在分别介绍了XML Signature和XML Encryption后,我们了解了如何用XML的形式来保证消息的完整性(Integrity)和机密性(Confidentiality)。如何将其运用到Web Service中从而保证Web Service的安全性,这就是WS-Security规范所描述的内容。我们知道Web Service的采用SOAP作为消息封装协议, 因此WS-Security规范主要描述了如何将XML Security(XML Signature和XML Encryption)与已有的安全技术(Kerberos,X.509,SAML)结合, 并把它们绑定到SOAP中.
NoteA good way to think about WS-Security is that it is a specification that takes XML security (XML Encryption and XML Signature); links that with pre-existing security technologies that it calls tokens, such as X.509, Kerberos, and SAML; and binds it all to SOAP so that it can become part of a secure Web service interaction.
NoteSOAP描述了Web Service消息的打包形式,而非消息的传输协议,Web Service的传输协议可以是http,tcp甚至smtp。
<S:Envelope> <S:Header> <wsse:Security> <!-- Security Token --> <wsse:UsernameToken> ...
</wsse:UsernameToken> <!-- XML Signature --> <ds:Signature> ...
<ds:Reference URI="#body"> ...
</ds:Signature> <!-- XML Encryption Reference List -->
<xenc:ReferenceList> <xenc:DataReference URI="#body"/> </xenc:ReferenceList> </wsse:Security> </S:Header> <S:Body> <!-- XML Encrypted Body --> <xenc:EncryptedData Id="body" Type="content"> ...
</xenc:EncryptedData> </S:Body></S:Envelope> 以上是一个典型的使用WS-Security协议来保证SOAP消息安全的例子。从中可以看出WS-Security协议主要对SOAP消息的Head部分做了扩展---加入了wsse:Security元素。其中针对安全的三个方面Authentication, Integrity, Confidentiality分别定义了Security Token, XML Signature以及XML Encryption Reference List三个子元素。而在SOAP包中的需要加密的业务内容(通常会加密整个Soap Body)被经过XML Encryption处理过的元素(EncryptedDate)所替代。
下面这张图大致描述了WS-Security所包含的元素以及它们之间的关系。
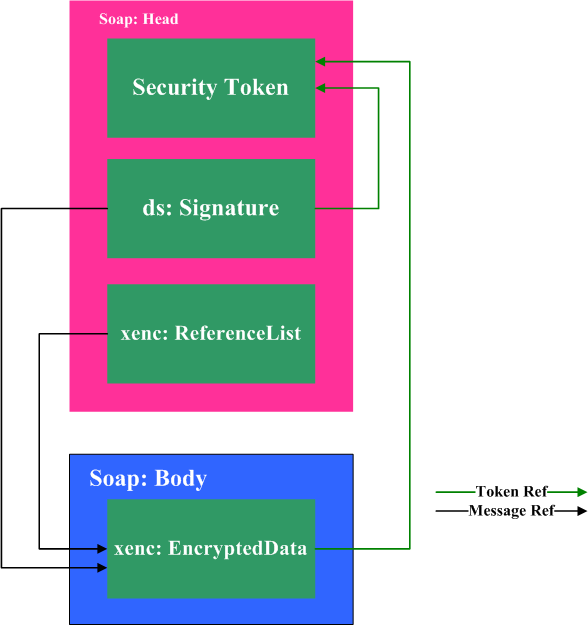
(注意这幅图只是一张示意图,比如ds:Signature也可以对Soap Head中的元素做签名)
从之前对XML Signature和XML Encryption介绍中,我们已经了解了签名和加密的具体过程,以及在整个过程中产生的各个元素的含义。下面就从一个具体的运用了WS-Security规范的Soap Envelop中来看看如何在WS-Security中使用XML Signature和XML Encryption。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<SOAP-ENV:Envelope xmlns:SOAP-ENV="http://www.w3.org/2001/12/soap-envelope"
xmlns:ds="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#"
xmlns:xenc="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc"
xmlns:wsu="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/07/utility">
<SOAP-ENV:Header>
<wsse:Security
xmlns:wsse="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2002/secext">
<wsse:UsernameToken wsu:Id="UserToken">
<wsse:Username>HotelService</wsse:Username>
<wsse11:Salt>sdfer..</wsse11:Salt>
<wsse11:Iteration>1000</wsse11:Iteration>
</wsse:UsernameToken>
<ds:Signature>
<ds:SignedInfo>
<ds:CanonicalizationMethod
Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/10/xml-exc-c14n#"/>
<ds:SignatureMethod
Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#hmac-sha1"/>
