ÕÄ¤ÕłøµĢ┤ńÉåõĖŹµśō’╝īĶĮ¼ĶĮĮĶ»Ęµ│©µśÄÕć║Õżä’╝ÜÕ£©java SpringÕ¤║ńĪĆõĖŖÕ«×ńÄ░Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåµĪåµ×ȵĢÖń©ŗ
õ╗ŻńĀüõĖŗĶĮĮÕ£░ÕØĆ’╝Ühttp://www.zuidaima.com/share/1774096228535296.htm
Õ║öńö©ķĪ╣ńø«Õż¦Ķć┤ńÜäõĮōń│╗ń╗ōµ×ä’╝Ü
┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā
┬Ā
┬ĀĶ»źÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåµĪåµ×ȵ╗ĪĶČ│ńÜäĶ”üµ▒é’╝Ü
┬Ā
- Õ«īµĢ┤ńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖń╗äń╗ćń╗ōµ×ä
- Õ╝éÕĖĖńÜäń╗¤õĖĆÕżäńÉå
- ÕÅ»ķģŹńĮ«’╝īÕÅŚń«ĪÕ╝Å’╝īµ¢╣õŠ┐õĮ┐ńö©
┬Ā
Õ«īµĢ┤ńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖń╗äń╗ćń╗ōµ×ä’╝Ü
- ńö©µłĘÕÅ»õ╗źµ¢╣õŠ┐ńÜäÕ«Üõ╣ēĶć¬ÕĘ▒ńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖ’╝īõĮåµēƵ£ēUncheckedExceptionķ£ĆĶ”üń╗¦µē┐BaseAppRuntimeException’╝īµēƵ£ēńÜächecked ExceptionÕÅ»õ╗źń╗¦µē┐BaseAppException’╝īµł¢ĶĆģķ£ĆĶ”üµŖøÕć║õĖöõĖŹķ£ĆĶ”ücheckµŚČńö©WrapperredAppExceptionÕ░üĶŻģÕÉĵŖøÕć║
- ÕÉłńÉåÕ£░õĮ┐ńö©checkedÕ╝éÕĖĖ
- Exceptionµ£ēÕö»õĖĆńÜäerror code’╝īĶ┐ÖµĀĘńö©µłĘµŖźÕæŖÕ╝éÕĖĖÕÉÄ’╝īÕÅ»õ╗źµĀ╣µŹ«Õ╝éÕĖĖÕÅʵēŠÕł░ńøĖÕ║öException’╝īµŖŖexceptionńø┤µÄźµśŠńż║ń╗Öńö©µłĘõ╣¤µ▓Īµ£ēÕż¬Õż¦ńÜäµäÅõ╣ē’╝īÕ”éõĮĢń║¬ÕĮĢexceptionķéŻÕ░▒µś»õĖŗµ¢ćĶ«▓Õł░ńÜäExceptionHandlerńÜäĶüīĶ┤Żõ║åŃĆé
- Õ”éµ×£µś»ń¼¼õĖēµ¢╣Õīģµŗ¼jdkõĖŁńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖ’╝īķ£ĆĶ”üÕ░üĶŻģµłÉBaseAppExceptionµł¢ĶĆģBaseAppRuntimeExceptionÕÉĵŖøÕć║
┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā
┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā
┬Ā
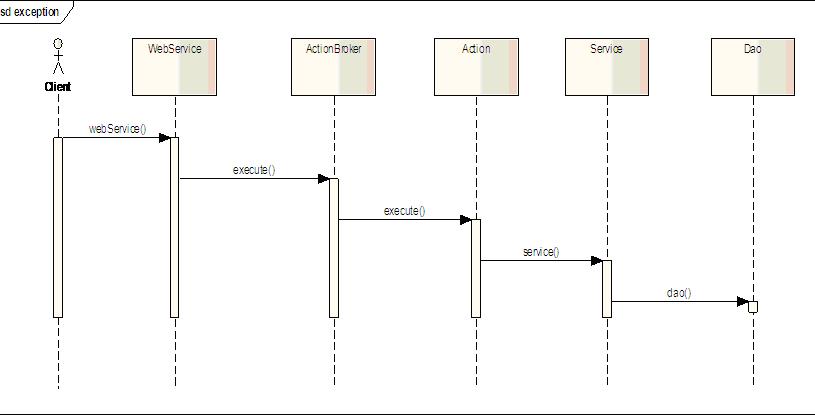
ń╗¤õĖĆńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉå
Õ╝éÕĖĖń╗¤õĖĆÕ£©µĪåµ×ČõĖŁĶ┐øĶĪīÕżäńÉå’╝īõĖŹķ£ĆĶ”üÕ£©õĖŖÕ▒éÕ║öńö©ńÜäõ╗ŻńĀüõĖŁÕÄ╗ÕżäńÉåµŖøÕć║ńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖŃĆéõĖ║õ║åÕ░ĮķćŵŹĢµŹēÕł░µēƵ£ēńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖ’╝īÕ░åÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåµöŠÕ£©õ║åActionBrokerõĖŁ’╝īĶ┐ÖµĀĘÕćĪµś»actionõ╗źÕÉĵŖøÕć║ńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖķāĮÕÅ»õ╗źµŹĢµŹēÕł░’╝īÕøĀõĖ║webserviceÕŬµś»ń«ĆÕŹĢńÜäĶ░āńö©actionń▒╗ńÜäµ¢╣µ│Ģ’╝īõĖĆĶł¼õĖŹõ╝ÜÕć║ńÄ░Õ╝éÕĖĖŃĆéÕĮōµłæõ╗¼µŹĢµŹēÕł░Õ╝éÕĖĖÕÉÄ’╝īķ£ĆĶ”üĶ┐øĶĪīÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉå’╝īÕ«Üõ╣ēõ║åExceptionHandlerµÄźÕÅŻ’╝īńö©µÄźÕÅŻµŖĮĶ▒ĪÕć║Õ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåń▒╗ńÜäÕģĘõĮōÕ«×ńÄ░ŃĆé
┬Ā
┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ┬Ā
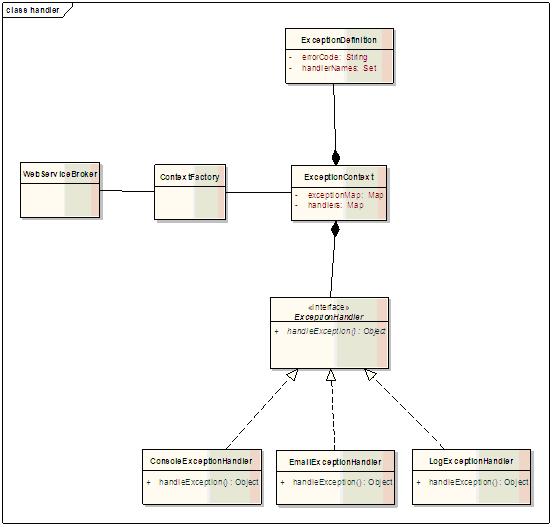
USFContextFactory: ÕłøÕ╗║ExceptionContextńÜäÕĘźÕÄé
package com.ldd0.exception.context;
public class CoreContextFactory {
private static CoreContextFactory instance;
private volatile ExceptionContext exceptionContext;
private Object exceptionContextLock = new Object();
private CoreContextFactory() {
}
public static synchronized CoreContextFactory getInstance() {
if (null == instance) {
instance = new CoreContextFactory();
}
return instance;
}
public ExceptionContext getExceptionContext() {
ExceptionContext tempExpContext = exceptionContext;
if (tempExpContext == null) {
synchronized (exceptionContextLock) {
tempExpContext = exceptionContext;
if (tempExpContext == null)
exceptionContext = tempExpContext = new ExceptionContext();
}
}
return tempExpContext;
}
}
ExceptionContext: ÕŁśµöŠÕģ©Õ▒ĆńÜäexceptionõ┐Īµü»
package com.ldd600.exception.context;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppRuntimeException;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.ConfigException;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.handler.ExceptionHandler;
import com.ldd600.exception.config.ExceptionDefinition;
