- µĄÅĶ¦ł: 451737 µ¼Ī
- µĆ¦Õł½:

- µØźĶć¬: ÕīŚõ║¼
-

µ¢ćń½ĀÕłåń▒╗
- Õģ©ķā©ÕŹÜÕ«ó (153)
- linux (17)
- struts2 (3)
- mongodb (1)
- mysql (13)
- ant (1)
- java (12)
- hibernate’╝īspring (4)
- µĄŗĶ»Ģ (3)
- eclipse (2)
- svn (2)
- hudson (2)
- ń©ŗÕ║ÅÕæś (1)
- maven (3)
- jenkins (1)
- vnc (1)
- sublime (1)
- shell (6)
- cookie’╝īsession’╝ītokenÕī║Õł½ (2)
- idea (4)
- git (6)
- hive (3)
- µĢłńÄć (2)
- nginx (2)
- vim (1)
- ķ½śµĆ¦ĶāĮmysql (1)
- js (1)
- http (1)
- µČłµü»ķś¤ÕłŚ (1)
- ÕŹĢńé╣ńÖ╗ÕĮĢ (1)
- ElementUI (1)
- springboot (1)
- redis (1)
- CommandLineRunner (1)
- ÕŁśÕé©Ķ┐ćń©ŗ (1)
- µģ󵤟Ķ»ó (1)
- mysqlõĖ╗õ╗Ä (1)
- canal (1)
- jdk proxy (1)
- cglib (1)
- JVM (8)
- ÕŁŚĶŖéńĀü (1)
- ÕłåÕĖāÕ╝Å (2)
- rpc (1)
- ńĮæÕŹĪ (2)
- IM (1)
- QA (1)
ńżŠÕī║ńēłÕØŚ
- µłæńÜäĶĄäĶ«» ( 0)
- µłæńÜäĶ«║ÕØø ( 0)
- µłæńÜäķŚ«ńŁö ( 0)
ÕŁśµĪŻÕłåń▒╗
- 2021-10 ( 1)
- 2021-08 ( 1)
- 2021-05 ( 2)
- µø┤ÕżÜÕŁśµĪŻ...
µ£Ćµ¢░Ķ»äĶ«║
-
sunshine_bean’╝Ü
ÕĆ╝ÕŠŚÕÅéĶĆā
Õ╝éÕĖĖ A web application registered the JBDC driver -
babyhhcsy’╝Ü
õĮĀĶʤĶ┐øÕć║µØźń╗ōµ×£µ▓Īµ£ēÕĢŖ
To prevent a memory leak, the JDBC Driver has been forcibly unregistered -
ÕĘ”Õ▓Ėõ╗ŻńĀüÕÅ│Õ▓ĖĶ»Ś’╝Ü
µŹótomcatńÜäńēłµ£¼õĖŹµś»Ķ¦ŻÕå│ķŚ«ķóśńÜäµĀ╣µ£¼µ¢╣µ│ĢÕĢŖ’╝īń╗¦ń╗ŁÕ»╗µēŠĶ¦ŻÕå│µ¢╣µĪł ...
Õ╝éÕĖĖ A web application registered the JBDC driver -
ywf008’╝Ü
µłæÕ£©win7ńÄ»ÕóāõĖŗµŖźjava.net.UnknownHostE ...
java.net.UnknownHostException Õ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉå -
javapub’╝Ü
ńö©ńø«ÕēŹoracleµÅÉõŠøńÜäjava7’╝īõĖŖķØóĶ»┤ńÜäµ¢░ńē╣µĆ¦ÕźĮÕāÅķāĮń╝¢Ķ»æõĖŹ ...
Java 7õĖāÕż¦µ¢░ÕŖ¤ĶāĮķóäĶ¦łz
µØźķś┐ķćīńÄ®Javaõ╣¤µ£ēõĖĆõĖ¬ÕżÜµ£łõ║å’╝īõĖĆńø┤Õ»╣JavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║µ»öĶŠāµä¤Õģ┤ĶČŻ’╝īĶĆīClassLoaderµś»µĢ┤õĖ¬classĶĮĮÕģźĶ┐ćń©ŗõĖŁÕŠłķćŹĶ”üńÜäń╗äõ╗ČŃĆéĶĆīclassloaderµ£ēõĖ¬ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īÕĖłÕģäĶ»┤Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬µ©ĪÕ×ŗõĖŹĶāĮńĀ┤ÕØÅ’╝īõ║ĵś»µēōĶĄīõĖĆĶ»ĢŃĆé
ńøĖõ┐ĪÕ”éµ×£ķŚ«’╝ÜõĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Š’╝īÕÅ»ĶāĮµ£ēõ║║ÕÅ»õ╗źõŠāõŠāĶĆīĶ░ł’╝īõĮåµś»Ķ»┤Õł░õĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üĶ┐Öõ╣łÕłåÕ▒é’╝īõĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üÕłåõĖēÕ▒é’╝īÕ”éõĮĢń╗ĢĶ┐ćÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗŃĆéŃĆéŃĆé
Ķ┐ÖÕ░▒õĖŹµś»ķéŻõ╣łÕ«╣µśōõ║å’╝īĶ┐ÖõĖ¬µŚČÕĆÖÕ░▒ķ£ĆĶ”üõĖĆõ║øõĖōńĀöõ║åŃĆé
õ║īŃĆüclassloaderńÜäõĮ£ńö©
Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬ķŚ«ķ󜵳æķŚ«õ║åÕĖłÕģä’╝ÜÕŖĀĶĮĮ+Ķ┐׵ğńÜäµēƵ£ēĶ┐ćń©ŗ’╝īõĮåµś»µĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║Ķ»┤ńÜäõĖŹÕż¬õĖƵĀĘ’╝łµēĆõ╗źµ£ēÕŠģĶĆāĶ»ü’╝ē
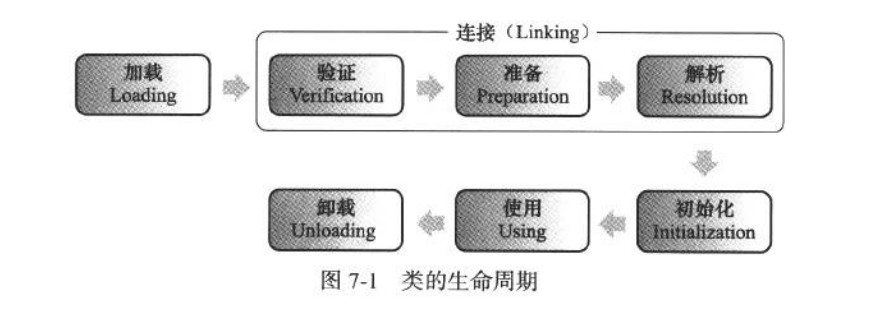
Ķ»ĘÕĤĶ░ģµłæĶ┤┤ÕøŠ’╝īõĮåõĖŗķØóõĖżÕ╝ĀÕøŠÕŁŚÕŁŚńÅĀńÄæ’╝łp228’╝ē’╝Ü


classloaderĶÖĮńäČÕŬńö©õ║ÄÕ«×ńÄ░ń▒╗ńÜäÕŖĀĶĮĮÕŖ©õĮ£’╝īõĮåÕ£©Javań©ŗÕ║ÅõĖŁõĮ£ńö©ÕŹ┤Ķ┐£Ķ┐£õĖŹķÖÉõ║Äń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮķśČµ«Ą’╝īõ╣¤Õ░▒µś»ÕÉÄķØóĶ»┤ńÜäÕÅ»õ╗źÕå│Õ«Üń▒╗ŃĆé
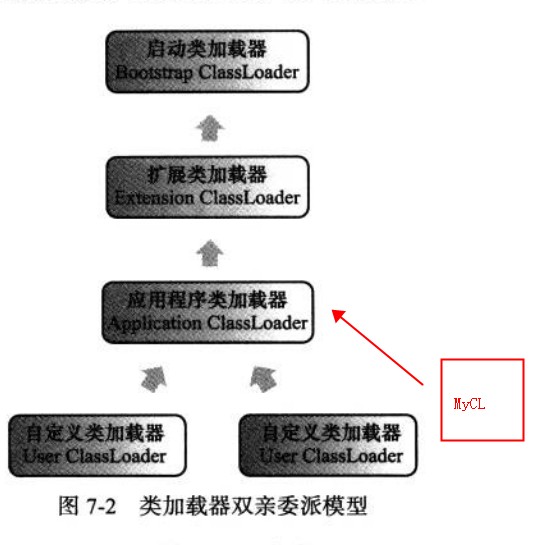
õĖēŃĆüõĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”ü3õĖ¬classloader
µłæõĖ¬õ║║Ķ«żõĖ║µ£ēõĖżõĖ¬ÕĤÕøĀ’╝īÕĮōńäČÕÅ»ĶāĮõĖŹµŁóŃĆé
1ŃĆüµś»õĖ║õ║åÕ«ēÕģ©
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/28011224/what-is-the-reason-for-having-3-class-loaders-in-java
The reason for having the three basic class loaders (Bootstrap, extension, system) is mostly security.
A key concept is the fact that the JVM will not grant package access (the access that methods and fields have if you didnŌĆÖt specifically mention private, public or protected) unless the class that asks for this access comes from the same class loader that loaded the class it wishes to access.