<ds:Reference URI="#DiscountedBookingForPartnersResponse">
<ds:DigestMethod Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#sha1"/>
<ds:DigestValue>JwFsd3eQc0iXlJm5PkLh7...</ds:DigestValue>
</ds:Reference>
</ds:SignedInfo>
<ds:SignatureValue>BSxlJbSiFdm5Plhk...</ds:SignatureValue>
<ds:KeyInfo>
<wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
<wsse:Reference URI="#UserToken"/>
</wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
</ds:KeyInfo>
</ds:Signature>
<xenc:ReferenceList>
<xenc:DataReference URI="#DiscountResponse"/>
</xenc:ReferenceList>
</wsse:Security>
</SOAP-ENV:Header>
<SOAP-ENV:Body wsu:Id="DiscountedBookingForPartnersResponse">
<s:GetSpecialDiscountedBookingForPartnersResponse
xmlns:s=?http://www.MyHotel.com/partnerservice?>
<xenc:EncryptedData
wsu:Id="DiscountResponse"
type="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#Element">
<xenc:EncryptionMethod
Algorithm="http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmlenc#aes256_cbc "/>
<ds:KeyInfo xmlns:ds='http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#'>
<wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
<wsse:Reference URI="#UserToken"/>
</wsse:SecurityTokenReference>
</ds:KeyInfo>
<CipherData>
<CipherValue>XDsFaDWsHdhrHdhcW0x...</CipherValue>
</CipherData>
</xenc:EncryptedData>
</s:GetSpecialDiscountedBookingForPartnersResponse>
</SOAP-ENV:Body>
</SOAP-ENV:Envelope>
Noteds:Signature和xenc:EncryptedData在wsse:Security 中出现的顺序决定了加密和签名的顺序。ds:Signature先出现表示先加密后签名,反之先签名后加密。通常采用先加密后签名的做法。
对于其中的大部分元素我们已经比较熟悉,而wsse:UsernameToken以及在ds:Signature和xenc:EncryptedData 中出现的wsse:SecurityTokenReference子元素则显得比较陌生。
我们知道为了保证消息的完整性和机密性需要用到密钥(对称或非对称),而在它们各自的ds:KeyInfo子元素中都使用wsse:SecurityTokenReference引用到了在Soap Head最开始定义的Security Token(这里是UsernameToken)。由此可以看出Security Token是保证消息的完整性和机密性的基础,同时密钥也是用户证明身份的标志,因此包含密钥信息的Security Token也是实现身份鉴别的基础。在已经介绍过XML Signature和XML Encryption的基础上,下面对WS-Security的介绍将主要集中在Security Token上。
分享到:





相关推荐
这包括添加必要的依赖到你的项目中,比如xfire-core、xfire-ws-security等。同时,确保你的开发环境(如IDE)能够识别并处理xfire相关的XML配置文件,如xfire.xml。 接下来,创建一个简单的SOAP服务和客户端。...
"globus for ws-core-4.0.5-bin.zip" 是一个包含 Globus Toolkit 的特定版本,即 ws-core-4.0.5 的二进制发行版。Globus Toolkit 是一个广泛使用的开源软件套件,专为构建和部署网格计算服务而设计。它提供了大量的...
CXF提供了全面的WS-*(Web Services)标准支持,包括SOAP、WSDL、WS-Security等,同时也支持RESTful API的开发。在进行CXF开发时,依赖的一系列jar包是不可或缺的,它们包含了CXF运行所需的类库和组件。 1. **CXF的...
6. **Web Services Security**:对于基于SOAP的Web服务,Spring Security提供了WS-Security的支持,可以保护服务端点免受未经授权的访问。 7. **CSRF Protection**:Spring Security 4.0.3包含内置的跨站请求伪造...
- **WS-Addressing – Core**: 定义了一组消息头元素,用于标识和描述消息的目的地。 - **WS-Addressing – WSDL Binding**: 规定了如何在WSDL文档中使用WS-Addressing。 - **WS-Addressing – SOAP Binding**: 规定...