public class ExceptionContext {
private Map<Class<?>, ExceptionDefinition> exceptionMap;
private Map<String, ExceptionHandler> handlers = new HashMap<String, ExceptionHandler>();
ExceptionContext() {
exceptionMap = new HashMap<Class<?>, ExceptionDefinition>();
}
public boolean containsException(Class<?> expClazz) {
return (exceptionMap.containsKey(expClazz));
}
public void addExceptionHander(Class<?> expClazz, Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazz) {
try {
ExceptionDefinition definition = getRealExceptionDefinition(expClazz);
if (null == definition) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(expClazz.getName() + "not in the context, please configure or add it to the context first!!");
}
ExceptionHandler handler = handlers.get(handlerClazz.getName());
if (null == handler) {
handler = handlerClazz.newInstance();
handlers.put(handlerClazz.getName(), handler);
}
definition.getHandlerNames().add(handlerClazz.getName());
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new ConfigException("Add exception handler to context failure!", ex);
}
}
public void addExceptionHandler(Class<?> expClazz, String errorCode, Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazz) {
Assert.hasLength(errorCode, expClazz + " errorCode must not be null or empty string!");
ExceptionDefinition definition = getRealExceptionDefinition(expClazz);
if(null == definition) {
definition = new ExceptionDefinition(errorCode);
exceptionMap.put(expClazz, definition);
}
addExceptionHander(expClazz, handlerClazz);
}
public void addExceptionHandlers(Class<?> expClazz, Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazzes) {
for(Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazz : handlerClazzes) {
addExceptionHander(expClazz, handlerClazz);
}
}
public void removeExceptionHandler(Class<?> expClazz, Class<? extends ExceptionHandler> handlerClazz) {
Assert.isTrue(containsException(expClazz));
String handlerName = handlerClazz.getName();
getExceptionDefinition(expClazz).getHandlerNames().remove(handlerName);
Collection<ExceptionDefinition> definitons = exceptionMap.values();
boolean isClearHandler = true;
for (ExceptionDefinition expDefinition : definitons) {
if (expDefinition.getHandlerNames().contains(handlerName)) {
isClearHandler = false;
break;
}
}
if (isClearHandler) {
handlers.remove(handlers.get(handlerName));
}
}
public void setExceptionDefinition(Class<?> expClazz, ExceptionDefinition definition) {
exceptionMap.put(expClazz, definition);
}
public ExceptionDefinition getExceptionDefinition(Class<?> expClazz) {
if (containsException(expClazz)) {
return exceptionMap.get(expClazz);
} else if (BaseAppRuntimeException.class.isAssignableFrom(expClazz.getSuperclass())) {
return getExceptionDefinition(expClazz.getSuperclass());
} else {
return null;
}
}
public ExceptionDefinition getRealExceptionDefinition(Class<?> expClazz) {
return exceptionMap.get(expClazz);
}
public List<ExceptionHandler> getExceptionHandlers(Class<?> expClazz){
ExceptionDefinition definition = getExceptionDefinition(expClazz);
if (null != definition) {
Set<String> handlerNames = definition.getHandlerNames();
List<ExceptionHandler> handlerList = new ArrayList<ExceptionHandler>(handlerNames.size());
for (String handlerName : handlerNames) {
ExceptionHandler handler = handlers.get(handlerName);
handlerList.add(handler);
}
List<ExceptionHandler> resultHandlerList = new ArrayList<ExceptionHandler>(handlerList);
return resultHandlerList;
} else {
return Collections.<ExceptionHandler> emptyList();
}
}
