redis插件的完整配置
input {
redis {
batch_count => 1 #返回的事件数量,此属性仅在list模式下起作用。
data_type => "list" #logstash redis插件工作方式
key => "logstash-test-list" #监听的键值
host => "127.0.0.1" #redis地址
port => 6379 #redis端口号
password => "123qwe" #如果有安全认证,此项为密码
db => 0 #redis数据库的编号
threads => 1 #启用线程数量
}
}
output {
stdout{}
}工作流程
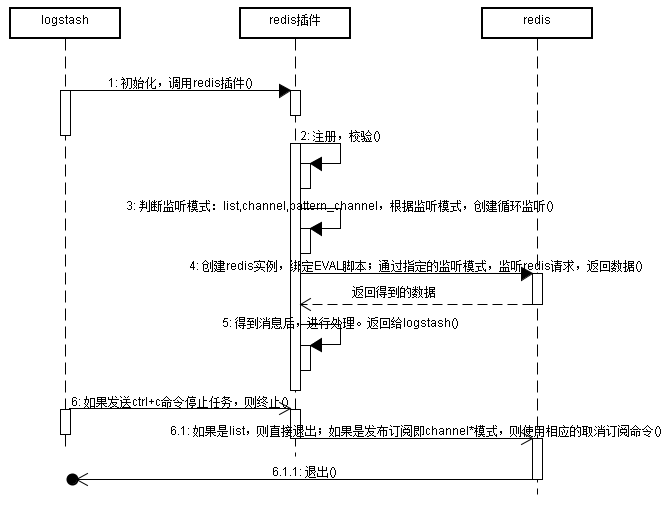
图不够专业,但是大致就如上图所示:
- logstash启动redis插件
- redis插件获取参数,进行校验工作
- 判断监听模式(list,channel,pattern_channel等),根据不同的监听模式创建监听任务
- 创建redis实例,绑定EVAL脚本;通过指定的redis模式,发送请求,监听数据
- redis返回指定内容的数(可能是列表list,也可能是某个特定的频道中的数据)
- 得到的数据,进行处理,返回给logstash
- 如果发送了停止信号,则根据不同的模式,发送不同的命令退出redis。
源码剖析
首先是程序的自定义,这里设置了redis插件需要的参数,默认值,以及校验等。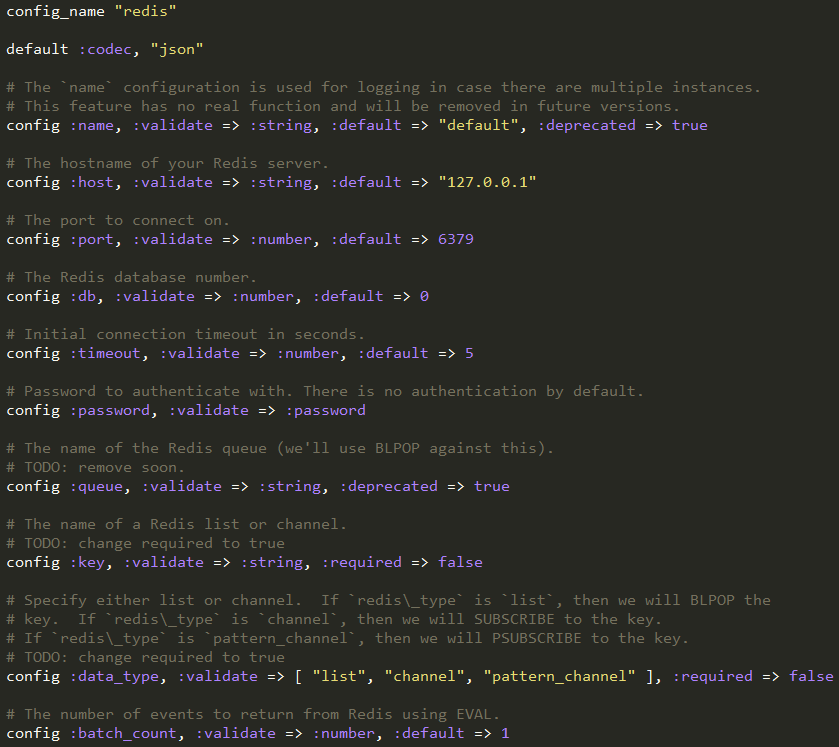
