- 浏览: 20990 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 北京
-

文章分类
最新评论
-
liangtu33:
图呢?哪里去了
软件性能 -
xhfei:
不错,我正需要,先拿去试试
TcpTimedWaitDelay和MaxUserPort设置 -
xhfei:
...
TcpTimedWaitDelay和MaxUserPort设置
Performance tuning is not a silver bullet. Simply put, good system performance depends on: good design, good implementation, defined performance objectives, and performance tuning.
Since JBoss tuning involves also tuning the environment on which jBoss is run, the first tutorial will start discussing about JVM settings and OS settings on which JBoss can produce best results. Then we'll see some specific JBoss config settings.
JBoss tuning tip 1: Tune the garbage collector
One strength of the J2SE platform is that it shields the developer from the complexity of memory allocation. However, once garbage collection is the principal bottleneck, it is worth understanding some aspects of this hidden implementation
An object is considered garbage when it can no longer be reached from any pointer in the running program. The most straightforward garbage collection algorithms simply iterate over every reachable object. Any objects left over are then considered garbage. The time this approach takes is proportional to the number of live objects,
The complete address space reserved for object memory can be divided into the young and tenured generations.

The young generation consists of eden and two survivor spaces. Most objects are initially allocated in eden. One survivor space is empty at any time, and serves as the destination of any live objects in eden and the other survivor space during the next copying collection. Objects are copied between survivor spaces in this way until they are old enough to be tenured (copied to the tenured generation).
A third generation closely related to the tenured generation is the permanent generation which holds data needed by the virtual machine to describe objects that do not have an equivalence at the Java language level. For example objects describing classes and methods are stored in the permanent generation
Use the the command line option -verbose:gc causes information about the heap and garbage collection to be printed at each collection. For example, here is output from a large server application:
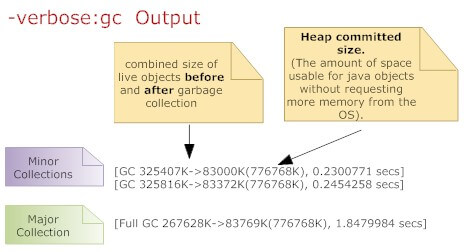
It's demonstrated that an application that spends 10% of its time in garbage collection can lose 75% of its throughput when scaled out to 32 processors
(http://java.sun.com/javase/technologies/hotspot/gc/gc_tuning_6.html)
JBoss tuning tip 2: Set -Xms and -Xmx to the same value
By default, the virtual machine grows or shrinks the heap at each collection to try to keep the proportion of free space to live objects at each collection within a specific range.
Setting -Xms and -Xmx to the same value. This increase predictability by removing the most important sizing decision from the virtual machine.
JBoss tuning tip 3: Use server VM
The server JVM is better suited to longer running applications. To enable it simply set the -server option on the command line.
JBoss tuning tip 4: Turn off distributed gc
The RMI system provides a reference counting distributed garbage collection algorithm. This system works by having the server keep track of which clients have requested access to remote objects running on the server. When a reference is made, the server marks the object as "dirty" and when a client drops the reference, it is marked as being "clean.". However this system is quite expensive and by default runs every minute.
Set it to run every 30 minute at least
-Dsun.rmi.dgc.client.gcInterval=1800000
-Dsun.rmi.dgc.server.gcInterval=1800000
JBoss tuning tip 6: Turn on parallel gc
If you have multiple proessors you can do your garbage collection with multiple threads. By default the parallel collector runs a collection thread per processor, that is if you have an 8 processor box then you'll garbage collect your data with 8 threads. In order to turn on the parallel collector use the flag -XX:+UseParallelGC. You can also specify how many threads you want to dedicate to garbage collection using the flag -XX:ParallelGCThreads=8.
JBoss tuning tip 7: Don't use Huge heaps, use a cluster
More JVMs/smaller heaps can outperform fewer JVMs/Larger Heaps. So instead of huge heaps, use additional server nodes. Set up a JBoss cluster and balance work between nodes.
JBoss tuning tip 8: Don't choose an heap larger then 70% of your OS memory
Choose a maximum heap size not more then 70% of the memory to avoid excessive page faults and thrashing.