public String getErrorCode(Class<?> expClazz){
ExceptionDefinition definition = getExceptionDefinition(expClazz);
if (null != definition) {
return definition.getErrorCode();
} else {
return "";
}
}
}
┬Ā
ExceptionDefinition: Exceptionõ┐Īµü»ÕŹĢÕģā
┬Ā
package com.ldd0.exception.config;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Set;
public class ExceptionDefinition {
private String errorCode;
private Set<String> handlerNames = new LinkedHashSet<String> ();
ExceptionDefinition() {
}
public ExceptionDefinition(String errorCode) {
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public String getErrorCode() {
return errorCode;
}
public void setErrorCode(String errorCode) {
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public Set<String> getHandlerNames() {
return handlerNames;
}
}
┬Ā
ExceptionDefinitonÕ«Üõ╣ēõ║åÕÆīµ¤ÉõĖ¬exceptionńøĖÕģ│ńÜäÕģĘõĮōõ┐Īµü»’╝īµĀ╣µŹ«exceptionńÜäclass nameÕÅ»õ╗źõ╗ÄexceptionContextõĖŁńÜäexceptionMapÕŠŚÕł░µīćÕ«ÜńÜäexceptionńÜäńøĖÕģ│õ┐Īµü»’╝īĶ┐Öõ║øõ┐Īµü»µś»Õ£©ń│╗ń╗¤ÕłØÕ¦ŗÕī¢µŚČĶ»╗ÕÅ¢Õł░exceptionContextõĖŁńÜäŃĆéÕ╣ČõĖöķü┐ÕģŹõ║åexception handlerńÜäķćŹÕżŹÕłØÕ¦ŗÕī¢ŃĆé
┬Ā
ÕÅ»ķģŹńĮ«’╝īÕÅŚń«ĪÕ╝Å’╝īµ¢╣õŠ┐õĮ┐ńö©
┬ĀķććÕÅ¢õĖżń¦ŹķģŹńĮ«µ¢╣Õ╝Å’╝īexceptionńÜäńøĖÕģ│õ┐Īµü»µ»öÕ”éÕ«āńÜäerrorCode’╝ī exceptionHandlersÕÅ»õ╗źķģŹńĮ«Õ£©Õż¢ķā©ńÜäxmlµ¢ćõ╗ČõĖŁ’╝īõ╣¤ÕÅ»õ╗źńö©annotationµĀćµ│©ŃĆéÕ»╣õ║ÄexceptionńÜäÕżäńÉåµś»µ£ēń╗¦µē┐µĆ¦Ķ┤©ńÜä’╝īÕ”éµ×£µ¤ÉõĖ¬exceptionµ▓Īµ£ēÕ£©exceptionContextõĖŁµ│©Õåī’╝īÕ░▒õĮ┐ńö©Õ«āńÜäńłČń▒╗ńÜäķģŹńĮ«õ┐Īµü»ŃĆéÕ”éµ×£µŚĀõ╗╗õĮĢńłČń▒╗Õ£©exceptionContextõĖŁµ│©Õåī’╝īÕ░▒õĮ┐ńö©ķ╗śĶ«żµ£║ÕłČĶ┐øĶĪīÕżäńÉåŃĆé
┬Ā
XML µ¢╣µĪł’╝Ü
┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā ÕøĀõĖ║spring2.0µö»µīüĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēschemaÕŖ¤ĶāĮ’╝īµłæõ╗¼ÕÅ»õ╗źµ¢╣õŠ┐Õ£░ķććńö©Ķć¬ÕĘ▒ńÜäschemaÕŬĶ”üÕ«×ńÄ░NamespaceHandlerÕÆīBeanDefinitionPaser’╝īÕÉÄķØóõĖĆõĖ¬µ»öĶŠāķćŹĶ”ü’╝īÕÅ»õ╗źÕ░åĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēxmlµ¢ćõ╗ČõĖŁńÜäńøĖÕģ│ń▒╗µ│©ÕåīÕł░springńÜäõĖŖõĖŗµ¢ćõĖŁ’╝īµłÉõĖ║spring beanŃĆé
Xml schema:
<xsd:complexType name="exceptionType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element name="level" default="error" minOccurs="0">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:enumeration value="error" />
<xsd:enumeration value="warning" />
<xsd:enumeration value="info" />
<xsd:enumeration value="confirmation" />
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="handler" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string" />
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:sequence>
<xsd:attribute name="errorCode">
<xsd:simpleType>
<xsd:restriction base="xsd:string">
<xsd:whiteSpace value="preserve" />
<xsd:pattern value="LDD600-+\d{1,5}.*" />
</xsd:restriction>
</xsd:simpleType>
</xsd:attribute>
<xsd:attribute name="class" type="xsd:string" use="required" />
</xsd:complexType>
┬Ā
Annotationµ¢╣µĪł’╝Ü
┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā┬Ā JDK1.5õ╗źõĖŖÕ░▒µ£ēõ║åannotation’╝īÕÅ»õ╗źń«ĆÕī¢µłæõ╗¼ńÜäķģŹńĮ«’╝īõĮ┐ÕŠŚķģŹńĮ«õ┐Īµü»ÕÆīõ╗ŻńĀüĶüöń│╗Õ£©õĖĆĶĄĘ’╝īÕó×ÕŖĀõ║åõ╗ŻńĀüńÜäÕÅ»Ķ»╗µĆ¦ŃĆéÕ”éõĮĢÕ£©springõĖŁµ│©ÕåīĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēńÜäannotationÕÆīńö©annotationµĀćµ│©ńÜäclass’╝īÕÅ»õ╗źÕÅéĶĆāµ¢ćń½Ā2ÕÆīµ¢ćń½Ā’╝Ü┬Ā┬Ā ŃĆéÕ»╣õ║ĵ»ÅõĖ¬µ│©Õåīõ║åńÜäclassńö©ExceptionalAnnotationBeanPostProcessorµØźparseÕģĘõĮōńÜäannotationõ┐Īµü»’╝łÕ»╣õ║ÄannotationńÜäparseµ¢╣µ│ĢĶ┐śõ╝ÜÕ£©õ╗źÕÉÄń╗¦ń╗Łµö╣Ķ┐ø’╝ēŃĆé
package com.ldd600.exception.processor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import com.ldd600.exception.annotation.Exceptional;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppException;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppRuntimeException;