然后注册Redis实例需要的信息,比如key的名字或者url等,可以看到默认的data_type是list模式。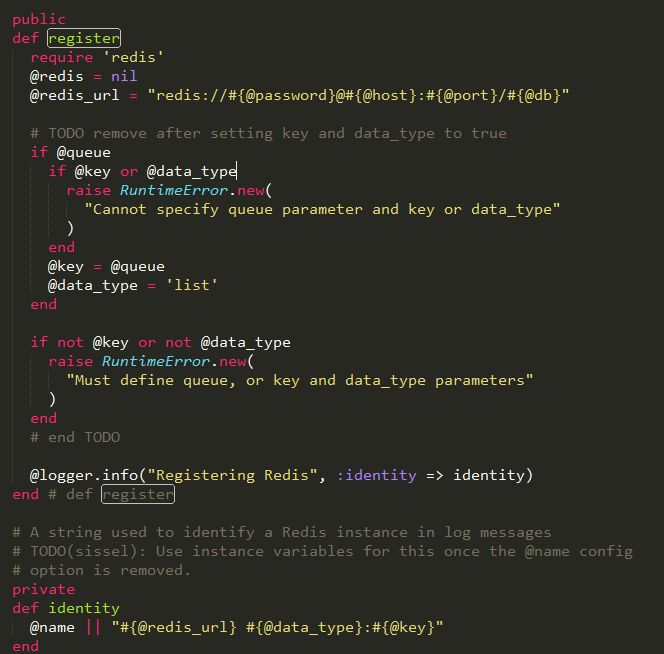
程序运行的主要入口,根据不同的data_type,传递不同的实现方法,然后调用listener_loop执行循环监听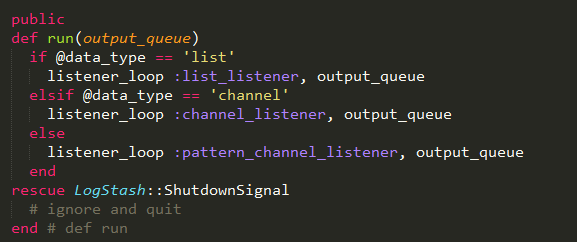
Listner_loop方法传递了两个参数,一个是监听器实现的方法,一个是处理的数据队列。循环是每秒钟执行一次,如果循环标识被设置,则退出。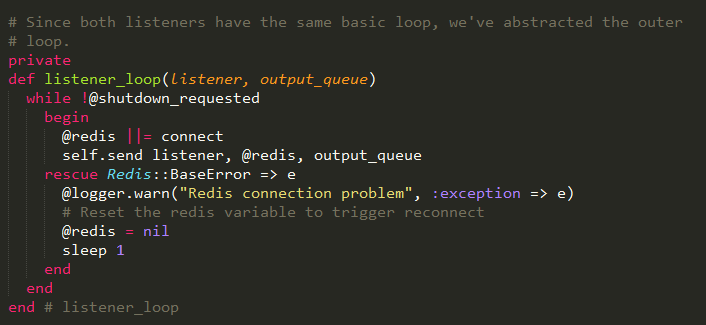
上面的循环方法可以看到,是通过一个参数shutdown_requested来判断是否继续循环。该参数通过tear_down方法设置为true,然后根据不同的模式,指定不同的退出方式。
如果是list模式,则直接退出;如果是channel模式,则发送redis的unsubsribe命令退出;如果是pattern_channel,则发送punsubscribe退出。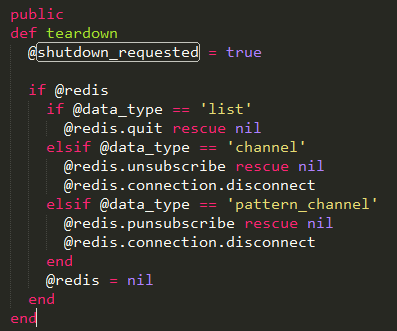
在循环内部,判断是否已经创建了redis实例,如果没有创建,则调用connect方法创建;否则直接执行。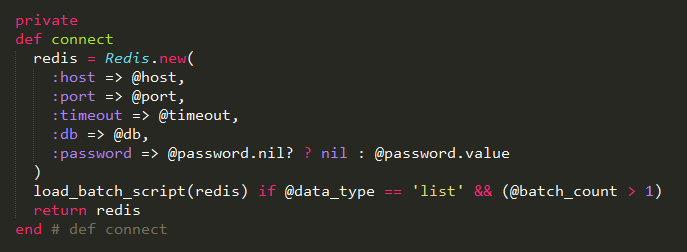
这里前一段是调用Redis的new方法,初始化一个redis实例。紧接着判断batch_count是否大于1,如果等于1,就什么也不做,然后返回redis。
如果batch_count大于1,那么就调用load_batch_script方法,加载Lua脚本,存储到redis中的lua脚本字典中,供后面使用。代码如下: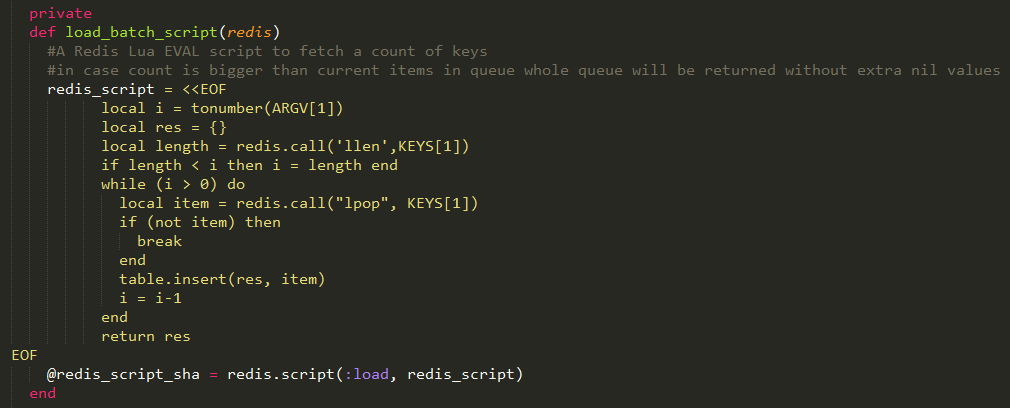
