https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/cluster-overview.html
This document gives a short overview of how Spark runs on clusters, to make it easier to understand the components involved. Read through theapplication submission guide to submit applications to a cluster.
Components
Spark applications run as independent sets of processes on a cluster, coordinated by the SparkContext object in your main program (called thedriver program). Specifically, to run on a cluster, the SparkContext can connect to several types of cluster managers (either Spark’s own standalone cluster manager or Mesos/YARN), which allocate resources across applications. Once connected, Spark acquires executors on nodes in the cluster, which are processes that run computations and store data for your application. Next, it sends your application code (defined by JAR or Python files passed to SparkContext) to the executors. Finally, SparkContext sends tasks for the executors to run.
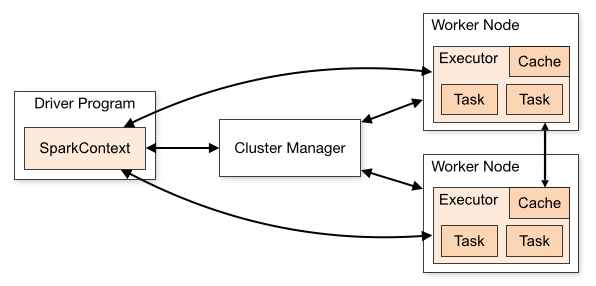
There are several useful things to note about this architecture:
- Each application gets its own executor processes, which stay up for the duration of the whole application and run tasks in multiple threads. This has the benefit of isolating applications from each other, on both the scheduling side (each driver schedules its own tasks) and executor side (tasks from different applications run in different JVMs). However, it also means that data cannot be shared across different Spark applications (instances of SparkContext) without writing it to an external storage system.
- Spark is agnostic to the underlying cluster manager. As long as it can acquire executor processes, and these communicate with each other, it is relatively easy to run it even on a cluster manager that also supports other applications (e.g. Mesos/YARN).
- The driver program must listen for and accept incoming connections from its executors throughout its lifetime (e.g., see spark.driver.port and spark.fileserver.port in the network config section). As such, the driver program must be network addressable from the worker nodes.
- Because the driver schedules tasks on the cluster, it should be run close to the worker nodes, preferably on the same local area network. If you’d like to send requests to the cluster remotely, it’s better to open an RPC to the driver and have it submit operations from nearby than to run a driver far away from the worker nodes.
Cluster Manager Types
The system currently supports three cluster managers:
- Standalone – a simple cluster manager included with Spark that makes it easy to set up a cluster.
- Apache Mesos – a general cluster manager that can also run Hadoop MapReduce and service applications.
- Hadoop YARN – the resource manager in Hadoop 2.
In addition, Spark’s EC2 launch scripts make it easy to launch a standalone cluster on Amazon EC2.
Submitting Applications
Applications can be submitted to a cluster of any type using the spark-submit script. The application submission guide describes how to do this.
Monitoring
Each driver program has a web UI, typically on port 4040, that displays information about running tasks, executors, and storage usage. Simply go to http://<driver-node>:4040 in a web browser to access this UI. The monitoring guide also describes other monitoring options.
Job Scheduling
Spark gives control over resource allocation both across applications (at the level of the cluster manager) and within applications (if multiple computations are happening on the same SparkContext). The job scheduling overview describes this in more detail.
Glossary
The following table summarizes terms you’ll see used to refer to cluster concepts:
| Application | User program built on Spark. Consists of a driver program and executors on the cluster. |
| Application jar | A jar containing the user's Spark application. In some cases users will want to create an "uber jar" containing their application along with its dependencies. The user's jar should never include Hadoop or Spark libraries, however, these will be added at runtime. |
| Driver program | The process running the main() function of the application and creating the SparkContext |
| Cluster manager | An external service for acquiring resources on the cluster (e.g. standalone manager, Mesos, YARN) |
| Deploy mode | Distinguishes where the driver process runs. In "cluster" mode, the framework launches the driver inside of the cluster. In "client" mode, the submitter launches the driver outside of the cluster. |
| Worker node | Any node that can run application code in the cluster |
| Executor | A process launched for an application on a worker node, that runs tasks and keeps data in memory or disk storage across them. Each application has its own executors. |
| Task | A unit of work that will be sent to one executor |
| Job | A parallel computation consisting of multiple tasks that gets spawned in response to a Spark action (e.g. save, collect); you'll see this term used in the driver's logs. |
| Stage | Each job gets divided into smaller sets of tasks called stages that depend on each other (similar to the map and reduce stages in MapReduce); you'll see this term used in the driver's logs. |







相关推荐
大数据时代的到来也促使信息检索研究者探索分布式计算框架下的高效检索方案,如MapReduce和Spark,以处理大规模的数据集。 目前,信息检索领域的前沿研究正朝着更加智能化、个性化和语义化的方向发展。深度学习和...
Get a gentle overview of big data and Spark Learn about DataFrames, SQL, and Datasets-Spark's core APIs-through worked examples Dive into Spark's low-level APIs, RDDs, and execution of SQL and ...
编译原理英文课件:BottoomUp(overview)-5.ppt
电子商务概论英文课件:ch01 Overview of Electronic Commerce.ppt
Recent Advances in Deep Learning: An Overview(深度学习最新进展综述),这篇综述论文列举出了近年来深度学习的重要研究成果,从方法、架构,以及正则化、优化技术方面进行概述。
ERP系统信息化资料:SD-Overview-组织架构、客户数据回顾.doc
这篇名为“Deep Learning in Neural Networks: An Overview”的论文为读者提供了一个全面且深入的深度学习概述,作者们详细介绍了该领域的基本概念、模型以及最新进展。 首先,深度学习的核心在于神经网络。神经...
ERP系统信息化资料:SD-Overview-价格条件、信贷管理、订单发运业务回顾 .doc
Redhat-Linux-Centos-5 Cluster Suite Overview
The recent increase of mobile data usage and emergence of new applications such as MMOG (Mul-timedia Online Gaming), mobile TV, Web 2.0, streaming contents have motivated the 3rd Generation ...
此为计算机入门基本教材,详细的对计算机科学进行了入门介绍。
计算机科学概论第12版,英文版
SAP: hr+overview.ppt
**Overview of Cisco IOS** Cisco IOS(Internetwork Operating System)是Cisco系统设备中使用的操作系统。它为Cisco网络设备提供了基础的操作环境,包括路由、交换、安全等功能。对于Catalyst 2900系列XL交换机而...
In this chapter, I review the main methods and techniques of complex systems science. As a first step, I distinguish among the broad patterns which recur across complex systems,the topics complex ...
Blackhat Arsenal: ModSecurity Overview.pdf
功能包说明packages-overview src : Spark的源代码,包括底层配置,硬件驱动,和各个应用功能包等。 doc : 软硬件依赖包。 使用usage 系统要求 Prequirement System: Ubuntu 14.04+ ROS Version: indigo or kinetic...