import com.ldd600.exception.config.ExceptionDefinition;
import com.ldd600.exception.context.ExceptionContext;
import com.ldd600.exception.context.CoreContextFactory;
public class ExceptionalAnnotationBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if(bean instanceof BaseAppRuntimeException || bean instanceof BaseAppException) {
Exceptional exceptional = bean.getClass().getAnnotation(Exceptional.class);
if(null != exceptional) {
ExceptionContext ctx = CoreContextFactory.getInstance().getExceptionContext();
if(!ctx.containsException(bean.getClass())) {
ExceptionDefinition expDefinition = new ExceptionDefinition(exceptional.errorCode());
ctx.setExceptionDefinition(bean.getClass(), expDefinition);
}
ctx.addExceptionHandlers(bean.getClass(), exceptional.handlers());
return null;
}
}
return bean;
}
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
┬Ā
ń╗ōµ×£µĄŗĶ»Ģ’╝Ü
package com.ldd600.exception.test;
import org.jmock.Expectations;
import org.jmock.Mockery;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import com.ldd600.exception.action.BusinessAction;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppException;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.BaseAppRuntimeException;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.ConfigException;
import com.ldd600.exception.base.handler.ConsoleHandler;
import com.ldd600.exception.context.CoreContextFactory;
import com.ldd600.exception.dto.DefaultRequest;
import com.ldd600.exception.dto.DefaultResponse;
import com.ldd600.exception.dto.Request;
import com.ldd600.exception.dto.Response;
import com.ldd600.exception.webservice.ActionBrokerImpl;
public class ExceptionTest extends DependencyInjectionExceptionTestCase {
Mockery context = new Mockery();
ActionBrokerImpl broker = new ActionBrokerImpl();
final Request request = new DefaultRequest();
final Response response = new DefaultResponse();
@Override
protected String[] getConfigLocations() {
return new String[] { "applicationContext.xml" };
}
public void testExceptionThrow() {
final BusinessAction<Response, Request> action = context
.mock(BusinessAction.class);
final BeanFactory beanFactory = context.mock(BeanFactory.class);
assertThrowing(new Closure() {
public void run() throws Throwable {
context.checking(new Expectations() {
{
allowing(beanFactory).getBean("action");
will(returnValue(action));
one(action).execute(request, response);
will(throwException(new BaseAppException()));
}
});
broker.setExceptionHandler(new ConsoleHandler());
broker.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
broker.execute("action", request, response);
}
}, BaseAppException.class);
}
public void testExceptionalAutoLoad() throws BaseAppException {
final BeanFactory beanFactory = context.mock(BeanFactory.class);
final BusinessAction<Response, Request> action = context
.mock(BusinessAction.class);
context.checking(new Expectations() {
{
allowing(beanFactory).getBean("action");
will(returnValue(action));
one(action).execute(request, response);
will(throwException(new ConfigException()));
}
});
broker.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
broker.execute("action", request, response);
assertEquals(CoreContextFactory.getInstance().getExceptionContext()
.getErrorCode(ConfigException.class), "LDD600-00002");
context.assertIsSatisfied();
}
public void testRuntimeException() {
final BusinessAction<Response, Request> action = context
