CSDN排序算法群星豪华大汇演
排序算法相对简单些,但是由于它的家族比较庞大——这也许是因为简单的缘故吧,网上整理排序算法实在太多了,什么经典排序算法,八大排序算法总结,精通八大排序算法等枚不胜举,当然这里也不例外,同样是整理,同样是学习的过程。
之前一些排序算法总是说不清楚(作者自己的感受),这倒不是因为太难,作者觉得是因为排序算法太繁复了(一些算法之间的区别不是很明显),那也没有他法,只有各个击破,认真理解每个排序的原理。经过一段时间的学习和整理,已经剧本一定的规模,故作一个总览,方便查阅。
交换排序(exchange sorts)算法大串讲
§1 冒泡(Bubble Sort)排序及其改进
§2 鸡尾酒(Cocktail Sort)排序
§3 奇偶(Odd-even Sort)排序
§4 快速(Quick Sort)排序及其改进
§5 梳(Comb Sort)排序
§6 地精(Gnome Sort)排序
选择排序(selection sorts)算法大串讲
§1 选择排序
§2 锦标赛排序
§3
堆排序
§4 Smooth Sort
插入排序(insertion sorts)算法大串讲
§1 基本插入排序算法和折半插入排序算法
§2 希尔排序(shell sort)算法
§3 图书馆排序(library sort)算法
§4 耐心排序(patience sort)算法
归并排序(merge sorts)算法大串讲
§1 归并排序(Merge Sort)
§2 归并排序算法改进和优化
§3
Strand Sort排序
分布排序(distribution sorts)算法大串讲
§1 鸽巢排序(Pigeonhole)
§2 桶排序(Bucket Sort)
§3 基数排序(Radix Sort)
§4 计数排序(Counting Sort)
§5 Proxmap Sort
§6 珠排序(Bead Sort)
当然,对于浩大的排序算法,这里只能列举部分,对其进行分别介绍,有的介绍相对简单,有的比较反复,日后有时间学习再详加论述,可能有些读者会觉得每个算法讲解时间复杂度(其实都尽力覆盖)和应用会相对少点(作者也是一直这么期待多点应用),但是作者觉得这些都是建立在对算法原理的充分理解的基础上的,换句话说,如果能充分理解算法的真谛,时间复杂度和空间复杂度那其实不是信手拈来的事吗,至于应用主要是要结合实际问题,就想人生的阅历一样只有在漫长时间的浸泡才会逐渐丰满起来,所以学习切勿本末倒置,孰能生巧(掌握基本的排序算法,混合排序算法(作者没有进行整理,作者认为只要充分掌握基本的原理,遇到实际问题自然就会想到的)就不在话下了才是学习真正在的过程,学习是要学习融会贯通的能力,当然这也需要积累的过程。
下面再附上维基百科的对Sort Algorithm的整理:
Comparison of algorithms
In this table, n is the number of records to be sorted. The columns "Average" and "Worst" give the time complexity in each case, under the assumption that the length of each key is constant, and that therefore all comparisons, swaps, and other needed operations can proceed in constant time. "Memory" denotes the amount of auxiliary storage needed beyond that used by the list itself, under the same assumption. These are all comparison sorts. The run time and the memory of algorithms could be measured using various notations like theta, omega, Big-O, small-o, etc. The memory and the run times below are applicable for all the 5 notations.
Comparison sorts Name Best Average Worst
Memory Stable Method
Other notes
Non-Comparison of algorithms
The following table describes integer sorting algorithms and other sorting algorithms that are not comparison sorts. As such, they are not limited by a  lower bound. Complexities below are in terms of n, the number of items to be sorted, k, the size of each key, and d, the digit size used by the implementation. Many of them are based on the assumption that the key size is large enough that all entries have unique key values, and hence that n << 2k, where << means "much less than."
lower bound. Complexities below are in terms of n, the number of items to be sorted, k, the size of each key, and d, the digit size used by the implementation. Many of them are based on the assumption that the key size is large enough that all entries have unique key values, and hence that n << 2k, where << means "much less than."
