转载地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/bobzeng/articles/1877140.html
一般的Web项目都会在web.xml中加入Spring监听器,内容如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath*:applicationContext-struts.xml,classpath*:spring/applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
|
我们的问题是,Spring是何时以及如何加载我们的配置文件来初始化Bean工厂的,带着这些问题,我们展开研究:
我们先来看看web.xml中配置的监听器的类,来回答我们的问题,Spring是何时来加载我们的配置文件的:
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
它继承了javax.servlet.ServletContextListener接口。
ServletContextListener是J2EE Servlet API中的一个标准接口,
它能够监听ServletContext对象的生命周期,实际上就是监听Web应用的生命周期。
当Servlet容器启动或终止Web应用时,会触发ServletContextEvent事件,该事件由ServletContextListener来处理。
这里面有两个方法我们比较感兴趣:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
/** * Create the ContextLoader to use. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @return the new ContextLoader
*/
protected ContextLoader createContextLoader() {
return new ContextLoader();
} |
这个方法构造一个默认的ContextLoader,ContextLoader可以理解为Spring上下文的加载器。之所以这样去定义这样一个类,是为了开发人员进行重写此方法来使用一个自定义的Spring上下文的加载器。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
/** * Initialize the root web application context.
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
} |
这个方法很简单,仅仅只是调用了createContextLoader()构造了ContextLoader,并调用其初始化方法。
由此,我们可以得出结论,Spring是在Web项目启动时,通过ServletContextListener机制,来加载以及初始化Spring上下文的。
下面,我们好好研究一下Spring是如何加载其上下文的:
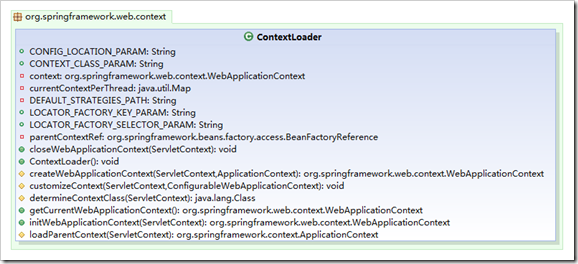
我们先定位ContextLoader类。
看看此类的initWebApplicationContext()方法(省略了不重要的语句)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
/** * Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @throws IllegalStateException if there is already a root application context present
* @throws BeansException if the context failed to initialize
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext)
throws IllegalStateException, BeansException {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
try {
// Determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext, parent);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,this.context);
currentContextPerThread.put(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),this.context);
return this.context;
}catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}catch (Error err) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", err);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err);
throw err;
}
} |
其中的有两句比较重要,我们来看看:
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
这个方法的用途主要是用来解决Spring共享环境的,即,如果我们有多个WAR包部署在同一个服务器上,而且这些WAR都共享某一套业务逻辑层。如何共享一套业务逻辑包配置而不要每个WAR都单独配置,这时我们就可能需要Spring的共享环境了。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
protected ApplicationContext loadParentContext(ServletContext servletContext) throws BeansException {
ApplicationContext parentContext = null;
// 从web.xml中读取父工厂的配置文件,默认为:"classpath*:beanRefContext.xml"
String locatorFactorySelector = servletContext.getInitParameter(LOCATOR_FACTORY_SELECTOR_PARAM);
// 从web.xml中读取父类工厂的名称
String parentContextKey = servletContext.getInitParameter(LOCATOR_FACTORY_KEY_PARAM);
if (parentContextKey != null) {
// locatorFactorySelector may be null, indicating the default "classpath*:beanRefContext.xml"
BeanFactoryLocator locator = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector);
this.parentContextRef = locator.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey);
parentContext = (ApplicationContext) this.parentContextRef.getFactory();
}
return parentContext;
} |
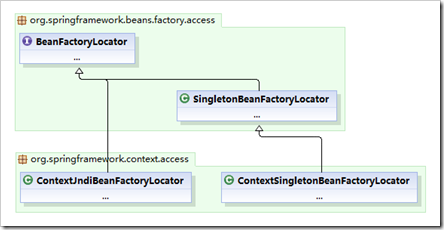
现在我们引入BeanFactoryLocator,它是Spring配置文件的一个定位器,Spring官方给它的定义是用来查找,使用和释放一个BeanFactory或其子类的接口。下面我们看看此图:
ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector);
