- жµПиІИ: 547555 жђ°
- жАІеИЂ:

- жЭ•иЗ™: еМЧдЇђ
-

жЦЗзЂ†еИЖз±ї
- еЕ®йГ®еНЪеЃҐ (740)
- css (4)
- jquery (8)
- javascript (23)
- html (0)
- uml (0)
- иЃЊиЃ°ж®°еЉП (1)
- еЉАеПСеЈ•еЕЈ (14)
- json (4)
- struts 1.x (3)
- spring (3)
- hibernate (6)
- struts 2.x (17)
- JFreechart (0)
- j2se (48)
- jsp (9)
- flex (22)
- жЙЊеЈ•дљЬ (1)
- жКАжЬѓжЭВи∞И (18)
- зљСзїЬзЉЦз®Л (5)
- ioжµБ (1)
- ORACLE (15)
- жК•и°® (3)
- extjs (11)
- jpbm (2)
- swing (5)
- jspereports (3)
- sql (1)
- linux (15)
- ps (1)
- storm (4)
- hbase (8)
- li (0)
- python (1)
- hive (3)
- жЬЇеЩ®е≠¶дє† (1)
- hdfs (1)
- elasticsearch (1)
- hadoop 2.2 (5)
- hadoop (1)
з§ЊеМЇзЙИеЭЧ
- жИСзЪДиµДиЃѓ ( 0)
- жИСзЪДиЃЇеЭЫ ( 0)
- жИСзЪДйЧЃз≠Ф ( 0)
е≠Шж°£еИЖз±ї
- 2014-01 ( 1)
- 2013-10 ( 28)
- 2013-07 ( 1)
- жЫіе§Ъе≠Шж°£...
жЬАжЦ∞иѓДиЃЇ
-
Tristan_SпЉЪ
ињЩдЄ™жЬЙзВєжДПжАЭ
ASM -
starryskydogпЉЪ
з®ЛеЇПдњЃжФєdetail¬† bandйГ®еИЖзЪДж†ЈеЉП¬† е¶ВеЖЕеЃєе≠ЧдљУе§Іе∞П ...
дљњзФ®jasperReportеЃЮзО∞еК®жАБи°®е§і -
samwongпЉЪ
Good, so usefule
дљњзФ®YUI CompressorеОЛзЉ©CSS/JS -
gc715409742пЉЪ
иГље§ЯеСКиѓЙжИСжАОдєИеЬ®webй°єзЫЃдЄ≠дљњзФ®YUI CompressorпЉЯ ...
дљњзФ®YUI CompressorеОЛзЉ©CSS/JS -
JsonTeyeпЉЪ
жВ®е•љпЉБ жИСзЬЛдљ†зЪДдї£з†БпЉМжИСзО∞еЬ®дєЯеЬ®еБЪеК®жАБжК•и°®пЉМеЃЮзО∞еКЯиГљзФ±зФ®жИЈиЗ™еЈ± ...
