- 浏览: 63124 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 广州
-

最新评论
-
weknow619:
详解Spring中Bean的加载(二)链接:http://ww ...
【Spring】详解Spring中Bean的加载 -
moxue0929:
答案答案答案答案答案答案答案vvvv答案答案
【Java每日一题】20170329 -
weknow619:
xiaoyu1985ban 写道编译无法通过。The fina ...
【Java每日一题】20170221 -
xiaoyu1985ban:
编译无法通过。The final local variable ...
【Java每日一题】20170221 -
ericchunli:
world cello
【Java每日一题】20170210
在该文中来讲讲Spring框架中BeanFactory解析bean的过程,该文之前在小编原文中有发表过,要看原文的可以直接点击原文查看,先来看一个在Spring中一个基本的bean定义与使用。
Spring配置文件root.xml定义如下:
下面使用XmlBeanFactory来获取该bean:
这个单元测试运行结果就是输出beanName,上面就是Spring最基本的bean的获取操作,这里我用BeanFactory作为容器来获取bean的操作并不多见,在企业开发中一般是使用功能更完善的ApplicationContext,这里先不讨论这个,下面重点讲解使用BeanFactory获取bean的过程。
现在就来分析下上面的测试代码,看看Spring到底为我们做了什么工作,上面代码完成功能的流程不外乎如此:
1. 读取Spring配置文件root.xml;
2. 根据root.xml中的bean配置找到对应的类的配置,并实例化;
3. 调用实例化后的对象输出结果。
先来看看XmlBeanFactory源码:
从上面可以看出XmlBeanFactory继承了DefaultListableBeanFactory,DefaultListableBeanFactory是Spring注册加载bean的默认实现,它是整个bean加载的核心部分,XmlBeanFactory与它的不同点就是XmlBeanFactory使用了自定义的XML读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader,实现了自己的BeanDefinitionReader读取。
XmlBeanFactory加载bean的关键就在于XmlBeanDefinitionReader,下面看看XmlBeanDefinitionReader的源码(只列出部分):
XmlBeanDefinitionReader继承自AbstractBeanDefinitionReader,下面是AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的源码(只列出部分):
XmlBeanDefinitionReader主要通过以下三步来加载Spring配置文件中的bean:
1. 通过继承自AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的方法,使用ResourLoader将资源文件(root.xml)路径转换为对应的Resource文件;
2. 通过DocumentLoader对Resource文件进行转换,将Resource文件转换为Ducument文件;
3. 通过DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类对Document进行解析,最后再对解析后的Element进行解析。
了解以上基础后,接下来详细分析下一开始例子中的代码:
先看看下面XmlBeanFactory初始化的时序图来进一步了解这段代码的执行,
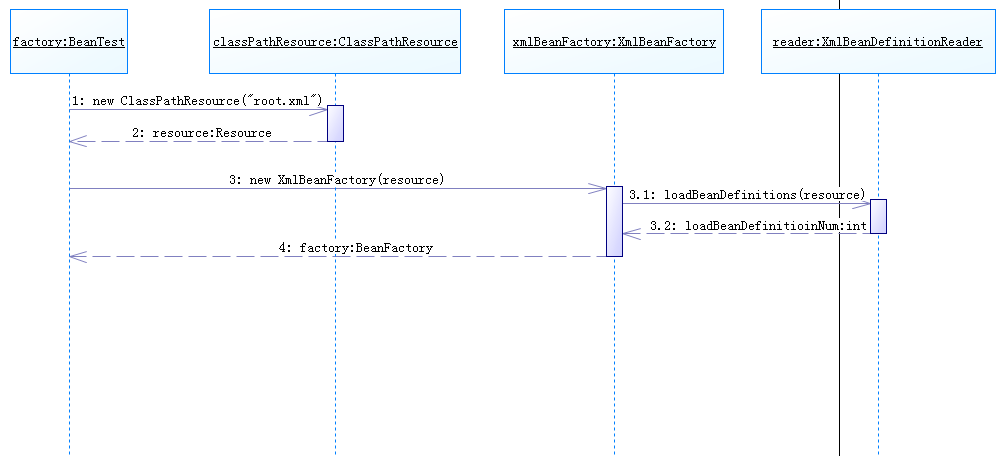
在这里可以看出BeanTest测试类通过向ClassPathResource的构造方法传入spring的配置文件构造一个Resource资源文件的实例对象,再通过这个Resource资源文件来构造我们想要的XmlBeanFactory实例。在前面XmlBeanFactory源码中的构造方法可以看出,
this.reader.loadBeanDefinition(resource)就是资源加载真正的实现,时序图中XmlBeanDefinitionReader加载数据就是在这里完成的。
接下来跟进this.reader.loadBeanDefinition(resource)方法里面,
在loadBeanDefinition(resource)方法里对资源文件resource使用EncodedResource进行编码处理后继续传入loadBeanDefinitions方法,继续跟进loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource))方法源码:
继续跟进doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())方法,这是整个bean加载过程的核心方法,在这个方法执行bean的加载。
跟进doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource)源码:
在doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource)方法里就使用到了前面讲的documentLoader加载Document,这里DocumentLoader是个接口,真正调用的是其实现类DefaultDocumentLoader的loadDocument方法,跟进源码:
从源码可以看出这里先创建DocumentBuilderFactory,再用它创建DocumentBuilder,进而解析inputSource来返回Document对象。得到Document对象后就可以准备注册我们的Bean信息了。
在上面的doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())方法中拿到Document对象后下面就是执行registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource)方法了,看源码:
这里的doc就是上面的loadDocument方法加载转换来的,从上面可以看出主要工作是交给BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions()方法实现的,这里BeanDefinitionDocumentReader是个接口,注册bean功能在默认实现类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的该方法实现,跟进它的源码:
到这里通过doc.getDocumentElement()获得Element对象后,交给doRegisterBeanDefinitions()方法后就是真正执行XML文档的解析了,跟进doRegisterBeanDefinitions()方法源码:
到这里处理流程就很清晰了,先是对profile进行处理,之后就通过parseBeanDefinitions()方法进行文档的解析操作,跟进parseBeanDefinitions()方法源码:
上面if-else语句块中的parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate)和delegate.parseCustomElement(ele)就是对Spring配置文件中的默认命名空间和自定义命名空间进行解析用的。在Spring的XML配置中,默认Bean声明就如前面定义的:
自定义的Bean声明如:
XmlBeanFactory加载bean的整个过程基本就讲解到这里了。