是根据参数locatorFactorySelector去一个单例工厂中去拿一个对应的BeanFactoryLocator,也即,如果工厂中没有对 应于locatorFactorySelector的BeanFactoryLocator对象,那就返回一个新的BeanFactoryLocator 实例(这里是ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator的实例),否则,就从工厂里取现有的 BeanFactoryLocator对象。
ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator里维护了一个静态的Map对象instances,每次需要新增 BeanFactoryLocator实例时都会更新这个Map对象,这个Map对象是以配置文件名为KEY,BeanFactoryLocator对象 为值。原因很简单,就是希望同一个配置文件只被初始化一次。
如果没有在web.xml中定义locatorFactorySelector这个参数,父环境的配置文件默认使用:"classpath*:beanRefContext.xml"
this.parentContextRef = locator.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey);
此方法定义在SingletonBeanFactoryLocator类中,同样是一个单例工厂模式,判断传入的参数parentContextKey对 应的BeanFactory是否有被初始化,经过上面的 ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector)指定 Spring父环境配置文件,这个方法判断指定的父环境是否被初始化,如果有则返回,没有就进行初始化。看看此方法的实现:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
public BeanFactoryReference useBeanFactory(String factoryKey) throws BeansException {
synchronized (this.bfgInstancesByKey) {
BeanFactoryGroup bfg = (BeanFactoryGroup) this.bfgInstancesByKey.get(this.resourceLocation);
if (bfg != null) {
bfg.refCount++;
}else {
// Create the BeanFactory but don't initialize it.
BeanFactory groupContext = createDefinition(this.resourceLocation, factoryKey);
// Record its existence now, before instantiating any singletons.
bfg = new BeanFactoryGroup();
bfg.definition = groupContext;
bfg.refCount = 1;
this.bfgInstancesByKey.put(this.resourceLocation, bfg);
this.bfgInstancesByObj.put(groupContext, bfg);
// Now initialize the BeanFactory. This may cause a re-entrant invocation
// of this method, but since we've already added the BeanFactory to our
// mappings, the next time it will be found and simply have its
// reference count incremented.
try {
initializeDefinition(groupContext);
}catch (BeansException ex) {
this.bfgInstancesByKey.remove(this.resourceLocation);
this.bfgInstancesByObj.remove(groupContext);
throw new BootstrapException("Unable to initialize group definition. " +
"Group resource name [" +this.resourceLocation + "], factory key [" + factoryKey + "]", ex);
}
}
try {
BeanFactory beanFactory = null;
if (factoryKey != null) {
beanFactory = (BeanFactory) bfg.definition.getBean(factoryKey, BeanFactory.class);
}else if (bfg.definitioninstanceof ListableBeanFactory) {
beanFactory = (BeanFactory) BeanFactoryUtils.beanOfType((ListableBeanFactory) bfg.definition, BeanFactory.class);
}else {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Factory key is null, and underlying factory is not a ListableBeanFactory: " + bfg.definition);
}
return new CountingBeanFactoryReference(beanFactory, bfg.definition);
}catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new BootstrapException("Unable to return specified BeanFactory instance: factory key [" +
factoryKey + "], from group with resource name [" +this.resourceLocation + "]", ex);
}
}
} |
此方法分为两作了两件事,
第一,初始化上下文,主意这里初始化的是从web.xml配置参数里的Spring配置文件,也是上面讲loadParentContext方法里的
BeanFactoryLocator locator = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector);
这句指定的参数。这里初始化的是这个配置文件所有Bean。我们指定的factoryKey对应的Bean也是其中之一。
第二,从已经初始化的Spring上下文环境中获取Spring父环境。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<beans>
<bean id="factoryBeanId" class="org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<value>sharebean.xml</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="factoryBeanId2" class="org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext">
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<value>sharebean2.xml</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
<!—========================= web.xml ========================= --> <context-param>