дљњзФ®jasperreportеК®жАБзФЯжИРpdf,excel,html
8.5 JAppletз±ї
JAppletз±їжШѓAWT Appletз±їзЪДжЙ©е±ХгАВдЄЇдЇЖеЬ®дљњзФ®SwingзїДдїґзЪДappletдЄ≠иГљж≠£з°ЃзЪДињЫи°МдЇЛдїґе§ДзРЖпЉМжИСдїђappletењЕй°їзїІжЙњJAppletпЉМиАМдЄНжШѓAppletгАВ
JAppletзЪДдљЬзФ®дЄОеЕґдїЦзЪДеЃЮзО∞дЇЖRootPaneContainerжО•еП£зЪДйЂШе±Вз™ЧеП£зЫЄеРМгАВJAppletдЄОAppletдєЛйЧідЄАдЄ™йЗНи¶БзЪДеМЇеИЂе∞±жШѓйїШиЃ§зЪДеЄГе±АзЃ°зРЖеЩ®гАВеЫ†дЄЇжИСдїђеРСJAppletзЪДеЖЕеЃєйЭҐжЮРжЈїеК†зїДдїґпЉМеЕґйїШиЃ§зЪДеЄГе±АзЃ°зРЖеЩ®дЄЇBorderLayoutгАВињЩдЄОAppletзЪДйїШиЃ§еЄГе±АзЃ°зРЖеЩ®FlowLayoutдЄНеРМгАВеП¶е§ЦпЉМSwing appletињШеПѓдї•еЕЈжЬЙдЄАдЄ™еЈ•еЕЈж†ПпЉМжИЦиАЕжЫідЄЇзЙєеЃЪзЪДJMenuBarпЉМињЩжШѓappletзЪДJRootPaneзЪДеП¶дЄАдЄ™е±ЮжАІгАВ
е¶ВжЮЬжИСдїђиЃ°еИТйГ®зљ≤дЄАдЄ™дљњзФ®SwingзїДдїґзЪДappletпЉМжЬАе•љжШѓдљњзФ®Sun MicrosystemsжЙАжПРдЊЫзЪДJavaжПТдїґпЉМеЫ†дЄЇињЩдЉЪйЪПињРи°МжЧґеЃЙи£ЕSwingеЇУгАВ
е¶ВжЯ•жИСдїђи¶БжЙ©е±ХJAppletз±їпЉМдїЦеП™жЬЙдЄАдЄ™йЗНи¶БзЪДprotectedжЦєж≥ХпЉЪ
protected JRootPane createRootPane()
 
8.6 йЕНеРИж°МйЭҐдљњзФ®
SpringжПРдЊЫдЇЖеѓєдЄАдЄ™йАЪеЄЄз™ЧеП£жИЦжШѓж°МйЭҐеЖЕзЪДз™ЧдљУйЫЖеРИињЫи°МзЃ°зРЖгАВж≠£е¶ВжИСдїђеЬ®зђђ1зЂ†жЙАиЃ®иЃЇзЪДпЉМињЩзІНзЃ°зРЖйАЪ媪襀зІ∞дєЛдЄЇMDIгАВз™ЧдљУеПѓдї•дљНдЇОеЕґдїЦзЪДз™ЧдљУдєЛдЄКпЉМжИЦиАЕжШѓеσ俕襀жЛЦеК®пЉМиАМеЕґе§ЦиІВйАВељУељУеЙНзЪДиІВжДЯгАВињЩдЇЫз™ЧдљУжШѓJInternalFrameз±їзЪДеЃЮдЊЛпЉМиАМж°МйЭҐжШѓдЄАдЄ™зІ∞дєЛдЄЇJDesktopPaneзЪДзЙєжЃКJLayeredPaneгАВж°МйЭҐеЖЕз™ЧдљУзЪДзЃ°зРЖжШѓDesktopManagerзЪДиі£дїїпЉМеЕґдЄ≠жЙАжПРдЊЫзЪДйїШиЃ§еЃЮзО∞жШѓDefaultDesktopManagerгАВж°МйЭҐдЄКзЪДJInternalFrameзЪДеЫЊж†З嚥еЉПжШѓйАЪињЗJDesktopIconзЪДеЖЕиБФз±їJInternalFrameжЭ•и°®з§ЇзЪДгАВеРМжЧґжЬЙInternalFrmaeListenerпЉМInternalFrameAdapterдї•еПКInternalFrameEventзФ®дЇОдЇЛдїґе§ДзРЖгАВ
й¶ЦеЕИпЉМжИСдїђжЭ•зЬЛдЄАдЄЛжЮДжИРж°МйЭҐзЪДйГ®еИЖпЉМзДґеРОжИСдїђдЉЪзЬЛеИ∞дљњзФ®ињЩдЇЫйГ®еИЖзЪДдЄАдЄ™еЃМжХіз§ЇдЊЛгАВ
8.6.1 JInternalFrameз±ї
JInternalFrameз±їдЄОJFrameз±їз±їдЉЉгАВдїЦжШѓдЄАдЄ™йЂШе±Вз™ЧеП£пЉМдљњзФ®RootPaneContainerжО•еП£пЉМдљЖжШѓеєґдЄНжШѓдЄАдЄ™й°ґе±Вз™ЧеП£гАВжИСдїђењЕй°їе∞ЖеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУжФЊеЬ®еП¶дЄАдЄ™й°ґе±Вз™ЧеП£дЄ≠гАВељУжИСдїђжЛЦеК®жЧґпЉМеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУдЉЪеБЬзХЩеЬ®еЕґз™ЧеП£зЪДиЊєзХМдєЛеЖЕпЉМињЩйАЪеЄЄжШѓдЄАдЄ™JDesktopPaneгАВеП¶е§ЦпЉМеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУжШѓиљїйЗПзЇІзЪДпЉМеєґдЄФжПРдЊЫдЇЖдЄАдЄ™UIеІФжЙШдїОиАМдљњеЊЧеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУзЬЛиµЈжЭ•з±їдЉЉељУеЙНйЕНзљЃзЪДиІВжДЯгАВ
еИЫеїЇJInternalFrame