JBoss tuning tip 9: Tune the Heap ratio
This is one of most important tuning factor: the heap ratio. The heap ratio specifies how the amount of the total heap will be partitioned between the young and the tenured space. What happens if you have lots of long lived data (cached data, collections ) ? maybe you're in this situation:
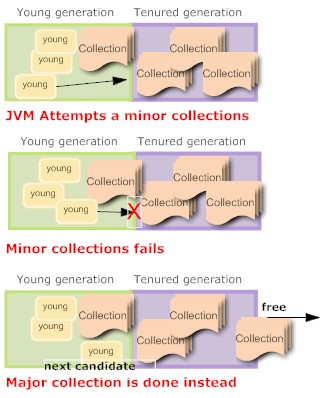
The problem here is that the long lived data overflows the tenured generation. When a collection is needed the tenured generation is basically full of live data. Much of the young generation is also filled with long lived data. The result was that a minor collection could not be done successfully (there wasn't enough room in the tenured generation for the anticipated promotions out of the young generation) so a major collection was done.
The major collection worked fine, but the results again was that the tenured generation was full of long lived data and there was long lived data in the young generation. There was also free space in the young generation for more allocations, but the next collection was again destined to be a major collection.
This will eventually bring your application to crawl !!!!!
By decreasing the space in the young generation and putting that space into the tenured generation (a value of NewRatio larger than the default value was chosen), there was enough room in the tenured generation to hold all the long lived data and also space to support minor collections. This particular application used lots of short lived objects so after the fix mostly minor collections were done.
NewRatio is a flag that specifies the amount of the total heap that will be partitioned into the young generation. It's the tenured-generation-size / young-generation-size. For example, setting -XX:NewRatio=3 means that the ratio between the young and tenured generation is 1:3
If you want a more precise control over the young generation : NewSize is the initial size of the young generation, MaxNewSize will specify the maximum size of the young generation
What is the recommeded heap ratios ? Set the tenured generation to be approximately two times the size of the young generation. With a 2GB of RAM the recommended sizes are 1200MB for the heap and 400MB for the young generation.
This recommendation is only a starting point, you have to tune from there and to do that you have to gather and analyze the garbage collection statistics
JBoss tuning tip 10: Monitor the free memory with monitors and snapshots
See this tips:
http://www.mastertheboss.com/en/jboss-howto/47-jboss-jmx/92-jboss-monitor-snapshot.html
http://www.mastertheboss.com/en/jboss-howto/47-jboss-jmx/91-jboss-monitor.html
JBoss tuning tip 11: Tune the Operating System
Each operating system sets default tuning parameters differently. For Windows platforms, the default settings are usually sufficient. However, the UNIX and Linux operating systems usually need to be tuned appropriately
Solaris tuning parameters:
Check the following TCP parameters with your sysadmin:
/dev/tcp tcp_time_wait_interval
/dev/tcp tcp_conn_req_max_q
/dev/tcp tcp_conn_req_max_q0
/dev/tcp tcp_ip_abort_interval
/dev/tcp tcp_keepalive_interval
/dev/tcp tcp_rexmit_interval_initial
/dev/tcp tcp_rexmit_interval_max
/dev/tcp tcp_rexmit_interval_min
/dev/tcp tcp_smallest_anon_port
/dev/tcp tcp_xmit_hiwat
/dev/tcp tcp_recv_hiwat
/dev/ce instance
/dev/ce rx_intr_time
Tip: Use the netstat -s -P tcp command to view all available TCP parameters.
Set TCP-related tuning parameters using the ndd command
Example: ndd -set /dev/tcp tcp_conn_req_max_q 16384
Tune /etc/system filesystem
Each socket connection to JBoss consumes a file descriptor. To optimize socket performance, you may need to configure your operating system to have the appropriate number of file descriptors.