- **Maven集成**: Spring WS项目通常使用Maven构建,确保你的项目中包含正确的依赖,如`spring-ws-core`、`spring-ws-security`等。 - **Spring Boot集成**: 如果你正在使用Spring Boot,可以通过添加`spring-boot-...
udp-3.0.11.jar,cxf-rt-wsdl-3.0.0.jar,cxf-rt-ws-security-3.0.0.jar,neethi-3.0.3.jar,slf4j-api-1.7.7.jar,stax2-api-3.1.4.jar,woodstox-core-asl-4.4.1.jar,wsdl4j-1.6.3.jar,wss4j-bindings-2.0.9.jar,xml...
3. **WS-* 支持**:CXF支持一系列的Web服务扩展,如WS-Security、WS-Addressing、WS-Policy等,这些扩展增强了Web服务的安全性、可靠性和可管理性。 4. **数据绑定**:CXF提供了XML到Java对象的绑定工具,例如JAXB...
4. **WS-Security**:如果需要实现Web服务安全,如WS-Security,那么需要`cxf-rt-ws-security.jar`,它提供了基于WS-Security的安全模型。 5. **JAX-WS**:CXF也支持JAX-WS标准,如`cxf-rt-frontend-jaxws.jar`和`...
CXF是Java世界中广泛使用的Web服务实现框架,它支持多种协议和标准,如SOAP、RESTful、WS-*(包括WS-Security、WS-ReliableMessaging等)、JAX-RS和JAX-WS。CXF的名字来源于其两个前身——XFire和Celtix的组合,这两...
它支持SOAP、REST、WS-*规范(如WS-Security和WS-ReliableMessaging)以及数据绑定技术,如JAXB,帮助开发者轻松地实现Web服务功能。 2. **neethi-2.0.1.jar**: Neethi是Apache软件基金会的一个项目,提供了一个...
3. **WS-*协议实现**:CXF实现了多个Web服务标准,如WS-Security、WS-Addressing、WS-ReliableMessaging等,以确保服务的安全性、可寻址性和可靠性。 4. **客户端和服务器端支持**:CXF可以创建Web服务客户端和...
支持多种Web服务业界重要标准如SOAP、WSDL、Web服务寻址(WS-Addressing)、Web服务安全(WS-Security)等; 支持JSR181,可以通过JDK5配置Web服务; 高性能的SOAP实现; 服务器端、客户端代码辅助生成; 对Spring、...
CXF的另一个重要特性是其强大的WS-*栈支持,包括WS-Security、WS-ReliableMessaging等,这些标准确保了Web服务的安全性和可靠性。WS-Security提供了身份验证、消息完整性以及加密等功能,确保服务不受未经授权的访问...
14. **cxf-rt-ws-security**: 提供了安全特性,如WS-Security,用于保护Web服务免受攻击。 15. **cxf-tools**: 包含了一系列工具,如WSDL生成器、客户端代码生成器等,方便开发者快速构建和测试Web服务。 以上各...
logging-1.1.1.jar,cxf-2.7.6.jar,cxf-manifest.jar,cxf-services-sts-core-2.7.6.jar,cxf-services-ws-discovery-api-2.7.6.jar,cxf-services-ws-discovery-service-2.7.6.jar,cxf-services-wsn-api-2.7.6.jar,cxf-...
5. `cxf-rt-ws-security.jar`: 提供Web服务安全特性,如WS-Security、SAML、X.509证书等。 6. `cxf-rt-bindings-soap.jar`和`cxf-rt-bindings-xml.jar`: 处理SOAP和XML绑定的库。 7. `cxf-rt-rs-extension-providers...
5. **WS-Security库**:如wsdl4j和neethi,支持Web服务安全标准,如WS-Security、WS-Trust和WS-SecureConversation。 6. **Spring框架库**:CXF与Spring集成紧密,这些库可能包括了springsupport和spring-beans,...
5. **安全库**:如`neethi-*.jar`和`ws-security-*.jar`,用于实现WS-Security等安全标准,确保Web服务的安全传输。 6. **其他依赖库**:可能还包括对其他Java库的依赖,如`commons-logging-*.jar`、`geronimo-stax-...