1.插入排序
基本思想:
将一个记录插入到已排序好的有序表中,从而得到一个新,记录数增1的有序表。即:先将序列的第1个记录看成是一个有序的子序列,然后从第2个记录逐个进行插入,直至整个序列有序为止。
要点:设立哨兵,作为临时存储和判断数组边界之用。
直接插入排序示例:
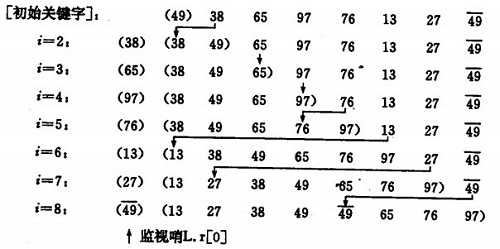
如果碰见一个和插入元素相等的,那么插入元素把想插入的元素放在相等元素的后面。所以,相等元素的前后顺序没有改变,从原无序序列出去的顺序就是排好序后的顺序,所以插入排序是稳定的。
算法的实现:
- public class ArraySort {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ArraySort sort = new ArraySort();
- // 插入排序排序后的数组
- int[] charu = sort.SortChaRu(arraysort);
- for (int n = 0; n < charu.length; n++) {
- //System.out.println(charu[n]);
- }
- /**
- * 插入排序的方法
- *
- * @param ChaRuSort
- * 传入的原始数据
- * @return 返回排序后的数组
- */
- public int[] SortChaRu(int[] ChaRuSort) {
- for (int i = 0; i < ChaRuSort.length; i++) {
- for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
- if (ChaRuSort[j] < ChaRuSort[j - 1]) {
- int temp = ChaRuSort[j];
- ChaRuSort[j] = ChaRuSort[j - 1];
- ChaRuSort[j - 1] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- return ChaRuSort;
- }
public class ArraySort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArraySort sort = new ArraySort();
// 插入排序排序后的数组
int[] charu = sort.SortChaRu(arraysort);
for (int n = 0; n < charu.length; n++) {
//System.out.println(charu[n]);
}
/**
* 插入排序的方法
*
* @param ChaRuSort
* 传入的原始数据
* @return 返回排序后的数组
*/
public int[] SortChaRu(int[] ChaRuSort) {
for (int i = 0; i < ChaRuSort.length; i++) {
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--) {
if (ChaRuSort[j] < ChaRuSort[j - 1]) {
int temp = ChaRuSort[j];
ChaRuSort[j] = ChaRuSort[j - 1];
ChaRuSort[j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return ChaRuSort;
}
运算结果:
- 原始数据11
- 原始数据22
- 原始数据332
- 原始数据223
- 原始数据20
- 原始数据234
- 11
- 20
- 22
- 223
- 234
- 332
原始数据11 原始数据22 原始数据332 原始数据223 原始数据20 原始数据234 11 20 22 223 234 332
2. 插入排序—希尔排序
希尔排序是1959 年由D.L.Shell 提出来的,相对直接排序有较大的改进。希尔排序又叫缩小增量排序
基本思想:
先将整个待排序的记录序列分割成为若干子序列分别进行直接插入排序,待整个序列中的记录“基本有序”时,再对全体记录进行依次直接插入排序。
操作方法:
- 选择一个增量序列t1,t2,…,tk,其中ti>tj,tk=1;
- 按增量序列个数k,对序列进行k 趟排序;
- 每趟排序,根据对应的增量ti,将待排序列分割成若干长度为m 的子序列,分别对各子表进行直接插入排序。仅增量因子为1 时,整个序列作为一个表来处理,表长度即为整个序列的长度。
希尔排序的示例:
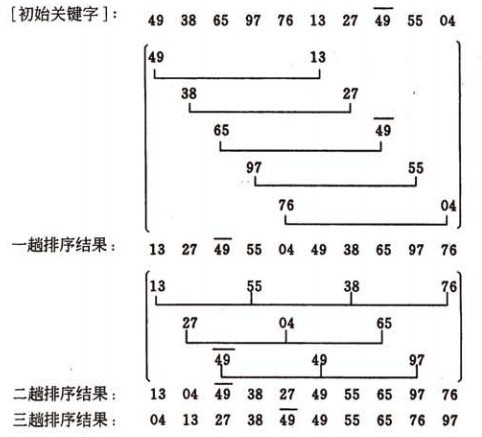
算法实现:
我们简单处理增量序列:增量序列d = {n/2 ,n/4, n/8 .....1} n为要排序数的个数
即:先将要排序的一组记录按某个增量d(n/2,n为要排序数的个数)分成若干组子序列,每组中记录的下标相差d.对每组中全部元素进行直接插入排序,然后再用一个较小的增量(d/2)对它进行分组,在每组中再进行直接插入排序。继续不断缩小增量直至为1,最后使用直接插入排序完成排序。
算法的实现:
- public class ArraySort {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ArraySort sort = new ArraySort();
- // 排序的原始数组
- int[] arraysort = { 11, 22, 332, 223, 20, 234 };
- // 遍历出原始数据
- for (int i = 0; i < arraysort.length; i++) {
- System.out.println("原始数据" + arraysort[i]);
- }
- //希尔排序
- int[] xier = sort.SortXiEr(arraysort);
- for(int x = 0;x<xier.length;x++){
- //System.out.println(xier[x]);
- }
- }
- /**
- * 希尔排序的方法
- *
- * @param XiErSort
- * 数组的原始数据
- * @return 返回排序后的数据
- */
- public int[] SortXiEr(int[] XiErSort) {
- // 分组
- for (int increment = XiErSort.length / 2; increment > 0; increment /= 2) {
- //每组内部排序