package bean;
public class TestBean {
private String beanName = "beanName";
public String getBeanName() {
return beanName;
}
public void setBeanName(String beanName) {
this.beanName = beanName;
}
}
Spring配置文件root.xml定义如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd">
<bean id="testBean" class="bean.TestBean">
</beans>
下面使用XmlBeanFactory来获取该bean:
public class BeanTest {
private static final java.util.logging.Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BeanTest.class);
@Test
public void getBeanTest() {
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("root.xml"));
TestBean bean = factory.getBean("testBean");
logger.info(bean.getBeanName);
}
}
这个单元测试运行结果就是输出beanName,上面就是Spring最基本的bean的获取操作,这里我用BeanFactory作为容器来获取bean的操作并不多见,在企业开发中一般是使用功能更完善的ApplicationContext,这里先不讨论这个,下面重点讲解使用BeanFactory获取bean的过程。
现在就来分析下上面的测试代码,看看Spring到底为我们做了什么工作,上面代码完成功能的流程不外乎如此:
1. 读取Spring配置文件root.xml;
2. 根据root.xml中的bean配置找到对应的类的配置,并实例化;
3. 调用实例化后的对象输出结果。
先来看看XmlBeanFactory源码:
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}
从上面可以看出XmlBeanFactory继承了DefaultListableBeanFactory,DefaultListableBeanFactory是Spring注册加载bean的默认实现,它是整个bean加载的核心部分,XmlBeanFactory与它的不同点就是XmlBeanFactory使用了自定义的XML读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader,实现了自己的BeanDefinitionReader读取。
XmlBeanFactory加载bean的关键就在于XmlBeanDefinitionReader,下面看看XmlBeanDefinitionReader的源码(只列出部分):
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
private Class<?> documentReaderClass = DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class;
private ProblemReporter problemReporter = new FailFastProblemReporter();
private ReaderEventListener eventListener = new EmptyReaderEventListener();
private SourceExtractor sourceExtractor = new NullSourceExtractor();
private NamespaceHandlerResolver namespaceHandlerResolver;
private DocumentLoader documentLoader = new DefaultDocumentLoader();
private EntityResolver entityResolver;
private ErrorHandler errorHandler = new SimpleSaxErrorHandler(logger);
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader继承自AbstractBeanDefinitionReader,下面是AbstractBeanDefinitionReader的源码(只列出部分):
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinitionReader implements EnvironmentCapable, BeanDefinitionReader {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private Environment environment;
private BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = new DefaultBeanNameGenerator();
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader主要通过以下三步来加载Spring配置文件中的bean:
1. 通过继承自AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的方法,使用ResourLoader将资源文件(root.xml)路径转换为对应的Resource文件;
2. 通过DocumentLoader对Resource文件进行转换,将Resource文件转换为Ducument文件;
3. 通过DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类对Document进行解析,最后再对解析后的Element进行解析。
了解以上基础后,接下来详细分析下一开始例子中的代码:
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("root.xml"));
先看看下面XmlBeanFactory初始化的时序图来进一步了解这段代码的执行,

在这里可以看出BeanTest测试类通过向ClassPathResource的构造方法传入spring的配置文件构造一个Resource资源文件的实例对象,再通过这个Resource资源文件来构造我们想要的XmlBeanFactory实例。在前面XmlBeanFactory源码中的构造方法可以看出,
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
this.reader.loadBeanDefinition(resource)就是资源加载真正的实现,时序图中XmlBeanDefinitionReader加载数据就是在这里完成的。
接下来跟进this.reader.loadBeanDefinition(resource)方法里面,
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
}
在loadBeanDefinition(resource)方法里对资源文件resource使用EncodedResource进行编码处理后继续传入loadBeanDefinitions方法,继续跟进loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource))方法源码:
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
// 通过属性记录已加载的资源
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
// 从resource中获取对应的InputStream,用于下面构造InputSource
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
// 调用doLoadBeanDefinitions方法
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
继续跟进doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())方法,这是整个bean加载过程的核心方法,在这个方法执行bean的加载。
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
/* 省略一堆catch */
}
跟进doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource)源码:
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}
在doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource)方法里就使用到了前面讲的documentLoader加载Document,这里DocumentLoader是个接口,真正调用的是其实现类DefaultDocumentLoader的loadDocument方法,跟进源码:
public class DefaultDocumentLoader implements DocumentLoader {
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
}
从源码可以看出这里先创建DocumentBuilderFactory,再用它创建DocumentBuilder,进而解析inputSource来返回Document对象。得到Document对象后就可以准备注册我们的Bean信息了。
在上面的doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource())方法中拿到Document对象后下面就是执行registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource)方法了,看源码:
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
documentReader.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
// 还没注册bean前的BeanDefinition加载个数
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 加载注册bean
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
// 本次加载注册的BeanDefinition个数
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
这里的doc就是上面的loadDocument方法加载转换来的,从上面可以看出主要工作是交给BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions()方法实现的,这里BeanDefinitionDocumentReader是个接口,注册bean功能在默认实现类DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的该方法实现,跟进它的源码:
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
到这里通过doc.getDocumentElement()获得Element对象后,交给doRegisterBeanDefinitions()方法后就是真正执行XML文档的解析了,跟进doRegisterBeanDefinitions()方法源码:
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
到这里处理流程就很清晰了,先是对profile进行处理,之后就通过parseBeanDefinitions()方法进行文档的解析操作,跟进parseBeanDefinitions()方法源码:
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
// 下面对bean进行处理
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
上面if-else语句块中的parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate)和delegate.parseCustomElement(ele)就是对Spring配置文件中的默认命名空间和自定义命名空间进行解析用的。在Spring的XML配置中,默认Bean声明就如前面定义的:
<bean id="testBean" class="bean.TestBean">
自定义的Bean声明如:
<tx:annotation-driven />
XmlBeanFactory加载bean的整个过程基本就讲解到这里了。
发表评论
-
【Spring】使用Spring和AMQP发送接收消息(下)
2017-06-07 09:28 1249上篇讲了使用RabbitMQ发送消息,本篇则来讲接收消息。 在 ... -
【Spring】详解Spring中Bean的加载
2017-04-06 16:17 1754之前写过bean的解析,这篇来讲讲bean的加载,加载要比be ... -
【Spring】使用Spring和AMQP发送接收消息(中)
2017-03-21 20:05 2507上篇讲了RabbitMQ连接工厂的作用是用来创建RabbitM ... -
【Spring】使用Spring和AMQP发送接收消息(上)
2017-03-19 20:36 1048讲AMQP之前,先讲下传统的JMS的消息模型,JMS中主要有三 ... -
【Spring】使用Spring发送邮件
2017-03-04 10:58 471Spring Email抽象的核心是MailSender接口, ... -
【Spring】使用Spring的AbstractRoutingDataSource实现多数据源切换
2017-02-19 15:26 1178最近因为项目需要在做两个项目间数据同步的需求,具体是项目1的数 ... -
【Spring】浅谈ContextLoaderListener及其上下文与DispatcherServlet的区别
2017-01-22 20:49 729一般在使用SpingMVC开发的项目中,一般都会在web.xm ...






相关推荐
- **概念**:`BeanFactory` 是Spring框架中最基本的IoC容器,它负责管理Bean的生命周期,包括创建、配置和装配等。 - **核心方法**: - `getBean(String name)`:根据Bean的名称获取Bean实例。 - `containsBean...
Spring 框架系列(8)- Spring IOC 实现原理详解之 Bean 实例化(生命周期、循环依赖等) 本文主要研究 Spring 框架中 Bean 的实例化过程,包括 Bean 的生命周期和循环依赖问题的解决方案。在 Spring 框架中,Bean ...