.mock(BusinessAction.class);
final BeanFactory beanFactory = context.mock(BeanFactory.class);
assertThrowing(new Closure() {
public void run() throws Throwable {
context.checking(new Expectations() {
{
allowing(beanFactory).getBean("action");
will(returnValue(action));
one(action).execute(request, response);
will(throwException(new BaseAppRuntimeException()));
}
});
broker.setExceptionHandler(new ConsoleHandler());
broker.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
broker.execute("action", request, response);
}
}, BaseAppRuntimeException.class);
// test config
assertEquals(CoreContextFactory.getInstance().getExceptionContext()
.getErrorCode(BaseAppRuntimeException.class), "LDD600-00001");
// test handler
assertFalse(response.isSuccess());
assertEquals(response.getErrorCode(), CoreContextFactory.getInstance()
.getExceptionContext().getErrorCode(
BaseAppRuntimeException.class));
context.assertIsSatisfied();
}
public void testCheckedException() {
final BusinessAction<Response, Request> action = context
.mock(BusinessAction.class);
final BeanFactory beanFactory = context.mock(BeanFactory.class);
assertThrowing(new Closure() {
public void run() throws Throwable {
context.checking(new Expectations() {
{
allowing(beanFactory).getBean("action");
will(returnValue(action));
one(action).execute(request, response);
will(throwException(new ExceptionFaker()));
}
});
broker.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
broker.execute("action", request, response);
}
}, ExceptionFaker.class);
// test config
assertEquals(CoreContextFactory.getInstance().getExceptionContext()
.getErrorCode(ExceptionFaker.class), "LDD600-00003");
// test handler
assertFalse(response.isSuccess());
assertEquals(response.getErrorCode(), CoreContextFactory.getInstance()
.getExceptionContext().getErrorCode(
ExceptionFaker.class));
context.assertIsSatisfied();
}
}
ÕÅéĶĆāĶĄäµ¢Ö’╝Ü
µ¢ćń½Ā1’╝Ühttp://www.onjava.com/pub/a/onjava/2006/01/11/exception-handling-framework-for-j2ee.html
µ¢ćń½Ā2’╝Ühttp://sannotations.sourceforge.net/
µ£¼µ¢ćµ║Éõ╗ŻńĀü’╝ܵ║Éõ╗ŻńĀüõĖŗĶĮĮ









ńøĖÕģ│µÄ©ĶŹÉ
õĖ║õ║åõĮ┐Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåńö¤µĢł’╝īĶ┐śķ£ĆĶ”üÕ£©Spring BootķģŹńĮ«µ¢ćõ╗ČõĖŁĶ┐øĶĪīńøĖÕ║öńÜäķģŹńĮ«ŃĆéķĆÜÕĖĖµāģÕåĄõĖŗ’╝īÕÅ»õ╗źķĆÜĶ┐ćÕ£©`application.yml`µł¢`application.properties`õĖŁµĘ╗ÕŖĀõ╗źõĖŗÕåģÕ«╣µØźÕÉ»ńö©Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉå’╝Ü ```yaml spring: main: ...
DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler µś» SpringCloud Gateway µÅÉõŠøńÜäķ╗śĶ«żÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåÕ«×ńÄ░’╝īµłæõ╗¼ÕÅ»õ╗źķĆÜĶ┐ćń╗¦µē┐Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗µØźĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµłæõ╗¼ńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåķĆ╗ĶŠæŃĆé Õ£© Finchley ńēłµ£¼ńÜä Gateway õĖŁ’╝īķ╗śĶ«żõĮ┐ńö© WebFlux ÕĮóÕ╝ÅõĮ£õĖ║Õ║ĢÕ▒éµĪåµ×Č’╝īĶĆī...
õŠŗÕ”é’╝īÕ”éµ×£õĖĆõĖ¬õ╝üõĖÜń║¦Õ║öńö©ķ£ĆĶ”üÕ»╣Õ«ēÕģ©µĆ¦Ķ┐øĶĪīµø┤ń╗åń▓ÆÕ║”ńÜäµÄ¦ÕłČ’╝īÕ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģÕÅ»õ╗źÕ£©Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬µĪåµ×ČńÜäÕ¤║ńĪĆõĖŖµĘ╗ÕŖĀńē╣Õ«ÜńÜäÕ«ēÕģ©µ©ĪÕØŚ’╝īµł¢ĶĆģÕ»╣ńÄ░µ£ēńÜäAOPÕ«×ńÄ░Ķ┐øĶĪīµē®Õ▒Ģ’╝īõ╗źõŠ┐µø┤ÕźĮÕ£░ÕżäńÉåÕ«ēÕģ©ńøĖÕģ│ńÜäÕłćķØóķĆ╗ĶŠæŃĆé ķĪ╣ńø«µĀćńŁŠŌĆ£Java Spring IoC AOP ...
Õ£©õĮ┐ńö©SpringµĪåµ×ČõĖŁńÜä`RestTemplate`Ķ┐øĶĪīHTTPĶ»Ęµ▒鵌Ȓ╝īµłæõ╗¼ÕÅ»ĶāĮõ╝ÜķüćÕł░ÕÉäń¦ŹÕ╝éÕĖĖµāģÕåĄ’╝īՔ鵣ŹÕŖĪĶČģµŚČŃĆüµ£ŹÕŖĪõĖŹÕŁśÕ£©ńŁē’╝īĶ┐Öõ║øÕ╝éÕĖĖķĆÜÕĖĖõ╝ÜÕ»╝Ķć┤ń©ŗÕ║ÅõĖŁµ¢Ł’╝īµŚĀµ│Ģń╗¦ń╗Łµē¦ĶĪīÕÉÄń╗Łõ╗ŻńĀüŃĆéÕ£©Ķ┐Öń¦ŹµāģÕåĄõĖŗ’╝īµłæõ╗¼ÕĖīµ£øÕŹ│õĮ┐Ķ»Ęµ▒éÕż▒Ķ┤ź’╝īõ╣¤ĶāĮĶÄĘÕÅ¢Õł░...
