Problem
In a typical data warehousing application, quite often during the ETL cycle you need to perform INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE operations on a TARGET table by matching the records from the SOURCE table. For example, a products dimension table has information about the products; you need to sync-up this table with the latest information about the products from the source table. You would need to write separate INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE statements to refresh the target table with an updated product list or do lookups. Though it seems to be straight forward at first glance, but it becomes cumbersome when you have do it very often or on multiple tables, even the performance degrades significantly with this approach. In this tip we will walk through how to use the MERGE statement and do this in one pass.
Solution
Beginning with SQL Server 2008, now you can use MERGE SQL command to perform these operations in a single statement. This new command is similar to the UPSERT (fusion of the words UPDATE and INSERT.) command of Oracle; it inserts rows that don't exist and updates the rows that do exist. With the introduction of the MERGE SQL command, developers can more effectively handle common data warehousing scenarios, like checking whether a row exists, and then executing an insert or update or delete.
The MERGE statement basically merges data from a source result set to a target table based on a condition that you specify and if the data from the source already exists in the target or not. The new SQL command combines the sequence of conditional INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE commands in a single atomic statement, depending on the existence of a record. The new MERGE SQL command looks like as below:
MERGE <target_table> [AS TARGET] USING <table_source> [AS SOURCE] ON <search_condition> [WHEN MATCHED THEN <merge_matched> ] [WHEN NOT MATCHED [BY TARGET] THEN <merge_not_matched> ] [WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE THEN <merge_ matched> ]; |
The MERGE statement basically works as separate insert, update, and delete statements all within the same statement. You specify a "Source" record set and a "Target" table, and the join between the two. You then specify the type of data modification that is to occur when the records between the two data are matched or are not matched. MERGE is very useful, especially when it comes to loading data warehouse tables, which can be very large and require specific actions to be taken when rows are or are not present.
Putting it all together
In this example I will take a Products table as target table and UpdatedProducts as a source table containing updated list of products. I will then use the MERGE SQL command to synchronize the target table with the source table.
-
First Let's create a target table and a source table and populate some data to these tables.
|
MERGE SQL statement - Part 1 |
--Create a target table CREATE TABLE Products ( ProductID INT PRIMARY KEY, ProductName VARCHAR(100), Rate MONEY ) GO --Insert records into target table INSERT INTO Products VALUES (1, 'Tea', 10.00), (2, 'Coffee', 20.00), (3, 'Muffin', 30.00), (4, 'Biscuit', 40.00) GO --Create source table CREATE TABLE UpdatedProducts ( ProductID INT PRIMARY KEY, ProductName VARCHAR(100), Rate MONEY ) GO --Insert records into source table INSERT INTO UpdatedProducts VALUES (1, 'Tea', 10.00), (2, 'Coffee', 25.00), (3, 'Muffin', 35.00), (5, 'Pizza', 60.00) GO SELECT * FROM Products SELECT * FROM UpdatedProducts GO |
-
Next I will use the MERGE SQL command to synchronize the target table with the refreshed data coming from the source table.
|
MERGE SQL statement - Part 2 |
--Synchronize the target table with --refreshed data from source table MERGE Products AS TARGET USING UpdatedProducts AS SOURCE ON (TARGET.ProductID = SOURCE.ProductID) --When records are matched, update --the records if there is any change WHEN MATCHED AND TARGET.ProductName <> SOURCE.ProductName OR TARGET.Rate <> SOURCE.Rate THEN UPDATE SET TARGET.ProductName = SOURCE.ProductName, TARGET.Rate = SOURCE.Rate --When no records are matched, insert --the incoming records from source --table to target table WHEN NOT MATCHED BY TARGET THEN INSERT (ProductID, ProductName, Rate) VALUES (SOURCE.ProductID, SOURCE.ProductName, SOURCE.Rate) --When there is a row that exists in target table and --same record does not exist in source table --then delete this record from target table WHEN NOT MATCHED BY SOURCE THEN DELETE --$action specifies a column of type nvarchar(10) --in the OUTPUT clause that returns one of three --values for each row: 'INSERT', 'UPDATE', or 'DELETE', --according to the action that was performed on that row OUTPUT $action, DELETED.ProductID AS TargetProductID, DELETED.ProductName AS TargetProductName, DELETED.Rate AS TargetRate, INSERTED.ProductID AS SourceProductID, INSERTED.ProductName AS SourceProductName, INSERTED.Rate AS SourceRate; SELECT @@ROWCOUNT; GO |
When the above is run this is the output. There were 2 updates, 1 delete and 1 insert.
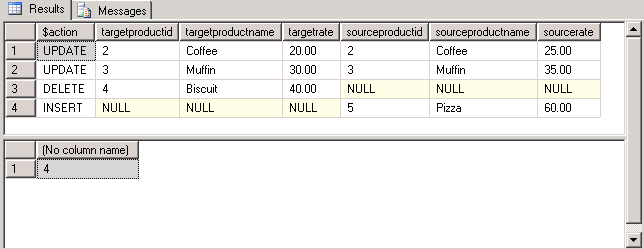
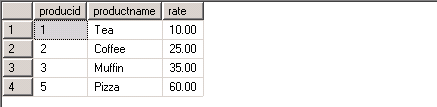
If we select all records from the Products table we can see the final results. We can see the Coffee rate was updated from 20.00 to 25.00, the Muffin rate was updated from 30.00 to 35.00, Biscuit was deleted and Pizza was inserted.