JInternalFrameжЬЙеЕ≠дЄ™жЮДйА†еЗљжХ∞пЉЪ
public JInternalFrame() JInternalFrame frame = new JInternalFrame(); public JInternalFrame(String title) JInternalFrame frame = new JInternalFrame("The Title"); public JInternalFrame(String title, boolean resizable) JInternalFrame frame = new JInternalFrame("The Title", true); public JInternalFrame(String title, boolean resizable, boolean closable) JInternalFrame frame = new JInternalFrame("The Title", false, true); public JInternalFrame(String title, boolean resizable, boolean closable, boolean maximizable) JInternalFrame frame = new JInternalFrame("The Title", true, false, true); public JInternalFrame(String title, boolean resizable, boolean closable, boolean maximizable, boolean iconifiable) JInternalFrame frame = new JInternalFrame("The Title", false, true, false, true);
 
ињЩдЇЫжЮДйА†еЗљжХ∞дї•дЄАдЄ™еРСеП¶дЄАдЄ™жЈїеК†еПВжХ∞зЪДжЦєеЉПињЫи°МзЇІиБФгАВжЧ†еПВжХ∞жЧґпЉМжЙАеИЫеїЇзЪДJInternalFrameж≤°жЬЙж†ЗйҐШпЉМеєґдЄФдЄНиГљи∞ГжХіе§Іе∞ПпЉМеЕ≥йЧ≠пЉМжЬАе§ІеМЦжИЦжШѓеЫЊж†ЗеМЦгАВзДґиАМпЉМеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУжАїжШѓеПѓдї•жЛЦеК®зЪДгАВ
JInternalFrameе±ЮжАІ
и°®8-9еИЧеЗЇдЇЖJInternalFrameз±їзЪД30дЄ™дЄНеРМе±ЮжАІгАВlayerе±ЮжАІеИЧеЗЇдЇЖдЄ§жђ°пЉМеЫ†дЄЇдїЦеЕЈжЬЙдЄ§дЄ™иЃЊзљЃжЦєж≥ХпЉМеЕґдЄ≠дЄАдЄ™зФ®дЇОintпЉМиАМеП¶дЄАдЄ™зФ®дЇОIntegerгАВ
JInternalFrameе±ЮжАІ
|   | ||
|
е±ЮжАІеРН |
жХ∞жНЃз±їеЮЛ |
иЃњйЧЃжАІ |
|
accessibleContext |
AccessibleContext |
еП™иѓї |
|
closable |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
closed |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
contentPane |
Container |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
defaultCloseOperation |
int |
иѓїеЖЩ |
|
desktopIcon |
JInternalFrame.JDesktopIcon |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
desktopPane |
JDesktopPane |
еП™иѓї |
|
focusCycleRoot |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩ |
|
focusCycleRootAncester |
Container |
еП™иѓї |
|
focusOwner |
Component |
еП™иѓї |
|
frameIcon |
Icon |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
glassPane |
Component |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
icon |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
iconifiable |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩ |
|
internalFrameListeners |
InternalFrameListener[] |
еП™иѓї |
|
jMenuBar |
JMenuBar |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
layer |
int |
иѓїеЖЩ |
