1.хаЖя╝ЪхаЖцШпф╕АчзНцаСя╝МчФ▒хоГхоЮчО░чЪДф╝ШхЕИч║зщШЯхИЧчЪДцПТхЕехТМхИащЩдчЪДцЧ╢щЧ┤хдНцЭВх║жщГ╜цШпO(logn)я╝МчФихаЖхоЮчО░чЪДф╝ШхЕИч║зщШЯхИЧшЩ╜чД╢хТМцХ░ч╗ДхоЮчО░чЫ╕цпФш╛ГхИащЩдцЕвф║Жф║Ыя╝Мф╜ЖцПТхЕечЪДцЧ╢щЧ┤х┐лчЪДхдЪф║ЖуАВх╜УщАЯх║жх╛ИщЗНшжБф╕ФцЬЙх╛ИхдЪцПТхЕецУНф╜ЬцЧ╢я╝МхПпф╗ещАЙцЛйхаЖцЭехоЮчО░ф╝ШхЕИч║зщШЯхИЧуАВ
┬а
ф╝ШхЕИщШЯхИЧхПпф╗ечФихаЖхоЮчО░ф╣ЯхПпчФицХ░ч╗ДхоЮчО░
ф╕АшИмчФицЭехнШцаСя╝ИхМЕцЛмхаЖя╝ЙчЪДцХ░ч╗ДщГ╜цШпцаСчЪДх▒Вх║ПщБНхОЖчЪДч╗УцЮЬ
хаЖчЪДщб║х║ПцШпх╝▒х║ПчЪДхПкцШпф┐ЭшпБхЮВчЫ┤ш╖пхК▓ф╕КцЬЙщб║х║Пя╝Ичз╗щЩдц╖╗хКаф╣ЛхРОцЦ░чЪДш┐ШцШпцЬЙщб║х║Пя╝МцЬАщб╢члпчЪДцШпцЬАхА╝я╝Мх╜УцККхЕищГихЗ║цЭечЪДцЛ╝хЬиф╕Аш╡╖х░▒цЬЙх║Пф║Жя╝Йя╝Мц░┤х╣│щб║х║Пф╕КцЧах║Пя╝Мф╕НхГПх╣│шббф║МхПЙцаСцШпф╕еца╝чЪДщб║х║Пя╝МхаЖхПкшГ╜чФицЭех╝╣хЗ║цЬАхдзуАБцЬАх░ПхА╝
┬а
┬а
2.javaчЪДхаЖхТМцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхаЖя╝ЪjavaчЪДхаЖцШпчиЛх║ПхСШчФиnewшГ╜х╛ЧхИ░чЪДшобчоЧцЬ║хЖЕхнШчЪДхПпчФищГихИЖуАВшАМцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДчЪДхаЖцШпф╕АчзНчЙ╣цоКчЪДф║МхПЙцаСуАВ
3.хаЖцШпхЕ╖цЬЙхжВф╕ЛчЙ╣чВ╣чЪДф║МхПЙцаСя╝Ъ
уААуАА3.1.хоГцШпхоМхЕиф║МхПЙцаСя╝Мф╣Ях░▒цШпшп┤щЩдф║ЖцаСчЪДцЬАхРОф╕Ах▒ВшКВчВ╣ф╕НщЬАшжБцШпц╗бчЪДя╝МхЕ╢ф╗ЦчЪДцпПф╕Ах▒Вф╗Ох╖жхИ░хП│щГ╜х┐Ещб╗цШпц╗бчЪДуАВ
уААуААуААуАА3.1.1.хоМхЕиф║МхПЙцаСхЫ╛шзгя╝Ъ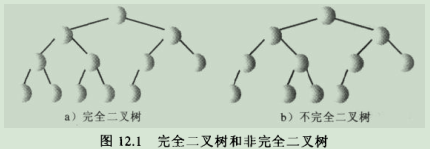
┬а
уААуАА3.2.хоГх╕╕х╕╕чФицХ░ч╗ДхоЮчО░уАВ
уААуААуААуАА3.2.1.цХ░ч╗ДхТМхаЖчЪДхп╣х║ФхЕ│ч│╗чд║цДПхЫ╛я╝Ъ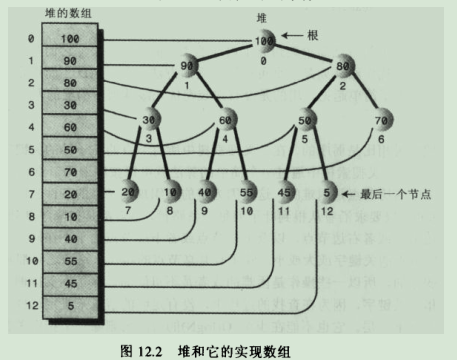
уААуАА3.3.хаЖф╕нцпПф╕Аф╕кшКВчВ╣щГ╜ц╗бш╢│хаЖчЪДцЭбф╗╢я╝Мф╣Ях░▒цШпшп┤цпПф╕Аф╕кхЕ│щФохнЧчЪДхА╝щГ╜хдзф║ОцИЦчнЙф║Ош┐Щф╕кшКВчВ╣чЪДхнРшКВчВ╣чЪДхЕ│щФохнЧхА╝уАВ
уААуААхаЖцШпхоМхЕиф║МхПЙцаСчЪДф║ЛхоЮшп┤цШОф║Жшбичд║хаЖчЪДцХ░ч╗Дф╕нц▓бцЬЙчй║щб╣я╝МхН│ф╗О0-->n-1чЪДцпПф╕кцХ░цНохНХхЕГщГ╜цЬЙцХ░цНощб╣уАВ
4.хаЖхЬихнШхВихЩиф╕нчЪДшбичд║цШпцХ░ч╗Дя╝МхаЖхПкцШпф╕Аф╕кцжВх┐╡ф╕КчЪДшбичд║уАВ
5.хаЖчЪДх╝▒х║Пя╝ЪхаЖхТМф║МхПЙцРЬч┤вцаСчЫ╕цпФцШпх╝▒х║ПчЪДя╝МхЬиф║МхПЙцРЬч┤вцаСф╕ня╝Мх╜УхЙНшКВчВ╣чЪДхА╝цА╗цШпцпФх╖жхнРшКВчВ╣чЪДхА╝хдзя╝МхН┤цпФхоГчЪДхП│хнРшКВчВ╣чЪДхА╝х░Пя╝МхЫацндцМЙх║ПщБНхОЖчЫ╕хп╣хо╣цШУуАВшАМхаЖчЪДч╗Дч╗ЗшзДхИЩх╝▒я╝МхоГхПкшжБц▒Вф╗Оца╣хИ░хП╢хнРшКВчВ╣чЪДцпПф╕АцЭбш╖пх╛Дя╝МшКВчВ╣щГ╜цШпцМЙщЩНх║ПцОТхИЧчЪДуАВхРМф╕АшКВчВ╣чЪДх╖жхП│хнРшКВчВ╣щГ╜ц▓бцЬЙшзДх╛ЛуАВхЫацндя╝МхаЖф╕НцФпцМБцМЙх║ПщБНхОЖя╝Мф╣Яф╕НшГ╜хЬихаЖф╕Кф╛┐хИйчЪДцЯецЙ╛цМЗхоЪхЕ│щФохнЧя╝МхЫаф╕║хЬицЯецЙ╛чЪДш┐ЗчиЛф╕ня╝Мц▓бцЬЙш╢│хдЯчЪДф┐бцБпхЖ│хоЪщАЙцЛйщАЪш┐ЗшКВчВ╣чЪДф╕дф╕кщВгф╕Аф╕кш╡░хРСф╕Лф╕Ах▒ВуАВхоГф╣Яф╕НшГ╜хЬих░Сф║ОO(logn)чЪДцЧ╢щЧ┤хЖЕхИащЩдф╕Аф╕кцМЗхоЪчЪДшКВчВ╣я╝МхЫаф╕║ц▓бцЬЙхКЮц│ХцЙ╛хИ░ш┐Щф╕кшКВчВ╣уАВхЫацндя╝МхаЖчЪДш┐ЩчзНш┐Сф╣ОцЧах║ПчЪДшзДхИЩф╝╝ф╣ОцплцЧачФихдДя╝Мф╕Нш┐Зхп╣ф║Ох┐лщАЯчз╗щЩдцЬАхдзшКВчВ╣чЪДцУНф╜Ья╝Мф╗ехПКх┐лщАЯцПТхЕецЦ░шКВчВ╣чЪДцУНф╜Ья╝Мш┐ЩчзНщб║х║Пх╖▓ч╗Пш╢│хдЯф║ЖуАВш┐Щф║ЫцУНф╜ЬцШпф╜┐чФихаЖф╜Ьф╕║ф╝ШхЕИч║зщШЯхИЧцЙАщЬАшжБчЪДхЕищГицУНф╜ЬуАВ
6.чз╗щЩдцУНф╜Ья╝Ъчз╗щЩдцШпцМЗхИацОЙхЕ│щФохнЧхА╝цЬАхдзчЪДшКВчВ╣я╝МхН│ца╣шКВчВ╣уАВчз╗щЩдцАЭш╖пхжВф╕Ля╝Ъ
уААуАА6.1.чз╗ш╡░ца╣я╝М
уААуАА6.2.цККх╖жхРОф╕Аф╕кшКВчВ╣чз╗хИ░ца╣чЪДф╜Нч╜оя╝М
уААуАА6.3.ф╕АчЫ┤хРСф╕ЛчнЫщАЙш┐Щф╕кшКВчВ╣я╝МчЯещБУхоГхЬиф╕Аф╕кхдзф║ОхоГчЪДшКВчВ╣ф╣Лф╕Ля╝Мх░Пф║ОхоГчЪДшКВчВ╣ф╣Лф╕Кф╕║цнвуАВ
уААуАА6.4.ш┐ЗчиЛхЫ╛шзгя╝Ъ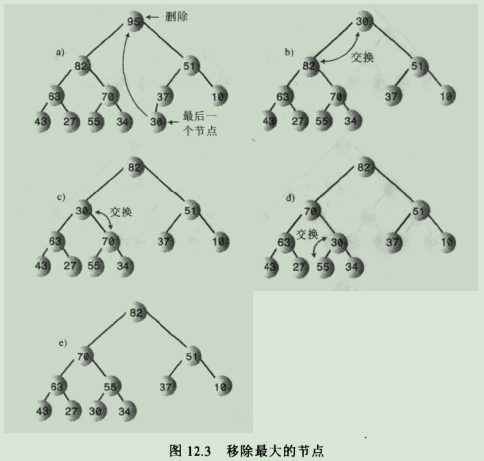
уААуААшп┤цШОя╝ЪхЬишвлчнЫщАЙшКВчВ╣чЪДцпПф╕кцЪВцЧ╢хБЬчХЩчЪДф╜Нч╜оя╝МхРСф╕ЛчнЫщАЙчЪДчоЧц│ХцА╗цШпшжБцгАцЯещВгф╕Аф╕кхнРшКВчВ╣цЫ┤хдзя╝МчД╢хРОчЫоцаЗшКВчВ╣хТМш╛ГхдзчЪДхнРшКВчВ╣ф║дцНвф╜Нч╜оя╝МхжВцЮЬшжБцККчЫоцаЗшКВчВ╣хТМш╛Гх░ПчЪДхнРшКВчВ╣ф║дцНвя╝МщВгф╣Иш┐Щф╕кхнРшКВчВ╣х░▒ф╝ЪхПШцИРхдзхнРшКВчВ╣чЪДчИ╢шКВчВ╣я╝Мш┐Щх░▒ш┐ЭшГМф║ЖхаЖчЪДцЭбф╗╢уАВ
7.хаЖчЪДцПТхЕея╝ЪцПТхЕеф╜┐чФихРСф╕КчнЫщАЙя╝МшКВчВ╣цЬАхРОцПТхЕехИ░цХ░ч╗ДцЬАхРОчммф╕Аф╕кчй║чЭАчЪДхНХхЕГф╕ня╝МцХ░ч╗Дхо╣щЗПхдзх░ПхвЮхКа1уАВ
уААуАА7.1.цПТхЕехЫ╛шзгя╝Ъ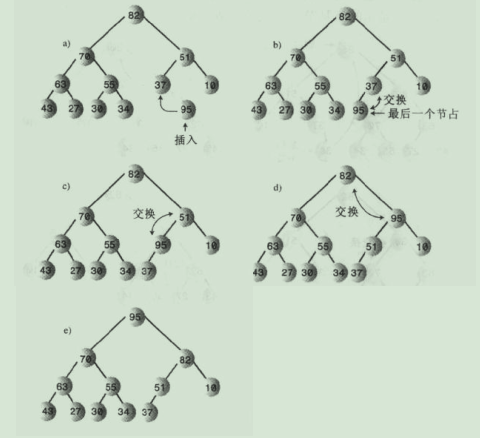
уААуААшп┤цШОя╝ЪхРСф╕КчнЫщАЙчЪДчоЧц│ХцпФхРСф╕ЛчнЫщАЙчЪДчоЧц│ХчЫ╕хп╣чоАхНХя╝МхЫаф╕║хоГф╕НщЬАшжБцпФш╛Гф╕дф╕кхнРшКВчВ╣хЕ│щФохнЧхА╝чЪДхдзх░Пя╝МшКВчВ╣хПкцЬЙф╕Аф╕кчИ╢шКВчВ╣уАВчЫоцаЗшКВчВ╣ф╕╗шжБхТМхоГчЪДчИ╢ф║▓шКВчВ╣цНвф╜НхН│хПпуАВ
уААуАА7.2.ф╕НцШпчЬЯчЪДф║дцНвя╝Ъ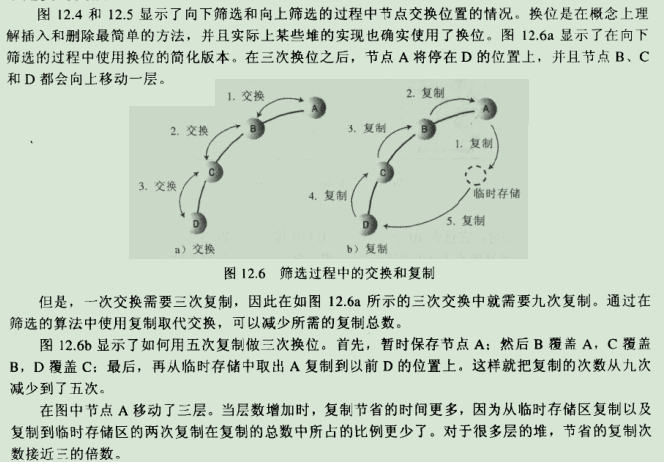
8.чФицХ░ч╗Дшбичд║ф╕Ацг╡цаСцЧ╢я╝МхжВцЮЬцХ░ч╗Дф╕ншКВчВ╣чЪДч┤вх╝Хф╜Нxя╝МхИЩ
уААуААa.хоГчЪДчИ╢шКВчВ╣чЪДф╕ЛцаЗцШпя╝Ъ(x-1)/2я╝Ы
уААуААb.хоГчЪДх╖жхнРшКВчВ╣чЪДф╕ЛцаЗф╕║2*x + 1я╝Ы
уААуААc.хоГчЪДхП│хнРшКВчВ╣чЪДф╕ЛцаЗцШп2*x + 2я╝Ы
9.хаЖчЪДф╗гчаБя╝Ъ
уААуАА9.1.Node.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * хаЖчЪДшКВчВ╣ч▒╗ 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Node { 8 private int iData; 9 public Node(int id){ 10 iData = id; 11 } 12 public int getkey(){ 13 return iData; 14 } 15 public void setkey(int id){ 16 iData = id; 17 } 18 }