Notes
- The MERGE SQL statement requires a semicolon (;) as a statement terminator. Otherwise Error 10713 is raised when a MERGE statement is executed without the statement terminator.
- When used after MERGE, @@ROWCOUNT returns the total number of rows inserted, updated, and deleted to the client.
- At least one of the three MATCHED clauses must be specified when using MERGE statement; the MATCHED clauses can be specified in any order. However a variable cannot be updated more than once in the same MATCHED clause.
- Of course it's obvious, but just to mention, the person executing the MERGE statement should have SELECT Permission on the SOURCE Table and INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE Permission on the TARGET Table.
- MERGE SQL statement improves the performance as all the data is read and processed only once whereas in previous versions three different statements have to be written to process three different activities (INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE) in which case the data in both the source and target tables are evaluated and processed multiple times; at least once for each statement.
- MERGE SQL statement takes same kind of locks minus one Intent Shared (IS) Lock that was due to the select statement in the ‘IF EXISTS' as we did in previous version of SQL Server.
- For every insert, update, or delete action specified in the MERGE statement, SQL Server fires any corresponding AFTER triggers defined on the target table, but does not guarantee on which action to fire triggers first or last. Triggers defined for the same action honor the order you specify.
Next Steps
- Review "MERGE (Transact-SQL)" on MSDN.
- Review Chad Boyd's blog.
About the author
View all my tips
Recommended For You
Comments and Feedback:
| Tuesday, March 10, 2009 - 10:54:55 AM - jcelko | Read The Tip |
|
Very nice job! The only thing I would add is an example with more predicates in the WHEN clause -- WHEN MATCHED AND SOURCE. foobar > TARGET.foobar THEN .. WHEN MATCHED AND SOURCE. foobar <= TARGET.foobar THEN .. You can get a lot of power in one statement and avoid procedural coding.
|
| Wednesday, March 11, 2009 - 1:33:23 PM - arshad0384 | Read The Tip |
|
First of all thanks for your appreciation and thanks again for addition, this will help the readers. |
| Tuesday, September 28, 2010 - 1:46:27 PM - kv | Read The Tip |
| How do we use the merge function when the source and target are on different databases? |
| Thursday, March 10, 2011 - 5:09:03 PM - Don | Read The Tip |
|
Best example and explanation of a multi-matched/not matched merge I have encountered. Well Done! |
| Friday, May 04, 2012 - 3:52:15 PM - joseph Jelasker | Read The Tip |
|
Sorry Please avoid the previous request becaust it has some typo mistakes..Please consider this. i have to have 3 insert statements ,to Target Table, inside "Not MATCHED BLOCK" .I can't do bulk insert because the subsequence insert has to take the previously inserted Identity Column(basically primary key).. i fail to do that.can you pls provide me the solution..
Thanks in Advance,Joseph S. Jelaskar |
| Monday, May 14, 2012 - 5:59:56 PM - George Quiroga | Read The Tip |
|
Will the MERGE work if the target table is not identical to the source table? For instance my target table only has a subset of the columns that are in the source table and it is those columns that I want updated. The columns are named the same in both tables but they are in different positions since the source table has many more columns than the destination table. Thanks, GQ |
| Friday, May 25, 2012 - 10:49:28 AM - Chandrashekar Venkatraman | Read The Tip |
|
Very Good Post. Am going to use this for a project of mine. |
| Wednesday, May 30, 2012 - 6:14:47 AM - sylvia moestl vasilik | Read The Tip |
|
Good solid sample code that I'll use again - especially like the output of the different actions (insert, delete, update) which I didn't realize you could do. |
| Thursday, June 21, 2012 - 6:27:16 AM - vinod | Read The Tip |
|
Nice one.... Thank you:) |
| Monday, July 30, 2012 - 10:11:20 PM - Vishal | Read The Tip |
|
Good 1 !! |
| Sunday, August 05, 2012 - 9:30:37 PM - SSMS | Read The Tip |
|
Can we use merge for tables from 2 different databases, for example the source table is from staging database and the targer table is in live database? |
| Friday, August 10, 2012 - 8:38:41 AM - Carrie Chung | Read The Tip |
|
Good and clear example to explain the concept. |
| Monday, August 13, 2012 - 2:11:51 AM - Arshad | Read The Tip |
|
Thanks Carrie Chung for your appreciation! |
| Friday, August 24, 2012 - 12:36:58 PM - Leo Korogodski | Read The Tip |
|
What if you don't have a source table? I want to insert a single row (id, value1, value2, value3, ...) if the id doesn't match or update the existing row if the id does match. Do I really have to create a one-row temporary table for this? |
| Wednesday, November 14, 2012 - 1:26:58 AM - Achilles | Read The Tip |
|
Thanks, solved my issue |
| Wednesday, August 07, 2013 - 12:54:52 PM - Abraham Babu | Read The Tip |
|
I do have a Update Trigger in a table. Update Trigger works fine when separate Update statement is fired. However, when MERGE statement issues a UPDATE command, the trigger is not invoked. Is there any precaution i need to make here? Regards, Abraham Babu |
| Thursday, September 12, 2013 - 1:06:39 PM - John | Read The Tip |
|
I do have one question regarding the MERGE command. Can it handle an update and then an insert. For example, if there is a match between the Target and Source then I want one field in the Target updated and then the Source record added. How would this be done in the MERGE command? Since SQL keeps giving the error that it does not allow INSERTS on MATCHES. Regards, John |
| Thursday, September 12, 2013 - 2:29:11 PM - Arshad Ali | Read The Tip |
|
Yes John, I think you are right you can use either UPDATE or INSERT at one time. But that does not mean you cannot achieve what you want to. There is a trick for this. Here is a tip which takes similar approach for managing slowly changing dimension. (it updates the matching target record and then insert the matched source record into target table along with the new records). http://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/2883/using-the-sql-server-merge-statement-to-process-type-2-slowly-changing-dimensions/ Please let me know if you face any issue.
