上文自定义布局管理器-FormLayout介绍了FormLayout的参考实现,利用FormLayout,通过指定left、top、
right(可选)、bottom(可选)布局约束可以对组件进行精确定位。然而有些组件在业务上是有固定尺寸的,例如自定义组件之Button介绍的一样,通过给按钮指定4种状态时的图片,那么组件的最佳尺寸就是图片的尺寸,因此组件的PreferredSize就可以确定,所以此时只需要组件中心的确定坐标就可以了,实际组件的Location只和其PreferredSize有关。如下图所示:
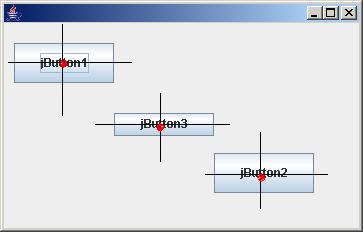
这就是CenterLayout的思想。
修改FormData,只需要添加两个变量即可。
public class FormData {
public FormAttachment left;
public FormAttachment right;
public FormAttachment top;
public FormAttachment bottom;
public FormAttachment centerX;
public FormAttachment centerY;
}
CenterLayout与FormLayout不同只在于addLayoutComponent、layoutContainer这两个
方法实现,其他接口方法均相同,所以下面只介绍这两个方法实现,其他接口方法请
参阅上文自定义布局管理器-FormLayout
在addLayoutComponent方法的开头,同样是对布局约束参数constraints合法性进行检查,这点与FormLayout大致相同。
if (constraints == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("constraints can't be
null");
} else if (!(constraints instanceof FormData)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("constraints must be a"
+ FormData.class.getName() + "instance");
} else {
......
}
进行空值判断和类型判断。然后在else块中的代码如下:
synchronized (comp.getTreeLock()) {
FormData formData = (FormData) constraints;
if (formData.centerX == null || formData.centerY == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"centerX FormAttachment and centerY
FormAttachment can't be null");
} else if (comp.getPreferredSize() == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"component must have preferred size before be
add into parent with CenterLayout");
}
componentMap.put(comp, (FormData) constraints);
}
对于CenterLayout来说,FormData对象的centerX、centerY必须给出,因为它代表,点的坐标,除此之外组件必须有PreferredSize属性来指定组件大小。
layoutContainer方法实现也大致相同
public synchronized void layoutContainer(Container target) {
synchronized (target.getTreeLock()) {
int w = target.getWidth();
int h = target.getHeight();
Component[] components = target.getComponents();
for (Component component : components) {
FormData formData = componentMap.get(component);
if (formData != null) {
......
}
}
}
}
上面这步与FormLayout一样。关键在if语句块内,代码如下:
FormAttachment centerX = formData.centerX;
FormAttachment centerY = formData.centerY;
int width = component.getPreferredSize().width;
int height = component.getPreferredSize().height;
int x = (int) (centerX.percentage * w) + centerX.offset
- width
/ 2;
int y = (int) (centerY.percentage * h) + centerY.offset
- height / 2;
component.setBounds(x, y, width, height);
获得centerX、centerY以及最佳尺寸,如上图所示,不难得出x、y的计算方法。
至此,自定义布局管理器就介绍到这里,这两个布局类可以解决很多静态布局需求,所谓静态布局是指容器内有什么组件是固定的。如果遇到动态界面,例如组件的内容依照用户级别、插件扩展点等因素决定,也并不是难事,因为了解了布局管理器运行机制以后可很容易地定义适合你需求的布局类。对于静态布局来说,你可能厌倦了hard coding来布局,你希望这一切由xml这样的配置搞定,好,下一部分则开始“压轴戏”——用配置文件解决布局。

分享到:











相关推荐
第二部分,我们将着重关注如何利用LWUIT创建基本的用户交互元素,例如按钮,以及如何进行定制和布局管理。 首先,我们从创建一个“HelloButton”开始。在LWUIT中,按钮(Button)是用户界面中常见的组件,用于触发...