So, suppose a user calls his class java.lang.MyClass. Theoretically, it could get package access to all the fields and methods in the java.lang package and change the way they work. The language itself doesnŌĆÖt prevent this. But the JVM will block this, because all the real java.lang classes were loaded by bootstrap class loader. Not the same loader = no access.
There are other security features built into the class loaders that make it hard to do certain types of hacking.
So why three class loaders? Because they represent three levels of trust. The classes that are most trusted are the core API classes. Next are installed extensions, and then classes that appear in the classpath, which means they are local to your machine.
For a more extended explanation, refer to Bill VennersŌĆÖs ŌĆ£Inside the Java Virtual MachineŌĆØ.
2ŃĆüÕÅ”Õż¢’╝īĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ÕĖ¢ÕŁÉµ▓Īµ£ēµÅÉÕł░ńÜäÕ║öĶ»źµś»ķÜöń”╗ŃĆé
javańÜäµēƵ£ēń▒╗ķāĮµś»ńö▒classloaderÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜä’╝īõĖŹÕÉīclassloaderõ╣ŗķŚ┤ÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜäń▒╗ÕĮ╝µŁżµś»õĖŹÕÅ»Ķ¦üńÜäŃĆétomcatÕŖĀĶĮĮõ║ålog4j’╝īÕ«╣ÕÖ©ķćīservletõ╣¤ÕŖĀĶĮĮõ║ålog4j’╝īservletµś»ń£ŗõĖŹĶ¦ütomcatÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜälog4jń▒╗ńÜä’╝īÕÅŹõ╣ŗõ║”ńäČŃĆé
Õ£©µĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║’╝īp278’╝īµÅÉÕł░’╝Ü
tomcatõĖ║õ║åµö»µīüµØāķÖÉńø«ÕĮĢń╗ōµ×ä’╝īÕ»╣ńø«ÕĮĢõĖŁńÜäń▒╗Õ║ōĶ┐øĶĪīÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÆīķÜöń”╗’╝ītomcatĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēõ║åÕżÜõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ŃĆé
õ╣¤Ķ»┤µśÄõ║åĶ┐Öńé╣ŃĆé
ÕøøŃĆüÕ░ØĶ»Ģń╗ĢĶ┐ćÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Š
µĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║’╝īp231’╝īÕåÖÕł░:
ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗÕ£©jdk1.2Õ╝ĢÕģź’╝īõĮåÕ«āõĖŹµś»õĖĆõĖ¬Õ╝║ÕłČµĆ¦ńÜäń║”µØ¤µ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īĶĆīµś»JavaĶ«ŠĶ«ĪĶĆģµÄ©ĶŹÉń╗ÖÕ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģńÜäõĖĆń¦Źń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮµ¢╣Õ╝ÅŃĆé
µŹóÕÅźĶ»ØĶ»┤’╝īõ╣¤Õ░▒µś»ÕÅ»õ╗źõĖŹńö©Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬µ©ĪÕ×ŗńÜä’╝īĶć¬ÕĘ▒Õ«×ńÄ░ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕ░▒ÕÅ»õ╗ź’╝īµ»Ģń½¤ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ńÜäÕĤզŗõĮ£ńö©Õ░▒µś»’╝ÜŌĆ£ķĆÜĶ┐ćń▒╗ńÜäÕģ©ķÖÉÕ«ÜÕÉŹÕŠŚÕł░ń▒╗ńÜäõ║īĶ┐øÕłČńĀüµĄüŌĆØ
µØźń£ŗń£ŗÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗµś»Õ”éõĮĢÕ«×ńÄ░ńÜä’╝Ü
/**
* Loads the class with the specified <a href="#name">binary name</a>. The
* default implementation of this method searches for classes in the
* following order:
*
* <ol>
*
* <li><p> Invoke {@link #findLoadedClass(String)} to check if the class
* has already been loaded. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Invoke the {@link #loadClass(String) <tt>loadClass</tt>} method
* on the parent class loader. If the parent is <tt>null</tt> the class
* loader built-in to the virtual machine is used, instead. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Invoke the {@link #findClass(String)} method to find the
* class. </p></li>
*
* </ol>
*
* <p> If the class was found using the above steps, and the
* <tt>resolve</tt> flag is true, this method will then invoke the {@link
* #resolveClass(Class)} method on the resulting <tt>Class</tt> object.
*
* <p> Subclasses of <tt>ClassLoader</tt> are encouraged to override {@link
* #findClass(String)}, rather than this method. </p>
*
* <p> Unless overridden, this method synchronizes on the result of
* {@link #getClassLoadingLock <tt>getClassLoadingLock</tt>} method
* during the entire class loading process.
*
* @param name
* The <a href="#name">binary name</a> of the class
*
* @param resolve
* If <tt>true</tt> then resolve the class
*
* @return The resulting <tt>Class</tt> object
*
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* If the class could not be found
*/
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
ķĆ╗ĶŠæÕŠłµĖģµÖ░’╝īõ╝śÕģłń╗ÖĶć¬ÕĘ▒ńÜäparentÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īńē╣Õł½µ│©µäÅ’╝īĶ┐ÖķćīńÜäńłČÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©’╝īõĖŹµś»ń▒╗ńÜäń╗¦µē┐’╝īÕøĀõĖ║õĖēõĖ¬classloaderķāĮµś»ÕåģÕŁśÕ»╣Ķ▒Ī’╝īµēĆõ╗źõ╗¢õ╗¼ÕŬµś»ķĆ╗ĶŠæõĖŖńÜäńłČÕŁÉÕģ│ń│╗ŃĆé
’╝ł1’╝ēbootstrap classloaderµś»nativeÕ«×ńÄ░ńÜä
’╝ł2’╝ēextclassloader ÕÆī APPclassloader ķāĮµś» URLclassloader ńÜäÕŁÉń▒╗Õ»╣Ķ▒Ī
ÕģČÕ«×µłæµā│ÕüÜńÜäõ║ŗµāģÕŠłń«ĆÕŹĢ’╝īÕ░▒µś»Õ░ØĶ»ĢĶć¬ÕĘ▒ÕåÖõĖĆõĖ¬Õ«īÕģ©õĖŹõŠØķØĀÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤ŠńÜäclassloader’╝īõĮåµś»ÕøĀõĖ║ń╝¢ńĀüķćŵ»öĶŠāÕż¦’╝īµēĆõ╗źµłæÕŬÕ░ØĶ»Ģń╗ĢĶ┐ćAPPclassloader’╝īĶ«®Ķć¬ÕĘ▒ńÜäÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ń╗¦µē┐’╝łÕåŹµ¼ĪĶ»┤µśÄµś»ķĆ╗ĶŠæõĖŖń╗¦µē┐’╝ēõ║Äextclassloader
õĖŖķØóńÜäõ╗ŻńĀüÕĘ▓ń╗ŵśŠńż║’╝īÕ”éµ×£parentÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©µ▓ĪÕŖ×µ│ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īÕ░▒µēŠÕŁÉclassloaderńÜäfindclassµ¢╣µ│Ģ’╝īõĮåµś»µłæµā│ńĀ┤ÕØÅĶ┐ÖõĖ¬µ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īÕ░▒Õ┐ģķĪ╗ķćŹÕåÖclassloaderńÜäloadclassµ¢╣µ│Ģ
õĖŖõ╗ŻńĀü’╝Ü
package classloader;
import java.io.*;
/**
* Created by hupo.wh on 2016/7/18.