Non-comparison sorts Name Best Average Worst
Memory
Stable n << 2k Notes
| Pigeonhole sort |
— |
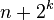 |
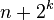 |
 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Bucket sort (uniform keys) |
— |
 |
 |
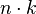 |
Yes |
No |
Assumes uniform distribution of elements from the domain in the array.[7]
|
|
Bucket sort (integer keys) |
— |
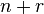 |
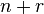 |
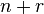 |
Yes |
Yes |
r is the range of numbers to be sorted. If r =  then Avg RT = then Avg RT =  [8] [8]
|
| Counting sort |
— |
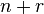 |
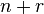 |
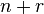 |
Yes |
Yes |
r is the range of numbers to be sorted. If r =  then Avg RT = then Avg RT =  [7] [7]
|
| LSD Radix Sort |
— |
 |
 |
 |
Yes |
No |
[7][8]
|
| MSD Radix Sort |
— |
 |
 |
 |
Yes |
No |
Stable version uses an external array of size n to hold all of the bins |
| MSD Radix Sort |
— |
 |
 |
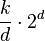 |
No |
No |
In-Place. k / d recursion levels, 2d for count array |
| Spreadsort |
— |
 |
 |
 |
No |
No |
Asymptotics are based on the assumption that n << 2k, but the algorithm does not require this. |
要是你有任何建议或批评和补充,希望您能留言指出,不胜感激,更多参考请移步互联网。
分享到:




相关推荐
快速排序 归并排序 希尔排序掌握常用的排序方法,并掌握用高级语言实现排序算法的方法; 深刻理解排序的定义和各种排序方法的特点,并能加以灵活应用; 了解各种方法的排序过程及其依据的原则,并掌握各种排序方法...
该程序包含7大排序算法: # sort.bubbleSort() #冒泡排序 # sort.shellSort() #希尔排序 # sort.insertionSort() #插入排序 # sort.Selectionsort1() #选择排序 # sort.heapSort() #堆排序 # sort.countSort() ...
它通过将待排序的数组元素按某个增量分组,对每组使用直接插入排序算法排序,然后逐渐减少增量,直到增量为1,整个数组成为一个有序序列。 6. **归并排序(Merge Sort)** 归并排序是一种分治的排序算法,将待排序的...
### 数据结构排序算法详解 #### 冒泡排序(Bubble Sort) 冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法。它重复地遍历要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果他们的顺序错误就把他们交换过来。遍历数列的工作是重复进行的,直到没有...
在计算机科学领域,排序算法是数据结构中至关重要的一部分,它涉及到如何有效地重新排列一组数据,使其按照特定的顺序(如升序或降序)排列。本资料“八大排序算法C语言”聚焦于八种常见的排序算法,每种都有C语言...
### Java冒泡排序算法知识点详解 #### 一、冒泡排序基本概念 冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)是一种简单的排序算法。它重复地遍历要排序的数列,一次比较两个元素,如果他们的顺序错误就把他们交换过来。遍历数列的工作是...
选择排序是一种简单的排序算法,它的基本思想是在未排序的序列中找到最小(或最大)的元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置,然后再从剩余未排序的元素中继续寻找最小(或最大)的元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾。...
此排序算法为本人平常学习练习所写,在学习的过程中也是非常希望和大家分享交流
冒泡排序是一种简单的排序算法,通过不断交换相邻两个元素的位置,使较大的元素逐渐“浮”到数组的一端。在PHP中,`bubbleSort()` 函数使用两个嵌套循环来实现这一过程。外层循环控制遍历整个数组,内层循环则用于...
简单的堆排序算法:以定长数组为例,动态数组等可以以此类推
常见10大算法,从原理,动图解析到代码实现,逐步分析,让你轻松入门算法
归并排序是另一种基于分治法的排序算法,它将数组分为两半,分别排序,然后合并两个已排序的部分。动画演示会显示递归分割和合并的过程。无论输入数据如何,归并排序的时间复杂度总是O(n log n)。 6. **堆排序...
双调排序算法是一种在数字电路设计中常用的高效排序方法,特别是在FPGA(Field-Programmable Gate Array)设计中。这种算法是基于冒泡排序的一种改进版本,它结合了升序和降序的交替比较,从而减少了交换次数,提高...
排序有内部排序和外部排序,内部排序是数据记录在内存中进行排序,而外部排序是因排序的数据很大,一次不能容纳全部的排序记录,在排序过程中需要访问外存。
冒泡排序法是一种基础但经典的排序算法,尤其适用于小规模数据的排序。它的工作原理可以形象地比喻为水底下的气泡逐个上浮的过程。在C++编程中,实现冒泡排序法主要涉及到数组操作和条件判断。下面将详细阐述冒泡...
数据结构课程设计是计算机科学教育中的重要组成部分,它涉及到如何高效地组织和处理数据,而排序算法则是数据结构中的一项基础但至关重要的内容。在这个课程设计中,我们重点关注了六种经典的内部排序算法:直接插入...
数据结构课程设计报告的核心主题是对比和分析不同的内部排序算法,包括它们在处理随机数据时的关键字比较次数和关键字移动次数。以下是对标题、描述和部分内容的详细解释: 1. **简介**: 这部分指出,传统的算法...
归并排序算法C语言版
它通过将待排序的元素按照一定的增量分组,对每组使用直接插入排序算法排序;随着增量逐渐减少,每组包含的关键词越来越多,当增量减至1时,整个文件恰被分成一组,算法便终止。希尔排序的Java实现需要设计合适的...