уААуАА9.2.Heap.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * хаЖчЪДхоЮчО░ч▒╗ 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Heap { 8 private Node[] heapArray; 9 private int maxSize; 10 private int currentSize; 11 public Heap(int mx){ 12 maxSize = mx; 13 heapArray = new Node[maxSize]; 14 currentSize = 0; 15 } 16 public boolean isEmpty(){ 17 return currentSize == 0 ; 18 } 19 public boolean insert(int key){ 20 if (currentSize == maxSize) 21 return false; 22 Node thenode = new Node(key); 23 heapArray[currentSize] = thenode; 24 trickleUp(currentSize ++); 25 return true; 26 } 27 public void trickleUp(int index){ 28 int parent = (index - 1) / 2; 29 Node bottom = heapArray[index]; 30 while (index > 0 && heapArray[parent].getkey() < bottom.getkey()){ 31 heapArray[index] = heapArray[parent]; 32 index = parent; 33 parent = (parent - 1) / 2; 34 } 35 heapArray[index] = bottom; 36 } 37 public Node remove(){ 38 Node root = heapArray[0]; 39 heapArray[0] = heapArray[-- currentSize]; 40 trickleDown(0); 41 return root; 42 } 43 public void trickleDown(int index){ 44 int largeChild; 45 Node top = heapArray[index]; 46 while (index < currentSize / 2){ 47 int leftChild = 2 * index + 1; 48 int rightChild = 2 * index + 2; 49 if (rightChild < currentSize && heapArray[leftChild].getkey() < heapArray[rightChild].getkey()) 50 largeChild = rightChild; 51 else 52 largeChild = leftChild; 53 if (top.getkey() >= heapArray[largeChild].getkey()) 54 break; 55 heapArray[index] = heapArray[largeChild]; 56 index = largeChild; 57 } 58 heapArray[index] = top; 59 } 60 public boolean change(int index,int newvalue){ 61 if (index < 0 || index >=currentSize) 62 return false; 63 int oldvalue = heapArray[index].getkey(); 64 heapArray[index].setkey(newvalue); 65 if (oldvalue < newvalue) 66 trickleUp(index); 67 else 68 trickleDown(index); 69 return true; 70 } 71 public void displayHeap(){ 72 System.out.print("heapArray:"); 73 for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) { 74 if (heapArray[i] != null) 75 System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" "); 76 else 77 System.out.print("--"); 78 } 79 System.out.println(""); 80 int nBlanks = 32; 81 int itemsPerrow = 1; 82 int column = 0; 83 int j = 0; 84 String dots = "........................"; 85 System.out.println(dots + dots); 86 while (currentSize > 0){ 87 if (column == 0) 88 for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks; i++) { 89 System.out.print(" "); 90 } 91 System.out.print(heapArray[j].getkey()); 92 if (++ j == currentSize) 93 break; 94 if (++ column == itemsPerrow){ 95 nBlanks /= 2; 96 itemsPerrow *= 2; 97 column = 0; 98 System.out.println(); 99 } 100 else 101 for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks * 2 - 2; i++) 102 System.out.print(' '); 103 } 104 System.out.println("\n"+dots + dots); 105 } 106 }
уААуАА9.3.HTest.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * heapч▒╗чЪДц╡ЛшпХ 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class HTest { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Heap h = new Heap(10); 10 h.insert(10); 11 h.insert(30); 12 h.insert(20); 13 h.insert(18); 14 h.insert(12); 15 h.displayHeap(); 16 h.remove(); 17 h.displayHeap(); 18 } 19 }
10.хаЖчЪДцХИчОЗя╝Ъф╕Кш┐░цУНф╜ЬчЪДцЧ╢щЧ┤хдНцЭВх║жцШпя╝ЪO(logn)уАВ
11.хаЖцОТх║ПхоЮчО░цАЭш╖пя╝Ъф╜┐чФиinsert()хРСхаЖф╕нцПТхЕецЙАцЬЙцЧах║ПчЪДцХ░цНощб╣я╝МчД╢хРОщЗНхдНф╜┐чФиremove()цЦ╣ц│Хя╝Мх░▒хПпф╗ецМЙх║Пчз╗щЩдцЙАцЬЙцХ░цНощб╣я╝МхоГчЪДцХИчОЗхТМх┐лщАЯцОТх║Пч▒╗ф╝╝я╝МщГ╜цШпO(NlogN)я╝Мф╜Жх┐лцОТчиНх╛ох┐лф║Ыя╝МхЫаф╕║хаЖцПТхЕецЧ╢чЪДхРСф╕ЛчнЫщАЙхдЪхЗ║чЪДцпФш╛ГцЙАхНачФичЪДцЧ╢щЧ┤уАВ
уААуАА11.1.Node.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * хаЖчЪДшКВчВ╣ч▒╗ 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Node { 8 private int iData; 9 public Node(int id){ 10 iData = id; 11 } 12 public int getkey(){ 13 return iData; 14 } 15 public void setkey(int id){ 16 iData = id; 17 } 18 }
уААуАА11.2.Heap.java

1 package com.cn.heap; 2 /** 3 * хаЖчЪДхоЮчО░ч▒╗ 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class Heap { 8 private Node[] heapArray; 9 private int maxSize; 10 private int currentSize; 11 public Heap(int mx){ 12 maxSize = mx; 13 heapArray = new Node[maxSize]; 14 currentSize = 0; 15 } 16 public boolean isEmpty(){ 17 return currentSize == 0 ; 18 } 19 public boolean insert(int key){ 20 if (currentSize == maxSize) 21 return false; 22 Node thenode = new Node(key); 23 heapArray[currentSize] = thenode; 24 trickleUp(currentSize ++); 25 return true; 26 } 27 public void trickleUp(int index){ 28 int parent = (index - 1) / 2; 29 Node bottom = heapArray[index]; 30 while (index > 0 && heapArray[parent].getkey() < bottom.getkey()){ 31 heapArray[index] = heapArray[parent]; 