- 浏览: 709654 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 北京
-

文章分类
- 全部博客 (272)
- Struts1.x (7)
- 事务 (2)
- Hibernate (11)
- 数据库 (14)
- JavaScript&Ajax (43)
- JSP&Servlet (2)
- Flex (1)
- 其它 (9)
- Java (22)
- 框架集成 (1)
- WebService (3)
- Tomcat (3)
- 加密和安全登录 (13)
- 基于原型的JavaScript (0)
- JavaDoc和Java编码规范 (3)
- CAS (1)
- 加密 (1)
- Axis2 (10)
- Ext2.x (3)
- SSH整合 (2)
- Ext (0)
- 正则表达式 (1)
- 设计模式 (4)
- 对象序列化技术 (3)
- CVS (2)
- Struts2 (6)
- Spring 2.x (7)
- Spring Security (2)
- Java 课程 (20)
- 程序员之死 (1)
- 软件测试 (6)
- UML (5)
- NetBeans (1)
- cxf (1)
- JMS (13)
- 设计 (5)
- ibatis2.x (3)
- Oracle (1)
- WebSphere (7)
- 概要设计 (1)
- DB2 (10)
- PowerDesigner (0)
- 软件工程 (5)
- rose (1)
- EA (1)
- LDAP (7)
- Portal&Portlet (3)
- MQ (10)
- ESB (4)
- EJB (2)
- JBoss (2)
最新评论
-
typeRos:
只有配置文件,没有代码么大神
Spring实现IBMMQ的JMS消息发布/订阅模式 -
panamera:
如果ActiveMQ服务器没有启动,这个时候消息生产者使用Jm ...
Spring JMSTemplate 与 JMS 原生API比较 -
lian819:
顶1楼, 引用文件, 配置属性, 太方便了
EXTJS 同步和异步请求 -
wilhard:
说得清楚明白
<%@ include file=""%>与<jsp:include page=""/>区别 -
刘琛颖:
总结的很好。受益了
javascript 父窗口(父页面)— 子窗口 (子页面)互相调用的方法
Design and implement POJO Web services using Spring and Apache CXF, Part 1: Intr
- 博客分类:
- cxf
Summary: Create a plain old Java™ object (POJO)-style Web service easily using Apache CXF, an open source Web service framework. This article, Part 1 of a series, shows you how to expose POJOs as Web services using Spring and CXF. It also illustrates CXF integration with the Spring Framework. View more content in this series Tags for this article: cxf, part1, spring, web_services Date: 24 Jul 2008 Design and implement POJO Web services using Spring and Apache CXF, Part 1: Introduction to Web services creation using CXF and Spring
Level: Intermediate
PDF: A4 and Letter (58KB)Get Adobe® Reader®
Also available in: Chinese Japanese
Activity: 43552 views
Comments: 8 (View | Add comment - Sign in)
In this article, you build and develop an order-processing Web service using CXF and Spring. This Web service processes or validates the order placed by a customer and returns the unique order ID. After reading this article, you can apply the concepts and features of CXF to build and develop a Web service. To run the examples in this article, make sure the following software is installed and set up on your machine: After the above distribution is installed, set up the following environment variables: By way of example, set CXF_HOME=C:\apache-cxf-2.1 and add the following to the PATH env variable: Apache CXF is an open source framework that provides a robust infrastructure for conveniently building and developing Web services. It lets you create high-performance and extensible services, which you can deploy in the Tomcat and Spring-based lightweight containers as well as on a more advanced server infrastructure, such as JBoss, IBM® WebSphere®, or BEA WebLogic. The framework provides the following features: Let's look specifically at how to create an order-processing Web service and then register it as a Spring bean using a JAX-WS front end. You use the code-first approach, which means you first develop a Java class and annotate it as a Web service. To do this, you typically perform the following steps: First let's create the order-processing Web service SEI. Create the order-processing Web service SEI Create an SEI named As you can see in Listing 1, the Write the implementation of the SEI To write the implementation of the SEI in the previous section, you again annotate your implementation class, You've created an SEI and its implementation. Using CXF, now you can make this an actual service component using a JAX-WS front end. Create a configuration file for CXF A CXF configuration file is actually a Spring configuration file that contains bean definitions. You create a bean definition for the Finally you need to: You've just finished developing the necessary server-side components. Now you can develop a client component that makes a request to the As you can see from Listing 5, it's very easy to create the client bean, just as it was easy to create the service endpoint. You create a Java main program that uses the Spring context to get the client bean defined, then invoke the Before running the program, create the directory structure shown in Figure 1 under your root C:\ folder and put the components covered previously in this article into it: For building, deploying, and running the The application folder (c:\orderapp) has the Ant build files. After running the above command, your The orderapp folder is created under the webapps folder of Tomcat. After the server is started, run the application by entering the This article briefly described the features of the CXF framework and demonstrated how it lets you create a Web service without much coding effort. You learned about Spring integration with CXF using a bean context file. You also looked at how the framework abstracts the actual semantics of creating a Web service infrastructure component and provides you with a shell of a simpler API that simply focuses on Web service creation. Now that you've seen the basics of Web service creation using CXF, check out Part 2 of this series, which shows you how to expose POJOs as RESTful services using CXF and Spring.