上面的代码应该是这个插件最难理解的部分了。为了弄清楚这段代码的工作,需要了解下面几个知识点:
- lua脚本基本概念
- Redis中的EVAL命令如何使用
- 理解上面脚本的工作
首先,要想运行上面的脚本,必须是Redis2.6+的版本,才支持EVAL,否则会报错!EVAL命令与js中的差不多,就是可以把某一个字符串当做命令解析,其中字符串就包括lua脚本。这样有什么好处呢?
说白了,就是能一次性进行多个操作。比如我们可以在脚本中写入一连串的操作,这些操作会以原子模式,一次性在服务器执行完,在返回回来。
Lua脚本
关于lua脚本,其实没有详细研究的必要,但是一定要知道一个local和table的概念。local是创建本地的变量,这样就不会污染redis的数据。table是lua的一种数据结构,有点类似于json,可以存储数据。
EVAL命令
另外还要知道EVAL命令的使用方法,看下面这个命令,就好理解了!EVAL "return KEYS[1] KEYS[2] ARGV[1] ARGV[2];" 2 name:xing age:13
就会返回:
name
age
xing
13这段代码没有经过真正的操作,但是有助于理解就好!也就是说,EVAL后面跟着一段脚本,脚本后面跟着的就是参数,可以通过KEYS和ARGV数组获得,但是下标从1开始。
再来说说EVAL命令,它的执行过程如下:
- 解析字符串脚本,根据校验和生成lua的方法
- 把校验和和函数放入一个lua_script字典里面,之后就可以通过EVALSHA命令直接使用校验和执行函数。
有了这些理论基础以后,就可以看看上面的代码都做了什么了!