32 index = parent; 33 parent = (parent - 1) / 2; 34 } 35 heapArray[index] = bottom; 36 } 37 public Node remove(){ 38 Node root = heapArray[0]; 39 heapArray[0] = heapArray[-- currentSize]; 40 trickleDown(0); 41 return root; 42 } 43 public void trickleDown(int index){ 44 int largeChild; 45 Node top = heapArray[index]; 46 while (index < currentSize / 2){ 47 int leftChild = 2 * index + 1; 48 int rightChild = 2 * index + 2; 49 if (rightChild < currentSize && heapArray[leftChild].getkey() < heapArray[rightChild].getkey()) 50 largeChild = rightChild; 51 else 52 largeChild = leftChild; 53 if (top.getkey() >= heapArray[largeChild].getkey()) 54 break; 55 heapArray[index] = heapArray[largeChild]; 56 index = largeChild; 57 } 58 heapArray[index] = top; 59 } 60 public boolean change(int index,int newvalue){ 61 if (index < 0 || index >=currentSize) 62 return false; 63 int oldvalue = heapArray[index].getkey(); 64 heapArray[index].setkey(newvalue); 65 if (oldvalue < newvalue) 66 trickleUp(index); 67 else 68 trickleDown(index); 69 return true; 70 } 71 public void displayHeap(){ 72 System.out.print("heapArray:"); 73 for (int i = 0; i < currentSize; i++) { 74 if (heapArray[i] != null) 75 System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" "); 76 else 77 System.out.print("--"); 78 } 79 System.out.println(""); 80 int nBlanks = 32; 81 int itemsPerrow = 1; 82 int column = 0; 83 int j = 0; 84 String dots = "........................"; 85 System.out.println(dots + dots); 86 while (currentSize > 0){ 87 if (column == 0) 88 for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks; i++) { 89 System.out.print(" "); 90 } 91 System.out.print(heapArray[j].getkey()); 92 if (++ j == currentSize) 93 break; 94 if (++ column == itemsPerrow){ 95 nBlanks /= 2; 96 itemsPerrow *= 2; 97 column = 0; 98 System.out.println(); 99 } 100 else 101 for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks * 2 - 2; i++) 102 System.out.print(' '); 103 } 104 System.out.println("\n"+dots + dots); 105 } 106 public void displayArray(){ 107 for (int i = 0; i < maxSize; i++) 108 System.out.print(heapArray[i].getkey()+" "); 109 System.out.println(); 110 } 111 public void insertAt(int index,Node newnode){ 112 heapArray[index] = newnode; 113 } 114 public void incrementSize(){ 115 currentSize ++; 116 } 117 }
