http://www.cnblogs.com/larryzeal/tag/spring/
еЕИиѓіиѓідЄЇдїАдєИйЬАи¶БAOP
 
жЬАзЃАеНХзЪДдЄАдЄ™дЊЛе≠Ре∞±жШѓжЧ•ењЧиЃ∞ељХпЉМе¶ВжЮЬжГ≥иЃ∞ељХдЄАдЇЫжЦєж≥ХзЪДжЙІи°МжГЕеЖµпЉМжЬАзђ®зЪДеКЮж≥Хе∞±жШѓдњЃжФєжѓПдЄАдЄ™йЬАи¶БиЃ∞ељХзЪДжЦєж≥ХгАВдљЖињЩпЉМзЬЯзЪДеЊИзђ®гАВгАВгАВ
е•љзЪДжЦєж≥ХпЉМеЇФиѓ•жШѓйАЪињЗеПНе∞ДиОЈеПЦжЦєж≥ХпЉМзДґеРОеОїеМєйЕНпЉМе¶ВжЮЬйЬАи¶БиЃ∞ељХжЧ•ењЧпЉМйВ£е∞±и∞ГзФ®жЧ•ењЧжЦєж≥ХеН≥еПѓгАВ
ињЩе∞±жШѓAOP зЪДWeavingпЉМдњЧзІ∞зЉЦзїЗгАБзїЗеЕ•пЉМе∞±жШѓе∞ЖйЬАи¶БжЈїеК†зЪДеКЯиГљзЉЦзїЗеИ∞зО∞жЬЙеКЯиГљдЄ≠пЉМиАМдЄНйЬАи¶БдњЃжФєзО∞жЬЙдї£з†БгАВ
 
еП¶дЄАдЄ™дЊЛе≠РпЉМдЄНйВ£дєИе§ІдЉЧзЪДйЬАж±ВпЉЪжИСжГ≥зїЩдЄАдЄ™еѓєи±°жЈїеК†жЦєж≥ХпЉМжАОдєИеЃЮзО∞пЉЯ
е¶ВжЮЬжЬЙе≠¶ињЗjsгАБPythonз≠ЙеК®жАБиѓ≠и®АпЉМдљ†иВѓеЃЪзЯ•йБУеЃГдїђжФѓжМБзїЩеѓєи±°жЈїеК†жЦєж≥ХпЉМзЫіжО•жЈїеК†еН≥еПѓгАВ
дљЖжШѓJavaдЄНи°МпЉМеЫ†дЄЇJavaзЪДз±їеЮЛжШѓе∞БйЧ≠зЪДгАВ
SpringзїЩеЗЇеКЮж≥Хе∞±жШѓйАЪињЗдї£зРЖпЉМжЛ¶жИ™иѓЈж±ВпЉМзДґеРОеОїи∞ГзФ®еЃЮйЩЕжЛ•жЬЙиѓ•жЦєж≥ХзЪДеѓєи±°зЪДиѓ•жЦєж≥ХпЉБпЉИзХ•зїХпЉЙ ињЩе∞±жШѓIntroductionпЉМдњЧзІ∞еЉХеЕ•гАВ
е¶ВеЫЊпЉЪ
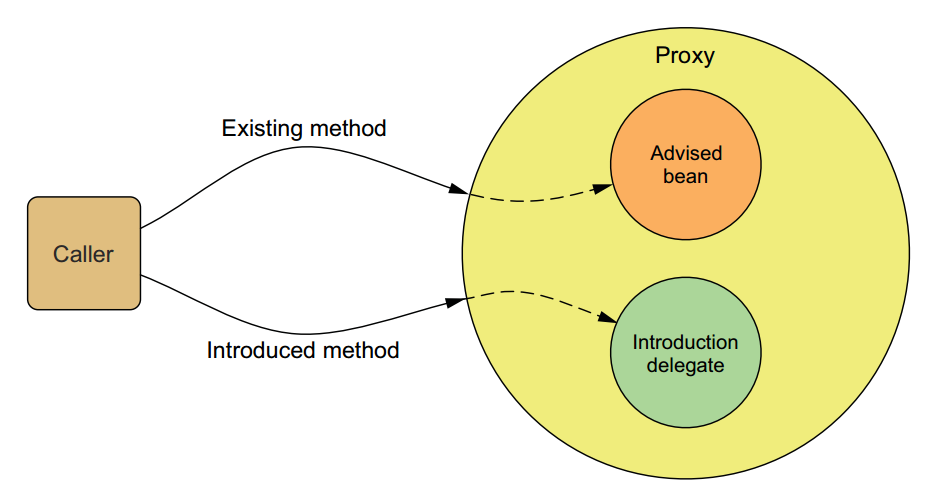
ињЩжШѓдє¶дЄ≠иЗ™еЄ¶зЪДеЫЊзЙЗпЉМеЊИ嚥豰гАВ
е¶ВеЫЊжЙАз§ЇпЉМе¶ВжЮЬи∞ГзФ®Advised beanзЪДExisting methodпЉМйВ£е∞±жШѓWeavingпЉИзїЗеЕ•пЉЙпЉЫе¶ВжЮЬи∞ГзФ®introduced methodпЉМйВ£е∞±жШѓIntroductionгАВ
дљЖжШѓпЉМжЧ†иЃЇйВ£зІНпЉМSpringйГљжШѓйАЪињЗеЕґдї£зРЖеКЯиГљеЃЮзО∞зЪДгАВпЉИе¶ВжЮЬдљ†еЈ≤зїПзЯ•йБУSpringзЪДдї£зРЖеКЯиГљдїЕйЩРдЇОmethodпЉМйВ£дљ†дєЯеПѓдї•жГ≥еИ∞Spring AOPдїЕйЩРдЇОmethod --- з®НеРОиЃ®иЃЇпЉЙ
 
дї•дЄКпЉМиЃ∞дљПдЄАзВєе∞±и°МпЉЪSpring AOPдЄ≠пЉМзїЩжЦєж≥ХжЈїеК†еКЯиГље∞±жШѓзїЗеЕ•пЉМзїЩеѓєи±°жЈїеК†еКЯиГље∞±жШѓеЉХеЕ•гАВ
пЉИиЗ≥дЇОдЄЇдїАдєИеЉЇи∞ГжШѓSpring AOPпЉМињЩжШѓеЫ†дЄЇињШжЬЙеЕґдїЦзЪДAOPж°ЖжЮґпЉМз®НеРОиЃ®иЃЇгАВпЉЙ
 
