- 浏览: 872127 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 上海
-

最新评论
-
waterflow:
感谢分享
简单的ChartDirector生成图表例子 -
YQuite:
写到最后一种文件才看到这个,洼的一声哭了出来 - - !
java简单解析docx、pptx、xlsx文档 -
q394469902:
Android通过selector改变界面状态 -
db6623919:
直接粘贴别人帖子还是英文的,有意思?
实现RTSP协议的简单例子 -
ykou314:
请问下,这些超级命令,是否需要android root权限,尤 ...
Android系统在超级终端下必会的命令大全(七)
下载Android安安软件请到:http://code.google.com/p/andbox
文章来自:http://mobworld.wordpress.com/2010/07/05/memory-management-in-android/ 有很好的学习价值。
Hi, You might be aware of the memory concept of android. Here I have described the basic memory concept in android,
Introduction about Android memory
Android
Android is a software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key applications. The Android SDK provides the tools and APIs necessary to begin developing applications on the Android platform using the Java programming language.
Android Memory
Android is a Linux based OS with 2.6.x kernel, stripped down to handle most tasks pretty well. It uses native open source C libraries that have powered Linux machines for years. All the basic OS operations like I/O, memory management, and so on, are handled by the native stripped-down Linux kernel.
How to use memory for each application
Android’s process and memory management is a little unusual. Like Java and .NET, Android uses its own run time and virtual machine to manage application memory. Unlike either of these frameworks, the Android run time also manages the process lifetimes. Android ensures application responsiveness by stopping and killing processes as necessary to free resources for higher-priority applications.
Each Android application runs in a separate process within its own Dalvik instance, relinquishing all responsibility for memory and process management to the Android run time, which stops and kills processes as necessary to manage resources.
Dalvik and the Android run time sit on top of a Linux kernel that handles low-level hardware interaction including drivers and memory management, while a set of APIs provides access to all of the under- lying services, features, and hardware.
Dalvik Virtual Machine Dalvik is a register-based virtual machine that’s been optimized to ensure that a device can run multiple instances efficiently. It relies on the Linux kernel for threading and low-level memory management.
The Dalvik Virtual Machine
One of the key elements of Android is the Dalvik virtual machine. Rather than use a traditional Java virtual machine (VM) such as Java ME (Java Mobile Edition), Android uses its own custom VM designed to ensure that multiple instances run efficiently on a single device.
The Dalvik VM uses the device’s underlying Linux kernel to handle low-level functionality including security, threading, and process and memory management.
All Android hardware and system service access is managed using Dalvik as a middle tier. By using a VM to host application execution, developers have an abstraction layer that ensures they never have to worry about a particular hardware implementation.
The Dalvik VM executes Dalvik executable files, a format optimized to ensure minimal memory foot- print. The .dex executables are created by transforming Java language compiled classes using the tools supplied within the SDK.
Understanding Application Priority and Process States
The order in which processes are killed to reclaim resources is determined by the priority of the hosted applications. An application’s priority is equal to its highest-priority component.
Where two applications have the same priority, the process that has been at a lower priority longest will be killed first. Process priority is also affected by interprocess dependencies; if an application has a dependency on a Service or Content Provider supplied by a second application, the secondary application will have at least as high a priority as the application it supports.
All Android applications will remain running and in memory until the system needs its resources for other applications.
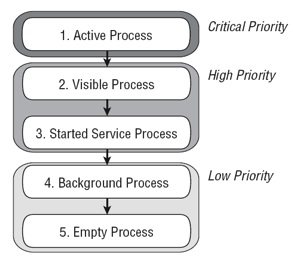
The following list details each of the application states shown in Figure , explaining how the state is determined by the application components comprising it:
Active Processes Active (foreground) processes are those hosting applications with components currently interacting with the user. These are the processes Android is trying to keep responsive by reclaiming resources. There are generally very few of these processes, and they will be killed only as a last resort.
Active processes include:
- Activities in an “active” state; that is, they are in the foreground and responding to user events. You will explore Activity states in greater detail later in this chapter.