|
| Monday, October 07, 2013 - 11:08:18 AM - Joan | Read The Tip |
|
Thanks for this useful post. |
| Tuesday, December 03, 2013 - 12:57:07 PM - Sean Ed | Read The Tip |
|
Thanks for the script! It helped me design my import.
One thind I'd recommend adding for indexes is an IS NOT NULL statement for the inserts. Even if there isn't a null, I saw an instance where the script was stopped with an error without the statement.
|
| Tuesday, April 08, 2014 - 10:15:48 AM - Erhan | Read The Tip |
|
Very useful, thank you! |





 Print
Print




相关推荐
在SQL Server中,触发器是一种数据库对象,它可以在数据更改(INSERT、UPDATE或DELETE)时自动执行。在处理大量数据的Merge操作时,触发器可能会一次性处理多行,这可能导致性能问题或者不符合预期的行为。标题和...
非常经典的SQL经验,适合于数据库初学者及长期从事软件开发者
delete the data using the DELETE statement, and how to update existing data using the UPDATE statement. This chapter also covers the SELECT…INTO, MERGE, and TRUNCATE TABLE statements, and it ...
Get started with the ... update, delete, and merge data Go beyond the fundamentals with pivoting techniques and set grouping Isolate inconsistent data and address deadlock and blocking scenarios
Pro SQL Server 2008 Replication is for Microsoft database developers and administrators who want to learn about the different types of replication and those best suited to SQL Server 2008. This book ...
SQLServer 2008中SQL增强之三 Merge(在一条语句中使用Insert,Update,Delete) SQL Server 2008中提供了一个增强的SQL命令Merge,用法参看MSDN:http://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/bb510625.aspx。Merge命令...
`Merge`函数是SQL Server 2008引入的一个强大的数据操纵语言(DML)关键字,它可以合并`Insert`、`Update`和`Delete`操作到一个单一的语句中,极大地提高了数据库维护的效率和代码的简洁性。在本文中,我们将深入...
Each index row in node pages contains an index key (or set of keys for a composite index) and a pointer to a page at the next level for which the first key value is the same as the key value in the ...
为 DELETE、INSERT、SELECT、UPDATE 和 MERGE 语句添加了查询提示 添加了对 BACKUP SYMMETRIC KEY 语法结构的支持 添加了对 RESTORE SYMMETRIC KEY 语法结构的支持 在完成列表、快速信息和参数信息中添加了对 DATE_...
SQL—and unveil the power of set-based querying—with comprehensive reference and advice from a highly regarded T-SQL expert and members of Microsoft's SQL Server development team. Database developers...
### SQL Server数据库占用过多内存的解决方法 #### 内存使用概述 在SQL Server数据库运行过程中,内存管理是一项至关重要的任务。SQL Server会利用内存来提高数据访问速度和查询性能。其中,数据缓存占据内存的...
在SQL标准中,MERGE是一种DML(数据操纵语言)操作,它结合了INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE的功能。通过比较源表和目标表的数据,MERGE可以判断哪些记录需要添加、哪些需要更新或删除,从而实现数据的一致性。它的基本语法...
### SQL Server Merger 实现数据同步与合并 #### 摘要 在日常工作中,我们需要处理数据同步问题,比如将一张表的数据导入另一张表,或是将多张表的数据进行合并处理。通常情况下,这些表的数据并非完全一致,即...
在SQL Server 2014中,自定义字符串聚合函数是一项重要的编程任务,尤其是在处理大量字符串数据时。标准的T-SQL提供了一些内置的聚合函数,如SUM、AVG、MAX和MIN,但它们并不支持将多个字符串合并为一个单一的字符串...
1. **基础概念**:理解SQL(Structured Query Language)的基本语法,包括SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE等语句的用法。了解表、视图、索引、存储过程、触发器等数据库对象。 2. **数据类型**:熟悉SQL Server中的...