首先是获取参数,这个参数赋值给i;然后创建了一个对象res;紧接着调用llen命令,获得指定list的长度;如果list的长度大于i,则什么也不做;如果小于i,那么i就等于lenth;然后执行命令lpop,取出list中的元素,一共取i次,放入res中,最后返回。
说得通俗点,就是比较一下list元素个数与设置batch_count的值。如果batch_count为5,列表list中有5条以上的数据,那么直接取5条,一次性返回;否则取length条返回。
可以看到这段脚本的作用,就是让logstash一次请求,最多获得batch_count条事件,减小了服务器处理请求的压力。
讲完这段代码,可以看看不同的工作模式的实现代码了:
首先是list的代码,其实就是执行BLPOP命令,获取数据。如果在list模式中,还会去判断batch_count的值,如果是1直接退出;如果大于1,则使用evalsha命令调用之前保存的脚本方法。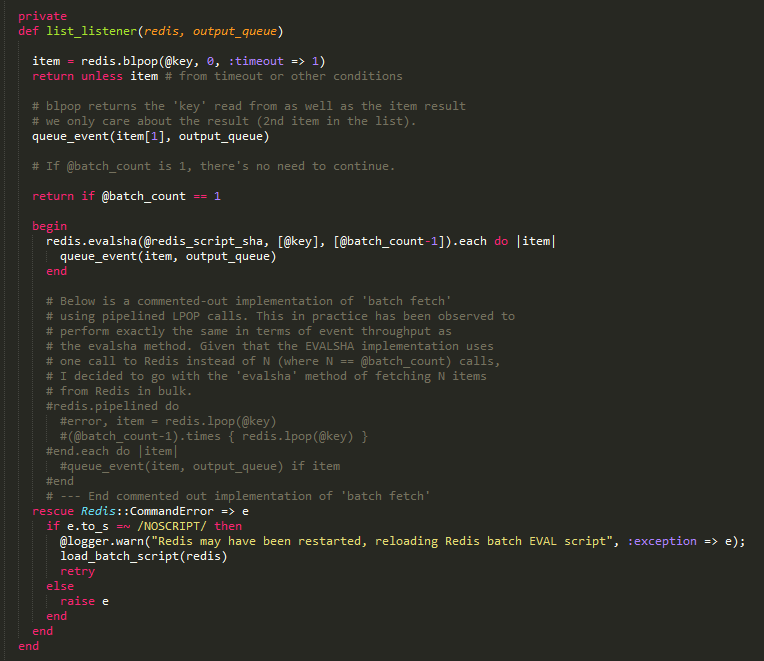
至于channel和pattern_channel,就没啥解释的了,就是分别调用subscribe和psubsribe命令而已。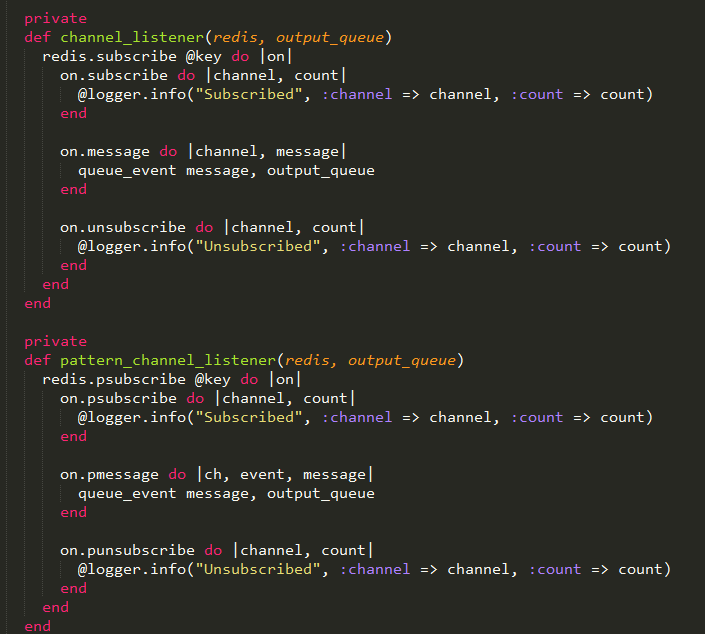
其实最难理解的,就是中间那段lua脚本~明白它的用处,redis插件也就不难理解了。
完整的代码:
# encoding: utf-8
require "logstash/inputs/base"
require "logstash/inputs/threadable"
require "logstash/namespace"
# This input will read events from a Redis instance; it supports both Redis channels and lists.
# The list command (BLPOP) used by Logstash is supported in Redis v1.3.1+, and
# the channel commands used by Logstash are found in Redis v1.3.8+.
# While you may be able to make these Redis versions work, the best performance
# and stability will be found in more recent stable versions. Versions 2.6.0+
# are recommended.
#
# For more information about Redis, see <http://redis.io/>
#
# `batch_count` note: If you use the `batch_count` setting, you *must* use a Redis version 2.6.0 or
# newer. Anything older does not support the operations used by batching.
#
class LogStash::Inputs::Redis < LogStash::Inputs::Threadable
config_name "redis"
default :codec, "json"