ÕåģÕ«╣µ”éĶ”ü’╝ܵ£¼µ¢ćĶ»”ń╗åõ╗ŗń╗Źõ║åSpring BootńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåµ£║ÕłČ’╝īÕīģµŗ¼JavaµĀćÕćåÕ╝éÕĖĖŃĆüSpringµĪåµ×ČÕ╝éÕĖĖÕÆīĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēÕ╝éÕĖĖńÜäÕżäńÉåµ¢╣Õ╝ÅŃĆéµ¢ćń½ĀĶ«▓Ķ¦Żõ║åÕ”éõĮĢÕłøÕ╗║Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēÕ╝éÕĖĖń▒╗’╝īķģŹńĮ«Õģ©Õ▒ĆÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåÕÖ©’╝īÕ╣ČķĆÜĶ┐ć@ControllerAdviceÕÆī@...
4. **Õ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉå**’╝ÜÕ£©Spring BootõĖŁ’╝īÕÅ»õ╗źõĮ┐ńö©@ControllerAdviceÕÆī@ExceptionHandlerµ│©Ķ¦ŻÕ«×ńÄ░Õģ©Õ▒ĆÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåŃĆéĶ┐ÖÕģüĶ«Ėµłæõ╗¼Õ£©õĖĆõĖ¬Õ£░µ¢╣µŹĢĶÄĘÕ╣ČÕżäńÉåµēƵ£ēµÄ¦ÕłČÕÖ©Õ▒éńÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖ’╝īń╗¤õĖĆĶ┐öÕø×µĀ╝Õ╝ÅÕī¢ńÜäķöÖĶ»»õ┐Īµü»’╝īÕÉīµŚČĶ«░ÕĮĢµŚźÕ┐Ś’╝īµÅÉķ½śń│╗ń╗¤ńÜä...
Õ£©ITĶĪīõĖÜõĖŁ’╝īĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēJavaÕ╝ĆÕÅæµĪåµ×ȵś»µÅÉÕŹćÕ╝ĆÕÅæµĢłńÄćÕÆīõ╗ŻńĀüĶ┤©ķćÅńÜäķćŹĶ”üÕĘźÕģĘŃĆéÕ«āķĆÜÕĖĖÕīģµŗ¼õĖĆń│╗ÕłŚĶ«ŠĶ«Īµ©ĪÕ╝ÅŃĆüń╗äõ╗ČÕÆīÕĘźÕģĘ’╝īµŚ©Õ£©ń«ĆÕī¢ķĪ╣ńø«ńÜäµ×äÕ╗║Ķ┐ćń©ŗ’╝īµÅÉõŠøÕ┐½ķƤńÜäõĖÜÕŖĪķĆ╗ĶŠæµÉŁÕ╗║ĶāĮÕŖø’╝īõ╗źÕÅŖķ½śµĢłńÜäĶĪ©ÕŹĢń«ĪńÉåÕÆīµĢ░µŹ«ÕżäńÉåÕŖ¤ĶāĮŃĆé"Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ē...
Õ£©ITĶĪīõĖÜõĖŁ’╝īSpringµĪåµ×ȵś»Javaõ╝üõĖÜń║¦Õ║öńö©Õ╝ĆÕÅæńÜäķ”¢ķĆēµĪåµ×Č’╝īĶĆīStrutsÕłÖµś»µŚ®µ£¤ķØ×ÕĖĖµĄüĶĪīńÜäMVC’╝łµ©ĪÕ×ŗ-Ķ¦åÕøŠ-µÄ¦ÕłČÕÖ©’╝ēµĪåµ×ČŃĆéµ£¼ĶĄäµ║É"Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēSpringµĪåµ×Č+StrutsµĪåµ×Č’╝łÕåģµ£ēĶ»”ń╗åµ│©ķćŖ’╝ē"µśŠńäȵś»õĖ║õ║åÕĖ«ÕŖ®Õ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģµĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻĶ┐ÖõĖżõĖ¬µĪåµ×ČńÜä...
µ£¼Õ«×ķ¬īµŖźÕæŖķćŹńé╣Ķ«©Ķ«║õ║åÕ£©Spring BootķĪ╣ńø«õĖŁÕ”éõĮĢĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåńÜäńŁ¢ńĢź’╝īõ╗źµÅÉÕŹćńö©µłĘõĮōķ¬īÕÆīń│╗ń╗¤ńÜäÕÅ»ń╗┤µŖżµĆ¦ŃĆé Õ£©Spring BootõĖŁ’╝īÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåķĆÜÕĖĖµś»ķĆÜĶ┐ć@ControllerAdviceµ│©Ķ¦ŻńÜäń▒╗µØźÕ«īµłÉńÜä’╝īĶ┐ÖõĖ¬ń▒╗ń¦░õĖ║Õģ©Õ▒ĆÕ╝éÕĖĖÕżäńÉåÕÖ©ŃĆéÕ«ā...
Õ£©Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµĪåµ×ČõĖŁ’╝īµłæõ╗¼ķ£ĆĶ”üÕ«×ńÄ░ń▒╗õ╝╝ńÜäÕŖ¤ĶāĮ’╝īÕģüĶ«ĖÕ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģķĆēµŗ®õĖŹÕÉīńÜäĶ¦åÕøŠµŖƵ£»’╝īÕ╣ČÕ«Üõ╣ēĶ¦åÕøŠĶ¦Żµ×ÉńŁ¢ńĢźŃĆé µ£ĆÕÉÄ’╝īķģŹńĮ«ÕÆīõŠØĶĄ¢µ│©Õģź’╝łDI’╝ēµś»SpringµĪåµ×ČńÜäõĖĆÕż¦ńē╣Ķē▓ŃĆéSpringķĆÜĶ┐ćXMLµł¢JavaķģŹńĮ«’╝īõ╗źÕÅŖ@Autowiredµ│©Ķ¦ŻÕ«×ńÄ░Õ»╣Ķ▒ĪńÜäÕłøÕ╗║...