- Activities, Services, or Broadcast Receivers that are currently executing an onReceive event handler.
- Services that are executing an onStart, onCreate, or onDestroy event handler.
Visible Processes Visible, but inactive processes are those hosting “visible” Activities. As the name suggests, visible Activities are visible, but they aren’t in the foreground or responding to user events. This happens when an Activity is only partially obscured (by a non-full-screen or transparent Activity). There are generally very few visible processes, and they’ll only be killed in extreme circumstances to allow active processes to continue.
Started Service Processes Processes hosting Services that have been started. Services support ongoing processing that should continue without a visible interface. Because Services don’t interact directly with the user, they receive a slightly lower priority than visible Activities. They are still considered to be foreground processes and won’t be killed unless resources are needed for active or visible processes.
Background Processes Processes hosting Activities that aren’t visible and that don’t have any Services that have been started are considered background processes. There will generally be a large number of background processes that Android will kill using a last-seen-first-killed pat- tern to obtain resources for foreground processes.
Empty Processes To improve overall system performance, Android often retains applications in memory after they have reached the end of their lifetimes. Android maintains this cache to improve the start-up time of applications when they’re re-launched. These processes are rou- tinely killed as required.
How to use memory efficiently
Android manages opened applications which are running in the background, so officially you shouldn’t care about that. This means that it closes the applications when the system needs more memory. However, most android users are not very satisfied with how it does its things because sometimes it leaves too many processes running which causes sluggishness’ in everyday performance. We can use advanced task killer/task manager and it does its job very well.
I think, Now you might be clear the memory concept of android. I will come soon with tracking the memory allocation and avoiding the memory leaks.
发表评论
-
One省电卫士 - Android内核级省电App
2013-02-03 19:32 3598One省电卫士是一款androi ... -
(转)Windows下Eclipse集成Cygwin配置Android NDK环境编译JNI库程序步骤
2012-05-09 16:11 5612前戏准备: 1. 搭建Eclipse Android ... -
Android-Task和Activity相关的一些属性[转]
2011-08-23 09:21 3083android:allowTaskReparenting用来标 ... -
GC_FOR_MALLOC
2011-07-01 11:44 2314GC_FOR_MALLOC means that the ... -
ProgressBar 样式
2011-05-01 23:06 3179The four attributes that you me ... -
ShellCommand.java
2011-04-07 19:38 1609/** * ShellCommand.java runs co ... -
Android任务管理终极发布AndTask 3.1(安安任务管理)
2011-04-04 07:50 1694安安任务管理是一款android任务管理软件,可通过手动或自动 ... -
AndMemory 安安内存管理 1.1 发布
2011-03-08 23:42 1917AndMemory is an android memory ... -
预测今年将是android应用普及年和android安全年
2011-03-06 21:53 2002经过去年一年的实践,预测今年将是android应用 ... -
Android之混淆(Obfuscate)
2011-03-06 16:07 2935下载Android安安软件请到:http://code. ... -
Android内存信息
2011-02-21 21:40 2183下载Android安安软件请到:http://code.goo ... -
How to decompile .dex file on Android(转)如何反编译.dex文件
2011-02-20 11:34 2919下载Android安安软件请到:http://code.goo ... -
(转)android JNI 学习笔记1
2011-02-17 10:08 2825下载Android安安软件请到:http://code.goo ... -
(转)Android内存管理机制之一:lowmemory killer
2011-02-15 15:00 2651下载Android安安软件请到 ... -
转-Andriod被排出Linux内核的原因
2011-01-12 22:36 1552下载Android安安软件请到:http://code.goo ... -
Ubuntu 开启 Android 的 USB 调试模式
2011-01-06 20:51 7817在Android开发者网站中, 它提供了在 Ubuntu 下实 ... -
解决Conversion to Dalvik format failed: Unable to execute dex: null
2010-12-12 23:17 2422解决Conversion to Dalvik format f ... -
AndBox发布最新版AndRootFile(安安文件管理) 3.0 beta 版
2010-11-27 09:56 1788The ultimate file manager for r ... -
(转)区分Activity的四种加载模式
2010-11-20 10:09 1822在多Activity开发中,有可能是自己应用之间的Activi ... -
(转)Android实现日历
2010-11-09 17:12 2648下载Android安安软件请到:http://code.goo ...