еЖНеИЧдЄАдЄЛеЕґдїЦж¶ВењµпЉЪ
WeavingзїЗеЕ•йГ®еИЖпЉЪ
гААгААAdvice пЉЪ йЬАи¶БжЈїеК†зЪДеКЯиГљпЉМдЊЛе¶ВжЧ•ењЧеКЯиГљгАБжЭГйЩРеКЯиГљз≠ЙпЉМдї•еПКдїАдєИжЧґеАЩжЈїеК†пЉИзЫЃж†ЗжЦєж≥ХжЙІи°МеЙНгАБеРОгАБеЉВеЄЄз≠ЙжЧґеАЩпЉЙгАВ
гААгААJoin-point пЉЪ зЫЃж†Зз±їдЄ≠иГље§ЯжЈїеК†еКЯиГљзЪДеЬ∞жЦєпЉБ
гААгААPointcut пЉЪ жМЗеЃЪзЫЃж†Зз±їдЄ≠жЈїеК†еКЯиГљзЪДеЬ∞жЦєпЉБеЫ†дЄЇдЄНеПѓиГљзїЩжЙАжЬЙJoin-pointзїЗеЕ•AdviceпЉБпЉИSpring AOPдїЕйЩРдЇОжЦєж≥ХпЉМеЫ†дЄЇеЃГеЯЇдЇОдї£зРЖеЃЮзО∞гАВеЕґдїЦзЪДж°ЖжЮґињШеПѓдї•йТИеѓєе≠ЧжЃµжЈїеК†еКЯиГљпЉБдЇЖиІ£е∞±и°МгАВпЉЙ
гААгААйЬАи¶Бж≥®жДПзЪДжШѓпЉМAdviceеЃЪдєЙдЇЖдїАдєИжЧґеАЩеБЪгАБеБЪдїАдєИпЉМиАМPointcutеИЩеЃЪдєЙдЇЖеЬ®еУ™йЗМеБЪгАВ
гААгААAspect = Advices + Pointcuts // AspectеПѓдї•иЃ§дЄЇжШѓдЄАе†ЖAdviceзЪДз±їпЉМдЄФеЕґдЄ≠жМЗеЃЪдЇЖжѓПдЄ™AdviceжЙІи°МзЪДPointcutгАВ
 
IntroductionеЉХеЕ•йГ®еИЖпЉЪ гААгААжЪВжЧ†
 
дї•дЄКпЉМPointcutжШѓеЕ≥йФЃпЉМеЃГеЖ≥еЃЪдЇЖдЄАдЄ™AOPж°ЖжЮґзЪДи°МдЄЇгАВ
еЫ†дЄЇPointcutжДПеС≥зЭАwhereпЉИfieldпЉЯmethodпЉЯexceptionпЉЯпЉЙеТМwhenпЉИзЉЦиѓСжЧґпЉЯеК†иљљжЧґпЉЯињРи°МжЧґпЉЯпЉЙгАВ
гАРгАСйАЪеЄЄпЉМдљњзФ®classеТМmethod nameжЭ•еЃЪдєЙPointcutпЉМжИЦиАЕдљњзФ®ж≠£еИЩи°®иЊЊеЉПеМєйЕНclassеТМmethod nameжЭ•еЃЪдєЙPointcutпЉБпЉБпЉБ
 
 
WeavingеЇФзФ®йГ®еИЖ
Spring AOPеТМAspectJжЬЙеЊИе§ЪеНПеРМгАВSpring AOPеАЯйЙідЇЖAspectJеЊИе§ЪзРЖењµгАВ
SpringеѓєAOPзЪДжФѓжМБжЬЙеЫЫзІН嚥еЉПпЉЪ
вС† зїПеЕЄзЪДSpringеЯЇдЇОдї£зРЖзЪДAOPгАВ
вС° зЇѓPOJO aspectгАВ
вСҐ @AspectJж≥®иІ£й©±еК®зЪДaspectгАВ
вС£ ж≥®еЕ•зЪДAspectJ aspectгАВ
дї•дЄКпЉМеЙНдЄЙзІНжШѓSpringиЗ™жЬЙAOPзЪДеПШдљУпЉМзФ±дЇОйГљжШѓеЯЇдЇОдї£зРЖпЉМжЙАдї•пЉМдїЕйЩРдЇОжЦєж≥ХжЛ¶жИ™пЉБпЉБпЉБ
Spring AOPеЉХзФ®дЇЖAspectJ ELгАВ
AspectJ ELи°®иЊЊеЉПпЉЪж†ЄењГе∞±жШѓexecutionпЉМеЕґдїЦзЪДйГљжШѓзФ®дЇОйЩРеИґеРДзІНеПВжХ∞зЪДгАВгАРгАСгАРгАС
дЊЛе¶ВпЉЪ
execution(* concert.Performance.perform(..)) && within(concert.*) // ињЩйЗМе∞±еЃЪдєЙдЇЖдЄАдЄ™pointcutпЉМиАМдЄФдїЕйЩРдЇО襀concertеМЕдЄЛзЪДaspectдљњзФ®гАВ¬†¬†
дЄКйЭҐзЪДAspectJ ELжШѓзФ±дЄ§йГ®еИЖзїДжИРпЉЪexecutionеЃЪдєЙеИЗеЕ•зВєпЉМwithinйЩРеЃЪеИЗеЕ•зВєгАВиІБдЄЛеЫЊпЉЪ
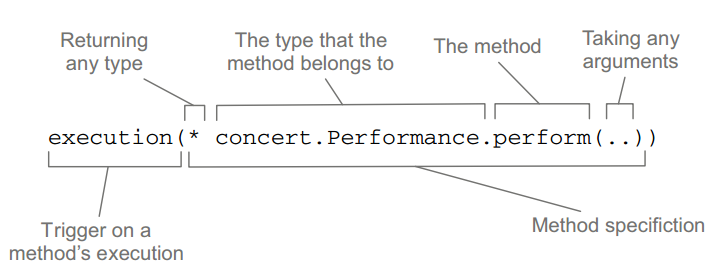
 

 
 
дЄКйЭҐпЉМеПѓдї•дљњзФ®&&жИЦandгАБ||жИЦorгАБпЉБжИЦnotгАВ з±їдЉЉELжИЦJSTLгАВ
SpringињШеҐЮеК†дЄАдЄ™bean()пЉМжДПжАЭжШѓдїЕйЩРдЇОиѓ•beanзЪДPointcutгАВ¬†¬† ¬†
дЊЛе¶ВпЉЪexecution(* concert.Performance.perform()) and bean('woodstock') ињЩйЗМе∞±еЃЪдєЙдЇЖдЄАдЄ™woodstockзЪДpointcutгАВ дЊЛе¶ВпЉЪexecution(* concert.Performance.perform()) and !bean('woodstock') ж≥®жДПињЩйЗМпЉБпЉБпЉБеЊИжЬЙжДПжАЭзЪДзФ®ж≥ХгАВ
 
AspectJ ж≥®иІ£еЉАеПСпЉЪ
AspectJ дїО 5 еЉАеІЛеЉХеЕ•дЇЖж≥®иІ£еЉАеПСпЉМSpring AOPеРМж†ЈеЉХеЕ•AspectJзЪДж≥®иІ£гАВ
дљЖжШѓпЉМSpring AOPдїЕдїЕжШѓеИ©зФ®AspectJзЪДж≥®иІ£еРНиѓНпЉМеЇХе±ВдїНзДґжШѓSpring AOPзЪДдї£зРЖеЃЮзО∞гАВ
 