# The `name` configuration is used for logging in case there are multiple instances.
# This feature has no real function and will be removed in future versions.
config :name, :validate => :string, :default => "default", :deprecated => true
# The hostname of your Redis server.
config :host, :validate => :string, :default => "127.0.0.1"
# The port to connect on.
config :port, :validate => :number, :default => 6379
# The Redis database number.
config :db, :validate => :number, :default => 0
# Initial connection timeout in seconds.
config :timeout, :validate => :number, :default => 5
# Password to authenticate with. There is no authentication by default.
config :password, :validate => :password
# The name of the Redis queue (we'll use BLPOP against this).
# TODO: remove soon.
config :queue, :validate => :string, :deprecated => true
# The name of a Redis list or channel.
# TODO: change required to true
config :key, :validate => :string, :required => false
# Specify either list or channel. If `redis\_type` is `list`, then we will BLPOP the
# key. If `redis\_type` is `channel`, then we will SUBSCRIBE to the key.
# If `redis\_type` is `pattern_channel`, then we will PSUBSCRIBE to the key.
# TODO: change required to true
config :data_type, :validate => [ "list", "channel", "pattern_channel" ], :required => false
# The number of events to return from Redis using EVAL.
config :batch_count, :validate => :number, :default => 1
public
def register
require 'redis'
@redis = nil
@redis_url = "redis://#{@password}@#{@host}:#{@port}/#{@db}"
# TODO remove after setting key and data_type to true
if @queue
if @key or @data_type
raise RuntimeError.new(
"Cannot specify queue parameter and key or data_type"
)
end
@key = @queue
@data_type = 'list'
end
if not @key or not @data_type
raise RuntimeError.new(
"Must define queue, or key and data_type parameters"
)
end
# end TODO
@logger.info("Registering Redis", :identity => identity)
end # def register
# A string used to identify a Redis instance in log messages
# TODO(sissel): Use instance variables for this once the @name config
# option is removed.
private
def identity
@name || "#{@redis_url} #{@data_type}:#{@key}"
end
private
def connect
redis = Redis.new(
:host => @host,
:port => @port,
:timeout => @timeout,
:db => @db,
:password => @password.nil? ? nil : @password.value
)
load_batch_script(redis) if @data_type == 'list' && (@batch_count > 1)
return redis
end # def connect
private
def load_batch_script(redis)
#A Redis Lua EVAL script to fetch a count of keys
#in case count is bigger than current items in queue whole queue will be returned without extra nil values
redis_script = <<EOF
local i = tonumber(ARGV[1])
local res = {}
local length = redis.call('llen',KEYS[1])
if length < i then i = length end
while (i > 0) do
local item = redis.call("lpop", KEYS[1])
if (not item) then
break
end
table.insert(res, item)
i = i-1
end
return res
EOF
@redis_script_sha = redis.script(:load, redis_script)
end
private
def queue_event(msg, output_queue)
begin
@codec.decode(msg) do |event|
decorate(event)
output_queue << event
end
rescue LogStash::ShutdownSignal => e
# propagate up
raise(e)
rescue => e # parse or event creation error
@logger.error("Failed to create event", :message => msg, :exception => e, :backtrace => e.backtrace);
end
end
private
def list_listener(redis, output_queue)
item = redis.blpop(@key, 0, :timeout => 1)
return unless item # from timeout or other conditions
# blpop returns the 'key' read from as well as the item result
# we only care about the result (2nd item in the list).
queue_event(item[1], output_queue)
# If @batch_count is 1, there's no need to continue.
return if @batch_count == 1
begin
redis.evalsha(@redis_script_sha, [@key], [@batch_count-1]).each do |item|
queue_event(item, output_queue)
