҢгҖӮеңЁе®һйҷ…...
еңЁServiceиҝҗиЎҢиҝҮзЁӢдёӯпјҢеҸҜд»ҘеҲ©з”Ёз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹж–№жі•зЎ®дҝқиө„жәҗзҡ„еҗҲзҗҶдҪҝз”ЁпјҢдҫӢеҰӮеңЁ`onDestroy()`дёӯйҮҠж”ҫи®Ўз®—иҝҮзЁӢдёӯеҚ з”Ёзҡ„иө„жәҗгҖӮ ж Үзӯҫдёӯзҡ„вҖңactivityвҖқжҸҗйҶ’жҲ‘们ServiceдёҺActivityд№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„йҖҡдҝЎгҖӮServiceеҸҜд»ҘйҖҡиҝҮBinderгҖҒ...
- жңӘз»‘е®ҡActivityзҡ„Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹеӣҫжҳҫзӨәдәҶstartService()еҗҜеҠЁзҡ„иҝҮзЁӢпјҢиҖҢз»‘е®ҡActivityзҡ„Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹеӣҫеҲҷеұ•зӨәдәҶbindService()еҗҜеҠЁзҡ„иҝҮзЁӢпјҢдёӨиҖ…еңЁз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹдёҠжңүжҳҫи‘—е·®ејӮгҖӮ зҗҶ解并зҶҹз»ғжҺҢжҸЎServiceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹеҸҠе…¶...
Android Activity з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹжҳҜжҢҮ Activity д»ҺеҲӣе»әеҲ°й”ҖжҜҒзҡ„ж•ҙдёӘиҝҮзЁӢпјҢиҜҘиҝҮзЁӢдёӯдјҡз»ҸеҺҶеӨҡдёӘзҠ¶жҖҒеҸҳеҢ–пјҢжҜҸдёӘзҠ¶жҖҒеҸҳеҢ–йғҪдјҡи§ҰеҸ‘зӣёеә”зҡ„еӣһи°ғж–№жі•гҖӮзҗҶи§Ј Activity з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹжҳҜ Android ејҖеҸ‘зҡ„еҹәзЎҖгҖӮ еңЁ Android дёӯпјҢActivity ...
- **Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ**пјҡ - `onCreate()`пјҡServiceйҰ–ж¬ЎеҲӣе»әж—¶и°ғз”ЁгҖӮ - `onStartCommand()`жҲ–`onBind()`пјҡж №жҚ®Serviceзұ»еһӢпјҲеҗҜеҠЁеһӢжҲ–з»‘е®ҡеһӢпјүпјҢеңЁServiceеҗҜеҠЁж—¶и°ғз”ЁгҖӮ - `onDestroy()`пјҡServiceй”ҖжҜҒеүҚи°ғз”ЁгҖӮ - **...
1. **Android Profiler**пјҡеҸҜд»Ҙе®һж—¶зӣ‘жҺ§Activityзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹзҠ¶жҖҒеҸҳеҢ–пјҢеҗҢж—¶еҲҶжһҗеҶ…еӯҳгҖҒCPUе’ҢзҪ‘з»ңдҪҝз”Ёжғ…еҶөгҖӮ 2. **Logcat**пјҡйҖҡиҝҮжү“еҚ°ж—Ҙеҝ—пјҢеҸҜд»ҘеңЁжҺ§еҲ¶еҸ°и·ҹиёӘActivityзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹеӣһи°ғгҖӮ 3. **Hierarchy Viewer**пјҲзҺ°е·І...
6. **Serviceз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹ**пјҡ Serviceзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹеҢ…жӢ¬`onCreate()`, `onStartCommand()`, `onBind()`, `onUnbind()`, `onDestroy()`зӯүе…ій”®ж–№жі•гҖӮеңЁеҲӣе»әServiceж—¶пјҢдјҡи°ғз”Ё`onCreate()`пјҢжҺҘзқҖеҰӮжһңжҳҜйҖҡиҝҮ`startService()`...