ж≥®иІ£еЉАеПСињЗз®ЛпЉЪ
@Aspectж≥®иІ£еИ∞aspectжЙАеЬ®зЪДз±їдЄКпЉМзДґеРО@Beforeз≠Йж≥®иІ£еИ∞adviceпЉИaspectеѓєеЇФзЪДжЦєж≥ХпЉЙдЄКгАВе¶ВдЄЛпЉЪ
@Component // ињЩдЄ™жШѓењЕй°їзЪДпЉБпЉБ @Aspect public class Audience { @Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") // иѓ•ж≥®иІ£е£∞жШОдЇЖsilenceCellPhones()йЬАи¶БеЇФзФ®еИ∞зЪДPointcutгАВ public void silenceCellPhones() { System.out.println("Silencing cell phones"); } @Before("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void takeSeats() { System.out.println("Taking seats"); } @AfterReturning("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void applause() { System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP!!!"); } @AfterThrowing("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void demandRefund() { System.out.println("Demanding a refund"); } }
дљЖжШѓпЉМдЄКйЭҐињЩзІНеЖЩж≥ХеЊИдЄНжЦєдЊњпЉМеЫ†дЄЇPointcutжШѓйЗНе§НзЪДгАВ
иІ£еЖ≥еКЮж≥ХпЉЪдљњзФ®@PointcutдЄАжђ°жАІеЃЪдєЙе•љдЄАдЄ™PointcutгАВе¶ВдЄЛпЉЪ
@Component // ињЩдЄ™жШѓењЕй°їзЪДпЉБпЉБпЉБ @Aspect public class Audience { @Pointcut("execution(** concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void perform(){}; // ењЕй°їи¶БеЃЪдєЙдЄАдЄ™жЦєж≥ХпЉМзФ®дЇОжЙњиљљpointcutпЉБ // еЕґдїЦзЪДж≠£еЄЄдї£з†БпЉМзХ• }
¬†дљЖжШѓпЉМеИ∞зЫЃеЙНдЄЇж≠ҐпЉМAOPдїНзДґжШѓжЧ†ж≥ХжЙІи°МзЪДпЉМеЫ†дЄЇSpring AOPдЄНзЯ•йБУињЩдЇЫж≥®иІ£дї£и°®дїАдєИпЉМжЙАдї•йЬАи¶БеЕИеЉАеРѓAspectJиЗ™еК®дї£зРЖгАВ
еЉАеРѓжЦєж≥ХпЉЪ@EnableAspectJAutoProxyж≥®иІ£еИ∞JavaConfigдЄКйЭҐгАВжИЦиАЕпЉМе¶ВжЮЬдљњзФ®XMLпЉМ<aop:aspectj-autoproxy>¬†гАВж≥®жДПеѓЉеЕ•еРНзІ∞з©ЇйЧігАВ
 
зО∞еЬ®пЉМдЄКйЭҐзЪДеЖЕеЃєеПѓдї•зЫіжО•ињЫи°МжµЛиѓХдЇЖпЉЪ
package aop.performance; /** * зФ®ињЩдЄ™жЉФз§Їjoin-pointеТМpointcutгАВ * perform()е∞±жШѓjoin-pointпЉБ * * @author Larry */ public interface Performance { void perform(); }
package aop.performance; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class PerformanceImpl implements Performance{ @Override public void perform() { System.out.println(this.getClass()+"ж≠£еЬ®жЉФеЗЇ~~~"); } }
package aop; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * зФ®Audienceз±їжЭ•жО©й•∞AspectJ 5зЪДж≥®иІ£зФ®ж≥ХгАВ * * @author Larry * */ @Component @Aspect public class Audience { @Before("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))") public void takeSeat() { System.out.println("жЉФеЗЇдєЛеЙНи¶БеЕ•еЇІ~"); } @Before("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))") public void silenceCellPhones() { System.out.println("жЉФеЗЇдєЛеЙНи¶БйЭЩйЯ≥~"); } @After("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))") public void applause() { System.out.println("жЉФеЗЇдєЛеРОи¶БйЉУжОМпЉБ"); } // TODO: и≤МдЉЉдЄНиГљињЩж†ЈзФ®пЉЯпЉЯиАМдЄФдЉЪеѓЉиЗіе§ІBUGпЉБпЉБпЉБйШїж≠ҐиЃњйЧЃPointcutпЉБпЉБпЉБиІБдЄЛйЭҐ //@Around("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))") public void greet() { System.out.println("жЉФеЗЇеЙНеРОи¶БиЗіжДП~"); } @AfterReturning("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))") public void leave() { System.out.println("зїУжЭЯеРОпЉМgoodbye~"); } @AfterThrowing("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))") public void demandRefund(){ System.out.println("йААйТ±пЉБпЉБпЉБ"); } //дЄКйЭҐпЉМдЄНе•љзЪДеЬ∞жЦєжШѓжѓПжђ°йГљи¶БеЖЩзЫЄеРМзЪДpointcutпЉБиІ£еЖ≥еКЮж≥Хе¶ВдЄЛпЉЪ @Pointcut("execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))") public void perform(){} // ињЩж†Је∞±еЃЪдєЙдЇЖдЄАдЄ™pointcutпЉЪperformance()пЉМзДґеРОе∞±еПѓдї•зЫіжО•дљњзФ®дЇЖпЉБе¶ВдЄЛпЉЪ @Before("perform()") public void wave(){ System.out.println("жМ•жМ•жЙЛ~"); } // TODO: еК°ењЕж≥®жДПпЉМ@AroundењЕй°їжЙЛеК®и∞ГзФ®PointcutпЉМеР¶еИЩдЉЪйШїж≠ҐеѓєPointcutзЪДиЃњйЧЃпЉБпЉБпЉБ @Around("perform()") public void greet2(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) { try { System.out.println("жЉФеЗЇеЙНеРОи¶БиЗіжДП~A"); jp.proceed();//TODO:ињЩйЗМињШеПѓдї•и∞ГзФ®еЄ¶еПВжХ∞зЪДпЉБ System.out.println("жЉФеЗЇеЙНеРОи¶БиЗіжДП~B"); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
package aop; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; import aop.performance.PerformanceImpl; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackageClasses={ Audience.class,PerformanceImpl.class,AudienceB.class,IntroductionEncoreable.class }) @EnableAspectJAutoProxy //жњАжіїAspectJ public class JavaConfig { }
package aop.test; import java.util.Arrays; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import aop.JavaConfig; import aop.performance.Performance; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = { JavaConfig.class }) public class PerformanceAOPTest { @Autowired Environment env; @Autowired ApplicationContext ac; @Autowired Performance p; @Test public void run() { String[] activeProfiles = env.getActiveProfiles(); System.out.println("activeProfilesзЪДйХњеЇ¶"+activeProfiles.length); for (String string : activeProfiles) { System.out.println("activeProfiles:" + string); } System.out.println("-------------------------------------"); String applicationName = ac.getApplicationName(); System.out.println("applicationNameпЉЪ"+applicationName); String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames(); String beans = Arrays.toString(beanDefinitionNames); System.out.println("applicationContextдЄ≠зЪДbeansпЉЪ"+beans); } @Test public void run1() { p.perform(); // ж≥®жДПжЬЙж≤°жЬЙжњАжіїAspectJпЉБ } }
дЄКйЭҐзЪДдї£з†Бе∞±жШѓдЄАдЄ™жµЛиѓХзЪДеЕ®ињЗз®ЛпЉМеЕґдЄ≠йБЗеИ∞зЪДдЄАдЄ™йЧЃйҐШе∞±жШѓзОѓзїХйАЪзЯ•@AroundпЉМињЩдЄ™ж≥®иІ£и¶Бж±ВењЕй°їжЙЛеК®и∞ГзФ®PointcutпЉИжЦєж≥ХпЉЙпЉМеР¶еИЩSpringдї£зРЖдЉЪ䪥姱胕жЦєж≥ХпЉБ
䪥姱胕жЦєж≥ХпЉМе∞±жДПеС≥зЭАеРОйЭҐзЪДдї£зРЖжЧ†ж≥ХзїІзї≠пЉБпЉБпЉБпЉИз±їдЉЉжЛ¶жИ™еЩ®жЛ¶жИ™иѓЈж±ВпЉМжЛ¶жИ™дєЛеРОињШи¶БжЙЛеК®жФЊи°МпЉМеР¶еИЩеРОйЭҐзЪДз®ЛеЇПжЧ†ж≥ХжО•жФґеИ∞иѓ•иѓЈж±ВпЉМдєЯе∞±жШѓ 䪥姱胣ж±ВпЉБпЉЙ
йЬАи¶Бж≥®жДПзЪДжШѓпЉМињШеПѓдї•е§Ъжђ°и∞ГзФ®иѓ•жЦєж≥ХпЉБпЉБпЉБеЇФзФ®еЬЇжЩѓпЉЪеЉВеЄЄеРОйЗНжЦ∞жЙІи°МгАВ
@Around("performance()")
public void watchPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) {
try {
System.out.println("Silencing cell phones"); // зЫЄељУдЇО@Before
System.out.println("Taking seats"); // зЫЄељУдЇО@Before
jp.proceed(); // гАРгАСгАРгАСињЩдЄ™пЉМе∞±жШѓи∞ГзФ®pointcutгАВеПѓиГљењШиЃ∞и∞ГзФ®пЉМдєЯеПѓиГљйЗНе§Ни∞ГзФ®гАВгАВгАВ
System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP!!!"); // зЫЄељУдЇО@After гАРе•ЗжА™пЉМйВ£@AfterReturningеСҐгАС
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("Demanding a refund"); // зЫЄељУдЇО@AfterThrowing
}
}
 