уААуАА11.3.HeapSort.java

1package com.cn.heap; 2 3import java.util.Scanner; 4 5/** 6 * хЯ║ф║ОхаЖчЪДцОТх║П----хаЖцОТх║П 7 * @author Administrator 8 * 9*/10publicclass HeapSort { 11publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { 12int size,j; 13 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 14 System.out.print("Enter number of items: "); 15 size = in.nextInt(); 16 Heap theheap = new Heap(size); 17for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 18int random = (int)(Math.random()*100); 19 Node node = new Node(random); 20 theheap.insertAt(i, node); 21 theheap.incrementSize(); 22 } 23 System.out.print("random: "); 24 theheap.displayArray(); 25for (int i = size / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i --) { 26 theheap.trickleDown(i); 27 } 28 System.out.print("heap: "); 29 theheap.displayArray(); 30 theheap.displayHeap(); 31for (int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i --) { 32 Node node = theheap.remove(); 33 theheap.insertAt(i,node); 34 } 35 System.out.print("sorted: "); 36 theheap.displayArray(); 37} 38 } хПВшАГя╝Ъ https://www.cnblogs.com/g177w/p/8469399.html









чЫ╕хЕ│цОишНР
цЬмхнжф╣аш╡ДцЦЩхМЕ"javaцХ░цНоч╗УцЮД--хнжф╣а"шБЪчДжф║ОхжВф╜ХхЬиJavaчОпхвГф╕ЛчРЖшзгхТМх║ФчФихРДчзНцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДя╝МцЧихЬицПРхНЗх╝АхПСшАЕчЪДцКАцЬпц░┤х╣│я╝Мф╜┐хЕ╢шГ╜хдЯч╝ЦхЖЩхЗ║цЫ┤хКащлШцХИхТМф╝ШхМЦчЪДф╗гчаБуАВ 1. **цХ░ч╗Д**я╝ЪцХ░ч╗ДцШпцЬАхЯ║цЬмчЪДцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДя╝МчФиф║ОхнШхВихРМч▒╗хЮЛхЕГч┤ачЪД...
Javaф╜Ьф╕║х╣┐ц│Ых║ФчФичЪДч╝ЦчиЛшпншиАя╝МхЕ╢хЬихоЮчО░цХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхТМчоЧц│ХцЧ╢цЬЙчЭАф╕░хпМчЪДх║УцФпцМБхТМф╝ШчзАчЪДхПпшп╗цАзуАВф╕ЛщЭвх░Жхп╣цаЗщвШхТМцППш┐░ф╕нцПРхИ░чЪДф╕Аф║ЫхЕ│щФочЯешпЖчВ╣ш┐ЫшбМшпжч╗ЖшзгщЗКуАВ 1. **цХ░цНоч╗УцЮД**я╝Ъ - **чиАчЦПцХ░ч╗Д**я╝Ъх╜УхдзщЗПцХ░цНоф╕нхдзщГихИЖф╕║щЫ╢цИЦ...
ф╕╗шжБхЖЕхо╣хМЕцЛмя╝ЪчоЧц│ХцХИчОЗчЪДш╛УхЕешзДцибуАБщШ╢хТМхдзOя╝МцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДчЪДцЧах║ПхТМцЬЙх║ПхИЧшбия╝МщШЯхИЧхТМцаИхЯ║ф║ОцХ░ч╗ДхТМщУ╛шбичЪДшо╛шобхоЮф╛Ля╝МщАТх╜Тшпжшзгя╝Мф║МхПЙцЯецЙ╛цаСхТМAVLцаСя╝МхаЖуАБцХгхИЧшбихТМцОТх║Пф╗ехПКхЫ╛шо║чнЙуАВхп╣ф║ОцпПф╕АчзНцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДчЪДцАзш┤ихТМчФищАФя╝МуАКшобчоЧцЬ║...