OrderProcess, which will have a method, processOrder, that takes an order bean and returns a string. The goal of the processOrder method is to process the order placed by the customer and return the unique order ID.
Listing 1. OrderProcess SEI
package demo.order;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService
public interface OrderProcess {
String processOrder(Order order);
}
OrderProcess SEI is simply a standard Java interface that's annotated as a Web service. The @WebService annotation simply makes the interface a Web service interface. This interface is used by the client or the consumer to invoke the service method. The OrderProcess SEI has one service method, processOrder, which takes Order as a parameter and returns the order ID as a string.
Listing 2. OrderProcess service implementation
package demo.order;
import javax.jws.WebService;
@WebService(endpointInterface = "demo.order.OrderProcess")
public class OrderProcessImpl implements OrderProcess {
public String processOrder(Order order) {
return order.validate();
}
}
OrderProcessImpl, as a Web service and provide an attribute, endpointInterface, with a value as a fully qualified name of the SEI you created in the previous step. This tells the class to implement the OrderProcess SEI. Because it's an implementation of an SEI, you have to provide implementation of the processOrder method that returns the order ID.
Listing 3. beans.xml configuration file
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-extension-soap.xml" />
<import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-servlet.xml" />
<jaxws:endpoint
id="orderProcess"
implementor="demo.order.OrderProcessImpl"
address="/OrderProcess" />
</beans>
OrderProcess Web service using JAX-WS front-end configuration. The <jaxws:endpoint> tag in the beans.xml file specifies the OrderProcess Web service as a JAX-WS endpoint. It effectively means that CXF internally uses JAX-WS to publish this Web service. You have to provide the implementation class name, which is OrderProcessImpl, and the address to the <jaxws:endpoint> tag. The address that you provide is relative to the Web context.
Listing 4. web.xml Web configuration file
<web-app>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>WEB-INF/beans.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>CXFServlet</servlet-name>
<display-name>CXF Servlet</display-name>
<servlet-class>
org.apache.cxf.transport.servlet.CXFServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>CXFServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
OrderProcess service.
JaxWsProxyFactory is used to create the client bean for the OrderProcess Web service. The factory bean expects the service class (OrderProcess) and the URL of your service. The client bean stub, OrderProcess, is then created by using the factory bean reference.
Listing 5. client-bean.xml client Web configuration file
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.0.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws
http://cxf.apache.org/schema/jaxws.xsd">
<bean id="client" class="demo.order.OrderProcess"
factory-bean="clientFactory" factory-method="create"/>
<bean id="clientFactory" class="org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="serviceClass" value="demo.order.OrderProcess"/>
<property name="address" value="http://localhost:8080/orderapp/OrderProcess"/>
</bean>
</beans>
processOrder method.
Listing 6. The client code
public final class Client {
public Client() {
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context
= new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]
{"demo/order/client/client-beans.xml"});
OrderProcess client = (OrderProcess)context.getBean("client");
Order order = new Order();
String orderID = client.processOrder(order);
System.out.println("Order ID: " + orderID);
System.exit(0);
}
}
Figure 1. Code directory structure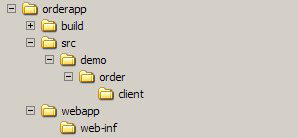
OrderProcess Web service and client, you use the Ant tool. The code is deployed on the Tomcat server. Deploy the code using the ant deploy command under the c:\orderapp folder.orderapp code is deployed in the Tomcat server environment as the orderapp.war file. Now start the Tomcat Web server by providing the catalina start command under the CATALINA_HOME\bin folder.ant client command. The output displays the order ID (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. Program output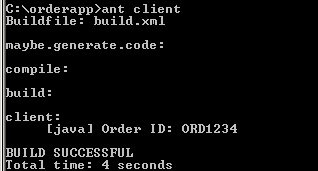






相关推荐
Marrying the two technologies is therefore a very natural choice.This book takes you through the design of RESTful web services and leverages the Spring Framework to implement these services....
1. **配置Spring**:首先,你需要在Spring的配置文件中引入Apache CXF的依赖,并声明一个`jaxws:endpoint`,这是CXF发布Web服务的核心元素。配置中需要指定服务接口、实现类、以及数据绑定类型(这里是Aegis)。 ``...