*/
public class OverwriteClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private String rootDir = "d:\\";
public Class<?> loadClass(String name)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findClass(name);
return c;
}
}
private byte[] getClassData(String className) {
//String path = classNameToPath(className);
String path = "D:\\xiaohua\\WhTest\\target\\classes\\helloworld\\HelloWorld.class";
try {
InputStream ins = new FileInputStream(path);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int bufferSize = 4096;
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferSize];
int bytesNumRead = 0;
while ((bytesNumRead = ins.read(buffer)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, bytesNumRead);
}
return baos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
byte[] classData = getClassData(name);
if (classData == null) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}
else {
System.out.println("name == "+name);
return defineClass(name, classData, 0, classData.length);
}
}
private String classNameToPath(String className) {
return rootDir + File.separatorChar
+ className.replace('.', File.separatorChar) + ".class";
}
public OverwriteClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(classLoader);
}
protected final Class<?> whdefineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len)
throws ClassFormatError
{
return defineClass("helloworld.HelloWorld", b, off, len, null);
}
}
/////Main.java
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
ClassLoader extcl =new Object(){}.getClass().getEnclosingClass().getClassLoader();
while(extcl.getParent()!=null){
extcl=extcl.getParent();
}
System.out.println("extcl == "+extcl);
System.out.println("overwriteclassloader == "+OverwriteClassLoader.class.getClassLoader());
OverwriteClassLoader cl = new OverwriteClassLoader(extcl);
Class<?> clazz = cl.loadClass("helloworld.HelloWorld");
System.out.println(clazz.getClassLoader());
}
}
ńäČĶĆīµłæńÜäń©ŗÕ║ŵŁóµŁźõ║ÄõĖĆõĖ¬Õ£░µ¢╣’╝Ü
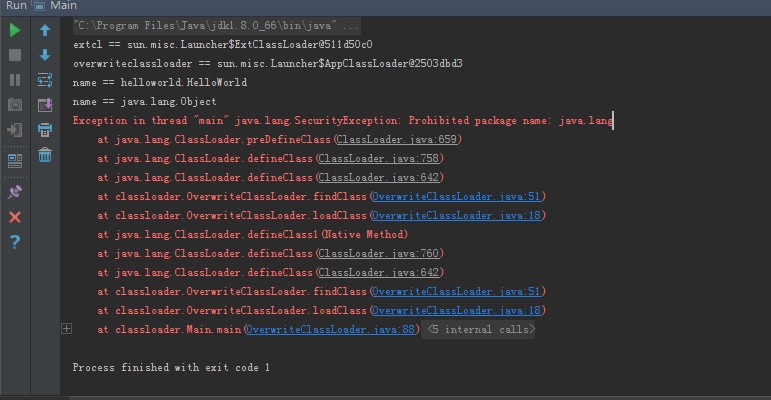
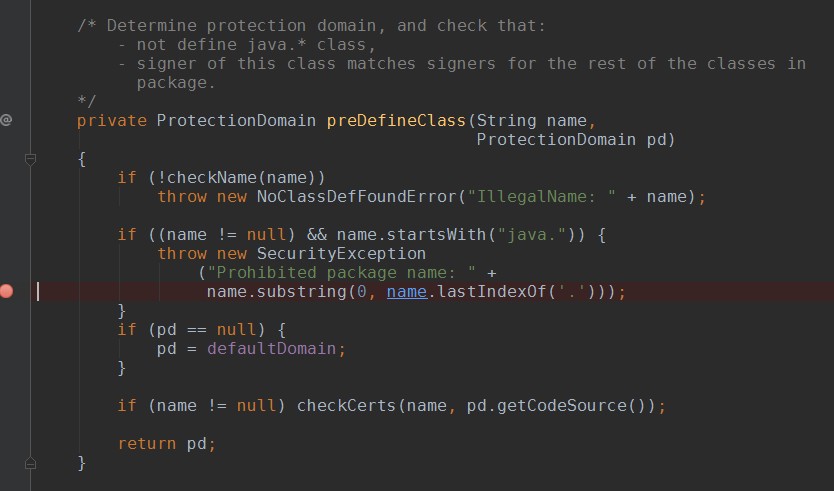
Ķ»”ń╗åĶʤµ¢Łńé╣Ķ┐øÕÄ╗’╝īÕÅæńÄ░Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬Õ£░µ¢╣µ£¼µØźµłæĶ”üÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īhelloworld.HelloWorldń▒╗’╝īõĮåµś»ÕŖĀĶĮĮjava.lang.Objectń▒╗ńÜ䵌ČÕĆÖ’╝īõĖĆõĖ¬nativeµ¢╣µ│ĢÕÅłĶ░āÕø×õ║åµłæńÜäclassloader’╝īĶ┐øÕģźń¼¼õĖēķā©ÕłåńÜäń¼¼1Õ░Åķā©ÕłåŃĆé
SecurityException: Prohibited package name: java.lang
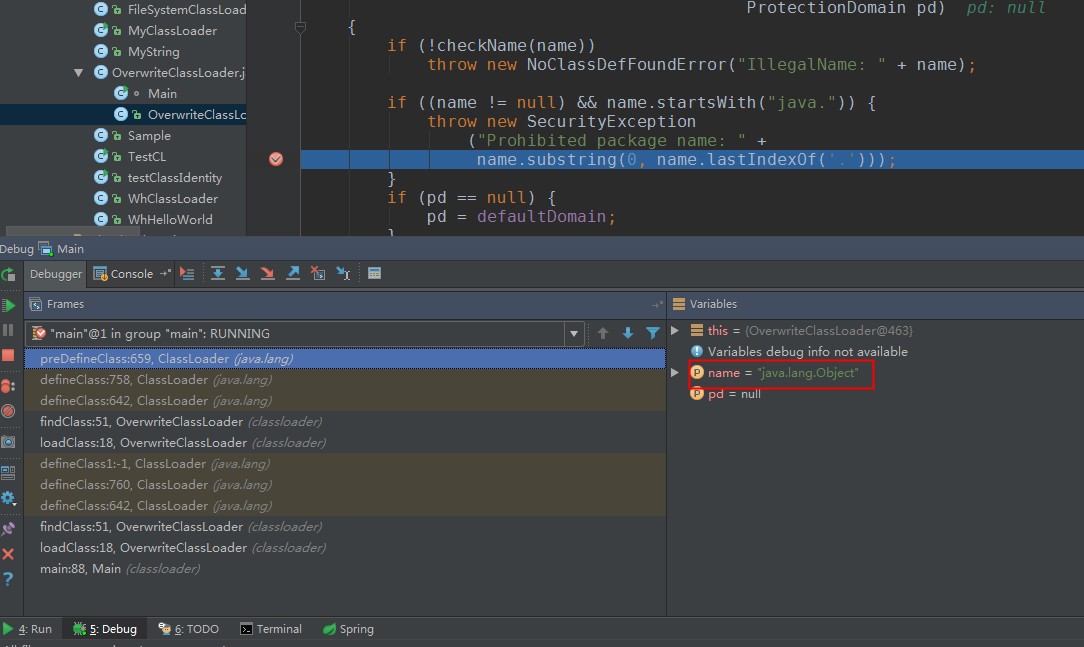
Ķ┐ÖÕÅłĶ»┤µśÄõ║åõĖĆõĖ¬ķŚ«ķóś’╝īclassloaderÕÄ╗loadĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗ńÜäńłČń▒╗’╝īõ╣¤µś»µēŠµłæĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗’╝īõĮåµś»µłæĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗ńÜäloadclassµ▓Īµ£ēÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Š’╝īÕÉīµŚČÕ«ēÕģ©µŻĆµ¤źÕÅłµś»ńö©ńÜäclassloaderĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕåģńĮ«ńÜä’╝īµēĆõ╗źķĆÜõĖŹĶ┐ćŃĆé
ÕÉÄµØźÕÅæńÄ░Ķ┐Öµ«Ąõ╗ŻńĀüÕ«×ķÖģõĖŖµś»µ£ēķŚ«ķóśńÜä’╝īÕøĀõĖ║µłæµŖŖInputStreamÕåÖµŁ╗õ║å’╝īõĖŗķØóõ╗ŻńĀüµēŹµś»µŁŻńĪ«ńÜä
ÕģČÕ«×Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬µŚČÕĆÖ’╝īµłæĶć¬ÕĘ▒ÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜäń▒╗ÕĘ▓ń╗Åń╗ĢĶ┐ćÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šõ║å’╝īÕøĀõĖ║Ķć¬ÕĘ▒Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗µś»µ▓Īµ£ēÕÄ╗µ¤źńłČõ║▓ńÜä’╝īõ║ĵś»µ£ēõ║åõĖŗķØóĶ┐ÖõĖ¬µø┤µ×üń½»ńÜ䵥ŗĶ»Ģ~~
package classloader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Created by hupo.wh on 2016/7/20.
*/
public class ClassLoaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassLoader myLoader = new ClassLoader() {
@Override
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) {
try {
InputStream is = null;
if(name == "helloworld.HelloWorld") {
is = new FileInputStream("D:\\xiaohua\\WhTest\\target\\classes\\helloworld\\HelloWorld.class");
}
else {
is = new FileInputStream("D:\\lang\\Object.class");
//return super.loadClass(name);
}
byte [] b = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(b);
return defineClass(name,b,0,b.length);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
};
Class<?> clazz = myLoader.loadClass("helloworld.HelloWorld");
System.out.println(clazz.getClassLoader());
}
}
µłæÕ░årt.jarõĖŁńÜäjava.langĶ¦ŻÕÄŗÕ£©dńøśõ║å’╝īÕĮōńäČĶ┐śµś»õ╝ܵŖźķéŻõĖ¬ķöÖĶ»»ŃĆéŃĆéŃĆé
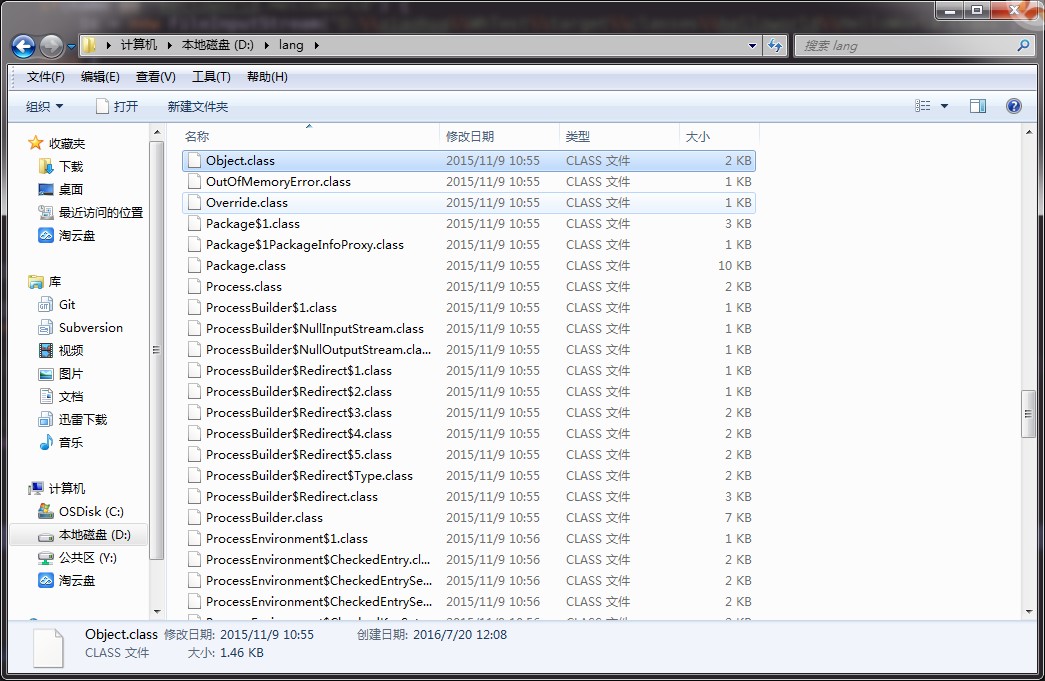
õ║ĵś»Ķ┐ÖµĀĘõ╣¤õ╝ܵŖźķöÖ’╝Ü
package java.lang;
/**
* Created by hupo.wh on 2016/7/20.
