
As we are entering
the age of "Personal
Genomics
" or "Personalized
Medicine
", it has been
expected
that the knowledge of human genetic
polymorphisms and
variations could provide a foundation for
understanding
differences in susceptibility to diseases and
designing
individualized therapeutic treatments (Cargill,
et al.
, 1999
; Collins,
et al.
, 1998
). Recent progresses
of the
International HapMap Project and similar
projects (International
HapMap Consortium, 2005
; Frazer,
et al.
, 2007
) have provided a
wealth of
information detailing tens of millions human
genetic
variations between individuals, including copy
number
variations (CNVs) (Redon,
et al.
, 2006
) and single
nucleotide polymorphisms
(SNPs) (Hinds,
et al.
, 2005
). It was estimated
that ~90%
of human genetic variations are due to SNPs (Collins,
et al.
, 1998
). In particular, by
changing
amino acids in proteins, non-synonymous SNPs
(nsSNPs)
in the gene coding regions could account for
nearly
half of the known genetic variations linked to
human
inherited diseases (Stenson,
et al.
, 2003
). In this regard,
numerous
efforts have been contributed to elucidate how
nsSNPs
generate deleterious effects on the stability
and function
of proteins. Obviously, an nsSNP might change
the physicochemical
property of a wild-type amino acid to affect
the protein
stability and dynamics, or disrupt the
interacting interface
that prohibits the protein to form a complex
with its
partners (Kono,
et al.
, 2008
; Stitziel,
et al.
, 2004
; Uzun,
et al.
, 2007
; Yue
and Moult, 2006
). Alternatively, nsSNPs
could also
influence post-translational modifications
(PTMs) of
proteins (eg., phosphorylation), by changing
the residue
types of the target sites or key flanking
amino acids
(Erxleben,
et al
., 2006
; Gentile,
et al
., 2008
; Ryu,
et al.
, 2009
; Savas
and Ozcelik, 2005
; Yang,
et al.
, 2008
). Previously, the
Armstrong group
firstly
coined the term of phosphorylopathy
to describe human genetic variation that
results in
aberrant regulation of protein phosphorylation
(Erxleben,
et al
., 2006
; Gentile,
et al
., 2008
).
In this work,
we performed a genome-wide analysis of genetic
polymorphisms
that influence protein phosphorylation in H.
Sapiens.
We collected 91,797 nsSNPs from NCBI dbSNP
build 130
(Sherry,
et al.
, 2001
). The human
mRNA/protein sequences
were taken from RefSeq build 31 (Pruitt,
et al.
, 2007
). We used our GPS
2.0 software
(Xue,
et al.
, 2008
) to predict
kinase-specific
phosphorylation sites for human proteins and
nsSNP data.
For simplicity, we defined a phosSNP
(Phosphorylation-related SNP) as an nsSNP that
might
influence protein phosphorylation status. We
classified
all phosSNPs into five
groups
. The first three types
(I, II,
and III) were similarly defined as previously
described
(Ryu,
et al
., 2009
), including change
of an amino
acid with S/T/Y residue or vice versa to
create a new
[Type I (+)] or remove an original
phosphorylation site
[Type I (-)], variations to add [Type II (+)]
or remove
adjacent phosphorylation sites [Type II (-)],
and mutations
to change PK types of adjacent phosphorylation
sites
(Type III) (Ryu,
et al
., 2009
). Also, we observed
that an
amino acid substitution among S, T or Y could
also change
the PK types in the phosphorylated position
(Type IV),
say, the target site could still be
phosphorylated but
by a different type of kinase. Moreover, we
defined
the type V phosSNP as a variation that results
in a
stop codon, which might remove its following
phosphorylation
sites in the protein C-terminus. Unexpectedly,
we computationally
detected 69.76%
of nsSNPs as potential phosSNPs (64, 035) in
17, 614
proteins. In this regard, we proposed that
most of nsSNPs
might affect protein phosphorylation and play
ubiquitous
roles in rewiring the biological pathways.
More interestingly,
we observed 74.58% of phosSNPs as type III
phosSNPs
(47, 760), which might suggest that nsSNPs
prefer to
alter PK types of flanking phosphorylation
sites rather
than creating or removing phosphorylation
sites. Taken
together, we proposed that our results could
be a useful
resource for future disease diagnostics and
provide
basis for better and individualized. Finally,
all phosSNPs
data were integrated into PhosSNP
1.0 database
, which was
implemented
in JAVA 1.5 (J2SE 5.0). The PhosSNP 1.0
supports Windows,
Unix/Linux and Mac and is freely available for
academic
researches at: http://phossnp.biocuckoo.org/
.
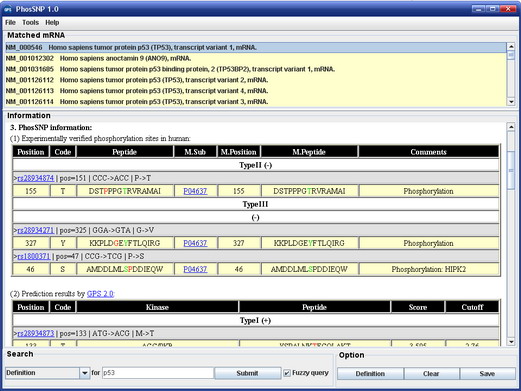
PhosSNP
1.0 User Interface
分享到:











相关推荐
标题中的“大数据-算法-东亚中东欧洲品种犬系统地理结构与家犬SNP数据库构建研”涉及的是在动物遗传学领域,尤其是狗的驯化研究中,如何利用大数据技术和算法来构建一个专门针对家犬全基因组SNP(单核苷酸多态性)的...