хЬиITщвЖхЯЯя╝Мх░дхЕ╢цШпхЬич╝ЦчиЛф╕ЦчХМя╝МцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДцШпшЗ│хЕ│щЗНшжБчЪДф╕Аф╕кцжВх┐╡я╝Мх░дхЕ╢хп╣ф║ОJavaх╝АхПСшАЕшАМшиАуАВцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДцШпч╗Дч╗ЗуАБчобчРЖхТМхнШхВицХ░цНочЪДцЦ╣х╝Пя╝МхоГхЕБшо╕цИСф╗мщлШцХИхЬ░шо┐щЧохТМф┐оцФ╣цХ░цНоуАВцЬмш╡Дц║РхМЕ"java---цХ░цНоч╗УцЮД"цШ╛чД╢цШпщТИхп╣JavaчиЛх║ПхСШ...
уАКJavaцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхТМчоЧц│Х-х╕жф╣жчн╛чЫох╜ХцЙлцППчЙИуАЛцШпф╕АцЬмц╖▒хЕецОвшоиJavaч╝ЦчиЛшпншиАф╕нцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхТМчоЧц│ХчЪДф╣жч▒НуАВцндцЙлцППчЙИчЙ╣хИлхМЕхРлф║ЖхоМцХ┤чЪДф╣жчн╛чЫох╜Хя╝Мф╜┐х╛Чшп╗шАЕхЬичФ╡хнРчЙИщШЕшп╗цЧ╢шГ╜хдЯх┐лщАЯхоЪф╜НхИ░цЙАщЬАчлашКВя╝МцПРщлШф║Жхнжф╣ахТМцЯещШЕчЪДцХИчОЗуАВ хЬи...
"java-data-struct.rar_цХ░цНоч╗УцЮД java_цХ░цНоч╗УцЮДц║РчаБ"ш┐Щф╕кхОЛч╝йхМЕцЦЗф╗╢хМЕхРлф║ЖчФиJavaхоЮчО░чЪДцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДчЪДчЫ╕хЕ│ф╗гчаБя╝Мхп╣ф║Охнжф╣ахТМчРЖшзгцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДчЪДхоЮчО░хЕ╖цЬЙх╛ИщлШчЪДхПВшАГф╗╖хА╝уАВ 1. **щУ╛шбия╝ИLinkedListя╝Й**я╝ЪщУ╛шбицШпф╕АчзНч║┐цАзцХ░цНоч╗УцЮД...
ш╡Дц║РцСШшжБф┐бцБпцШпхЕ│ф║ОJavaцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхТМчоЧц│ХчЪДчЯешпЖчВ╣цА╗ч╗Уя╝Мц╢╡чЫЦф║ЖцХ░ч╗ДуАБцаИф╕ОщШЯхИЧуАБщУ╛шбиуАБщАТх╜ТуАБхУИх╕МшбиуАБщлШч║зцОТх║ПуАБф║МхПЙцаСуАБч║вщ╗СцаСуАБхаЖуАБх╕жцЭГхЫ╛чнЙцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхТМчоЧц│ХцжВх┐╡уАВ ф╕АуАБцХ░ч╗Д * цХ░ч╗ДцШпчЫ╕хРМч▒╗хЮЛхПШщЗПчЪДщЫЖхРИя╝МхПпф╗еф╜┐чФи...
### JavaцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДф╕ОчоЧц│Ххнжф╣ачмФшо░чЯешпЖчВ╣цА╗ч╗У #### ф╕АуАБцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДцжВш┐░ цХ░цНоч╗УцЮДцШпхп╣цХ░цНочЪДф╕АчзНч╗Дч╗Зх╜вх╝Пя╝МхоГхЖ│хоЪф║ЖцХ░цНочЪДхнШхВицЦ╣х╝Пф╗ехПКхдДчРЖцХ░цНочЪДцЦ╣ц│ХуАВх╕╕шзБчЪДцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхМЕцЛмф╜Жф╕НщЩРф║ОцХ░ч╗ДуАБщУ╛шбиуАБцаИуАБщШЯхИЧуАБф║МхПЙцаСуАБхЫ╛чнЙ...
хЬицЬАх░ПхаЖф╕ня╝МцаСчЪДца╣шКВчВ╣цШпцЙАцЬЙшКВчВ╣ф╕нцЬАх░ПчЪДя╝Мш┐ЩчзНцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДх╕╕чФиф║ОхоЮчО░ф╝ШхЕИщШЯхИЧуАБхаЖцОТх║Пф╗ехПКхЕ╢хоГщЬАшжБх┐лщАЯцЙ╛хИ░цЬАх░ПхЕГч┤ачЪДчоЧц│ХуАВ JavaцШпф╕АчзНх╣┐ц│Ыф╜┐чФичЪДч╝ЦчиЛшпншиАя╝МхоГцПРф╛Ыф║Жф╕АчзНщЭвхРСхп╣ш▒бчЪДч╝ЦчиЛшМГх╝ПуАВхЬиJavaф╕нхоЮчО░цЬАх░ПхаЖ...