Õ£©SpringµĪåµ×ČõĖŁ’╝īSpring ContextõĖŖõĖŗµ¢ćµś»µĀĖÕ┐āń╗äõ╗Čõ╣ŗõĖĆ’╝īÕ«āõĖ║Õ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģµÅÉõŠøõ║åÕ╝║Õż¦ńÜäõŠØĶĄ¢µ│©Õģź’╝łDependency Injection’╝īń«Ćń¦░DI’╝ēÕÆīµÄ¦ÕłČÕÅŹĶĮ¼’╝łInversion of Control’╝īń«Ćń¦░IoC’╝ēÕŖ¤ĶāĮŃĆéµ£¼ń»ćµ¢ćń½ĀÕ░åµĘ▒ÕģźµÄóĶ«©Õ”éõĮĢÕł®ńö©Spring ...
Spring Security µś»õĖĆõĖ¬Õ╝║Õż¦ńÜäÕ«ēÕģ©µĪåµ×Č’╝īÕ╣┐µ│øńö©õ║ÄJava WebÕ║öńö©ńÜäÕ«ēÕģ©ń«ĪńÉå’╝īÕīģµŗ¼Ķ║½õ╗Įķ¬īĶ»üŃĆüµÄłµØāÕÆīĶ«┐ķŚ«µÄ¦ÕłČŃĆéÕ£©Spring BootõĖŁ’╝īSpring SecurityµÅÉõŠøõ║åÕ╝Ćń«▒ÕŹ│ńö©ńÜäÕŖ¤ĶāĮ’╝īõĮ┐ÕŠŚÕ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģÕÅ»õ╗źÕ┐½ķĆ¤Õ£░õĖ║Õ║öńö©µĘ╗ÕŖĀÕ«ēÕģ©ńē╣µĆ¦ŃĆéµ£¼ĶĄäµ║É...
Õ£©"springĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµĀćńŁŠõŠŗÕŁÉ"Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬ķĪ╣ńø«õĖŁ’╝īµłæõ╗¼ÕÅ»õ╗źµĘ▒ÕģźńÉåĶ¦ŻĶ┐ÖõĖĆńē╣µĆ¦’╝īńē╣Õł½µś»ķĆÜĶ┐ćChapter2ÕĘźń©ŗńÜäÕ«×õŠŗµØźÕŁ”õ╣ĀŃĆé SpringµĪåµ×ČńÜäĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµĀćńŁŠķĆÜÕĖĖńö©õ║Äń«ĆÕī¢XMLķģŹńĮ«’╝īµÅÉÕŹćÕÅ»Ķ»╗µĆ¦ÕÆīÕÅ»ń╗┤µŖżµĆ¦ŃĆéĶ┐Öõ║øµĀćńŁŠµś»Õ¤║õ║ÄJavańÜä`org.spring...
Õ£©Javań╝¢ń©ŗĶ»ŁĶ©ĆõĖŁ’╝īSpring BootµĪåµ×ȵÅÉõŠøõ║åõĖĆõĖ¬Õ╝║Õż¦ńÜäÕ¤║ńĪĆµØźÕ┐½ķƤµ×äÕ╗║ÕÆīķā©ńĮ▓Õ║öńö©ń©ŗÕ║ÅŃĆéSpring Bootõ╗źÕģȵ©ĪÕØŚÕī¢ŃĆüĶć¬ÕŖ©Õī¢ķģŹńĮ«ÕÆīÕ╝Ćń«▒ÕŹ│ńö©ńÜäÕŖ¤ĶāĮÕÅŚÕł░Õ╣┐Õż¦Õ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģÕ¢£ńł▒ŃĆéÕ£©Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬ńē╣Õ«ÜńÜäÕ£║µÖ»õĖŁ’╝īµłæõ╗¼µÄóĶ«©ńÜ䵜»Õ”éõĮĢÕ£©Spring Boot...
Spring Security µś»õĖĆõĖ¬Õ╝║Õż¦ńÜäJavaÕ«ēÕģ©µĪåµ×Č’╝īÕ«āõĖ║WebÕ║öńö©ń©ŗÕ║ŵÅÉõŠøõ║åÕģ©ķØóńÜäÕ«ēÕģ©Ķ¦ŻÕå│µ¢╣µĪłŃĆéÕ£©Spring SecurityõĖŁ’╝īÕ»åńĀüńÜäÕŖĀÕ»åµś»ķØ×ÕĖĖÕģ│ķö«ńÜäõĖĆķā©Õłå’╝īÕøĀõĖ║Ķ┐Öńø┤µÄźÕģ│ń│╗Õł░ńö©µłĘµĢ░µŹ«ńÜäÕ«ēÕģ©µĆ¦ŃĆéµ£¼ńż║õŠŗÕ░åõ╗ŗń╗ŹÕ”éõĮĢÕ£©Spring ...