жҖ»з»“жқҘиҜҙпјҢжң¬жј”зӨәж¶өзӣ–дәҶAndroidејҖеҸ‘дёӯзҡ„ж ёеҝғзҹҘиҜҶзӮ№пјҢеҢ…жӢ¬Activityзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹз®ЎзҗҶгҖҒServiceзҡ„дҪҝз”Ёд»ҘеҸҠUIи®ҫи®ЎжҠҖе·§пјҢиҝҷдәӣйғҪжҳҜжһ„е»әй«ҳж•ҲгҖҒз”ЁжҲ·еҸӢеҘҪзҡ„Androidеә”з”ЁжүҖеҝ…йңҖзҡ„жҠҖиғҪгҖӮйҖҡиҝҮеҜ№"android.test"ж–Ү件зҡ„еӯҰд№ е’Ңе®һи·өпјҢ...
жң¬е®һйӘҢжҠҘе‘Ҡе°Ҷж·ұе…ҘжҺўи®ЁAndroidеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸпјҢе°Өе…¶жҳҜActivityгҖҒServiceе’ҢIntent Receiverзҡ„з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘ЁжңҹпјҢ并解йҮҠеҰӮдҪ•жӯЈзЎ®з®ЎзҗҶиҝҷдәӣ组件д»ҘйҒҝе…ҚдёҚеҝ…иҰҒзҡ„иҝӣзЁӢй”ҖжҜҒгҖӮ йҰ–е…ҲпјҢAndroidеә”з”ЁйҖҡеёёеңЁзӢ¬з«Ӣзҡ„LinuxиҝӣзЁӢдёӯиҝҗиЎҢгҖӮеҪ“еә”з”ЁйңҖиҰҒ...
жҖ»д№ӢпјҢAndroid ServiceжҳҜе®һзҺ°еҗҺеҸ°ж“ҚдҪңзҡ„йҮҚиҰҒе·Ҙе…·пјҢйҖҡиҝҮеҗҲзҗҶзҡ„дҪҝз”Ёе’ҢжңҚеҠЎз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹз®ЎзҗҶпјҢеҸҜд»Ҙдёәз”ЁжҲ·жҸҗдҫӣй«ҳж•ҲгҖҒзЁіе®ҡзҡ„еҗҺеҸ°жңҚеҠЎгҖӮиҖҢ Binder жңәеҲ¶еҲҷи®©Serviceе…·еӨҮдәҶи·ЁиҝӣзЁӢйҖҡдҝЎзҡ„иғҪеҠӣпјҢжһҒеӨ§ең°жү©еұ•дәҶServiceзҡ„еә”з”ЁеңәжҷҜгҖӮ...
startServiceеҗҜеҠЁж–№ејҸпјҢеҸӘеңЁactivityдёӯеҗҜеҠЁе’Ңй”ҖжҜҒпјҢе’Ңactivityе…ізі»дёҚеӨ§пјҢеҚідҪҝantivityйҖҖеҮәпјҢжңҚеҠЎд»»з„¶иҝҗиЎҢпјҢжҜ”еҰӮеҗҺеҸ°ж”ҫйҹід№җпјҢеҜ№еә”з”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹпјҡ bindServiceеҗҜеҠЁж–№ејҸпјҢе’Ңactivityз»‘е®ҡеҗҺпјҢе’Ңactivityе…ұеӯҳдәЎпјҢactivity...
иҰҒе®һзҺ°дёҖдёӘжңүз”ҹе‘Ҫе‘Ёжңҹж„ҹзҹҘзҡ„зҪ‘з»ңиҜ·жұӮжЎҶжһ¶пјҢжҲ‘们йҰ–е…ҲйңҖиҰҒй…ҚзҪ®Retrofit2пјҢе®ҡд№үдёҖдёӘеҢ…еҗ«жүҖжңүзҪ‘з»ңжҺҘеҸЈзҡ„Serviceзұ»пјҢеҰӮ`ApiService`пјҢ并дҪҝз”ЁRetrofit.BuilderиҝӣиЎҢжһ„е»әгҖӮжҺҘзқҖпјҢжҲ‘们еҸҜд»ҘдҪҝз”ЁRxJavaзҡ„ObservableжқҘеҢ…иЈ…...