Bounce,一组Java和Swing扩展,包括...布局管理器,例如FormLayout和CenterLayout,图像过滤器,全面的消息传递机制,带有语法突出显示和自动缩进的XMLEditorKit等。
* Java图形用户界面的布局方式有顺序布局(FlowLayout)、边界布局(BorderLayout)和网络布局(GridLayout),但没有中央布局(CenterLayout)(问题13) * 建立窗口需要定义JFrame类的对象(问题14) 七、数组和...
CenterLayout FitLayout AbsoluteLayout AnchorLayout FormLayout HBoxLayout VBoxLayout RowLayout ColumnLayout TableLayout 37. Removed [XType] Attribute ...
【计算机求职笔试】资源
# 基于Apache Spark Mllib的Bronze机器学习平台 ## 项目简介 Bronze是一个构建在Apache Spark Mllib之上的机器学习平台,旨在提供全面的数据接入、转换、训练、测试和输出功能。该平台支持多种机器学习算法模型,并提供丰富的插件来处理数据预处理、特征工程、模型训练和验证等任务。 ## 项目的主要特性和功能 ### 数据处理流程 1. 数据采集从各种数据源(如Fake、File、HDFS)接入数据。 2. 数据预处理对数据进行清洗、转换和格式化。 3. 特征工程生成和选择特征,包括特征提取、转换和选择。 4. 模型训练使用多种分类和回归模型进行训练。 5. 模型验证对训练好的模型进行验证和评估。 6. 模型持久化将训练好的模型保存到持久化存储中。 7. 模型结果输出输出模型的最终结果。 ### 支持的算法模型 #### 分类模型 逻辑回归支持大规模特征和无限训练样例,输出类别数小于1000万。
Java项目基于Springboot框架的课程设计,包含LW+ppt
资源内项目源码是均来自个人的课程设计、毕业设计或者具体项目,代码都测试ok,都是运行成功后才上传资源,答辩评审绝对信服的,拿来就能用。放心下载使用!源码、数据集、部署说明一站式服务,拿来就能用的绝对好资源!!! 项目备注 1、该资源内项目代码都经过测试运行成功,功能ok的情况下才上传的,请放心下载使用! 2、本项目适合计算机相关专业(如计科、人工智能、通信工程、自动化、电子信息等)的在校学生、老师或者企业员工下载学习,也适合小白学习进阶,当然也可作为毕设项目、课程设计、大作业、项目初期立项演示等。 3、如果基础还行,也可在此代码基础上进行修改,以实现其他功能,也可用于毕设、课设、作业等。 下载后请首先打开README.dataset.txt文件,仅供学习参考, 切勿用于商业用途。 4、如有侵权请私信博主,感谢支持
内容概要:本文详细探讨了全球定位系统(GPS)的信号产生、捕获和追踪三个核心步骤,并通过Matlab源码实现相关算法。首先介绍了GPS信号产生的关键要素,包括伪随机码生成、数据编码和信号发射。接着讨论了信号捕获过程,涉及天线接收、码相位测量及其常用方法如滑动相关法。最后阐述了信号追踪的三边测量原理及误差修正措施,如电离层延迟补偿、地形效应补偿和多路径效应修正。通过具体Matlab代码示例展示了整个流程的实现,并附带了详细的运行步骤和结果分析。 适合人群:对GPS系统有兴趣的研究人员和技术爱好者,尤其是有一定编程基础并希望深入了解GPS内部机制的人群。 使用场景及目标:适用于学术研究、工程开发等领域,旨在帮助读者掌握GPS信号处理的基本理论和实践技能,提升定位精度和可靠性。 其他说明:文中提供的Matlab代码已在特定版本下测试通过,但不同版本可能存在差异。此外,还列举了一些参考文献供进一步学习。
基于Andorid条形二维码识别设计实现源码,主要针对计算机相关专业的正在做毕设的学生和需要项目实战练习的学习者,也可作为课程设计、期末大作业。