*/
public class sayHello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
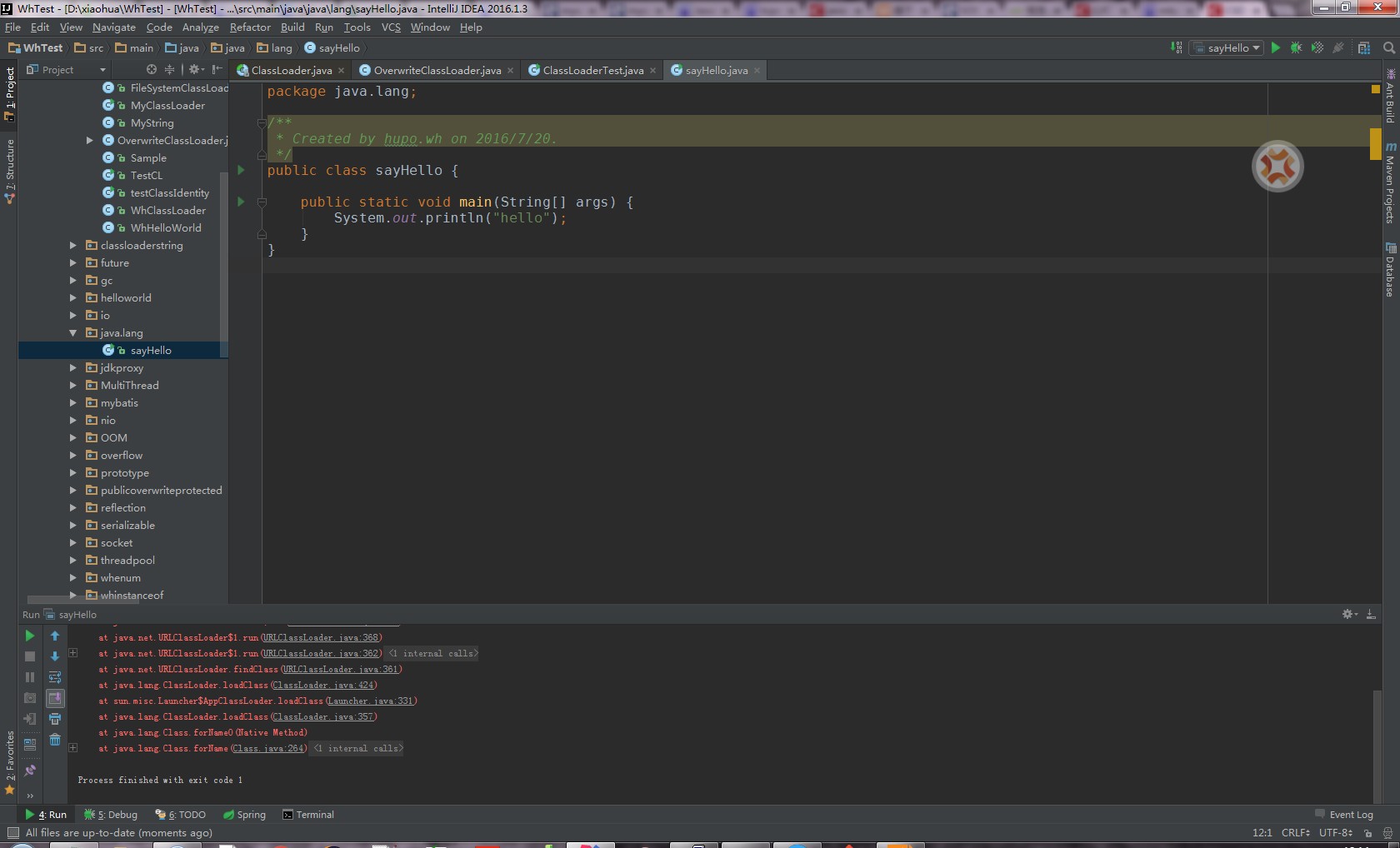
ÕĮōńäČõ╣¤µś»µ£ēµ¢╣µ│ĢńÜä’╝īÕ░▒µś»Õ«īÕģ©Ķć¬ÕĘ▒Õ«×ńÄ░classloaderĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗’╝īõĖŹń╗¦µē┐õ║Äõ╗╗õĮĢõĖ£Ķź┐’╝īĶ┐ÖµĀĘńÜäĶ»Ø’╝ījvmõ╣¤µŗ┐õĮĀµ▓ĪÕŖ×µ│Ģõ║åŃĆé
ķÖäõĖŖµĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║µŁŻńĪ«Ķ┐ÉĶĪīµ║ÉńĀü’╝łp228’╝ē
package classloader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Created by hupo.wh on 2016/7/20.
*/
public class ClassLoaderTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassLoader myLoader = new ClassLoader() {
@Override
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) {
try {
String fileName = name.substring(name.lastIndexOf(".")+1)+".class";
InputStream is = getClass().getResourceAsStream(fileName);
if (is == null) {
return super.loadClass(name);
}
byte [] b = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(b);
return defineClass(name,b,0,b.length);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
};
Class<?> clazz = myLoader.loadClass("helloworld.HelloWorld");
System.out.println(clazz.getClassLoader());
Class<?> clazz1 = myLoader.loadClass("org.omg.CORBA.Any");
System.out.println(clazz1.getClassLoader());
}
}
ÕÅéĶĆāĶĄäµ¢Ö
[1] µĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║
ŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆö
ńēłµØāÕŻ░µśÄ’╝ܵ£¼µ¢ćõĖ║CSDNÕŹÜõĖ╗ŃĆīThis is billŃĆŹńÜäÕÄ¤Õłøµ¢ćń½Ā’╝īķüĄÕŠ¬CC 4.0 BY-SAńēłµØāÕŹÅĶ««’╝īĶĮ¼ĶĮĮĶ»ĘķÖäõĖŖÕĤµ¢ćÕć║ÕżäķōŠµÄźÕÅŖµ£¼ÕŻ░µśÄŃĆé
ÕĤµ¢ćķōŠµÄź’╝Ühttps://blog.csdn.net/Scythe666/article/details/51956047
ńøĖõ┐ĪÕ”éµ×£ķŚ«’╝ÜõĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Š’╝īÕÅ»ĶāĮµ£ēõ║║ÕÅ»õ╗źõŠāõŠāĶĆīĶ░ł’╝īõĮåµś»Ķ»┤Õł░õĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üĶ┐Öõ╣łÕłåÕ▒é’╝īõĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üÕłåõĖēÕ▒é’╝īÕ”éõĮĢń╗ĢĶ┐ćÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗŃĆéŃĆéŃĆé
Ķ┐ÖÕ░▒õĖŹµś»ķéŻõ╣łÕ«╣µśōõ║å’╝īĶ┐ÖõĖ¬µŚČÕĆÖÕ░▒ķ£ĆĶ”üõĖĆõ║øõĖōńĀöõ║åŃĆé
õ║īŃĆüclassloaderńÜäõĮ£ńö©
Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬ķŚ«ķ󜵳æķŚ«õ║åÕĖłÕģä’╝ÜÕŖĀĶĮĮ+Ķ┐׵ğńÜäµēƵ£ēĶ┐ćń©ŗ’╝īõĮåµś»µĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║Ķ»┤ńÜäõĖŹÕż¬õĖƵĀĘ’╝łµēĆõ╗źµ£ēÕŠģĶĆāĶ»ü’╝ē

Ķ»ĘÕĤĶ░ģµłæĶ┤┤ÕøŠ’╝īõĮåõĖŗķØóõĖżÕ╝ĀÕøŠÕŁŚÕŁŚńÅĀńÄæ’╝łp228’╝ē’╝Ü


classloaderĶÖĮńäČÕŬńö©õ║ÄÕ«×ńÄ░ń▒╗ńÜäÕŖĀĶĮĮÕŖ©õĮ£’╝īõĮåÕ£©Javań©ŗÕ║ÅõĖŁõĮ£ńö©ÕŹ┤Ķ┐£Ķ┐£õĖŹķÖÉõ║Äń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮķśČµ«Ą’╝īõ╣¤Õ░▒µś»ÕÉÄķØóĶ»┤ńÜäÕÅ»õ╗źÕå│Õ«Üń▒╗ŃĆé
õĖēŃĆüõĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”ü3õĖ¬classloader
µłæõĖ¬õ║║Ķ«żõĖ║µ£ēõĖżõĖ¬ÕĤÕøĀ’╝īÕĮōńäČÕÅ»ĶāĮõĖŹµŁóŃĆé
1ŃĆüµś»õĖ║õ║åÕ«ēÕģ©
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/28011224/what-is-the-reason-for-having-3-class-loaders-in-java
The reason for having the three basic class loaders (Bootstrap, extension, system) is mostly security.
A key concept is the fact that the JVM will not grant package access (the access that methods and fields have if you didnŌĆÖt specifically mention private, public or protected) unless the class that asks for this access comes from the same class loader that loaded the class it wishes to access.
So, suppose a user calls his class java.lang.MyClass. Theoretically, it could get package access to all the fields and methods in the java.lang package and change the way they work. The language itself doesnŌĆÖt prevent this. But the JVM will block this, because all the real java.lang classes were loaded by bootstrap class loader. Not the same loader = no access.
There are other security features built into the class loaders that make it hard to do certain types of hacking.
So why three class loaders? Because they represent three levels of trust. The classes that are most trusted are the core API classes. Next are installed extensions, and then classes that appear in the classpath, which means they are local to your machine.
For a more extended explanation, refer to Bill VennersŌĆÖs ŌĆ£Inside the Java Virtual MachineŌĆØ.
2ŃĆüÕÅ”Õż¢’╝īĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ÕĖ¢ÕŁÉµ▓Īµ£ēµÅÉÕł░ńÜäÕ║öĶ»źµś»ķÜöń”╗ŃĆé
javańÜäµēƵ£ēń▒╗ķāĮµś»ńö▒classloaderÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜä’╝īõĖŹÕÉīclassloaderõ╣ŗķŚ┤ÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜäń▒╗ÕĮ╝µŁżµś»õĖŹÕÅ»Ķ¦üńÜäŃĆétomcatÕŖĀĶĮĮõ║ålog4j’╝īÕ«╣ÕÖ©ķćīservletõ╣¤ÕŖĀĶĮĮõ║ålog4j’╝īservletµś»ń£ŗõĖŹĶ¦ütomcatÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜälog4jń▒╗ńÜä’╝īÕÅŹõ╣ŗõ║”ńäČŃĆé
Õ£©µĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║’╝īp278’╝īµÅÉÕł░’╝Ü
tomcatõĖ║õ║åµö»µīüµØāķÖÉńø«ÕĮĢń╗ōµ×ä’╝īÕ»╣ńø«ÕĮĢõĖŁńÜäń▒╗Õ║ōĶ┐øĶĪīÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÆīķÜöń”╗’╝ītomcatĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēõ║åÕżÜõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ŃĆé
õ╣¤Ķ»┤µśÄõ║åĶ┐Öńé╣ŃĆé
ÕøøŃĆüÕ░ØĶ»Ģń╗ĢĶ┐ćÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Š
µĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║’╝īp231’╝īÕåÖÕł░:
ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗÕ£©jdk1.2Õ╝ĢÕģź’╝īõĮåÕ«āõĖŹµś»õĖĆõĖ¬Õ╝║ÕłČµĆ¦ńÜäń║”µØ¤µ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īĶĆīµś»JavaĶ«ŠĶ«ĪĶĆģµÄ©ĶŹÉń╗ÖÕ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģńÜäõĖĆń¦Źń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮµ¢╣Õ╝ÅŃĆé
µŹóÕÅźĶ»ØĶ»┤’╝īõ╣¤Õ░▒µś»ÕÅ»õ╗źõĖŹńö©Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬µ©ĪÕ×ŗńÜä’╝īĶć¬ÕĘ▒Õ«×ńÄ░ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕ░▒ÕÅ»õ╗ź’╝īµ»Ģń½¤ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ńÜäÕĤզŗõĮ£ńö©Õ░▒µś»’╝ÜŌĆ£ķĆÜĶ┐ćń▒╗ńÜäÕģ©ķÖÉÕ«ÜÕÉŹÕŠŚÕł░ń▒╗ńÜäõ║īĶ┐øÕłČńĀüµĄüŌĆØ
µØźń£ŗń£ŗÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗµś»Õ”éõĮĢÕ«×ńÄ░ńÜä’╝Ü
/**
* Loads the class with the specified <a href="#name">binary name</a>. The
* default implementation of this method searches for classes in the
* following order:
*
* <ol>
*
* <li><p> Invoke {@link #findLoadedClass(String)} to check if the class
* has already been loaded. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Invoke the {@link #loadClass(String) <tt>loadClass</tt>} method
* on the parent class loader. If the parent is <tt>null</tt> the class
* loader built-in to the virtual machine is used, instead. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Invoke the {@link #findClass(String)} method to find the
* class. </p></li>
*
* </ol>
*
* <p> If the class was found using the above steps, and the
* <tt>resolve</tt> flag is true, this method will then invoke the {@link
* #resolveClass(Class)} method on the resulting <tt>Class</tt> object.
*
* <p> Subclasses of <tt>ClassLoader</tt> are encouraged to override {@link
* #findClass(String)}, rather than this method. </p>
*
* <p> Unless overridden, this method synchronizes on the result of
* {@link #getClassLoadingLock <tt>getClassLoadingLock</tt>} method
* during the entire class loading process.
*
* @param name
* The <a href="#name">binary name</a> of the class
*
* @param resolve
* If <tt>true</tt> then resolve the class
*
* @return The resulting <tt>Class</tt> object
*
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* If the class could not be found
*/
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
ķĆ╗ĶŠæÕŠłµĖģµÖ░’╝īõ╝śÕģłń╗ÖĶć¬ÕĘ▒ńÜäparentÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īńē╣Õł½µ│©µäÅ’╝īĶ┐ÖķćīńÜäńłČÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©’╝īõĖŹµś»ń▒╗ńÜäń╗¦µē┐’╝īÕøĀõĖ║õĖēõĖ¬classloaderķāĮµś»ÕåģÕŁśÕ»╣Ķ▒Ī’╝īµēĆõ╗źõ╗¢õ╗¼ÕŬµś»ķĆ╗ĶŠæõĖŖńÜäńłČÕŁÉÕģ│ń│╗ŃĆé
’╝ł1’╝ēbootstrap classloaderµś»nativeÕ«×ńÄ░ńÜä
’╝ł2’╝ēextclassloader ÕÆī APPclassloader ķāĮµś» URLclassloader ńÜäÕŁÉń▒╗Õ»╣Ķ▒Ī
ÕģČÕ«×µłæµā│ÕüÜńÜäõ║ŗµāģÕŠłń«ĆÕŹĢ’╝īÕ░▒µś»Õ░ØĶ»ĢĶć¬ÕĘ▒ÕåÖõĖĆõĖ¬Õ«īÕģ©õĖŹõŠØķØĀÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤ŠńÜäclassloader’╝īõĮåµś»ÕøĀõĖ║ń╝¢ńĀüķćŵ»öĶŠāÕż¦’╝īµēĆõ╗źµłæÕŬÕ░ØĶ»Ģń╗ĢĶ┐ćAPPclassloader’╝īĶ«®Ķć¬ÕĘ▒ńÜäÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ń╗¦µē┐’╝łÕåŹµ¼ĪĶ»┤µśÄµś»ķĆ╗ĶŠæõĖŖń╗¦µē┐’╝ēõ║Äextclassloader
õĖŖķØóńÜäõ╗ŻńĀüÕĘ▓ń╗ŵśŠńż║’╝īÕ”éµ×£parentÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©µ▓ĪÕŖ×µ│ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īÕ░▒µēŠÕŁÉclassloaderńÜäfindclassµ¢╣µ│Ģ’╝īõĮåµś»µłæµā│ńĀ┤ÕØÅĶ┐ÖõĖ¬µ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īÕ░▒Õ┐ģķĪ╗ķćŹÕåÖclassloaderńÜäloadclassµ¢╣µ│Ģ

õĖŖõ╗ŻńĀü’╝Ü
package classloader;
import java.io.*;
/**
* Created by hupo.wh on 2016/7/18.