See solaris documentation about this parameters:
set rlim_fd_cur
set rlim_fd_max
set tcp:tcp_conn_hash_size (Solaris 8 and 9)
set ip:ipcl_conn_hash_size (Solaris 10)
set shmsys:shminfo_shmmax Note: This should only be set for machines that have at least 4 GB RAM or higher.
set autoup
set tune_t_fsflushr
Linux tuning parameters:
Since in Linux everything is a file, check the file-max parameter
cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
set fs.file-max=102642 into /etc/sysctl.conf
Raise ulimit with /etc/limits.conf (or ulimit -n for current session)
Increase default socket send/receive buffer
sysctl -w net.core.rmem_default=262144
(default socket receive buffer)
sysctl -w net.core.wmem_default=262144
(default socket send buffer)
sysctl -w net.core.rmem_max=262144
(max socket receive buffer)
sysctl -w net.core.wmem_max=262144
(max socket send buffer size)
Optimize MTU. The TCP maximum transfer unit is 1512 on the Internet. If you are sending larger packets it's a good idea to increase MTU size in order to reduce packet fragmentation (especially if you have a slow network)
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-xxx (eth0 for instance)
– add "MTU=9000" (for gigabit ethernet)
– restart the interface (ifdown eth0;ifup eth0)
Use Big Memory Pages
Default page size is 4KB (usually too small!)
Check page size with:
$ cat /proc/meminfo
If you see "HugePage_Total," "HugePages_Free" and "Hugepagesize", you can apply this optimization
Here's how to do it (2GB Heap Size Example)
$ echo 2147483647 > /proc/sys/kernel/shmmax
$ echo 1000 > /proc/sys/vm/nr_hugepages
In Sun's JVM, add this flag: XX:+UseLargePages
JBoss tuning tip 12: Lots of Requests ? check JBoss thread pool
JBoss thread pool is defined into conf/jboss-service.xml
- <mbean code="org.jboss.util.threadpool.BasicThreadPool"
- name="jboss.system:service=ThreadPool">
- <attribute name="Name">JBoss System Threads</attribute>
- <attribute name="ThreadGroupName">System Threads</attribute>
- <attribute name="KeepAliveTime">60000</attribute>
- <attribute name="MaximumPoolSize">10</attribute>
- <attribute name="MaximumQueueSize">1000</attribute>
- <attribute name="BlockingMode">run</attribute>
- </mbean>
<mbean code="org.jboss.util.threadpool.BasicThreadPool"
name="jboss.system:service=ThreadPool">
<attribute name="Name">JBoss System Threads</attribute>
<attribute name="ThreadGroupName">System Threads</attribute>
<attribute name="KeepAliveTime">60000</attribute>
<attribute name="MaximumPoolSize">10</attribute>
<attribute name="MaximumQueueSize">1000</attribute>
<attribute name="BlockingMode">run</attribute>
</mbean>
For most applications this defaults will just work well, however if you are running an application with issues lots of requests to jboss (such as EJB invocations) then monitor your thread pool. Open the Web Console and look for the MBean jboss.system:service=ThreadPool.
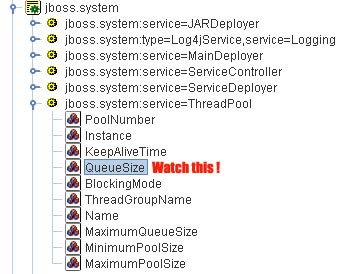
Start a monitor on the QueueSize parameter. Have you got a QueueSize which reaches MaximumPoolSize ? then probably you need to set a higher MaximumPoolSize pool size attribute
 Watchout! Speak at first with your sysadmin and ensure that the CPU capacity support the increase in threads.
Watchout! Speak at first with your sysadmin and ensure that the CPU capacity support the increase in threads.
 Watchout! if your threads make use of JDBC connections you'll probably need to increase also the JDBC connection pool accordingly. Also verify that your HTTP connector is enabled to handle that amount of requests
Watchout! if your threads make use of JDBC connections you'll probably need to increase also the JDBC connection pool accordingly. Also verify that your HTTP connector is enabled to handle that amount of requests
JBoss tuning tip 13: Check the Embedded web container
JBoss supports connectors for http, https, and ajp. The configuration file is server.xml and it's deployed in the root of JBoss web container (In JBoss 4.2.0 it's: "JBOSS_HOME\server\default\deploy\jboss-web.deployer")
- <Connector port="8080" address="${jboss.bind.address}"
- maxThreads="250" maxHttpHeaderSize="8192"
- emptySessionPath="true" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
- enableLookups="false" redirectPort="8443" acceptCount="100"
- connectionTimeout="20000" disableUploadTimeout="true" />
<Connector port="8080" address="${jboss.bind.address}"
maxThreads="250" maxHttpHeaderSize="8192"
emptySessionPath="true" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
enableLookups="false" redirectPort="8443" acceptCount="100"
connectionTimeout="20000" disableUploadTimeout="true" />
The underlying HTTP connector of JBoss needs to be fine tuned for production settings. The important parameters are:
maxThreads - This indicates the maximum number of threads to be allocated for handling client HTTP requests. This figure corresponds to the concurrent users that are going to access the application. Depending on the machine configuration, there is a physical limit beyond which you will need to do clustering.