<param-name>locatorFactorySelector</param-name>
<param-value>beanRefFactory.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<context-param>
<param-name>parentContextKey</param-name>
<param-value>factoryBeanId</param-value>
</context-param>
|
这个一个典型的构造父环境的配置,web项目在启动的时候就会发现里面有Spring父环境的配置,那么Spring首先就会生成一个对应的配置文件为 beanRefFactory.xml的BeanFactory(web.xml中的locatorFactorySelector参数指定),同时 Spring在解析的时候,会发现factoryBeanId的配置同样为BeanFacotry(beanRefFactory.xml中 factoryBeanId对应的Bean),所以Spring在拿父环境时就会写成:
beanFactory = (BeanFactory) bfg.definition.getBean(factoryKey, BeanFactory.class);
方法实现里引入了BeanFactoryGroup类。类的结构很简单
refCount:用来记录实例被外部引用的记数,当调用locator.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey)方法时,引 用数就会加1,当调用CountingBeanFactoryReference#release方法时,引用数就会减1,当它变成0时,Spring就 会释放掉它占用的内存,同时也会销毁掉它definition变量引用的BeanFactory。下次再调用 locator.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey)就会重新初始化BeanFactory。说到release,请同学 们参考ContextLoader中如下的两条语句:
// 在调用CountingBeanFactoryReference#release后,即使对象已经销毁,这个Map仍然可以返回locator对象。
BeanFactoryLocator locator = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector);
// 如果对象已经销毁,再调用此方法会再一次初始化BeanFactory
this.parentContextRef = locator.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey);
bfgInstancesByKey:一个Map对象,以配置文件名为Key,配置文件解析后生成的BeanFactory构成的BeanFactoryGroup为值。
bfgInstancesByObj:一个Map对象,以BeanFactoryGroup.definitiion为Key,以 BeanFactoryGroup为值。这个对象主要还是在CountingBeanFactoryReference#release时使用。
下面,我看再看看另一个地方:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
if (parentContextKey != null) {
// locatorFactorySelector may be null, indicating the default "classpath*:beanRefContext.xml"
BeanFactoryLocator locator = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector);
this.parentContextRef = locator.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey);
parentContext = (ApplicationContext) this.parentContextRef.getFactory();
}BeanFactoryLocator locator = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(locatorFactorySelector); |
上面这句仅仅是做了如下工作:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
BeanFactoryLocator bfl = (BeanFactoryLocator) instances.get(resourceLocation); if (bfl == null) {
// 仅仅只是设置了ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator里的resourceLocation属性的值,并没有初始化工厂。
bfl = new ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator(resourceLocation);
instances.put(resourceLocation, bfl);
} |
而我们使用工厂模式的时候,一般是把对象初始化好了,再给外部使用,为什么Spring这里要多此一举,在调用getInstance这后还要去调用useBeanFactory来初始化父环境?为什么Spring开发者不写成如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
BeanFactoryLocator bfl = (BeanFactoryLocator) instances.get(resourceLocation); if (bfl == null) {
bfl = new ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator(resourceLocation);
// 下面这句可能换成 initBeanFactory 类似语句,这里只是打个比方
bfl.useBeanFactory(parentContextKey);
instances.put(resourceLocation, bfl);
} |
本来我认为这个写法是必须的,后来想想也不是,不过这里体现了Spring的灵活设计。如果按排上面的方法进行改造有几点不妥,1,每次都会初始化,开销 比较大,可能有需求是需要延迟初始化的。2,每次都需要初始化都需要传入两个参数,分别为:配置文件名与父工厂名,3,类职责混乱,比如一个配置文件中可 能定义了多个父环境的Bean,采用Spring这种方法是很清晰的:
|
1
2
3
4
|
// 返回BeanFactoryLocator方便定位某个配置文件。BeanFactoryLocator locator = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance(“classpath*: parentBeanFactory.xml”);parentContextRef1 = locator.useBeanFactory("parent1Key");
parentContextRef2 = locator.useBeanFactory("parent2Key");
|
而使用我们改造的方法,则要写成如下:
|
1
2
|
parentContextRef1 = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance("parentBeanFactory.xml","parent1Key");
parentContextRef2 = ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator.getInstance("parentBeanFactory.xml","parent2Key");