在IT行业中,Spring框架是Java领域最常用的轻量级应用框架之一,而Cxf则是一个强大的服务导向架构(SOA)工具集,主要用于构建和开发Web服务。本示例将探讨如何通过Spring集成Cxf来暴露Web服务,帮助开发者更好地...
Apache CXF是一个开源的Java框架,主要用于构建和部署SOAP和RESTful Web服务,而Spring则是一个广泛使用的应用框架,提供了依赖注入和面向切面编程等功能。下面我们将按照给出的目录逐步解析整合过程。 一、准备...
Apache CXF是一个开源的Java框架,它主要用于构建和开发Web服务。CXF这个名字来源于两个它合并的项目:Celtix和XFire。这个框架允许开发者使用多种编程模型,包括JAX-WS和JAX-RS,来创建和消费Web服务。在本案例中,...
BI Design and implementation, BI Design and implementation, BI Design and implementation, BI Design and implementation,
Spring作为一个全面的轻量级应用框架,提供了强大的依赖注入、AOP(面向切面编程)等功能,而CXF则是一个优秀的服务端和客户端Web服务实现框架,支持多种Web服务标准,如SOAP、RESTful等。本文将详细介绍如何将...
在本篇中,我们将深入探讨如何将Apache CXF 2.7.5版本与Spring 3.0框架集成,以便在Java应用程序中创建和消费Web服务。 **一、CXF简介** Apache CXF是一个全面的Web服务框架,它支持多种协议,如SOAP、RESTful HTTP...
Spring框架与Apache CXF的整合是企业级Java应用中常见的实践,主要用于构建基于SOAP和RESTful服务。这个"Spring整合CXF demo"项目提供了一个直观的例子,帮助开发者理解如何在Spring环境中配置和使用CXF服务。 ### ...
Apache CXF是一个开源的Java框架,它主要用于构建和开发服务导向架构(SOA)和Web服务。本示例将引导你了解如何使用Apache CXF创建一个简单的“Hello World”应用程序,涉及客户端和服务端的实现。 首先,让我们从...
Apache CXF 是一个强大的开源框架,用于构建和服务 WebServices。它不仅支持传统的 SOAP 协议,同时也支持 RESTful 风格的服务。通过 CXF,开发者可以轻松地将 Java 类作为 Web 服务公开,同时也能够消费其他服务。 ...
在企业级应用开发中,Apache CXF 和 Spring 框架的整合是非常常见的,因为它们分别提供了强大的服务端和客户端的 Web 服务支持以及灵活的依赖注入和配置管理。本教程将详细介绍如何将 CXF 与 Spring 整合,帮助...
在本文中,我们将深入探讨Apache CXF框架在创建服务器端Web服务接口中的应用。Apache CXF是一个开源的Java框架,它允许开发者构建和部署SOAP(简单对象访问协议)和RESTful(表述性状态转移)Web服务。CXF以其灵活性...
1. **Spring与CXF整合的基础** 在整合Spring和CXF之前,我们需要确保环境配置正确。这包括安装Java JDK、Apache CXF库和Spring框架。Spring可以通过Maven或Gradle引入依赖,而CXF同样可以在构建工具中配置相关依赖...
在本文中,我们将深入探讨如何使用Apache CXF 2与Spring 2.5框架来开发Web服务实例。Apache CXF是一个流行的开源项目,它提供了一种简单且强大的方式来实现和消费SOAP和RESTful Web服务。Spring框架则以其模块化、...
【CXF_Spring】是一个基于Spring框架的Apache CXF服务集成教程,主要涵盖了如何在Spring环境中配置和使用CXF来创建和消费Web服务。Apache CXF是一个开源的Java框架,它允许开发者创建和消费各种Web服务,包括SOAP和...
总结来说,Spring与Apache CXF的整合提供了强大的Web服务开发能力,结合了Spring的灵活性和CXF的Web服务实现效率。通过上述步骤,开发者可以方便地创建、管理和部署符合JAX-WS标准的SOAP服务,以满足企业级应用的...
【标题】"基于maven的cxf+spring简单demo"是一个示例项目,它演示了如何结合Apache CXF和Spring框架来构建一个简单的Web服务。Apache CXF是一个开源的Java框架,主要用于创建、部署和管理Web服务。而Spring是另一个...
在本文中,我们将深入探讨如何将Spring框架与Apache CXF集成,以便利用CXF的Web服务功能。Apache CXF是一个开源框架,它提供了创建、部署和管理SOAP和RESTful Web服务的能力,而Spring则是一个广泛使用的Java应用...
Spring addresses and offers simple solutions for most aspects of your Java/Java EE application development, and guides you to use industry best practices to design and implement your applications. ...