NRF24L01收发例程
AcWing算法基础课Notion笔记html页面
[Excel在财务管理中的应用(第六版)(微课版)]配书资源
# 基于多线程的Web客户端程序 ## 项目简介 本项目是一个基于多线程的Web客户端程序,旨在并发地从Web服务器获取多个文件。通过使用多线程技术,程序能够高效地处理多个文件请求,提高整体性能。 ## 项目的主要特性和功能 多线程并发请求支持同时从多个Web服务器获取文件,提高请求效率。 TCP连接管理每个线程负责建立TCP连接并发送HTTP GET请求。 线程同步与通信使用互斥锁和条件变量确保线程间的同步和数据一致性。 命令行参数解析支持解析命令行参数,获取连接的最大数量和要获取的文件列表。 文件处理每个线程负责读取服务器的响应并处理文件内容。 ## 安装使用步骤 1. 下载源码假设用户已经下载了本项目的源码文件。 2. 编译项目使用合适的编译器(如GCC)编译项目源码。 bash gcc o webclient main.c lpthread
中学学生“诚信”教育班会课件
1、文件说明: Centos8操作系统tacacs-devel-F4.0.4.28.7fb~20231005g4fdf178-2.el8.rpm以及相关依赖,全打包为一个tar.gz压缩包 2、安装指令: #Step1、解压 tar -zxvf tacacs-devel-F4.0.4.28.7fb~20231005g4fdf178-2.el8.tar.gz #Step2、进入解压后的目录,执行安装 sudo rpm -ivh *.rpm
内容概要:本文详细介绍了如何利用LabVIEW通过网口与西门子PLC进行高效通讯的方法和技术细节。首先解释了西门子S7Comm协议的三层结构(TPKT+COTP+S7),并通过具体实例展示了如何构造和发送十六进制命令帧。接着提供了完整的LabVIEW代码片段,涵盖从TCP连接建立、命令帧发送、响应接收及数据解析的全过程。文中还分享了多种实用技巧,如批量读写、强制写入、自动重连机制等,并对比了原生TCP与OPC UA的性能差异。最后,通过实际案例验证了该方案在工业应用中的优越性和稳定性。 适合人群:从事工业自动化领域的工程师和技术人员,尤其是熟悉LabVIEW和西门子PLC的用户。 使用场景及目标:适用于需要与西门子PLC进行高效、稳定的网口通讯的应用场景,旨在提高通讯效率、降低系统复杂度和成本。 其他说明:文中提供的代码和技巧可以帮助开发者更好地理解和掌握LabVIEW与西门子PLC之间的通讯机制,从而应用于各种工业控制系统中。
matlab
内容概要:本文详细介绍了基于CH579芯片的以太网转串口服务器的实现过程。首先,文章讲解了硬件配置,包括使用的芯片及其特性,如CH579M、PHY芯片HR911105A和电平转换电路SGM48017。接着,重点剖析了网络初始化代码,强调了PHY复位时序、MAC地址传递和硬件协议栈处理ARP和ICMP协议的重要性。随后,文章深入探讨了串口数据处理,展示了环形缓冲区的实现和中断服务函数的优化。此外,还介绍了协议转换的状态机实现,以及内存池分配的精妙之处。最后,文章总结了资源管理策略,如DMA自动搬运数据、中断嵌套机制和零拷贝技术,使得服务器能够实现稳定的3Mbps转发速率。 适合人群:具有一定嵌入式开发经验的研发人员,尤其是对以太网转串口服务器感兴趣的工程师。 使用场景及目标:适用于需要深入了解嵌入式系统中以太网转串口服务器的工作原理和技术实现的人群。目标是掌握CH579芯片的硬件配置、网络初始化、串口数据处理、协议转换和资源管理等方面的知识。 其他说明:文中提供了详细的代码示例和硬件设计要点,帮助读者更好地理解和应用相关技术。建议读者结合实际项目进行实践,逐步掌握核心技术。
Java项目基于Springboot框架的课程设计,包含LW+ppt