еИ∞зЫЃеЙНдЄЇж≠ҐпЉМдїЛзїНзЪДйГљжШѓжЧ†еПВжХ∞зЪДPointcutпЉИжШѓжМЗAdviceдЄНдљњзФ®PointcutзЪДеПВжХ∞пЉЙпЉМдЄЛйЭҐеЉАеІЛеЄ¶еПВжХ∞зЪДPointcutгАВ
еЄ¶еПВжХ∞зЪДPointcutпЉИAdviceдљњзФ®PointcutзЪДеПВжХ∞пЉЙ
// ж†ЈеЉП execution(* soundsystem.CompactDisc.playTrack(int)) && args(trackNumber)
ж≥®жДПпЉМйЬАи¶БеЬ®PointcutдЄ≠зїЩеЃЪеПВжХ∞з±їеЮЛпЉМдї•еПК嚥еПВеРНгАВзДґеРОпЉМеЖНзїЩAdviceжЈїеК†зЫЄеРМзЪД嚥еПВеН≥еПѓпЉИз±їеЮЛеТМ嚥еПВеРНпЉЙгАВе¶ВдЄЛпЉЪ
/* ж≥®жДПпЉМињЩйЗМеЃЮзО∞зЪДеКЯиГљжШѓзїЯиЃ°trackNumberзЪДжТ≠жФЊжђ°жХ∞пЉБ */ @Aspect @Component public class TrackCounter { private Map<Integer, Integer> trackCounts = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); // еЃЪдєЙPointcut @Pointcut("execution(* soundsystem.CompactDisc.playTrack(int)) && args(trackNumber)") public void trackPlayed(int trackNumber) {} гАА// AdviceгАА @Before("trackPlayed(trackNumber)") // trackNumberе∞±жШѓpointcutжЦєж≥ХзЪД嚥еПВеРНпЉБпЉБпЉБ public void countTrack(int trackNumber) { int currentCount = getPlayCount(trackNumber); trackCounts.put(trackNumber, currentCount + 1); } гАА// жЩЃйАЪзЪДжЦєж≥ХгАА public int getPlayCount(int trackNumber) { return trackCounts.containsKey(trackNumber) ? trackCounts.get(trackNumber) : 0; } }
 
 
IntroductionеЇФзФ®йГ®еИЖ
Introductionе∞±жШѓзїЩеѓєи±°пЉИBeanпЉЙеЉХеЕ•йЬАи¶БзЪДеКЯиГљпЉМиАМдЄНдњЃжФєеОЯжЬЙдї£з†БгАВпЉИдЊЛе¶Вдљ†жЛњдЄНеИ∞жЇРдї£з†БзЪДжГЕеЖµ~пЉЙ
Spring AOPзЪДеЃЮзО∞жЦєж≥Хе∞±жШѓжЛ¶жИ™иѓЈж±ВпЉМеЖНиљђиАМи∞ГзФ®еЃЮзО∞дЇЖжЙАйЬАжЦєж≥ХзЪДеѓєи±°еН≥еПѓгАВ
з§ЇдЊЛпЉЪ
гААгААзО∞еЬ®йЬАи¶БзїЩPerformanceеЉХеЕ•дЄАдЄ™performEncoreеКЯиГљпЉИеЖНжЭ•дЄАдЄ™гАБеК†жЉФгАБйҐЭе§ЦжЉФеЗЇ зЪДжДПжАЭпЉЙгАВ
гААгААж†єжНЃSpring AOPзЪДеОЯзРЖпЉМжИСдїђйЬАи¶БдЄАдЄ™жЛ•жЬЙиѓ•жЦєж≥ХзЪДBeanпЉМжЙАдї•жИСдїђеЕИеЃЪдєЙдЄАдЄ™жО•еП£пЉМеЖНеОїеЃЮзО∞еЃГгАВ
гААгАА
package aop.performance; /** * EncoreпЉМеК†жЉФгАВеїґйХњжЉФеЗЇзЪДжДПжАЭгАВ * @author Larry * */ public interface Encoreable { void performEncore(); }
package aop.performance; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class EncoreableImpl implements Encoreable{ @Override public void performEncore() { System.out.println("еК†жЉФдЄАеЬЇ~~~"); } }
package aop; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.DeclareParents; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import aop.performance.Encoreable; import aop.performance.EncoreableImpl; /** * AOPеЇФзФ®дєЛIntroductionпЉМе∞±жШѓзїЩеѓєи±°пЉИbeanпЉЙжЈїеК†еКЯиГљпЉМз±їдЉЉjsдєЛз±їзЪДеК®жАБиѓ≠и®АзїЩеѓєи±°жЈїеК†жЦєж≥ХгАВгАВ * @author Larry * */ @Component @Aspect public class IntroductionEncoreable { @DeclareParents(value="aop.performance.Performance+",defaultImpl=EncoreableImpl.class) // з®НеРОиЃ≤ public static Encoreable encoreable; // еЕИеЉХеЕ•йЬАи¶БеЉХеЕ•зЪДжЦєж≥ХжЙАеЬ®зЪДжО•еП£ }
package aop; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; import aop.performance.PerformanceImpl; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackageClasses={ PerformanceImpl.class,IntroductionEncoreable.class }) @EnableAspectJAutoProxy //жњАжіїAspectJ public class JavaConfig { }
package IntroductionEncoreable; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import aop.JavaConfig; import aop.performance.Encoreable; import aop.performance.Performance; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes={JavaConfig.class}) public class IntroductionAOPTest { @Autowired ApplicationContext ac; @Autowired Performance p; @Test public void run1(){ ((Encoreable)p).performEncore(); // йАЪињЗз±їеЮЛеЉЇиљђи∞ГзФ®IntroductionзЪДжЦєж≥ХпЉБпЉБпЉБ } }
дЄКйЭҐе∞±жШѓжµЛиѓХIntroductionзЪДеЕ®йГ®дї£з†БгАВ
йЬАи¶Бж≥®жДПдЄ§зВєпЉЪ
гААгААвС† @DeclareParents FieldпЉМеЕґvalueдЄЇPointcutжЙАеЬ®зЪДз±їпЉИињЩйЗМжШѓжО•еП£пЉМ+и°®з§ЇеЕґжЙАжЬЙеЃЮзО∞з±їжИЦе≠Рз±їпЉЙпЉМdefaultImplеИЩжШѓжО•еП£зЪДйїШиЃ§еЃЮзО∞з±їпЉМиАМFieldеИЩжШѓжЙАйЬАжЦєж≥ХжЙАеЬ®зЪДжО•еП£гАВ
гААгААвС° йАЪињЗз±їеЮЛеЉЇиљђпЉМе∞ЖзЫЃж†ЗBeanиљђжИР@DeclareParents Fieldз±їеЮЛпЉМеЖНеОїи∞ГзФ®жЦєж≥ХпЉБ
 