уАРJavaхоЪцЧ╢хЩиф╕ОцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДшпжшзгуАС 1. **хоЪцЧ╢хЩия╝ИTimerя╝Й** - хоЪцЧ╢хЩихЬиJavaф╕нчФиф║ОхоЙцОТхЬих░ЖцЭецЯРф╕кцЧ╢щЧ┤чВ╣цЙзшбМчЪДф╗╗хКбуАВхоГф╜┐чФи`java.util.Timer`ч▒╗хТМ`java.util.TimerTask`ч▒╗цЭехоЮчО░уАВ`TimerTask`цШпхоЮчО░хоЪцЧ╢ф╗╗хКбчЪДхЯ║чбАя╝МхоГ...
уАКJavaцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхТМчоЧц│ХуАЛчммф║МчЙИцШпф╕АцЬмц╖▒хЕецОвшоиJavaч╝ЦчиЛф╕нцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДф╕ОчоЧц│ХчЪДцЭГхиБф╣жч▒НуАВш┐ЩцЬмф╣жц╢╡чЫЦф║ЖхЬиш╜пф╗╢х╝АхПСф╕ншЗ│хЕ│щЗНшжБчЪДхЯ║чбАчЯешпЖя╝МцЧихЬих╕охКйчиЛх║ПхСШцПРхНЗшзгхЖ│щЧощвШчЪДшГ╜хКЫхТМф╗гчаБцХИчОЗуАВщлШц╕ЕцЙлцППчЙИцПРф╛Ыф║Жц╕ЕцЩ░чЪДцЦЗцЬмхТМхЫ╛шбия╝М...
CуАБC++хТМJavaщГ╜цШпх╣┐ц│Ыф╜┐чФичЪДч╝ЦчиЛшпншиАя╝МхоГф╗мхЬихдДчРЖцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДхТМчоЧц│ХцЧ╢хРДцЬЙчЙ╣чВ╣уАВф╗еф╕ЛцШпхп╣ш┐Щф╕ЙчзНшпншиАхЬицХ░цНоч╗УцЮДф╕ОчоЧц│ХцЦ╣щЭвчЪДф╕Аф║ЫхЕ│щФочЯешпЖчВ╣чЪДшпжч╗ЖщШРш┐░я╝Ъ 1. **цХ░цНоч╗УцЮД**я╝Ъ - **цХ░ч╗Д**я╝ЪхЯ║цЬмчЪДцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДя╝МчФиф║ОхнШхВихРМ...
хЬиJavaщЭвшпХф╕ня╝МцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДцШпф╕НхПпцИЦч╝║чЪДф╕Аф╕кщЗНшжБчОпшКВя╝МхЫаф╕║хоГчЫ┤цОех╜▒хУНхИ░чиЛх║ПчЪДцХИчОЗхТМшо╛шобш┤ищЗПуАВцЬмш╡ДцЦЩхМЕ"щЭвшпХ-Javaф╕Аф║Ых╕╕шзБщЭвшпХщвШ+щвШшзгф╣ЛцХ░цНоч╗УцЮД-DataStructure.zip"шБЪчДжф║ОJavaф╕нчЪДцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДя╝МцЧихЬих╕охКйц▒ВшБМшАЕцЫ┤хе╜хЬ░хЗЖхдЗ...
уАКJava-C-JSцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДф╕ОчоЧц│ХхРИщЫЖуАЛцШпщТИхп╣ч╝ЦчиЛщвЖхЯЯчЪДф╕Йхдзф╕╗ц╡БшпншиАтАФтАФJavaуАБCхТМJavaScriptя╝Мц╖▒хЕецОвшоицХ░цНоч╗УцЮДф╕ОчоЧц│ХчЪДхоЭш┤╡ш╡Дц║РуАВцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДцШпшобчоЧцЬ║хнШхВиуАБч╗Дч╗ЗцХ░цНочЪДцЦ╣х╝Пя╝МшАМчоЧц│ХцШпшзгхЖ│щЧощвШчЪДч▓╛чбоцнещкдя╝МхоГф╗мцШпш╜пф╗╢х╝АхПСчЪД...
### JavaчЙИцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДчЯешпЖчВ╣цжВш┐░ #### ф╕АуАБх╝ХшиА уАКJavaчЙИцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДуАЛцШпф╕АщГищТИхп╣JavaчиЛх║ПхСШчЪДч╗ПхЕ╕ф╣Лф╜Ья╝МчФ▒Robert LaforeцТ░хЖЩуАВцЬмф╣жф╕Нф╗ЕщАВчФиф║ОхИЭхнжшАЕя╝Мф╣ЯщАВхРИщВгф║Ых╕МцЬЫц╖▒хЕечРЖшзгцХ░цНоч╗УцЮДф╕ОчоЧц│ХчЪДщлШч║зх╝АхПСшАЕуАВхоГщАЪш┐Зц╕ЕцЩ░уАБ...