*/
public class OverwriteClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private String rootDir = "d:\\";
public Class<?> loadClass(String name)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findClass(name);
return c;
}
}
private byte[] getClassData(String className) {
//String path = classNameToPath(className);
String path = "D:\\xiaohua\\WhTest\\target\\classes\\helloworld\\HelloWorld.class";
try {
InputStream ins = new FileInputStream(path);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
int bufferSize = 4096;
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferSize];
int bytesNumRead = 0;
while ((bytesNumRead = ins.read(buffer)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer, 0, bytesNumRead);
}
return baos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
byte[] classData = getClassData(name);
if (classData == null) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException();
}
else {
System.out.println("name == "+name);
return defineClass(name, classData, 0, classData.length);
}
}
private String classNameToPath(String className) {
return rootDir + File.separatorChar
+ className.replace('.', File.separatorChar) + ".class";
}
public OverwriteClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(classLoader);
}
protected final Class<?> whdefineClass(String name, byte[] b, int off, int len)
throws ClassFormatError
{
return defineClass("helloworld.HelloWorld", b, off, len, null);
}
}
/////Main.java
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
ClassLoader extcl =new Object(){}.getClass().getEnclosingClass().getClassLoader();
while(extcl.getParent()!=null){
extcl=extcl.getParent();
}
System.out.println("extcl == "+extcl);
System.out.println("overwriteclassloader == "+OverwriteClassLoader.class.getClassLoader());
OverwriteClassLoader cl = new OverwriteClassLoader(extcl);
Class<?> clazz = cl.loadClass("helloworld.HelloWorld");
System.out.println(clazz.getClassLoader());
}
}
ńäČĶĆīµłæńÜäń©ŗÕ║ŵŁóµŁźõ║ÄõĖĆõĖ¬Õ£░µ¢╣’╝Ü


Ķ»”ń╗åĶʤµ¢Łńé╣Ķ┐øÕÄ╗’╝īÕÅæńÄ░Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬Õ£░µ¢╣µ£¼µØźµłæĶ”üÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īhelloworld.HelloWorldń▒╗’╝īõĮåµś»ÕŖĀĶĮĮjava.lang.Objectń▒╗ńÜ䵌ČÕĆÖ’╝īõĖĆõĖ¬nativeµ¢╣µ│ĢÕÅłĶ░āÕø×õ║åµłæńÜäclassloader’╝īĶ┐øÕģźń¼¼õĖēķā©ÕłåńÜäń¼¼1Õ░Åķā©ÕłåŃĆé
SecurityException: Prohibited package name: java.lang

Ķ┐ÖÕÅłĶ»┤µśÄõ║åõĖĆõĖ¬ķŚ«ķóś’╝īclassloaderÕÄ╗loadĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗ńÜäńłČń▒╗’╝īõ╣¤µś»µēŠµłæĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗’╝īõĮåµś»µłæĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗ńÜäloadclassµ▓Īµ£ēÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Š’╝īÕÉīµŚČÕ«ēÕģ©µŻĆµ¤źÕÅłµś»ńö©ńÜäclassloaderĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕåģńĮ«ńÜä’╝īµēĆõ╗źķĆÜõĖŹĶ┐ćŃĆé
ÕÉÄµØźÕÅæńÄ░Ķ┐Öµ«Ąõ╗ŻńĀüÕ«×ķÖģõĖŖµś»µ£ēķŚ«ķóśńÜä’╝īÕøĀõĖ║µłæµŖŖInputStreamÕåÖµŁ╗õ║å’╝īõĖŗķØóõ╗ŻńĀüµēŹµś»µŁŻńĪ«ńÜä
ÕģČÕ«×Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬µŚČÕĆÖ’╝īµłæĶć¬ÕĘ▒ÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜäń▒╗ÕĘ▓ń╗Åń╗ĢĶ┐ćÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šõ║å’╝īÕøĀõĖ║Ķć¬ÕĘ▒Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗µś»µ▓Īµ£ēÕÄ╗µ¤źńłČõ║▓ńÜä’╝īõ║ĵś»µ£ēõ║åõĖŗķØóĶ┐ÖõĖ¬µø┤µ×üń½»ńÜ䵥ŗĶ»Ģ~~
package classloader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Created by hupo.wh on 2016/7/20.
*/
public class ClassLoaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassLoader myLoader = new ClassLoader() {
@Override
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) {
try {
InputStream is = null;
if(name == "helloworld.HelloWorld") {
is = new FileInputStream("D:\\xiaohua\\WhTest\\target\\classes\\helloworld\\HelloWorld.class");
}
else {
is = new FileInputStream("D:\\lang\\Object.class");
//return super.loadClass(name);
}
byte [] b = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(b);
return defineClass(name,b,0,b.length);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
};
Class<?> clazz = myLoader.loadClass("helloworld.HelloWorld");
System.out.println(clazz.getClassLoader());
}
}
µłæÕ░årt.jarõĖŁńÜäjava.langĶ¦ŻÕÄŗÕ£©dńøśõ║å’╝īÕĮōńäČĶ┐śµś»õ╝ܵŖźķéŻõĖ¬ķöÖĶ»»ŃĆéŃĆéŃĆé

õ║ĵś»Ķ┐ÖµĀĘõ╣¤õ╝ܵŖźķöÖ’╝Ü
package java.lang;
/**
* Created by hupo.wh on 2016/7/20.
*/
public class sayHello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello");
}
}

ÕĮōńäČõ╣¤µś»µ£ēµ¢╣µ│ĢńÜä’╝īÕ░▒µś»Õ«īÕģ©Ķć¬ÕĘ▒Õ«×ńÄ░classloaderĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗’╝īõĖŹń╗¦µē┐õ║Äõ╗╗õĮĢõĖ£Ķź┐’╝īĶ┐ÖµĀĘńÜäĶ»Ø’╝ījvmõ╣¤µŗ┐õĮĀµ▓ĪÕŖ×µ│Ģõ║åŃĆé
ķÖäõĖŖµĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║µŁŻńĪ«Ķ┐ÉĶĪīµ║ÉńĀü’╝łp228’╝ē
package classloader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Created by hupo.wh on 2016/7/20.
*/
public class ClassLoaderTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassLoader myLoader = new ClassLoader() {
@Override
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) {
try {
String fileName = name.substring(name.lastIndexOf(".")+1)+".class";
InputStream is = getClass().getResourceAsStream(fileName);
if (is == null) {
return super.loadClass(name);
}
byte [] b = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(b);
return defineClass(name,b,0,b.length);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
};
Class<?> clazz = myLoader.loadClass("helloworld.HelloWorld");
System.out.println(clazz.getClassLoader());
Class<?> clazz1 = myLoader.loadClass("org.omg.CORBA.Any");
System.out.println(clazz1.getClassLoader());
}
}
ÕÅéĶĆāĶĄäµ¢Ö
[1] µĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻJavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║
ŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆöŌĆö
ńēłµØāÕŻ░µśÄ’╝ܵ£¼µ¢ćõĖ║CSDNÕŹÜõĖ╗ŃĆīThis is billŃĆŹńÜäÕÄ¤Õłøµ¢ćń½Ā’╝īķüĄÕŠ¬CC 4.0 BY-SAńēłµØāÕŹÅĶ««’╝īĶĮ¼ĶĮĮĶ»ĘķÖäõĖŖÕĤµ¢ćÕć║ÕżäķōŠµÄźÕÅŖµ£¼ÕŻ░µśÄŃĆé
ÕĤµ¢ćķōŠµÄź’╝Ühttps://blog.csdn.net/Scythe666/article/details/51956047
- 2020-07-20 19:55
- µĄÅĶ¦ł 250
- Ķ»äĶ«║(0)
- Õłåń▒╗:ń╝¢ń©ŗĶ»ŁĶ©Ć
- µ¤źń£ŗµø┤ÕżÜ
ÕÅæĶĪ©Ķ»äĶ«║
-
õĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©
2020-07-22 10:46 829ķÖżõ║åńö▒ Java µĀĖÕ┐āń▒╗Õ║ōµÅÉõŠøńÜäń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©Õż¢’╝īµłæõ╗¼Ķ┐śÕÅ»õ╗źÕŖĀÕģźĶć¬Õ«Ü ... -
JVMń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮµ£║ÕłČ-ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Š
2020-07-21 17:42 489µ”éÕ┐Ą ĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║µŖŖµÅÅĶ┐░ń▒╗ń ... -
JavaõĖŁńÜäÕĖĖķćŵ▒Āõ╣ŗClassÕĖĖķćŵ▒Ā
2020-07-21 17:22 531Õ£©JavaõĖŁ’╝īÕĖĖķćŵ▒ĀńÜäµ”éÕ┐Ąµā│Õ┐ģÕŠłÕżÜõ║║ķāĮÕɼĶ»┤Ķ┐ćŃĆéĶ┐Öõ╣¤µś»ķØóĶ»ĢõĖŁµ»öĶŠā ... -
õĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üµ£ēÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ
2020-07-20 19:55 834µØźķś┐ķćīńÄ®Javaõ╣¤µ£ēõĖĆõĖ¬ÕżÜµ£łõ║å’╝īõĖĆńø┤Õ»╣JavaĶÖܵŗ¤µ£║µ»öĶŠāµä¤Õģ┤ĶČŻ ... -
ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗń¤źĶ»åńé╣
2020-07-20 18:56 1151õĖĆŃĆé JVMĶ«ŠĶ«ĪĶĆģµŖŖń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮķśČµ«ĄõĖŁńÜäŌĆ£ķĆÜĶ┐ć'ń▒╗Õģ©ÕÉŹ'µØźĶÄĘÕÅ¢Õ«Üõ╣ēµŁż ... -
JVMń¤źĶ»å
2020-07-15 22:35 252https://www.cnblogs.com/doyi111 ... -
[JVM]JIT,JVMÕŹ│µŚČń╝¢Ķ»æµŖƵ£»
2020-07-15 21:18 273ńēłµØāÕŻ░µśÄ’╝ܵ£¼µ¢ćõĖ║CSDNÕŹ ...