相关推荐
C_C++ 内存管理算法和实现 Memory Management Algorithms and Implementation in C_C++ C_C++ 内存管理算法和实现 Memory Management Algorithms and Implementation in C_C++ C_C++ 内存管理算法和实现 ...
《Memory Management in the Java HotSpot™ Virtual Machine》一文深入探讨了Java HotSpot虚拟机中的内存管理机制,这是Java性能优化的关键领域。HotSpot虚拟机是Oracle JDK和JRE的一部分,以其高性能和优化能力而...
本文档提供了Java HotSpot虚拟机(JVM)中内存管理的广泛概述,特别是在Sun公司的Java 2平台标准版(J2SE)5.0版本的发布中。文档描述了可供使用的垃圾收集器(Garbage Collectors),给出了关于如何选择和配置收集...
“Memory Management: Algorithms and Implementation in C_C++.chm”文件可能包含了上述部分或全部知识点的详细讲解和实例,对于希望深入理解C/C++内存管理的开发者来说,是一份宝贵的参考资料。通过学习,开发者...
《内存管理:算法与C/C++实现》是Bill Blunden撰写的一部深入探讨计算机内存管理原理及其实现的著作。本书由Wordware Publishing出版,详细介绍了内存管理在计算机科学中的重要性、各种计算机算法以及C和C++编程语言...
Linux操作系统内存管理 Linux操作系统的内存管理是计算机科学中一个重要的领域。本文将详细阐述Linux操作系统的内存管理机制,包括物理内存和虚拟内存的管理机制、地址映射机制、内存碎片和内存不连续的问题解决等...
C/C++实现的内存管理算法教材,CHM格式
由于提供的文件信息中包含了重复的标签和无关内容(WeChatOfficialAccounts:BigData321),我将忽略这些部分,并基于标题和描述中所提及的“Understanding-Memory-Management-In-Spark-For-Fun-And-Profit.pdf”和...
《Pro .NET Memory Management》这本书由Konrad Kokosa撰写,旨在帮助开发者更好地理解.NET内存管理的内部机制,从而提高代码质量、性能和可扩展性。 #### 二、.NET内存管理概述 .NET内存管理主要涉及两个方面:...
### 内存管理:算法与C/C++中的实现 #### 内容概览 《内存管理:算法与C/C++中的实现》是一本深入探讨内存管理机制、策略及其在C/C++编程语言中具体实现的专业书籍。作者Bill Blunden通过本书系统地介绍了内存管理...
memory management 动态内存分配 FIFO算法
更详细的资料可参阅“Memory Resource Management in VMware ESX Server”。 ESX利用高级资源管理策略计算每个虚拟机的目标内存分配,该分配基于当前系统负载以及虚拟机的设置参数(如份额、预留和限制)。计算出的...
在“Virtual memory management ppt”中,主要探讨了虚拟内存管理的多个关键概念和策略。 11.1 引言:这部分介绍了虚拟内存管理的基本原理,包括替换策略和获取策略。替换策略是当内存满时,系统用来选择哪些页面...
本书介绍了垃圾回收和显式内存管理算法的几种具体实现。
aarch64 Linux Kernel Memory Management, aarch64 Linux Kernel Memory Management, aarch64 Linux Kernel Memory Management
sdk2003 win32 Memory Management sdk2003 win32 Memory Management
"Memory Management Simulator" 是一个模拟器,用于帮助理解并可视化内存管理的过程。这个模拟器利用了Java Swing库来构建用户界面,使得用户能够交互地探索内存分配和回收的机制。 在Java中,内存分为堆(Heap)和...
Goals of memory management To provide a convenient abstraction for programming To allocate scarce memory resources among competing processes to maximize performance with minimal overhead
一个用C写的内存管理系统,模拟操作系统内存