end
# Below is a commented-out implementation of 'batch fetch'
# using pipelined LPOP calls. This in practice has been observed to
# perform exactly the same in terms of event throughput as
# the evalsha method. Given that the EVALSHA implementation uses
# one call to Redis instead of N (where N == @batch_count) calls,
# I decided to go with the 'evalsha' method of fetching N items
# from Redis in bulk.
#redis.pipelined do
#error, item = redis.lpop(@key)
#(@batch_count-1).times { redis.lpop(@key) }
#end.each do |item|
#queue_event(item, output_queue) if item
#end
# --- End commented out implementation of 'batch fetch'
rescue Redis::CommandError => e
if e.to_s =~ /NOSCRIPT/ then
@logger.warn("Redis may have been restarted, reloading Redis batch EVAL script", :exception => e);
load_batch_script(redis)
retry
else
raise e
end
end
end
private
def channel_listener(redis, output_queue)
redis.subscribe @key do |on|
on.subscribe do |channel, count|
@logger.info("Subscribed", :channel => channel, :count => count)
end
on.message do |channel, message|
queue_event message, output_queue
end
on.unsubscribe do |channel, count|
@logger.info("Unsubscribed", :channel => channel, :count => count)
end
end
end
private
def pattern_channel_listener(redis, output_queue)
redis.psubscribe @key do |on|
on.psubscribe do |channel, count|
@logger.info("Subscribed", :channel => channel, :count => count)
end
on.pmessage do |ch, event, message|
queue_event message, output_queue
end
on.punsubscribe do |channel, count|
@logger.info("Unsubscribed", :channel => channel, :count => count)
end
end
end
# Since both listeners have the same basic loop, we've abstracted the outer
# loop.
private
def listener_loop(listener, output_queue)
while !@shutdown_requested
begin
@redis ||= connect
self.send listener, @redis, output_queue
rescue Redis::BaseError => e
@logger.warn("Redis connection problem", :exception => e)
# Reset the redis variable to trigger reconnect
@redis = nil
sleep 1
end
end
end # listener_loop
public
def run(output_queue)
if @data_type == 'list'
listener_loop :list_listener, output_queue
elsif @data_type == 'channel'
listener_loop :channel_listener, output_queue
else
listener_loop :pattern_channel_listener, output_queue
end
rescue LogStash::ShutdownSignal
# ignore and quit
end # def run
public
def teardown
@shutdown_requested = true
if @redis
if @data_type == 'list'
@redis.quit rescue nil
elsif @data_type == 'channel'
@redis.unsubscribe rescue nil
@redis.connection.disconnect
elsif @data_type == 'pattern_channel'
@redis.punsubscribe rescue nil
@redis.connection.disconnect
end
@redis = nil
end
end
end # class LogStash::Inputs::Redis






相关推荐
**Logstash 6.6.2 版本详解** Logstash 是一款强大的开源数据处理工具,广泛应用于日志管理和分析领域。它属于 ELK(Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana)堆栈的重要组成部分,旨在帮助用户从各种数据源收集、解析、...
**Windows版Logstash 8.4.2详解** Logstash是一款强大的开源数据收集、转换和转发工具,由Elastic公司开发。它在大数据处理和日志管理领域扮演着重要角色,能够从各种数据源中摄取数据,进行过滤、转换,并将处理后...
如果没有提供配置文件,可以使用 `-e` 参数,传递一个字符串作为配置,例如,仅打印输入的文本,可以使用 `logstash -e ''`,此时Logstash默认从标准输入读取日志,输出到标准输出。 Logstash的工作流程采用管道...
3. Logstash Indexer 从 Redis 中获取日志,并将其发送给 Elasticsearch 进行存储。 4. 用户可以通过 Kibana 结合 Elasticsearch 中的自定义搜索功能进行页面展示。 #### 四、ELK帮助资源 - **ELK 官网**:...
【ELK Stack 6.2.4 知识点详解:收集 Nginx 日志】 ELK Stack(Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana)是用于日志管理和分析的一套开源工具,常用于实时监控和故障排查。在这个场景中,我们将搭建 ELK Stack 6.2.4 版本...
【ELK阅读笔记1】- Logstash 日志处理配置详解 Logstash 是 Elastic Stack(ELK Stack)中的重要组件,负责收集、解析、过滤和转发各种日志数据。本笔记主要探讨基于 Logstash 的日志处理配置语法以及相关知识点。 ...
- `logstash.conf`:Logstash的主要配置文件,包含输入(input)、过滤(filter)和输出(output)部分。输入部分指定从Redis获取数据,过滤部分可能包括字段拆分等操作,输出部分则定义将数据写入Elasticsearch。 ...
使用 Redis 作为中间件,可以提高 Logstash 的可靠性和可扩展性。 **通过 Kafka 传输** Kafka 是另一种流行的中间件,用于高吞吐量的数据流处理,Logstash 可以与 Kafka 结合使用。 ##### Beats **Filebeat** ...
通过使用Redis,可以确保即使在Logstash处理能力暂时不足的情况下,也能有效地缓冲收集到的日志数据,从而避免数据丢失或客户端发送日志时出现阻塞。 ##### 日志过滤处理层:Logstash **Logstash**是一款强大的...