|
相当麻烦且无语,引用了也只是这个配置文件中的某一个Bean的引用,没什么意义。
这就是为什么BeanFactoryLocator接口存在的一个原因,用于查找某个配置文件中的一个BeanFactory。
|
1
2
3
|
public interface BeanFactoryLocator {
BeanFactoryReference useBeanFactory(String factoryKey) throws BeansException;
} |
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext, parent);
我们来看看这个函数做了些什么:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
|
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(
ServletContext servletContext, ApplicationContext parent) throws BeansException {
// 获得需要实例化的CONTEXT类名,确定ContextClass的类型。如果在web.xml中配置了contextClass这个parameter,
// 使用这个指定的类作为ContextClass,会抛出ClassNotFound的异常。反之,使用默认的XmlWebApplicationContext
Class contextClass = determineContextClass(servletContext);
// 所有的WebApplicationContext必须实现ConfigurableWebApplicationContext接口
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// 设置父环境
wac.setParent(parent);
// 设置Servlet上下文环境
wac.setServletContext(servletContext);
// 设置Spring配置文件路径
wac.setConfigLocation(servletContext.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM));
customizeContext(servletContext, wac);
wac.refresh();
return wac;
}protected Class determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) throws ApplicationContextException {
// 获得需要实例化的CONTEXT类名,在web.xml中有设置,如果没有设置,那么为空
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName);
}catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load custom context class.", ex);
}
}else {
//如果在spring web.xml中没有设置context类位置,那么取得默认context
//取得defaultStrategies配置文件中的WebApplicationContext属性
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Failed to load default context class.", ex);
}
}
} |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
} |
// 在ContextLoader.properties里定义如下
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
再来看看Spring是如果进行初始化ApplicationContext的。就以XmlWebApplicationContext来说,它继承了 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext这个接口,里面有个refresh()方法,我们可以看看它的实现 (AbstractApplicationContext):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
public void refresh()throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
beanFactory.destroySingletons();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
} |
这个方法的实现由于涉及的东西比较多,比较国际化,事件等等,等我们理解了后续的源代码分析之后再重新过来进行研究。这样效率更高点。
这样关于Spring在web项目中加载及初始化的方式我们大概也了解的比较清楚了,我们可以看到,Spring就第一步,加载都已经做了很多工作,不得不佩服Spring团队的智慧。
最后,Spring加载完成之前,会将ApplicationContext放入ServletContext中,方便程序进行访问。
|
1
2
|
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,this.context);
currentContextPerThread.put(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(),this.context);
|
其中WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE定义如下:
String ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";
Spring环境
加载组件:ContextLoaderListener
配置路径:Servlet环境初始化参数contextConfigLocation指定的路径
缺省路径: 没有缺省路径
Spring环境的父环境
加载组件:ContextLoaderListener和ContextSingletonBeanFactoryLocator
配置路径:Servlet环境初始化参数locatorFactorySelector指定Bean工厂定位器使用的给BeanFactory,Servlet环境初始化参数parentContextKey指定Bean工厂定位器用于查找BeanFactory的关键字
缺省路径: parentContextKey的缺省路径是classpath*:beanRefFactory.xml
这里我们还有一个功能相近的类没有进行说明:
ContextJndiBeanFactoryLocator










相关推荐
Spring源码学习九:DispatcherServlet初始化源码分析1 DispatcherServlet是SpringMVC的核心分发器,它实现了请求分发,是处理请求的入口,本篇将深入源码分析它的初始化过程。 首先,从DispatcherServlet的名称上...
在Spring框架中,Bean的初始化是其生命周期中的关键步骤,特别是在单例模式下,Spring容器会确保在应用程序启动时创建并初始化所有非延迟加载的单例Bean。在本篇文章中,我们将深入探讨Spring源码中关于Bean初始化的...
在 Spring 框架中,控制多个 bean 的初始化顺序是一个常见的问题。本篇文章将详细介绍如何控制 2 个 bean 的初始化顺序,提供了多种实现方式,并分析了每种方式的优缺。 问题场景 在实际开发中,我们经常会遇到...
在Spring框架中,Bean的创建和初始化是IoC(Inversion of Control)容器的核心功能,这一过程涉及到多个步骤。以下是对Spring Bean创建初始化流程的详细解释: 1. **初始化ApplicationContext**: 开始时,通过`...