通过设置资源解析器和环境、设置配置路径、初始化 BeanFactory、加载 Bean 定义资源、解析 Bean 定义资源和注册 BeanDefinition,这些步骤组成了 IOC 初始化流程。 在 Spring 框架中,IOC 容器是核心组件,负责管理...
4. 设置BeanFactory:在这个阶段,Bean已经实例化,并且已经设置了BeanFactory。 5. 设置ApplicationContext:在这个阶段,Bean已经实例化,并且已经设置了ApplicationContext。 6. 实现 Aware 接口:在这个阶段,...
XmlBeanFactory 已经被置为 Deprecated,从 Spring 3.1 开始,但是 Spring 并没有定义出更加高级的基于 XML 加载 bean 的 BeanFactory,而是推荐采用更加原生的方式,即组合使用 DefaultListableBeanFactory 和 ...
### Spring Bean 属性详解 Spring框架是Java平台上的一个开源框架,主要用来简化企业级应用程序的开发。在Spring中,核心概念之一就是Bean,它是一个简单的Java对象,由Spring IoC容器管理。Spring通过XML配置文件...
在Spring框架中,`BeanFactory`是工厂模式的一种实现,它负责管理容器中的Bean的生命周期与依赖注入。了解`BeanFactory`及其相关接口的功能对于掌握Spring的核心原理至关重要。 #### 二、`BeanFactory`接口的关键...
### Spring源码解析:从IOC创建到Bean的注册 #### 概述 Spring框架作为Java领域内最流行的轻量级框架之一,其核心是依赖注入(Dependency Injection, DI)和面向切面编程(Aspect Oriented Programming, AOP)。在...
### Spring的Bean配置详解 #### 一、Spring配置文件根元素`<beans>`解析 - **功能概述**:`<beans>`是Spring配置文件的根元素,用来包含一个或多个`<bean>`元素,用于定义Spring容器管理的各种Bean。 #### 二、`...
除了XmlBeanFactory,Spring还提供了其他类型的bean工厂,如ApplicationContext,它不仅包含BeanFactory的所有功能,还增加了消息源、事件发布等高级特性。ApplicationContext通常被视为Spring应用的标准入口点,它...
Spring中Bean的命名方式代码详解 在 Spring 框架中,Bean 的命名方式是非常重要的,因为它关系到 Bean 的唯一性和可读性。在本文中,我们将详细介绍 Spring 中 Bean 的命名方式代码详解,包括 Bean 的命名规则、...
Spring框架广泛运用了多种设计模式,如工厂模式(BeanFactory)、单例模式(Singleton)、代理模式(AOP代理)、装饰器模式(BeanPostProcessor)等,这些模式的运用使得Spring具有高度的灵活性和可扩展性。...
### Spring_IOC详解:深入探索Spring框架的IOC容器原理 #### 引言 Spring框架作为Java企业级应用开发的基石,其核心组件之一便是IOC(Inverse of Control)容器。IOC容器负责管理应用程序中的对象及其依赖关系,...
总之,BeanFactory是Spring容器的基础,负责管理和实例化Bean,而FactoryBean是Spring容器内部的一个特殊组件,用于创建更复杂的对象。两者在Spring框架中协同工作,提供强大的对象管理和依赖注入能力。在面试或实际...
此外,Spring还提供了Bean工厂(BeanFactory)和ApplicationContext作为依赖注入的容器。BeanFactory是Spring中最基本的容器,它可以管理Bean的生命周期和依赖关系;而ApplicationContext不仅包含BeanFactory的所有...
Spring基于xml文件配置Bean过程详解 Spring 框架是一个功能强大且灵活的Java应用程序框架,它提供了一个完整的ioc容器,来管理Bean的生命周期。Spring框架基于xml文件配置Bean是指通过xml文件来配置Bean的创建过程...
在实现原理上,Spring通过解析XML或注解配置来构建BeanDefinition对象,然后根据BeanDefinition创建Bean实例。在处理依赖关系时,Spring使用了依赖注入(DI)的概念,它可以是设值注入(setter-based injection)...
本资料“spring框架,技术详解及使用指导”是一本深入解析Spring框架的电子书,内容详尽且清晰,旨在帮助开发者掌握Spring的核心概念和技术。 首先,Spring的核心特性包括: 1. **依赖注入**:通过DI,Spring框架...
Spring 中使用编码方式动态配置 Bean 详解 在 Spring 框架中,Bean 的配置是通过 XML 文件或注解方式实现的。但是,在某些情况下,我们需要动态地配置 Bean,以满足不同的业务需求。本文将详细介绍如何在 Spring 中...