ńøĖÕģ│µÄ©ĶŹÉ
ķ”¢Õģł’╝īµłæõ╗¼Ķ”üµśÄńÖĮõ╗Ćõ╣łµś»ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗŃĆéÕ£©JavaõĖŁ’╝īµ»ÅõĖ¬ń▒╗ķāĮńö▒õĖĆõĖ¬ńē╣Õ«ÜńÜäń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©µØźĶ┤¤Ķ┤ŻÕŖĀĶĮĮŃĆéÕĮōõĖĆõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©µöČÕł░ÕŖĀĶĮĮń▒╗ńÜäĶ»Ęµ▒鵌Ȓ╝īÕ«āõĖŹõ╝Üń½ŗÕŹ│ÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īĶĆīµś»µŖŖĶ┐ÖõĖ¬õ╗╗ÕŖĪÕ¦öµēśń╗ÖÕ«āńÜäńłČń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ÕÄ╗Õ«īµłÉ’╝īńø┤Õł░Õł░ĶŠŠķĪČÕ▒éńÜäÕÉ»ÕŖ©ń▒╗...
õĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üńĀ┤ÕØÅÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗÕæó’╝¤ÕģČÕ«×Õ£©µ¤Éõ║øµāģÕåĄõĖŗ’╝īµłæõ╗¼ÕÅ»ĶāĮķ£ĆĶ”üńĀ┤ÕØÅÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īõ╗źµ╗ĪĶČ│ńē╣µ«ŖńÜäõĖÜÕŖĪķ£Ćµ▒éŃĆéõĮåµś»’╝īĶ┐Öń¦ŹÕüܵ│Ģķ£ĆĶ”üķØ×ÕĖĖÕ░ÅÕ┐ā’╝īÕøĀõĖ║ńĀ┤ÕØÅÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗÕÅ»ĶāĮõ╝ÜÕ»╝Ķć┤ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮĶ┐ćń©ŗõĖŁńÜäķŚ«ķóśŃĆé ń¤źĶ»åńé╣õ║ö’╝ÜClassLoader...
JavańÜäń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮµ£║ÕłČķüĄÕŠ¬ŌĆ£ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗŌĆØ’╝īĶ┐ÖµäÅÕæ│ńØĆÕĮōõĖĆõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ķ£ĆĶ”üÕŖĀĶĮĮń▒╗µŚČ’╝īÕ«āķ”¢Õģłõ╝ÜÕ¦öµēśÕģČńłČń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©Õ░ØĶ»ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īÕŬµ£ēÕĮōńłČń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©µŚĀµ│ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮµŚČ’╝īµēŹõ╝ÜĶć¬ÕĘ▒Õ░ØĶ»ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮŃĆé Õ£©JavańÜäClassLoaderÕ▒éµ¼Īń╗ōµ×äõĖŁ’╝īõĖ╗Ķ”üµ£ēõ╗źõĖŗÕćĀ...
µÄźńØĆ’╝īµ¢ćµĪŻĶ»óķŚ«õĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üĶ»╗µ║ÉńĀüõ╗źÕÅŖĶ»╗µ║ÉńĀüńÜäµöČĶÄĘŃĆéńÉåµā│Õ£░’╝īÕ║öĶüśĶĆģÕ║öĶ»źĶāĮÕż¤ĶĪ©ĶŠŠÕć║ķśģĶ»╗µ║ÉńĀüõĖŹõ╗ģõ╗ģµś»õĖ║õ║åÕ║öõ╗śķØóĶ»Ģ’╝īĶĆīµś»õĖ║õ║åµÅÉķ½śń╝¢ńĀüĶāĮÕŖøŃĆüńÉåĶ¦ŻķØóÕÉæÕ»╣Ķ▒ĪµĆصā│ŃĆüĶ«ŠĶ«Īµ©ĪÕ╝Åõ╗źÕÅŖĶ¦ŻÕå│Õ«×ķÖģÕ╝ĆÕÅæõĖŁķüćÕł░ńÜäķŚ«ķóśŃĆéÕÉīµŚČ’╝īķśģĶ»╗µ║ÉńĀüõ╣¤µś»...
5. ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©’╝ÜõĖŹµü░ÕĮōńÜäń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÅ»ĶāĮÕ»╝Ķć┤ń▒╗Õå▓ń¬ü’╝īńÉåĶ¦ŻÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗµ£ēÕŖ®õ║Äķü┐ÕģŹĶ┐Öń▒╗ķŚ«ķóśŃĆé õ║īŃĆüJavaÕ«óµłĘń½»ķÖĘķś▒ 1. GUIĶ«ŠĶ«Ī’╝ÜSwingÕÆīJavaFXńŁēÕ║ōńö©õ║ĵ×äÕ╗║ńö©µłĘńĢīķØó’╝īõĮåķ£ĆĶ”üµ│©µäÅń║┐ń©ŗÕ«ēÕģ©’╝īķü┐ÕģŹÕ£©õ║ŗõ╗ČÕżäńÉåń║┐ń©ŗõĖŁµē¦ĶĪīĶĆŚµŚČµōŹõĮ£...
Õ£©JavaõĖŁ’╝īń▒╗ńÜäÕŖĀĶĮĮķĆÜÕĖĖķüĄÕŠ¬ŌĆ£ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗŌĆØŃĆéĶ┐ÖõĖ¬µ©ĪÕ×ŗńÜäÕĘźõĮ£ÕĤńÉåµś»’╝ÜÕĮōõĖĆõĖ¬ClassLoaderµÄźµöČÕł░ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮĶ»Ęµ▒鵌Ȓ╝īÕ«āķ”¢ÕģłõĖŹõ╝ÜĶć¬ÕĘ▒ÕÄ╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īĶĆīµś»Õ¦öµēśń╗ÖńłČClassLoaderÕÄ╗Õ░ØĶ»ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īÕŬµ£ēÕĮōńłČClassLoaderµŚĀµ│ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮµŚČ’╝īÕŁÉ...
ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗµś»ÕģČÕģĖÕ×ŗńē╣ÕŠü’╝īńĪ«õ┐Øń▒╗ńÜäÕö»õĖƵƦŃĆé 4. **ÕŁŚĶŖéńĀüµē¦ĶĪī**’╝ÜJVMķĆÜĶ┐ćĶ¦ŻķćŖÕÖ©Õ░åÕŁŚĶŖéńĀüĶĮ¼µŹóõĖ║µ£║ÕÖ©ńĀüµē¦ĶĪī’╝īJava 6õ╣ŗÕÉÄÕ╝ĢÕģźõ║åÕŹ│µŚČń╝¢Ķ»æ’╝łJIT’╝ē’╝īÕ░åńāŁńé╣õ╗ŻńĀüń╝¢Ķ»æõĖ║µ£¼Õ£░µ£║ÕÖ©õ╗ŻńĀü’╝īµÅÉÕŹćµĆ¦ĶāĮŃĆé 5. **Õ×āÕ£ŠµöČķøå**’╝ÜJVM...
ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜäÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗµś»µīćń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©õ╣ŗķŚ┤ńÜäÕ¦öµ┤ŠÕģ│ń│╗’╝īÕŹ│µ»ÅõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ķāĮµ£ēõĖĆõĖ¬ńłČÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©’╝īBootstrap Loaderµś»µēƵ£ēń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ńÜäńłČÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ŃĆéÕĮōµłæõ╗¼µā│Ķ”üÕŖĀĶĮĮõĖĆõĖ¬ń▒╗µŚČ’╝īJVMõ╝Üķ”¢ÕģłµŻĆµ¤źĶ»źń▒╗µś»ÕÉ”ÕĘ▓ń╗ÅĶó½ÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īÕ”éµ×£µ▓Īµ£ēÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īÕłÖõ╝Ü...
JavańÜäń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮµ£║ÕłČķüĄÕŠ¬ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īÕŹ│õĖĆõĖ¬ń▒╗ķ”¢Õģłõ╝ÜÕ░ØĶ»Ģńö▒ÕģČńłČń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īÕŬµ£ēÕĮōńłČń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©µŚĀµ│ĢÕ«īµłÉÕŖĀĶĮĮµŚČ’╝īµēŹõ╝Üńö▒ÕĮōÕēŹń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©Ķ┐øĶĪīÕŖĀĶĮĮŃĆéĶ┐Öń¦Źµ£║ÕłČõ┐ØĶ»üõ║åń│╗ń╗¤ń▒╗’╝łÕ”éjava.lang.String’╝ēńÜäõĖĆĶć┤µĆ¦ÕÆīÕ«ēÕģ©µĆ¦ŃĆé ...
ÕÉīµŚČ’╝īõ║åĶ¦ŻÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗõ╣¤µ£ēÕŖ®õ║ÄÕ«×ńÄ░Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēńÜäń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ŃĆé 4. **Õó×Õ╝║ń╝¢ń©ŗµŖĆĶāĮ** - **ÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗµ£║ÕłČ**’╝ÜJVMµÅÉõŠøõ║åõĖ░Õ»īńÜäÕ╣ČÕÅæµÄ¦ÕłČµ£║ÕłČ’╝īÕ”éń║┐ń©ŗÕÉīµŁźŃĆüķöüµ£║ÕłČńŁēŃĆéµĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻĶ┐Öõ║øµ£║ÕłČÕÅ»õ╗źÕĖ«ÕŖ®Õ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģń╝¢ÕåÖµø┤ÕüźÕŻ«ńÜäÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗń©ŗÕ║ÅŃĆé ...