acceptCount - This is the number of request threads that are put in request queue when all available threads are used. When this exceeds, client machines get a request timeout response.
compression - If you set this attribute to “force”, the content will be compressed by JBoss and will be send to browser. Browser will extract it and display the page on screen. Enabling compression can substantially reduce bandwidth requirements of your application.
So how do you know if it's necessary to raise your maxThreads number ? again open the web console and look for the MBean jboss.web:name=http-127.0.0.1-8080,type=ThreadPool. The key attribute is currentThreadsBusy. If it's about 70-80% of the the maxThreads you should consider raising the number of maxThreads. 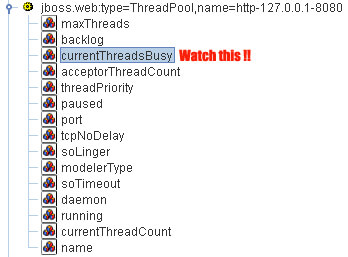
 Watch out! if you increase the maxThreads count you need to raise your JBoss Thread pool accordingly.
Watch out! if you increase the maxThreads count you need to raise your JBoss Thread pool accordingly.
JBoss tuning tip 14: Turn off JSP Compilation in production
JBoss application server regularly checks whether a JSP requires compilation to a servlet before executing a JSP. In a production server, JSP files won’t change and hence you can configure the settings for increased performance.
Open the web.xml in deploy/jboss-web.deployer/conf folder. Look for the jsp servlet in the file and modify the following XML fragment as given below,
<init-param>
<param-name>development</param-name>
<param-value>false</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>checkInterval</param-name>
<param-value>300</param-value>
</init-param>
References:
http://java.sun.com/javase/technologies/hotspot/gc/gc_tuning_6.html
http://people.redhat.com/alikins/system_tuning.html
http://community.jboss.org/wiki/JBossASTuningSliming
Tip 15: Lots of EJB requests ? switch to the PoolInvoker
JBoss uses RMI for EJB communication and by default creates a single thread for every incoming request.
When the number of requests is very large this could be a bottleneck. However you can switch from the
standard jrmp service invoker to the pool invoker.
How to do it ? open standardjboss.xml and find the following fragment:
<invoker-mbean>jboss:service=invoker,type=jrmp</invoker-mbean>
On JBoss 4.x you should find 4 occurrences of it: stateless-rmi-invoker, clustered-stateless-rmi-invoker, stateful-rmi-invoker,entity-rmi-invoker. Now replace this fragment with :
<invoker-mbean>jboss:service=invoker,type=pooled</invoker-mbean>
Notice you can even have a mixed environment: that is stateless invocation managed by the pool and all others by jrmp.