 
жЬАеРОпЉМXMLдЄ≠йЕНзљЃWeavingзїЗеЕ•пЉМжЗТеЊЧеЉДдЇЖпЉМзЫіжО•дЄКеЫЊеРІ

 
еЬ®XMLдЄ≠пЉМдЄАж†ЈеПѓдї•еЃЪдєЙPointcutпЉМзДґеРОеЬ®еЕґдїЦеЬ∞жЦєеЉХзФ®пЉЪ
<aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="audience"> <aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))" /> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="silenceCellPhones"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/> <aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applause"/> <aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
XMLйЕНзљЃеТМж≥®иІ£йЕНзљЃз±їдЉЉпЉМеФѓдЄАйЬАи¶Бж≥®жДПзЪДжШѓзОѓзїХйАЪзЯ•@AroundпЉМињШжШѓйЬАи¶БжМЗеЃЪдЄАдЄ™жЦєж≥ХпЉМиѓ•жЦєж≥ХжО•жФґProceedingJoinPointеѓєи±°гАВ
е∞±жШѓиѓіпЉМеЃЮйЩЕдЄКеРМ@Aspect ClassзЪД@Around MethodдЄАж†ЈпЉМеП™дЄНињЗзО∞еЬ®еОїжОЙ@AspectеТМ@AroundпЉМжФєдЄЇXMLйЕНзљЃгАВ
package aop; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; public class Audience { public void greet3(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) { try { System.out.println("жЉФеЗЇеЙНеРОи¶БиЗіжДП~A"); jp.proceed(); // TODO:ињЩйЗМињШеПѓдї•и∞ГзФ®еЄ¶еПВжХ∞зЪДпЉБ System.out.println("жЉФеЗЇеЙНеРОи¶БиЗіжДП~B"); } catch (Throwable e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
<aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="audience"> <aop:pointcut id="performance" expression="execution(** aop.performance.Performance.perform(..))" /> <aop:around pointcut-ref="performance" method="greet3"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
 
еП¶е§ЦпЉМXMLйЕНзљЃдЄ≠зЪДеЄ¶еПВжХ∞PointcutпЉМзХ•гАВиІБSpring in Action, 4th Edition¬†¬† p147гАВ
 
XMLдЄ≠IntroductionеЉХеЕ•йЕНзљЃ
 
<aop:aspect> <aop:declare-parents types-matching="aop.performance.Performance+" implement-interface="aop.performance.Encoreable" default-impl="aop.performance.DefaultEncoreable" /> </aop:aspect>
 
жИЦиАЕпЉМдЄНдљњзФ®default-implпЉМиАМдљњзФ®delegate-refгАВ
<bean id="encoreableDelegate" class="aop.performance.DefaultEncoreable" /> <aop:aspect> <aop:declare-parents types-matching="aop.performance.Performance+" implement-interface="aop.performance.Encoreable" delegate-ref="encoreableDelegate" /> </aop:aspect>
 