õ╣”õĖŁµĘ▒ÕģźĶ«©Ķ«║õ║åĶ┐Öõ║øµŁźķ¬ż’╝īÕīģµŗ¼ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗŃĆüń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēńŁēķ½śń║¦Ķ»ØķóśŃĆé 4. **ÕåģÕŁśń«ĪńÉå**’╝ÜJVMńÜäÕåģÕŁśÕī║Õ¤¤’╝īÕ”éÕĀåŃĆüµĀłŃĆüµ¢╣µ│ĢÕī║ŃĆüµ£¼Õ£░µ¢╣µ│ĢµĀłńŁē’╝īµś»µĆ¦ĶāĮõ╝śÕī¢ńÜäÕģ│ķö«ŃĆéõ╣”õĖŁĶ»”ń╗åķśÉĶ┐░õ║åÕ×āÕ£ŠµöČķøåń«Śµ│Ģ’╝łÕ”éÕłåõ╗ŻµöČķøåŃĆüµĀćĶ«░-...
ńŗ¼ÕŁżõ╣ØÕēæ-------ķØóĶ»Ģķóś õ╗źõĖŗµś»õ╗Äń╗ÖÕ«ÜńÜäµ¢ćõ╗ČõĖŁńö¤µłÉńÜäńøĖÕģ│ń¤źĶ»åńé╣’╝Ü Spring * Spring õ╝śńé╣’╝ÜÕ╝Ƶ║ÉŃĆüÕģŹĶ┤╣ŃĆüĶĮ╗ķćÅń║¦ŃĆüķØ×ÕģźõŠĄÕ╝ÅŃĆüµö»µīüõ║ŗÕŖĪÕżäńÉåŃĆüµö»µīüÕ»╣...* õ╗Ćõ╣łÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝¤’╝Ü + õĖĆõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮµ£║ÕłČ + µö»µīüÕżÜń¦Źń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮńŁ¢ńĢź
8. **ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮµ£║ÕłČ**’╝ÜÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗµś»JVMÕŖĀĶĮĮń▒╗ńÜäķ╗śĶ«żµ£║ÕłČ’╝īÕ«āõ┐ØĶ»üõ║åń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜäÕö»õĖƵƦ’╝īķü┐ÕģŹõ║åń▒╗ńÜäķćŹÕżŹÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÆīÕå▓ń¬üŃĆé 9. **ÕÅŹÕ░ä**’╝ÜJavaÕÅŹÕ░äAPIÕģüĶ«Ėń©ŗÕ║ÅÕ£©Ķ┐ÉĶĪīµŚČÕŖ©µĆüĶ«┐ķŚ«ń▒╗ńÜäõ┐Īµü»’╝īÕłøÕ╗║ÕÆīµōŹõĮ£ń▒╗ńÜäÕ»╣Ķ▒Ī’╝īÕó×Õ╝║õ║åń©ŗÕ║ÅńÜäńüĄµ┤╗...
ķ╗śĶ«żµāģÕåĄõĖŗ’╝īJavaõĮ┐ńö©ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝łParent Delegation Model’╝ēÕŖĀĶĮĮń▒╗’╝īÕŹ│ÕŁÉń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ÕģłÕ░ØĶ»ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īÕ”éµ×£Õż▒Ķ┤źÕłÖÕ¦öµēśń╗ÖńłČń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©’╝īńø┤Ķć│µĀ╣ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ŃĆéĶ┐Öń¦Źµ£║ÕłČµŚ©Õ£©ń╗┤µŖżń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮńÜäõĖĆĶć┤µĆ¦’╝īõĮåõ╣¤ÕÅ»ĶāĮµłÉõĖ║Õå▓ń¬üńÜäµØźµ║ÉŃĆé Õ£©µÅÅĶ┐░ńÜä...
- µ│øÕ×ŗ’╝ÜńÉåĶ¦Żµ│øÕ×ŗńÜäĶŠ╣ńĢī’╝īń¤źķüōķĆÜķģŹń¼”ńÜäõĮ┐ńö©’╝īõ╗źÕÅŖõĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üµ£ēń▒╗Õ×ŗµō”ķÖżŃĆé - ķøåÕÉłµōŹõĮ£’╝ܵÄīµÅĪķüŹÕÄåŃĆüµĘ╗ÕŖĀŃĆüÕłĀķÖżÕģāń┤ĀńÜäµ¢╣µ│Ģ’╝īõ║åĶ¦ŻÕ╣ČÕÅæõ┐«µö╣Õ╝éÕĖĖ’╝łConcurrentModificationException’╝ēŃĆé 3. **ÕżÜń║┐ń©ŗ**’╝Ü - ń║┐ń©ŗńÜäÕłøÕ╗║’╝Ü...
3. õĖ║õ╗Ćõ╣łĶ”üÕ«×ńÄ░Õ║ÅÕłŚÕī¢µÄźÕÅŻ’╝¤Õ«×ńÄ░Õ║ÅÕłŚÕī¢µÄźÕÅŻÕÅ»õ╗źÕ░åÕ»╣Ķ▒ĪĶĮ¼µŹóõĖ║ÕŁŚĶŖ鵥ü’╝īõ╗źõŠ┐õ║ÄńĮæń╗£õ╝ĀĶŠōµł¢µ¢ćõ╗ČÕŁśÕé©ŃĆé 4. HashMap Õåģķā©ńÜäµĢ░µŹ«ń╗ōµ×䵜»õ╗Ćõ╣ł’╝¤HashMap õĮ┐ńö©ÕōłÕĖīĶĪ©µØźÕŁśÕé©ķö«ÕĆ╝Õ»╣’╝īÕ║ĢÕ▒éÕ«×ńÄ░µś»µĢ░ń╗ä+ķōŠĶĪ©ń╗ōµ×äŃĆé Java ķ½śń║¦ 1. ...
ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮķüĄÕŠ¬ÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īÕŹ│Õģłńö▒Õ╝ĢÕ»╝ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©’╝łBootstrap ClassLoader’╝ēÕ░ØĶ»ĢÕŖĀĶĮĮ’╝īĶŗźÕż▒Ķ┤źÕłÖõ║żń╗Öµē®Õ▒Ģń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©’╝īÕåŹÕż▒Ķ┤źµēŹõ║żń╗ÖÕ║öńö©ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ŃĆéĶ┐Öń¦Źµ¢╣Õ╝ÅÕÅ»õ╗źńĪ«õ┐صĀĖÕ┐āÕ║ōõĖŹõ╝ÜĶó½ńö©µłĘĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēń▒╗Ķ”åńø¢ŃĆé `serializable`µÄźÕÅŻµś»...
ŃĆÉJVMŃĆæÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗõĖŁ’╝īõ╗ÄķĪČÕ▒éÕł░Õ║ĢÕ▒é’╝īķāĮµś»Õō¬õ║øń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©’╝īÕłåÕł½ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕō¬õ║øń▒╗’╝¤ 55 ŃĆÉJVMŃĆæĶāĮõĖŹĶāĮĶć¬ÕĘ▒ÕåÖõĖ¬ń▒╗ÕŽjava.lang.System’╝¤ 57 ŃĆÉJVMŃĆæń▒╗ńÜäÕŖĀĶĮĮĶ┐ćń©ŗ 58 ŃĆÉJVMŃĆæń▒╗ńÜäÕłØÕ¦ŗÕī¢ 58 ń▒╗õ╗Ćõ╣łµŚČÕĆÖµēŹĶó½ÕłØÕ¦ŗÕī¢’╝Ü 58 ń▒╗ńÜäÕłØÕ¦ŗ...
- ń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮµ£║ÕłČ’╝ÜńÉåĶ¦ŻÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ’╝īõ╗źÕÅŖÕ”éõĮĢĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēń▒╗ÕŖĀĶĮĮÕÖ©ŃĆé 6. **Õ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉå** - Õ╝éÕĖĖÕłåń▒╗’╝Üõ║åĶ¦ŻµŻĆµ¤źÕ╝éÕĖĖÕÆīĶ┐ÉĶĪīµŚČÕ╝éÕĖĖńÜäÕī║Õł½ŃĆé - try-catch-finally’╝ܵÄīµÅĪÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåńÜäÕ¤║µ£¼ń╗ōµ×ä’╝īńÉåĶ¦ŻfinallyÕØŚńÜäµē¦ĶĪīµŚČµ£║ŃĆé - ...
8’╝Ä1’╝Ä2 ń▒╗ĶŻģĶĮĮÕÖ©õĖÄÕÅīõ║▓Õ¦öµ┤Šµ©ĪÕ×ŗ 8’╝Ä1’╝Ä3 ÕĖĖķćŵ▒ĀĶ¦Żµ×É 8’╝Ä1’╝Ä4 Ķ¦Żµ×ÉCONSTANT_Class_infoÕģźÕÅŻ 8’╝Ä1’╝Ä5 Ķ¦Żµ×ÉCONSTANT_Fieldref_info ÕģźÕÅŻ S’╝Ä1’╝Ä6 Ķ¦Żµ×ÉCONSTANT_Methodref_info ÕģźÕÅŻ 8’╝Ä1’╝Ä7 Ķ¦Żµ×ÉCONSTANT_Interface- ...