If you want to change the default attributes of your pool then open jboss-service.xml
- <mbean code="org.jboss.invocation.pooled.server.PooledInvoker"
- name="jboss:service=invoker,type=pooled">
- <attribute name="NumAcceptThreads">1</attribute>
- <attribute name="MaxPoolSize">300</attribute>
- <attribute name="ClientMaxPoolSize">300</attribute>
- <attribute name="SocketTimeout">60000</attribute>
- <attribute name="ServerBindAddress">${jboss.bind.address}</attribute>
- <attribute name="ServerBindPort">4445</attribute>
- <attribute name="ClientConnectAddress">${jboss.bind.address}</attribute>
- <attribute name="ClientConnectPort">0</attribute>
- <attribute name="ClientRetryCount">1</attribute>
- <attribute name="EnableTcpNoDelay">false</attribute>
- </mbean>
<mbean code="org.jboss.invocation.pooled.server.PooledInvoker"
name="jboss:service=invoker,type=pooled">
<attribute name="NumAcceptThreads">1</attribute>
<attribute name="MaxPoolSize">300</attribute>
<attribute name="ClientMaxPoolSize">300</attribute>
<attribute name="SocketTimeout">60000</attribute>
<attribute name="ServerBindAddress">${jboss.bind.address}</attribute>
<attribute name="ServerBindPort">4445</attribute>
<attribute name="ClientConnectAddress">${jboss.bind.address}</attribute>
<attribute name="ClientConnectPort">0</attribute>
<attribute name="ClientRetryCount">1</attribute>
<attribute name="EnableTcpNoDelay">false</attribute>
</mbean>
There are two key attributes for the PooledInvoker in regards to how many threads are used in processing requests. The first is the NumAcceptThreads attribute. The value for this attribute will determine how many threads are created to listen for incoming requests. These threads will be the ones that call the accept() method of the server socket (which is a blocking call and will wait there till data is received on the network interface for the server socket).
The MaxPoolSize is the other key factor: it's the size of the pool containing the ServerThreads .
How can MaxPoolSize become a bottleneck ? if the accept thread can not get a worker thread from the pool and the pool size has reached the MaxPoolSize value, it will wait for one to become available (instead of creating a new one).
Tip 16: Have you got readonly Entity Beans ? tell it to JBoss
JBoss offers a way to handle this situation by defining either an entire EJB as being "read-only" or simply as a subset of its methods. When accessing a read-only method (or EJB), while JBoss still prevents concurrent access to the same bean instance, the bean will not be enrolled in the transaction and will not be locked during the whole transaction lifetime. Consequently, other transactions can directly use it for their own work.
- <enterprise-beans>
- <entity>
- <ejb-name>MyEntity</ejb-name>
- <method-attributes>
- <method>
- <method-name>get*</method-name>
- <read-only>true</read-only>
- </method>
- <method-attributes>
- </entity>
- </enterprise-beans>
<enterprise-beans>
<entity>
<ejb-name>MyEntity</ejb-name>
<method-attributes>
<method>
<method-name>get*</method-name>
<read-only>true</read-only>
</method>
<method-attributes>
</entity>
</enterprise-beans>
Tip 17: Disable the hot deployer in production
See this tip:
http://www.mastertheboss.com/en/jboss-howto/42-jboss-config/68-configure-jboss-disable-hot-deployment-.html
Tip 18: Configure the EJB container to use cache, when possible.
If the EJB container has exclusive access to the persistent store, it doesn’t need to synchronize the in-memory bean state from the persistent store at the beginning of each transaction.
So you could activate the so-called Commit-A option that caches entity bean state between transactions. In order to activate this option :
- <jboss>
- <enterprise-beans>
- <container-configurations>
- <container-configuration extends=
- "Standard CMP 2.x EntityBean">
- <container-name>CMP 2.x and Cache</container-name>
- <commit-option>A</commit-option>
- </container-configuration>
- </container-configurations>
- <entity>
- <ejb-name>MyEntity</ejb-name>
- <configuration-name
- CMP 2.x and Cache</configuration-name>
- <method-attributes>
- <method>
- <method-name>get*</method-name>
- <read-only>true</read-only>
- </method>
- <method-attributes>
- </entity>
- </jboss>
<jboss>
<enterprise-beans>
<container-configurations>
<container-configuration extends=
"Standard CMP 2.x EntityBean">
<container-name>CMP 2.x and Cache</container-name>
<commit-option>A</commit-option>
</container-configuration>
</container-configurations>
<entity>
<ejb-name>MyEntity</ejb-name>
<configuration-name
CMP 2.x and Cache</configuration-name>
<method-attributes>
<method>
<method-name>get*</method-name>
<read-only>true</read-only>
</method>
<method-attributes>
</entity>
</jboss>
Tip 19: Use Cache invalidation in a Cluster for Commit Option A
Commit option A can boost your Entity Bean but what happens when running in a cluster ? in a cluster configuration more than one JBoss node will access the same database. Furthermore, they will not only read data, but may also update the db store.Consequently, we now have as many points of write access to the database as we have JBoss instances in the cluster.