|
layer |
Integer |
еП™еЖЩ |
|
layeredPane |
JLayeredPane |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
layout |
LayoutManager |
еП™еЖЩ |
|
maximizable |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
maximum |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩ |
|
mostRecentFocusOwner |
Component |
еП™иѓї |
|
normalBounds |
Rectangle |
иѓїеЖЩ |
|
resizable |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
rootPane |
JRootPane |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
selected |
boolean |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
title |
String |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
|
UI |
InternalFrameUI |
иѓїеЖЩ |
|
UIClassID |
String |
еП™иѓї |
|
warningString |
String |
еП™иѓї |
еѓєдЇОJava 1.3еПКдї•еРОзЪДзЙИжЬђпЉМJInternalFrameзЪДеИЭеІЛdefaultCloseOperationе±ЮжАІиЃЊзљЃдЄЇDISPOSE_ON_CLOSEгАВдї•еЙНзЙИжЬђзЪДйїШиЃ§иЃЊзљЃдЄЇHIDE_ON_CLOSEгАВжИСдїђеПѓдї•е∞ЖињЩдЄ™е±ЮжАІиЃЊзљЃдЄЇеЙНйЭҐзЪДи°®8-6дЄ≠еИЧеЗЇзЪДWindowConstantsзЪДеАЉгАВ
normalBoundsе±ЮжАІжППињ∞дЇЖељУдЄАдЄ™еЫЊж†ЗеМЦзЪДеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУеПЦжґИжБѓеЫЊж†ЗеМЦжЧґеЇФиѓ•еЬ®еУ™йЗМжШЊз§ЇгАВfocusOwnerе±ЮжАІеЬ®зЙєеЃЪзЪДJInternalFrame襀жњАжіїжЧґжПРдЊЫдЇЖдЄАдЄ™еЃЮйЩЕеЄ¶жЬЙиЊУеЕ•зД¶зВєзЪДComponentгАВ
еЬ®Swingз±їдЄ≠пЉМJInternalFrameеП™еМЕеРЂеЫЫдЄ™йЩРеИґе±ЮжАІпЉЪclosed, icon, maximumдї•еПКselectedгАВдїЦдїђдЄОеЫЫдЄ™booleanжЮДйА†еЗљжХ∞еПВжХ∞зЫіжО•зЫЄеЕ≥гАВжѓПдЄАдЄ™йГљеПѓдї•еЕБиЃЄжИСдїђеЬ®жФєеПШеЕґиЃЊзљЃжЧґж£АжµЛељУеЙНзЪДе±ЮжАІзКґжАБгАВзДґиАМпЉМеЫ†дЄЇе±ЮжАІжШѓеПЧйЩРеИґзЪДпЉМељУжИСдїђи¶БиЃЊзљЃдЄАдЄ™е±ЮжАІжЧґпЉМжИСдїђжЙАеБЪзЪДе∞ЭиѓХењЕй°їдљНдЇОдЄАдЄ™try-catchеЭЧдЄ≠пЉМжНХжНЙPropertyVetoExceptionпЉЪ
try { // Try to iconify internal frame internalFrame.setIcon(false); } catch (PropertyVetoException propertyVetoException) { System.out.println("Rejected"); }
 
дЄЇдЇЖжЬЙеК©дЇОжИСдїђдљњзФ®ињЩдЇЫзїСеЃЪе±ЮжАІпЉМJInternalFrameз±їеЃЪдєЙдЇЖдЄАдЄ™11дЄ™еЄЄйЗПпЉМе¶Ви°®8-10жЙАз§ЇгАВдїЦдїђи°®з§ЇеЬ®PropertyChangeListenerдЄ≠йАЪињЗPropertyChangeEventзЪДgetPropertyName()жЦєж≥ХињФеЫЮзЪДе≠Чзђ¶дЄ≤гАВ
JInternalе±ЮжАІеЄЄйЗП
|
е±ЮжАІеРНеЄЄйЗП |
еЕ≥иБФе±ЮжАІ |
| CONTENT_PANE_PROPERTY |
contentPane |
| FRAME_ICON_PROPERTY |
frameIcon |
| GLASS_PANE_PROPERTY |
glassPane |
| IS_CLOSED_PROPERTY |
closed |
| IS_ICON_PROPERTY |
icon |
| IS_MAXIMUM_PROPERTY |
maximum |
| IS_SELECTED_PROPERTY |
selected |
| LAYERED_PANE_PROPERTY |
layeredPane |
|
MENU_BAR_PROPERTY |
