线性布局中,有
4
个及其重要的参数,直接决定元素的布局和位置,这四个参数是
android:layout_gravity
(
是本元素相对于父元素的重力方向
)
android:gravity
(是本元素所有子元素的重力方向)
android:orientation
(线性布局以列或行来显示内部子元素)
android:layout_weight
(线性布局内子元素对未占用空间【水平或垂直】分配权重值,其值越小,权重越大。
前提是子元素
设置了
android:layout_width
=
"fill_parent"
属性(水平方向)
或
android:layout_height
=
"fill_parent"
属性(垂直方向)
fill_parent 就是让控件宽或者高占全屏,而wrap_content是让控件的高或宽仅仅把控件里的内容包裹住,而不是全屏,你自己动手试试就知道了,很直观
如果某个子元素的
android:layout_width
=
"wrap_content"
或
android:layout_height
="
wrap_content”
,
则
android:layout_weight
的设置值
对该方向上空间的分配刚好相反。
下面以一个简单例子来说明这
4个参数
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"utf-8"
?>
<
LinearLayout
xmlns:android
=
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height
=
"200dp"
android:layout_width
=
"200dp"
android:background
=
"#AABBCC"
android:orientation=
"horizontal"
android:layout_gravity=
"center"
>
<
TextView
android:text
=
"ONE"
android:background
=
"#aa0000"
android:layout_height
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_width
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_margin
=
"1dp"
/>
<
TextView
android:text
=
"TWO"
android:background
=
"#aa0000"
android:layout_height
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_width
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_margin
=
"1dp"
/>
</
LinearLayout
>
说明:在上面的例子中,根布局是LinearLayout,
其包含有2
个TextView
视图,为了对参数
android:layout_gravity
有直观的了解,对根布局
LinearLayout
特意加了
3
个参数
android:layout_height
=
"200dp"
android:layout_width
=
"200dp"
android:background
=
"#AABBCC"
为布局指定了固定的宽度和高度,以及背景颜色,上面的例子运行后效果如下图:
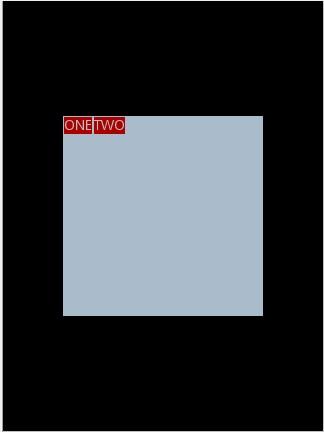
说明:对LinearLayout
中的参数android:layout_gravity
来说,其意义是指定本布局相对于父布局的重力方向,由于该布局的已经是根布局,其父布局是整个屏幕,那么该参数设置的是相对于屏幕的位置,可以换不同的参数
top|bottom|left|right
等等参数来试验。
现在增加参数
android:gravity
=
"bottom|right"
完整
XML
如下,看看效果
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"utf-8"
?>
<
LinearLayout
xmlns:android
=
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height
=
"200dp"
android:layout_width
=
"200dp"
android:background
=
"#AABBCC"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_gravity=
"center"
android:gravity
=
"bottom|right
"
>
<
TextView
android:text
=
"ONE"
android:background
=
"#aa0000"
android:layout_height
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_width
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_margin
=
"1dp"
/>
<
TextView
android:text
=
"TWO"
android:background
=
"#aa0000"
android:layout_height
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_width
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_margin
=
"1dp"
/>
</
LinearLayout
>

通过改变android:gravity
参数的值可以看到实际效果。
参数
android:orientation=
"
horizontal
"
决定了每个子元素各占一列,如果
参数
android:orientation=
"
vertical
"
,
则每个子元素各占一行,也就是从上到下排列了。
对于
LinearLayout
布局的子元素,给每个子元素加上参数
android:layout_weight
看看效果
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"utf-8"
?>
<
LinearLayout
xmlns:android
=
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height
=
"200dp"
android:layout_width
=
"200dp"
android:background
=
"#AABBCC"
android:layout_gravity
=
"center"
android:gravity
=
"bottom|right"
android:orientation
=
"horizontal"
>
<
TextView
android:text
=
"ONE"
android:background
=
"#aa0000"
android:layout_height
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_width
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_margin
=
"1dp"
android:layout_weight
=
"1"
/>
<
TextView
android:text
=
"TWO"
android:background
=
"#aa0000"
android:layout_height
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_width
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_margin
=
"1dp"
android:layout_weight
=
"2"
/>
</
LinearLayout
>
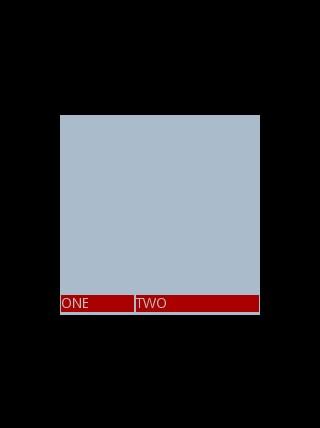
Text
为ONE
的权重为1
,但明显占的宽度比TWO
的小,百思不得其解,后来得知,如果把TextView
的参数android:layout_width
=
"wrap_content"
全部修改为
android:layout_width
=
"fill_parent"
,
则
ok
,代码如下
<?