《大数据与算法在家犬SNP数据库构建中的应用》 狗的驯化是遗传学研究领域的一个热点话题,作为人类的紧密伙伴,狗吸引了全世界生物学家的关注。从驯化初期开始,狗的行为、食性和形态就与野生祖先灰狼显著不同。...
标题和描述中提到的研究主要集中在狗的遗传学和地理分布,特别是通过大数据和算法来构建一个...建立的SNP数据库为家犬的遗传学研究提供了新的工具和资源,有助于推动狗的驯化历史、遗传多样性和相关生物学问题的研究。
在深入分析SNP70032这款DSP(数字信号处理器)芯片的编程指南前,我们首先要明确DSP芯片的基本概念与功能。DSP芯片是一种特殊的微处理器,其设计初衷是快速高效地进行数字信号处理,如信号滤波、压缩、解码等。与...
SNP在致病基因发现、司法鉴定、个体化医疗等方面的应用得到了极大的关注和发展,因此有必要建立一个整合的人类SNP数据库。在整合中需要进行大规模的单核苷酸多态性位点的验证,该工作通过一个自主开发的、健壮的、...
### SNP检测方法——全面解析各种技术 #### 一、引言 单核苷酸多态性(Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, SNP)是指在基因组水平上由单个核苷酸的变异所引起的DNA序列多态性。它是人类遗传变异中最常见的一种形式,...
标题中的“snp.rar”可能是指一个RAR格式的压缩文件,其中包含了与SNP(单核苷酸多态性)相关的研究数据或分析结果。SNP是基因组中单个核苷酸位置上的变异,是遗传多样性的重要表现形式。在遗传学和医学研究中,SNP...
dbSNP数据库是一个全球性的公共资源库,专门用于存储和管理生物体内的单核苷酸多态性(Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, SNP)信息。SNP是指在DNA序列中,一个位置上出现两种或多种不同的核苷酸,是人类遗传变异中最...
【标题】"snp2uvc\snp2uvc.dc下载" 涉及到的知识点主要集中在snp2uvc.dc这个组件上,它很可能是一个驱动程序或者软件的一部分,用于处理与USB视频类(UVC)设备相关的功能。snp2uvc可能是该软件或驱动的主模块,而"....
同时,基于公共数据库的分析方法也是发现SNP的重要策略,研究者可以利用已有的序列信息通过生物信息学软件进行SNP的识别。 连锁不平衡(Linkage Disequilibrium, LD)是指染色体上两个等位基因间的非随机相关性。LD...
中国农业科学院柑橘研究所的一项重大突破,标志着全球首个园艺类作物全基因变异数据库——柑橘全基因组变异数据库 CitGVD 的发布。这一创新性成果不仅对柑橘研究具有里程碑意义,也为整个园艺作物的遗传改良和品种...
### SNP Calling与QUL算法详解 #### 一、引言 在生物信息学领域,单核苷酸多态性(Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, SNP)是基因组中最常见的一种变异类型。随着高通量测序技术的发展,对SNP进行准确检测变得尤为...
标题 "IQtree:使用 SNP 数据(vcf file)构建系统发育树(数据)" 描述了一个使用IQtree软件处理SNP(单核苷酸多态性)数据来构建系统发育树的过程。这篇描述可能来自于一个关于生物信息学的博客文章,它详细介绍了...
使用GATK进行 SNP Callling的自动化流程。基于GATK3.3以上版本的HaplotypeCaller标准流程进行,测试脚本以sra文件为最初输入,将读取文件见内的所有sra文件(视为同一个样本的数据),进行SNP Calling产生GVCF,然后...
**SNP检测方法详解** SNP,全称为Single Nucleotide Polymorphism,即单核苷酸多态性,是生物基因组中最...随着科技的进步,未来可能会有更高效、更经济的SNP检测方法出现,进一步推动基因组学和个体化医疗的发展。
, fetch_genotypes() , genotypes() , phenotypes() , phenotypes_byid() , users() NCBI的dbSNP SNP数据库有关更多详细信息,请参见 相关功能: ncbi_snp_query()安装从CRAN安装install.packages( " rsnps " )...
【GT-PRO数据的SNP反卷积】是一种在生物信息学领域中处理基因型数据的技术,主要用于解析复杂的遗传结构。GT-PRO是Genotype Probability Matrix的缩写,它表示个体样本的基因型概率矩阵,通常来自高通量测序数据。...
dbSNP数据库会提供SNP的位置、侧翼序列、多群体报道、提交情况等相关详细信息。例如,对于rs36014863这样的SNP,用户可以深入查看其所有详细信息,包括它在基因组中的具体位置、影响的基因区域等。 其次,...
Snp文件,全称为Scattering Parameters文件,是射频和微波工程领域中常见的数据格式,用于描述电子元器件或系统在不同频率下的散射特性。S参数是衡量信号通过网络时,输入与输出之间相互关系的一种方式。它们通常以...