JavaÕ╝éÕĖĖµĪåµ×ČÕżäńÉåµś»Javań╝¢ń©ŗõĖŁÕŹüÕłåÕģ│ķö«ńÜäõĖĆķā©Õłå’╝īõĖ╗Ķ”üµČēÕÅŖÕł░JavaÕ╝éÕĖĖń▒╗ńÜäÕ▒éµ¼Īń╗ōµ×äŃĆüÕ╝éÕĖĖńÜäÕłåń▒╗ŃĆüÕ╝éÕĖĖńÜäÕżäńÉåµ¢╣Õ╝Å’╝īõ╗źÕÅŖÕ”éõĮĢÕ£©Õ«×ķÖģÕ╝ĆÕÅæõĖŁõĮ┐ńö©Õ╝éÕĖĖµĪåµ×ČµØźÕżäńÉåÕÉäń¦ŹĶ┐ÉĶĪīµŚČķöÖĶ»»ŃĆé ķ”¢Õģł’╝īµłæõ╗¼ķ£ĆĶ”üõ║åĶ¦ŻJavańÜäÕ╝éÕĖĖń▒╗ńÜäÕ▒éµ¼Ī...
Ķ┐ÖõĖ¬µēŗÕŖ©Õ«×ńÄ░ńÜäSpringµĪåµ×ČķĪ╣ńø«õĖ╗Ķ”üÕÅéńģ¦õ║åńĮæń╗£õĖŖńÜäĶ¦åķóæµĢÖń©ŗ’╝īńø«ńÜ䵜»õĖ║õ║åÕŁ”õ╣ĀÕÆīÕ«×ĶĘĄŃĆéķĪ╣ńø«õĖŁ’╝īPOM.xmlµ¢ćõ╗Čõ╗ģÕīģÕɽõ║åõĖĆõĖ¬ServletõŠØĶĄ¢ńÜäjarÕīģ’╝īĶ┐ÖĶĪ©µśÄÕ«×ńÄ░õĖ╗Ķ”üķøåõĖŁÕ£©SpringńÜäµĀĖÕ┐āÕŖ¤ĶāĮõĖŖ’╝īÕ”éIoC’╝łµÄ¦ÕłČÕÅŹĶĮ¼’╝ēÕÆīDI’╝łõŠØĶĄ¢µ│©Õģź...
- Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµĪåµ×ČÕƤķē┤õ║åStrutsńÜäµ×ȵ×ä’╝īõĮåÕÅ»ĶāĮÕ£©ÕģĘõĮōÕ«×ńÄ░õĖŖµ£ēµēĆõĖŹÕÉī’╝īµ»öÕ”éĶ»Ęµ▒éÕżäńÉåµ£║ÕłČŃĆüµŗ”µł¬ÕÖ©ŃĆüAOP’╝łķØóÕÉæÕłćķØóń╝¢ń©ŗ’╝ēµö»µīüńŁēŃĆé - Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµĪåµ×ČńÜäõ╝śńé╣Õ£©õ║ÄÕÅ»õ╗źµĀ╣µŹ«ķĪ╣ńø«ķ£Ćµ▒éĶ┐øĶĪīÕ«ÜÕłČ’╝īķü┐ÕģŹĶ┐ćÕ║”õŠØĶĄ¢ń¼¼õĖēµ¢╣Õ║ō’╝īµÅÉķ½śõ╗ŻńĀüńÜäÕÅ»µÄ¦...
µ£¼µĢÖń©ŗÕ░åµÄóĶ«©Õ”éõĮĢõĮ┐ńö©JavaĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµ│©Ķ¦ŻµØźµ©Īµŗ¤Õ«×ńÄ░Ķ┐Öõ║øSpringBootńøĖÕģ│ńÜäµ│©Ķ¦ŻÕŖ¤ĶāĮŃĆé ķ”¢Õģł’╝īµłæõ╗¼µØźń£ŗ`@Autowired`µ│©Ķ¦ŻŃĆé`@Autowired`µś»SpringµĪåµ×ČõĖŁńÜäõĖĆõĖ¬Õģ│ķö«µ│©Ķ¦Ż’╝īńö©õ║ÄĶć¬ÕŖ©ĶŻģķģŹbeanŃĆéÕĮōµłæõ╗¼µā│Õ£©ń▒╗õĖŁµ│©Õģźµ¤ÉõĖ¬õŠØĶĄ¢µŚČ’╝īĶĆī...
Java Ķć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµ│©Ķ¦Żķ¬īĶ»üµś»JavaÕ╝ĆÕÅæõĖŁńÜäõĖĆõĖ¬ķćŹĶ”üńē╣µĆ¦’╝īÕ«āÕģüĶ«ĖÕ╝ĆÕÅæĶĆģÕłøÕ╗║Ķć¬ÕĘ▒ńÜäÕģāµĢ░µŹ«’╝īõ╗źõŠ┐Õ£©ń╝¢Ķ»æµŚČµł¢Ķ┐ÉĶĪīµŚČÕ»╣õ╗ŻńĀüĶ┐øĶĪīķ¬īĶ»üÕÆīÕżäńÉåŃĆéĶć¬Õ«Üõ╣ēµ│©Ķ¦ŻõĖ║õ╗ŻńĀüµÅÉõŠøõ║åķóØÕż¢ńÜäõ┐Īµü»’╝īõĮ┐ÕŠŚń©ŗÕ║ŵø┤ÕģĘÕÅ»Ķ»╗µĆ¦ŃĆüÕÅ»ń╗┤µŖżµĆ¦ÕÆīńüĄµ┤╗µĆ¦ŃĆéÕ£©µ£¼µĪłõŠŗ...