xml
version
=
"1.0"
encoding
=
"utf-8"
?>
<
LinearLayout
xmlns:android
=
"http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height
=
"200dp"
android:layout_width
=
"200dp"
android:background
=
"#AABBCC"
android:layout_gravity
=
"center"
android:gravity
=
"bottom|right"
android:orientation
=
"horizontal"
>
<
TextView
android:text
=
"ONE"
android:background
=
"#aa0000"
android:layout_height
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_width
=
"
fill_parent
"
android:layout_margin
=
"1dp"
android:layout_weight
=
"1"
/>
<
TextView
android:text
=
"TWO"
android:background
=
"#aa0000"
android:layout_height
=
"wrap_content"
android:layout_width
=
"
fill_parent
"
android:layout_margin
=
"1dp"
android:layout_weight
=
"2"
/>
</
LinearLayout
>
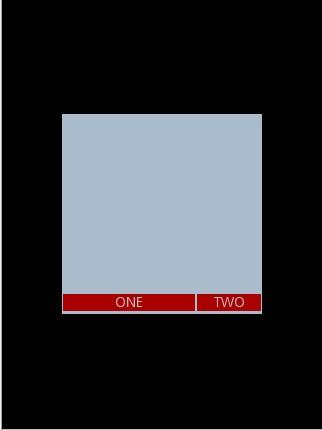
分享到:














相关推荐
总之,Android线性布局通过`android:orientation`、`android:layout_gravity`、`android:gravity`和`android:layout_weight`这四个关键参数,提供了灵活的视图布局方式。理解这些参数的含义和用法对于构建高效的用户...
Android 中有七种常见的布局方式,即线性布局(Linear Layout)、相对布局(Relative Layout)、表格布局(Table Layout)、网格视图(Grid View)、标签布局(Tab Layout)、列表视图(List View)和绝对布局...
Android提供了多种布局类型,如LinearLayout(线性布局,水平或垂直排列)、RelativeLayout(相对布局,基于相对位置放置组件)、FrameLayout(帧布局,按顺序叠加组件)、TableLayout(表格布局)等。每种布局都有...
LinearLayout是一种线性布局,它可以水平或垂直排列子视图(View)。其主要属性包括: 1. `orientation`:定义子视图的排列方向,可设置为`vertical`(垂直)或`horizontal`(水平)。 2. `layout_weight`:这是一...
通过LinearLayout,我们可以创建简单的线性布局,控制控件的排列方式和大小。随着学习的深入,还可以探索更复杂的布局容器,如RelativeLayout、ConstraintLayout等,以满足更复杂的界面设计需求。同时,熟悉XML语法...
它提供了控件水平垂直排列的模型,同时可以通过设置子控件的 weight 布局参数控制各个控件在布局中的相对大小。LinearLayout 有两种排列方式:水平排列(horizontal)和垂直排列(vertical)。 在 LinearLayout 中...
Android提供了五种基本布局容器:LinearLayout(线性布局)、RelativeLayout(相对布局)、FrameLayout(帧布局)、TableLayout(表格布局)和ConstraintLayout(约束布局)。每种布局都有其独特的排列方式: 1. ...
本文将详细解析Android中的七大布局:线性布局(Linear Layout)、相对布局(Relative Layout)、表格布局(Table Layout)、网格视图(Grid View)、标签布局(Tab Layout)、列表视图(List View)以及绝对布局...
一、LinearLayout(线性布局) LinearLayout 是最基本和最常用的布局方式,它提供了控件水平垂直排列的模型。LinearLayout 可以水平或垂直排列控件,可以通过设置子控件的 weight 布局参数控制各个控件在布局中的...
- `LinearLayout`: 表示该布局为线性布局,`android:orientation`属性设置为"vertical"表示子View将以垂直方式排列。 - `TextView`: 显示文本的控件,其文本内容由`android:text`属性指定。 在Activity的`onCreate`...
本文将深入解析Android中的布局管理器,包括线性布局(LinearLayout)、相对布局(RelativeLayout)、表格布局(TableLayout)、网格视图(GridView)、列表视图(ListView)、绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout)以及标签...
线性布局的一个关键知识点是`android:layout_weight`。当设置该属性时,子视图的大小不再由自身的`layout_width`或`layout_height`决定,而是根据权重比例分配。在上面的例子中,两个Button设置了相同的`layout_...
`LinearLayout`是一个线性布局,它可以按照垂直或水平的方式排列子视图,非常适合用于创建列表或表单这样的线性布局。 1. **页面布局结构** - 页面整体分为两个部分,分别放置在`LinearLayout`的上下区域。上部...
1. **LinearLayout**:线性布局是最基础的布局,按照垂直或水平方向将子视图(View)排列。通过设置`android:orientation`属性可以选择排列方向。`android:layout_weight`属性用于分配子视图的权重,可以实现灵活的...
4.1.4 布局参数(LayoutParams) 4.2 常用Widget组件 4.2.1 文本框视图(TextView) 4.2.2 按钮(Button) 4.2.3 图片按钮(ImageButton) 4.2.4 编辑框(EditText) 4.2.5 多项选择(CheckBox) 4.2.6 单项选择...
2.2 android线性布局的介绍 2.3 android框架布局的使用 2.4 相对布局的使用 2.5 表格布局的介绍 三、Android解析xml文件 3.1 android解析xml文件 3.2 android使用pull解析xml 3.3 android使用dom解析xml 四、...
本教程将详细讲解如何利用Android Shader来实现一个类似于歌词逐字同步的线性渲染效果。 首先,我们需要了解Shader的基本概念。在Android中,Shader是OpenGL ES着色器的接口,它允许我们在GPU上执行计算,以生成或...
在Android中,常见的布局类型有线性布局(LinearLayout)、相对布局(RelativeLayout)、帧布局(FrameLayout)以及网格布局(GridLayout)。线性布局按照垂直或水平方向排列子视图,而相对布局允许视图根据它们之间...