- for (int i = increment; i < XiErSort.length; i++) {
- int temp = XiErSort[i];
- int j = 0;
- for (j = i; j >= increment; j -= increment) {
- if (temp < XiErSort[j - increment]) {
- XiErSort[j] = XiErSort[j - increment];
- } else {
- break;
- }
- }
- XiErSort[j] = temp;
- }
- }
- return XiErSort;
- }
- }
public class ArraySort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArraySort sort = new ArraySort();
// 排序的原始数组
int[] arraysort = { 11, 22, 332, 223, 20, 234 };
// 遍历出原始数据
for (int i = 0; i < arraysort.length; i++) {
System.out.println("原始数据" + arraysort[i]);
}
//希尔排序
int[] xier = sort.SortXiEr(arraysort);
for(int x = 0;x<xier.length;x++){
//System.out.println(xier[x]);
}
}
/**
* 希尔排序的方法
*
* @param XiErSort
* 数组的原始数据
* @return 返回排序后的数据
*/
public int[] SortXiEr(int[] XiErSort) {
// 分组
for (int increment = XiErSort.length / 2; increment > 0; increment /= 2) {
//每组内部排序
for (int i = increment; i < XiErSort.length; i++) {
int temp = XiErSort[i];
int j = 0;
for (j = i; j >= increment; j -= increment) {
if (temp < XiErSort[j - increment]) {
XiErSort[j] = XiErSort[j - increment];
} else {
break;
}
}
XiErSort[j] = temp;
}
}
return XiErSort;
}
}
3. 选择排序
基本思想:
在要排序的一组数中,选出最小(或者最大)的一个数与第1个位置的数交换;然后在剩下的数当中再找最小(或者最大)的与第2个位置的数交换,依次类推,直到第n-1个元素(倒数第二个数)和第n个元素(最后一个数)比较为止。
简单选择排序的示例:
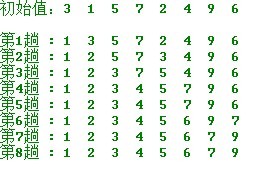
操作方法:
第一趟,从n 个记录中找出关键码最小的记录与第一个记录交换;
第二趟,从第二个记录开始的n-1 个记录中再选出关键码最小的记录与第二个记录交换;
以此类推.....
第i 趟,则从第i 个记录开始的n-i+1 个记录中选出关键码最小的记录与第i 个记录交换,
直到整个序列按关键码有序。
算法实现:
- public class ArraySort {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ArraySort sort = new ArraySort();
- // 排序的原始数组
- int[] arraysort = { 11, 22, 332, 223, 20, 234 };
- // 遍历出原始数据
- for (int i = 0; i < arraysort.length; i++) {
- System.out.println("原始数据" + arraysort[i]);
- }
- // 选择排序排序后的数组
- int[] xuanze = sort.SortXuanZe(arraysort);
- for (int j = 0; j < xuanze.length; j++) {
- // System.out.println(xuanze[j]);
- }
- }
- /**
- * 选择排序排序数组
- *
- * @param XuanZesort
- * 传入的数组
- * @return 返回排序后的数组
- *
- * 思路:在遍历数组时先把第一个当作最小的,然后与后面的比较
- */
- public int[] SortXuanZe(int[] XuanZesort) {
- for (int i = 0; i < XuanZesort.length; i++) {
- // 假设i是最小的数
- int lowerIndex = i;
- for (int j = i + 1; j < XuanZesort.length; j++) {
- if (XuanZesort[j] < XuanZesort[lowerIndex]) {
- // 此时j是最小的
- lowerIndex = j;
- }
- }
- // 交换
- int temp = XuanZesort[i];
- XuanZesort[i] = XuanZesort[lowerIndex];
- XuanZesort[lowerIndex] = temp;
- }
- // 将数组返回
- return XuanZesort;
- }
public class ArraySort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArraySort sort = new ArraySort();
// 排序的原始数组
int[] arraysort = { 11, 22, 332, 223, 20, 234 };
// 遍历出原始数据
for (int i = 0; i < arraysort.length; i++) {
System.out.println("原始数据" + arraysort[i]);
}
// 选择排序排序后的数组
int[] xuanze = sort.SortXuanZe(arraysort);
for (int j = 0; j < xuanze.length; j++) {
// System.out.println(xuanze[j]);
}
}
/**
* 选择排序排序数组
*
* @param XuanZesort
* 传入的数组
* @return 返回排序后的数组
*