For these scenarios, JBoss incorporates a handy tool: the cache invalidation framework. It provides automatic invalidation of cache entries in a single node or across a cluster of JBoss instances. As soon as an entity bean is modified on a node, an invalidation message is automatically sent to all related containers in the cluster and the related entry is removed from the cache. The next time the data is required by a node, it will not be found in cache, and will be reloaded from the database.
In order to activate it, add to your Entity Bean the cache-invalidation tag.
- <entity>
- <ejb-name>MyEntity</ejb-name>
- <configuration-name>
- Standard CMP 2.x with cache invalidation
- </configuration-name>
- <method-attributes>
- <method>
- <method-name>get*</method-name>
- <read-only>true</read-only>
- </method>
- <method-attributes>
- <cache-invalidation>True</cache-invalidation>
- </entity>
<entity>
<ejb-name>MyEntity</ejb-name>
<configuration-name>
Standard CMP 2.x with cache invalidation
</configuration-name>
<method-attributes>
<method>
<method-name>get*</method-name>
<read-only>true</read-only>
</method>
<method-attributes>
<cache-invalidation>True</cache-invalidation>
</entity>
Tip 20: Synchronize at commit time when possible.
The sync-on-commit-only element configures a performance optimization that will cause entity bean state to be synchronized with the database only at commit time. Normally the state of all the beans in a transaction would need to be synchronized when an finder method is called or when an remove method is called :
<container-configuration>
<container-name>Standard Pessimistic CMP 2.x EntityBean</container-name>
<call-logging>false</call-logging>
<invoker-proxy-binding-name>entity-pooled-invoker</invoker-proxy-binding-name>
<sync-on-commit-only>true</sync-on-commit-only>
....
</container-configuration>
Tip 21: Use Prepared Statement Cache:
In JBoss, by default,prepared statements are not cached. To improve performance one can configure a prepared statement cache of an arbitrary size. You can use in your -ds.xml file the <prepared-statement-cache-size> : this is the number of prepared statements per connection to be kept open and reused in subsequent requests.
Tip 22: Remove services you don't need
JBoss ships with lots of services, however you'll seldom need to use them all. The service is usually deployed as *-service.xml under the deploy directory. Sometimes it's also deployed as .sar/.rar archive.
In order to remove the service, remove the file in the "Server/deploy" column. If needed remove also the relative libs stated under "Server/lib"
发表评论






相关推荐
### JBoss Tuning详解 JBoss作为一款广泛使用的开源应用服务器,在企业级应用程序部署与运行中扮演着重要的角色。为了确保其稳定性和性能表现,进行合理的调优是必不可少的步骤。本文将根据提供的资料深入探讨JBoss...
JBoss AS 5 Performance Tuning will teach you how to deliver fast applications on the JBoss Application Server and Apache Tomcat, giving you a decisive competitive advantage over your competitors. ...
JBoss Application Server Tuning Guide 是一份由 JBoss Inc. 在 2005 年发布的官方文档,主要用于指导用户如何针对 JBoss 4.0.2 和 Tomcat 5.5.9 进行性能优化配置。本文档提供了详细的调优步骤和技术,旨在帮助...
最后,文档中还提到了许多与Red Hat相关的商标,包括Red Hat Enterprise Linux、Shadowman logo、JBoss、Fedora等。这些商标都已在相关国家注册,并归Red Hat公司所有。此外,文档中也提到了其他的注册商标,如Linux...
Later chapters cover advanced features such as configuration and performance tuning, illustrating each concept with a running real-world stock portfolio application. Readers will learn to integrate ...
可以作为Web应用程序部署到每个JEE或Web容器(Glassfish,JBoss,Tomcat ...) 也可以作为Docker映像使用而无需任何外部依赖 这个GitHub项目旨在使用集成的JETTY应用程序服务器构建捆绑的Web存档文件。该功能通过上...
1 What is Liferay? 1 1.1 Building a site with Liferay Web Content . . . . . . . ....1.2 Using Liferay Portal as a collaborative platform ....1.3 Using Liferay as a social platform ....1.4 Using Liferay as a ...