本文主要围绕"Spring源码学习七:web应用自动装配Spring配置文件1"这一主题,详细解析Web环境中Spring的初始化过程。 首先,我们注意到在传统的Java应用程序中,通常使用`ClassPathXmlApplicationContext`手动创建...
在Spring Boot应用中,我们经常需要在项目启动时执行一次初始化操作,比如加载配置、预设数据等。这里我们将详细探讨如何实现这个需求,主要涉及`@PostConstruct`注解、`CommandLineRunner`接口以及在启动类中直接...
### Spring的IoC容器初始化源码解析 #### 一、Spring框架的核心——IoC容器 Spring框架是一个开源的轻量级Java开发框架,其核心功能是IoC(Inversion of Control,控制反转)容器和AOP(Aspect Oriented ...
Spring Bean 加载过程是 Spring 框架中最核心的部分之一,涉及到 ApplicationContext 的初始化、Bean 的加载和注册等过程。在 Spring Boot 应用程序中,SpringApplication 负责加载和管理 Bean。 SpringApplication...
### Spring源码分析_Spring_IOC:深入理解Spring的IOC容器机制 #### 基本概念与核心作用 在探讨Spring框架的核心组件之一——IOC(Inversion of Control,控制反转)容器之前,首先需要理解它在Spring框架中的角色...
以上只是Spring源码分析的部分内容,实际源码中还包括Spring的其他模块,如Spring Batch(批处理)、Spring Security(安全)、Spring Integration(集成)等。理解并掌握Spring源码,有助于我们更好地利用Spring...
1. **初始化**: 加载Bean定义,可以来自XML、Java配置或注解,解析并创建BeanDefinition对象。 2. **Bean实例化**: 当调用`getBean`方法时,根据BeanDefinition创建Bean实例,可能是单例或多例。 3. **依赖注入**: ...
在Spring初始化时,会读取XML配置文件,将配置信息转化为BeanDefinition对象,并存储在BeanFactory中。 首先,我们从`ClassPathXmlApplicationContext`的构造函数出发。这个类是Spring中用来加载XML配置文件的上...
在Spring框架中,bean的默认行为是在应用启动时创建并初始化。然而,有时我们希望某些bean在实际需要时才进行初始化,这就是所谓的“懒加载”(Lazy Initialization)。Spring Boot 2.2及更高版本引入了一个全局懒...
本篇文章主要分析了Spring如何通过`ClassPathXmlApplicationContext`来启动和初始化Bean的过程。 首先,`ClassPathXmlApplicationContext`是Spring的一种ApplicationContext实现,用于从类路径下的XML配置文件加载...
然后,我们调用 initBeanDefinitionReader 方法来初始化 beanDefinitionReader 对象,最后,我们调用 loadBeanDefinitions 方法来装载 BeanDefinition。 loadBeanDefinitions 方法 现在,让我们深入探讨 ...
### Spring源码分析:配置文件读取流程 - ImportNew #### 概述 Spring框架作为Java企业级开发中广泛使用的轻量级框架之一,其核心功能之一便是通过依赖注入(DI)来管理对象间的依赖关系。Spring框架的核心是其IOC...
`InitializingBean`接口包含一个`afterPropertiesSet()`方法,它会在Bean的所有属性被设置好之后被调用,用于执行初始化任务。这与在配置文件中通过`init-method`指定的方法类似,但`afterPropertiesSet()`方法会先...
7. **Spring Boot**:为简化Spring应用的初始化和配置,Spring Boot应运而生。它提供了一种快速启动Spring应用的方式,内置了Tomcat服务器,自动配置了许多Spring组件,并可以通过起步依赖(Starter POMs)轻松添加...
8. **事件驱动**:Spring框架允许应用在特定事件(如bean的初始化或销毁)发生时进行响应。`ApplicationEvent`和`ApplicationListener`接口是实现事件驱动的关键。 9. **国际化与本地化**:Spring提供了`...
Spring支持三种织入时机:编译时(使用AspectJ编译器)、加载时(使用AspectJ LTW)和运行时(Spring容器初始化时)。 7. **源码分析**: 在Spring AOP的源码中,`org.springframework.aop.framework....