* 思路:在遍历数组时先把第一个当作最小的,然后与后面的比较
*/
public int[] SortXuanZe(int[] XuanZesort) {
for (int i = 0; i < XuanZesort.length; i++) {
// 假设i是最小的数
int lowerIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < XuanZesort.length; j++) {
if (XuanZesort[j] < XuanZesort[lowerIndex]) {
// 此时j是最小的
lowerIndex = j;
}
}
// 交换
int temp = XuanZesort[i];
XuanZesort[i] = XuanZesort[lowerIndex];
XuanZesort[lowerIndex] = temp;
}
// 将数组返回
return XuanZesort;
}
4. 交换排序—冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
冒泡排序;http://baihe747.iteye.com/blog/2067294
基本思想:
在要排序的一组数中,对当前还未排好序的范围内的全部数,自上而下对相邻的两个数依次进行比较和调整,让较大的数往下沉,较小的往上冒。即:每当两相邻的数比较后发现它们的排序与排序要求相反时,就将它们互换。
冒泡排序的示例:
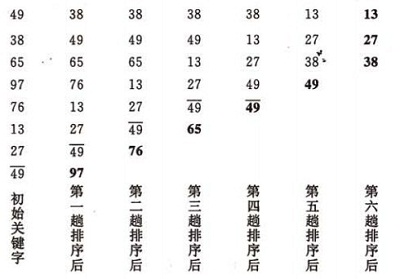
算法的实现:
- public class ArraySort {
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ArraySort sort = new ArraySort();
- // 排序的原始数组
- int[] arraysort = { 11, 22, 332, 223, 20, 234 };
- // 遍历出原始数据
- for (int i = 0; i < arraysort.length; i++) {
- System.out.println("原始数据" + arraysort[i]);
- }
- // 冒泡排序后的数
- int[] maopao = sort.SortMaoPao(arraysort);
- for (int i = 0; i < maopao.length; i++) {
- // System.out.println(maopao[i]);
- }
- }
- /**
- * 冒泡排序的方法
- *
- * @param arraysort传入的原始数组
- * @return返回排序好了的数组
- *
- * 思路:将第一个与后面的比较
- */
- public int[] SortMaoPao(int[] MaoPaosort) {
- for (int i = 0; i < MaoPaosort.length; i++) {
- for (int j = i + 1; j < MaoPaosort.length; j++) {
- // 判断两个数的大小
- if (MaoPaosort[i] > MaoPaosort[j]) {
- int temp = MaoPaosort[i];
- MaoPaosort[i] = MaoPaosort[j];
- MaoPaosort[j] = temp;
- }
- }
- }
- return MaoPaosort;
- }
public class ArraySort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArraySort sort = new ArraySort();
// 排序的原始数组
int[] arraysort = { 11, 22, 332, 223, 20, 234 };
// 遍历出原始数据
for (int i = 0; i < arraysort.length; i++) {
System.out.println("原始数据" + arraysort[i]);
}
// 冒泡排序后的数
int[] maopao = sort.SortMaoPao(arraysort);
for (int i = 0; i < maopao.length; i++) {
// System.out.println(maopao[i]);
}
}
/**
* 冒泡排序的方法
*
* @param arraysort传入的原始数组
* @return返回排序好了的数组
*
* 思路:将第一个与后面的比较
*/
public int[] SortMaoPao(int[] MaoPaosort) {
for (int i = 0; i < MaoPaosort.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < MaoPaosort.length; j++) {
// 判断两个数的大小
if (MaoPaosort[i] > MaoPaosort[j]) {
int temp = MaoPaosort[i];
MaoPaosort[i] = MaoPaosort[j];
MaoPaosort[j] = temp;
}
}
}
return MaoPaosort;
}








相关推荐
数据结构是计算机科学中的核心课程之一,主要研究如何在计算机中高效地组织和存储数据,以便于进行各种操作。上海交通大学的数据结构课件是学习这一主题的重要资源,它涵盖了广泛的知识点,帮助学生深入理解数据结构...
PTA-数据结构与算法题目集 PTA-数据结构与算法题目集 PTA-数据结构与算法题目集 PTA-数据结构与算法题目集 PTA-数据结构与算法题目集 PTA-数据结构与算法题目集 PTA-数据结构与算法题目集 PTA-数据结构与算法题目集 ...
### 数据结构基础知识点详解 #### 一、基础知识概念解析 **1. 算法的复杂性** - **题目**: 算法的计算量的大小称为计算的()。 - **答案**: B. 复杂性 - **解析**: 算法的复杂性通常用来衡量算法执行效率的...
数据结构是计算机科学中的核心课程,它探讨如何高效地组织和管理数据,以便进行快速查找、插入和删除等操作。这份“数据结构1800试题”提供了丰富的练习题目,涵盖了数据结构的主要概念和算法,适合学生进行复习和...
西安理工大学863数据结构真题集锦 作为一名 IT 行业大师,我将根据提供的文件信息,生成相关的知识点,以下是详细的输出结果: 一、数据结构概述 数据结构是计算机科学中的一门基础学科,旨在研究如何存储和组织...