 
жЬ™еЃМеЊЕзї≠
https://www.cnblogs.com/larryzeal/p/5423411.html








зЫЄеЕ≥жО®иНР
4thгАЛе≠¶дє†зђФиЃ∞ зђђдЄАйГ®еИЖ SpringзЪДж†ЄењГ 1. SpringдєЛжЧЕ дЊЭиµЦж≥®еЕ• AOP beanзЪДеИЭеІЛеМЦињЗз®Л springеЃєеЩ® 2. и£ЕйЕНBean вАЬinitialization on demand holderвАЭеИЫеїЇеНХдЊЛж®°еЉПзЪДзРЖиІ£,еПВиАГ SpringдЄ≠еНХдЊЛзЪДж¶ВењµйЩРдЇОSpringдЄКдЄЛжЦЗдЄ≠пЉМ...
еЖНиАЕпЉМдЄ≠жЦЗзЙИзЪДгАКSpring in Action, 4th EditionгАЛжЙЂжППзЙИеПѓиГљеМЕеРЂдЇЖдЄАдЇЫйҐЭе§ЦзЪДж≥®иІ£жИЦиАЕзђФиЃ∞пЉМињЩдЇЫеПѓиГљжШѓдљЬиАЕжИЦиѓїиАЕеЬ®йШЕиѓїињЗз®ЛдЄ≠жЈїеК†зЪДпЉМеѓєдЇОжЈ±еЕ•зРЖиІ£жЯРдЇЫж¶ВењµеПѓиГљдЉЪжЬЙжЙАеЄЃеК©гАВ жЬАеРОпЉМSpringiA4_SourceCode.zipжЦЗдїґ...
1.зЙИжЬђпЉЪmatlab2014/2019a/2024a 2.йЩД赆ж°ИдЊЛжХ∞жНЃеПѓзЫіжО•ињРи°Мmatlabз®ЛеЇПгАВ 3.дї£з†БзЙєзВєпЉЪеПВжХ∞еМЦзЉЦз®ЛгАБеПВжХ∞еПѓжЦєдЊњжЫіжФєгАБдї£з†БзЉЦз®ЛжАЭиЈѓжЄЕжЩ∞гАБж≥®йЗКжШОзїЖгАВ 4.йАВзФ®еѓєи±°пЉЪиЃ°зЃЧжЬЇпЉМзФµе≠Рдњ°жБѓеЈ•з®ЛгАБжХ∞е≠¶з≠ЙдЄУдЄЪзЪДе§Іе≠¶зФЯиѓЊз®ЛиЃЊиЃ°гАБжЬЯжЬЂе§ІдљЬдЄЪеТМжѓХдЄЪиЃЊиЃ°гАВ
1.зЙИжЬђпЉЪmatlab2014/2019a/2024a 2.йЩД赆ж°ИдЊЛжХ∞жНЃеПѓзЫіжО•ињРи°Мmatlabз®ЛеЇПгАВ 3.дї£з†БзЙєзВєпЉЪеПВжХ∞еМЦзЉЦз®ЛгАБеПВжХ∞еПѓжЦєдЊњжЫіжФєгАБдї£з†БзЉЦз®ЛжАЭиЈѓжЄЕжЩ∞гАБж≥®йЗКжШОзїЖгАВ 4.йАВзФ®еѓєи±°пЉЪиЃ°зЃЧжЬЇпЉМзФµе≠Рдњ°жБѓеЈ•з®ЛгАБжХ∞е≠¶з≠ЙдЄУдЄЪзЪДе§Іе≠¶зФЯиѓЊз®ЛиЃЊиЃ°гАБжЬЯжЬЂе§ІдљЬдЄЪеТМжѓХдЄЪиЃЊиЃ°гАВ
,,еЯЇдЇОSMOзЪДдЄЙзЫЄPMSMжЧ†йАЯеЇ¶дЉ†жДЯеЩ®жОІеИґпЉИеЯЇдЇОеПНж≠£еИЗеЗљжХ∞пЉЙ ,ж†ЄењГеЕ≥йФЃиѓНпЉЪSMOпЉИжїСж®°иІВжµЛеЩ®пЉЙ; дЄЙзЫЄPMSMпЉИж∞Єз£БеРМж≠•зФµжЬЇпЉЙ; жЧ†йАЯеЇ¶дЉ†жДЯеЩ®жОІеИґ; еПНж≠£еИЗеЗљжХ∞; жОІеИґз≥їзїЯгАВ,еЯЇдЇОSMOзЃЧж≥ХзЪДдЄЙзЫЄPMSMжЧ†йАЯеЇ¶дЉ†жДЯеЩ®еПНж≠£еИЗеЗљжХ∞жОІеИґ
зљСзїЬжЦЗеМЦдЇТеК®дЄ≠зЪДиИЖиЃЇеЉХеѓЉдЄОеН±жЬЇеЇФеѓє
дЇЇеКЫиµДжЇР+е§ІжХ∞жНЃ+иЦ™йЕђжК•еСК+жґ®иЦ™и∞ГиЦ™пЉМеЬ®е≠¶дє†гАБеЈ•дљЬзФЯжіїдЄ≠пЉМиґКжЭ•иґКе§ЪзЪДдЇЛеК°йГљдЉЪдљњзФ®еИ∞жК•еСКпЉМйАЪеЄЄжГЕеЖµдЄЛпЉМжК•еСКзЪДеЖЕеЃєеРЂйЗПе§ІгАБзѓЗеєЕиЊГйХњгАВйВ£дєИдїАдєИж†ЈзЪДиЦ™йЕђжК•еСКжЙНжШѓжЬЙжХИзЪДеСҐпЉЯдї•дЄЛжШѓе∞ПзЉЦз≤ЊењГжХізРЖзЪДи∞ГиЦ™зФ≥иѓЈжК•еСКпЉМ搥ињОе§ІеЃґеИЖдЇЂгАВзЫЄдњ°иАБжЭњзЬЛеИ∞ињЩж†ЈзЪДжК•еСКпЉМдЄАеЃЪдЉЪиАГиЩСжґ®иЦ™зЪДеУ¶гАВ
еЖЕеЃєж¶Ви¶БпЉЪжЬђжЦЗеЕ®йЭҐжОҐиЃ®дЇЖе§Іе≠¶зФЯж≤ЙињЈзљСзїЬжЄЄжИПзЪДзО∞зКґеПКжИРеЫ†пЉМеЉЇи∞Гиѓ•йЧЃйҐШеЈ≤дЄ•йЗНељ±еУНе§Іе≠¶зФЯзЪДе≠¶дЄЪеТМдЄ™дЇЇеПСе±ХгАВжНЃзїЯиЃ°жШЊз§ЇпЉМдЄ≠еЫље§Іе≠¶зФЯзљСзїЬжЄЄжИПжИРзШЊжВ£зЧЕзОЗиґЕињЗ15%пЉМйЧЃйҐШеєњж≥ЫдЄФдЄ•йЗНгАВеИЖжЮРжМЗеЗЇж≤ЙињЈеОЯеЫ†жґµзЫЦдЄ™дЇЇеЫ†зі†пЉИе¶ВиЗ™жИСзЃ°зРЖиГљеКЫ犯姱гАБйАГйБњзО∞еЃЮеОЛеКЫпЉЙгАБеЃґеЇ≠еЫ†зі†пЉИдЊЛе¶ВеЃґеЇ≠жХЩиВ≤犯姱еТМеЃґеЇ≠ж∞ЫеЫідЄНеТМи∞РпЉЙгАБе≠¶ж†°еЫ†зі†пЉИе¶Ве§Іе≠¶зЃ°зРЖжЭЊжХ£еТМж†°еЫ≠жЦЗеМЦжіїеК®еМЃдєПпЉЙпЉМдї•еПКз§ЊдЉЪеЫ†зі†пЉИдЊЛе¶ВзљСжЄЄиЃЊиЃ°еРЄеЉХдЇЇеТМзЫСзЃ°йГ®йЧ®дЄНдЄ•пЉЙгАВеЯЇдЇОдї•дЄКжИРеЫ†пЉМжПРеЗЇдЇЖе§Ъе±Вжђ°зїЉеРИж≤їзРЖжЦєж°ИпЉМеМЕжЛђдљЖдЄНйЩРдЇОеЉЇеМЦеЃґеЇ≠жХЩиВ≤еТМж≤ЯйАЪгАБжФєеЦДе§Іе≠¶зЃ°зРЖж®°еЉПгАБдЄ∞еѓМж†°еЫ≠жЦЗеМЦгАБеК†еЉЇзљСзїЬжЄЄжИПеЃ°жЯ•еКЫеЇ¶еТМз§ЊдЉЪењГзРЖеБ•еЇЈиЊЕеѓЉз≠ЙжЦєйЭҐзЪДеѓєз≠ЦгАВ йАВзФ®дЇЇзЊ§пЉЪжЬђз†Фз©ґйАВзФ®дЇОйЂШж†°иЊЕеѓЉеСШгАБењГзРЖе≠¶еЃґгАБжХЩиВ≤жФњз≠ЦеЖ≥з≠ЦдЇЇеСШпЉМдї•еПКеЕ≥ењГйЭТеєіжИРйХњзЪДз§ЊдЉЪеРДзХМдЇЇе£ЂгАВ дљњзФ®еЬЇжЩѓеПКзЫЃж†ЗпЉЪжЬђжЦЗжЧ®еЬ®еЉХиµЈз§ЊдЉЪеѓєиѓ•йЧЃйҐШзЪДеЕ≥ж≥®пЉМеєґдЄЇжХЩиВ≤зХМеТМеЕґдїЦзЫЄеЕ≥зЊ§дљУжПРдЊЫдЇЖиѓ¶зїЖзЪДеПВиАГиµДжЦЩзФ®дЇОеИґеЃЪзЫЄеЇФзЪДеє≤йҐДжО™жЦљпЉМдї•еЗПе∞Се§Іе≠¶зФЯжЄЄжИПжИРзШЊжГЕеЖµзЪДеПСзФЯгАВж≠§е§ЦпЉМдєЯеПѓдЊЫеЃґйХње≠¶дє†зІСе≠¶иВ≤е≠РзЯ•иѓЖгАВ еЕґдїЦиѓіжШОпЉЪйЩ§дЇЖзЫіжО•жПРеЗЇеЕЈдљУж≤їзРЖеКЮж≥Хе§ЦпЉМињШзЙєеИЂжПРеИ∞дЇЖиР•йА†еБ•еЇЈзЪДзљСзїЬжЦЗеМЦзОѓеҐГзЪДйЗНи¶БжАІпЉМжПРеА°е§ЪжЦєеНПдљЬеЕ±дњГе≠¶зФЯеБ•еЇЈеПСе±ХгАВеРМжЧґеСЉеРБињЫдЄАж≠•еК†еЉЇеѓєзљСзїЬжЄЄжИПдЇІдЄЪзЪДз†Фз©ґдЄОзЃ°зРЖпЉМз°ЃдњЭдЇІдЄЪзЪДиЙѓжАІеПСе±ХзЪДеРМжЧґдєЯиГљ
1.зЙИжЬђпЉЪmatlab2014/2019a/2024a 2.йЩД赆ж°ИдЊЛжХ∞жНЃеПѓзЫіжО•ињРи°Мmatlabз®ЛеЇПгАВ 3.дї£з†БзЙєзВєпЉЪеПВжХ∞еМЦзЉЦз®ЛгАБеПВжХ∞еПѓжЦєдЊњжЫіжФєгАБдї£з†БзЉЦз®ЛжАЭиЈѓжЄЕжЩ∞гАБж≥®йЗКжШОзїЖгАВ 4.йАВзФ®еѓєи±°пЉЪиЃ°зЃЧжЬЇпЉМзФµе≠Рдњ°жБѓеЈ•з®ЛгАБжХ∞е≠¶з≠ЙдЄУдЄЪзЪДе§Іе≠¶зФЯиѓЊз®ЛиЃЊиЃ°гАБжЬЯжЬЂе§ІдљЬдЄЪеТМжѓХдЄЪиЃЊиЃ°гАВ
1.зЙИжЬђпЉЪmatlab2014/2019a/2024a 2.йЩД赆ж°ИдЊЛжХ∞жНЃеПѓзЫіжО•ињРи°Мmatlabз®ЛеЇПгАВ 3.дї£з†БзЙєзВєпЉЪеПВжХ∞еМЦзЉЦз®ЛгАБеПВжХ∞еПѓжЦєдЊњжЫіжФєгАБдї£з†БзЉЦз®ЛжАЭиЈѓжЄЕжЩ∞гАБж≥®йЗКжШОзїЖгАВ 4.йАВзФ®еѓєи±°пЉЪиЃ°зЃЧжЬЇпЉМзФµе≠Рдњ°жБѓеЈ•з®ЛгАБжХ∞е≠¶з≠ЙдЄУдЄЪзЪДе§Іе≠¶зФЯиѓЊз®ЛиЃЊиЃ°гАБжЬЯжЬЂе§ІдљЬдЄЪеТМжѓХдЄЪиЃЊиЃ°гАВ
зЯҐйЗПиЊєзХМпЉМи°МжФњеМЇеЯЯиЊєзХМпЉМз≤Њз°ЃеИ∞дє°йХЗи°ЧйБУпЉМеПѓзЫіжО•еѓЉеЕ•arcgisдљњзФ®
TIзїідєЯзЇ≥жХіжµБеЩ®иЃЊиЃ°.rar
иЗ™й©ЊжЄЄдЄ≠зЪДжЙЛжЬЇAPPжО®иНР
1.зЙИжЬђпЉЪmatlab2014/2019a/2024a 2.йЩД赆ж°ИдЊЛжХ∞жНЃеПѓзЫіжО•ињРи°Мmatlabз®ЛеЇПгАВ 3.дї£з†БзЙєзВєпЉЪеПВжХ∞еМЦзЉЦз®ЛгАБеПВжХ∞еПѓжЦєдЊњжЫіжФєгАБдї£з†БзЉЦз®ЛжАЭиЈѓжЄЕжЩ∞гАБж≥®йЗКжШОзїЖгАВ 4.йАВзФ®еѓєи±°пЉЪиЃ°зЃЧжЬЇпЉМзФµе≠Рдњ°жБѓеЈ•з®ЛгАБжХ∞е≠¶з≠ЙдЄУдЄЪзЪДе§Іе≠¶зФЯиѓЊз®ЛиЃЊиЃ°гАБжЬЯжЬЂе§ІдљЬдЄЪеТМжѓХдЄЪиЃЊиЃ°гАВ
1.зЙИжЬђпЉЪmatlab2014/2019a/2024a 2.йЩД赆ж°ИдЊЛжХ∞жНЃеПѓзЫіжО•ињРи°Мmatlabз®ЛеЇПгАВ 3.дї£з†БзЙєзВєпЉЪеПВжХ∞еМЦзЉЦз®ЛгАБеПВжХ∞еПѓжЦєдЊњжЫіжФєгАБдї£з†БзЉЦз®ЛжАЭиЈѓжЄЕжЩ∞гАБж≥®йЗКжШОзїЖгАВ 4.йАВзФ®еѓєи±°пЉЪиЃ°зЃЧжЬЇпЉМзФµе≠Рдњ°жБѓеЈ•з®ЛгАБжХ∞е≠¶з≠ЙдЄУдЄЪзЪДе§Іе≠¶зФЯиѓЊз®ЛиЃЊиЃ°гАБжЬЯжЬЂе§ІдљЬдЄЪеТМжѓХдЄЪиЃЊиЃ°гАВ
иІЖиЃѓйХЬе§ідЄУеИ©е§НзО∞пЉМеЯЇжЬђе§НзО∞
,,OMRON CP1H PLCиДЙеЖ≤жОІеИґдЄЙиљідЉЇжЬНпЉМ з†БеЮЫжЬЇпЉМеЃЮйЩЕй°єзЫЃпЉМз®ЛеЇПзїУжЮДжЄЕжЮРпЉМжЬЙеЃМжХізЪДж≥®йЗКпЉМйЗНе§НеКЯиГљеБЪжИРFBеКЯиГљеЭЧпЉМеЬ®еЕґеЃГй°єзЫЃеПѓдї•еѓЉеЗЇзЫіжО•зФ®пЉМMCGSиІ¶жСЄе±Пз®ЛеЇПпЉМжЬЙзФµж∞ФCADеЫЊзЇЄгАВ ,еЕ≥йФЃиѓНпЉЪOMRON CP1H PLCпЉЫиДЙеЖ≤жОІеИґпЉЫдЄЙиљідЉЇжЬНпЉЫз†БеЮЫжЬЇпЉЫз®ЛеЇПзїУжЮДжЄЕжЩ∞пЉЫеЃМжХіж≥®йЗКпЉЫFBеКЯиГљеЭЧпЉЫMCGSиІ¶жСЄе±Пз®ЛеЇПпЉЫзФµж∞ФCADеЫЊзЇЄгАВ,OMRON PLCдЄЙиљідЉЇжЬНиДЙеЖ≤жОІеИґз®ЛеЇПпЉЪзїУжЮДжЄЕжЩ∞гАБж≥®йЗКеЃМжХіпЉМFBеКЯиГљеЭЧеПѓе§НзФ®пЉМйЕНеРИMCGSиІ¶жСЄе±ПеПКCADеЫЊзЇЄзЪДеЃЮйЩЕй°єзЫЃеЇФзФ®
жШѓдЄАжђЊеЯЇдЇОJAVAзЪДдЄ≤еП£и∞ГиѓХеЈ•еЕЈ,жФѓжМБж≥ҐзЙєзОЗ9600-115200пЉМдїЕдЊЫеПВиАГе≠¶дє†дљњзФ®пЉМ
,,CO2жњАеЕЙеИЗеЙ≤жЬЇйЫХеИїжЬЇжЙУж†ЗжЬЇеЖЩе≠ЧжЬЇеЦЈжґВжЬЇеЈ°иЊєжЬЇжОІеИґиљѓдїґпЉМеМЕеРЂдЄКдљНжЬЇеТМжОІеИґжЭњпЉМдєЯеПѓжЇРз†Б иІЖйҐСе±Хз§ЇеП™дљУзО∞еЈ•дљЬжµБз®ЛеТМеК†еЈ•жХИжЮЬпЉМе¶ВжЮЬжњАеЕЙеКЯзОЗиґ≥е§Яе§ІжЬАењЂйАЯеЇ¶иГљиЈСеИ∞жѓПзІТдЄ§з±≥ жФѓжМБжЦЗдїґж†ЉеЉПиѓіжШОпЉЪ жОІеИґзЙИеТМдЄКдљНжЬЇйАЪдњ°жО•еП£дЄЇзЩЊеЕЖ俕姙зљСжО•еП£пЉМжХ∞жНЃиљљдљУдЄЇж†ЗеЗЖTCPеНПиЃЃ 1.gдї£з†Б 2.жЙУеН∞еЫЊзЙЗ 3.pltж†ЉеЉПжЦЗдїґ 4.жњАеЕЙжЬЇеЬ®еИЗеЙ≤жЬЙжХИзЇњжЭ°жЧґеМАйАЯеИЗеЙ≤ 5.жЬЙжХИзЇњжЭ°еИЗеЙ≤йАЯеЇ¶еТМз©Їз®ЛйАЯеЇ¶еИЖеИЂиЃЊзљЃ 6.з©Їз®ЛињРи°МеЕЈе§ЗеК†еЗПйАЯжОІеИґ 7.еЫЊзЙЗжЙУеН∞жЧґдЄКдљНжЬЇзХМйЭҐеЃЮжЧґжШЊз§ЇжЙУеН∞ињЫеЇ¶ 8.жЙУеЉАзЪДеЫЊзЙЗеТМеی嚥жЦЗдїґеПѓйЉ†ж†ЗзЉ©жФЊеТМжЛЦеК® 9.еЫЊзЙЗж†ЉеЉПиљђеєґдњЭе≠ШиљђеЃМжИРзЪДжМЗеЃЪж†ЉеЉПеЫЊзЙЗ 10.жЙЛеК®еЫЮеОЯзВєжОІеИґ ,ж†ЄењГеЕ≥йФЃиѓНпЉЪ CO2жњАеЕЙеИЗеЙ≤жЬЇ; йЫХеИїжЬЇ; жЙУж†ЗжЬЇ; еЖЩе≠ЧжЬЇ; еЦЈжґВжЬЇ; еЈ°иЊєжЬЇ; жОІеИґиљѓдїґ; дЄКдљНжЬЇ; жОІеИґжЭњ; жЇРз†Б; иІЖйҐСе±Хз§Ї; еЈ•дљЬжµБз®Л; еК†еЈ•жХИжЮЬ; жњАеЕЙеКЯзОЗ; йАЯеЇ¶; дЄ§зІТ; жЦЗдїґж†ЉеЉП; gдї£з†Б; жЙУеН∞еЫЊзЙЗ; pltж†ЉеЉПжЦЗдїґ; жЬЙжХИзЇњжЭ°еИЗеЙ≤; з©Їз®ЛйАЯеЇ¶иЃЊзљЃ; еК†еЗПйАЯжОІеИґ; дЄКдљНжЬЇзХМйЭҐеЃЮжЧґжШЊз§Ї; еЫЊзЙЗзЉ©жФЊеТМжЛЦеК®; еЫЊзЙЗж†ЉеЉПиљђжНҐ; жЙЛеК®еЫЮеОЯзВєжОІеИґгАВ еЕ≥йФЃиѓНзФ®еИЖеПЈйЪФеЉАпЉЪ CO2жњАеЕЙеИЗеЙ≤жЬЇ; еЦЈжґВжЬЇ; жОІеИґиљѓдїґ; gдї£з†Б; еЫЊзЙЗж†ЉеЉПиљђ
1.зЙИжЬђпЉЪmatlab2014/2019a/2024a 2.йЩД赆ж°ИдЊЛжХ∞жНЃеПѓзЫіжО•ињРи°Мmatlabз®ЛеЇПгАВ 3.дї£з†БзЙєзВєпЉЪеПВжХ∞еМЦзЉЦз®ЛгАБеПВжХ∞еПѓжЦєдЊњжЫіжФєгАБдї£з†БзЉЦз®ЛжАЭиЈѓжЄЕжЩ∞гАБж≥®йЗКжШОзїЖгАВ 4.йАВзФ®еѓєи±°пЉЪиЃ°зЃЧжЬЇпЉМзФµе≠Рдњ°жБѓеЈ•з®ЛгАБжХ∞е≠¶з≠ЙдЄУдЄЪзЪДе§Іе≠¶зФЯиѓЊз®ЛиЃЊиЃ°гАБжЬЯжЬЂе§ІдљЬдЄЪеТМжѓХдЄЪиЃЊиЃ°гАВ