jMenuBar |
| ROOT_PANE_PROPERTY |
rootPane |
| TITLE_PROPERTY |
title |
дЄЛйЭҐзЪДз±їз§ЇдЊЛжЉФз§ЇдЇЖеЬ®PropertyChangeListenerдЄ≠еЄЄйЗПзЪДдљњзФ®гАВ
package swingstudy.ch08; import java.beans.PropertyChangeEvent; import java.beans.PropertyChangeListener; import javax.swing.JInternalFrame; public class InternalFramePropertyChangeHandler implements PropertyChangeListener { @Override public void propertyChange(PropertyChangeEvent event) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String propertyName = event.getPropertyName(); if(propertyName.equals(JInternalFrame.IS_ICON_PROPERTY)) { System.out.println("Icon property changed. React."); } } }
 
е§ДзРЖJInternalFrameдЇЛдїґ
дЄЇдЇЖеЄЃеК©жИСдїђеГПдљњзФ®JFrameдЄАж†ЈжЭ•дљњзФ®JInternalFrameпЉМжЬЙдЄАдЄ™йҐЭе§ЦзЪДдЇЛдїґзЫСеРђеЩ®жЭ•иіЯиі£еЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУзЪДжЙУеЉАдЄОеЕ≥йЧ≠зЪДзЫЄеЕ≥дЇЛдїґгАВињЩдЄ™жО•еП£еРНдЄЇInternalFrameListenerпЉМеЕґеЃЪдєЙе¶ВдЄЛгАВеЕґдљЬзФ®з±їдЉЉдЇОAWTзЪДWindowListenerжО•еП£пЉМдљЖжШѓжЙАзФ®зЪДJInternalFrameз±їпЉМиАМдЄНжШѓAWTзЪДWindowз±їгАВ
public interface InternalFrameListener extends EventListener { public void internalFrameActivated(InternalFrameEvent internalFrameEvent); public void internalFrameClosed(InternalFrameEvent internalFrameEvent); public void internalFrameClosing(InternalFrameEvent internalFrameEvent); public void internalFrameDeactivated(InternalFrameEvent internalFrameEvent); public void internalFrameDeiconified(InternalFrameEvent internalFrameEvent); public void internalFrameIconified(InternalFrameEvent internalFrameEvent); public void internalFrameOpened(InternalFrameEvent internalFrameEvent); }
 
еП¶е§ЦпЉМдЄОеЕЈжЬЙжЙАжЬЙWindowListenerжЦєж≥Хж°©зЪДWindowApapterз±їз±їдЉЉпЉМдєЯжЬЙдЄАдЄ™еЕЈжЬЙжЙАжЬЙInternalFrameListenerжЦєж≥Хж°©зЪДInternalFrameAdapterз±їгАВе¶ВжЮЬжИСдїђеєґдЄНжШѓеѓєJInternalFrameеПСзФЯзЪДжЙАжЬЙдЇЛдїґжДЯеЕіиґ£пЉМжИСдїђеПѓдї•зїІжЙњInternalFrameAdapterз±їпЉМеєґдЄФеП™йЗНеЖЩжИСдїђжЙАжДЯеЕіиґ£зЪДжЦєж≥ХгАВдЊЛе¶ВпЉМеИЧи°®8-5дЄ≠жЙАз§ЇзЪДзЫСеРђеЩ®еП™еѓєеЫЊж†ЗеМЦжЦєж≥ХжДЯеЕіиґ£гАВжЧ†йЬАжПРдЊЫInternalFrameListenerзЪДеЕґдїЦдЇФдЄ™жЦєж≥ХзЪДж°©еЃЮзО∞пЉМжИСдїђеП™йЬАи¶БзїІжЙњInternalFrameAdapterпЉМеєґйЗНеЖЩдЄ§дЄ™зЫЄеЕ≥зЪДжЦєж≥ХгАВ
package swingstudy.ch08; import javax.swing.JInternalFrame; import javax.swing.event.InternalFrameAdapter; import javax.swing.event.InternalFrameEvent; public class InternalFrameIconifyListener extends InternalFrameAdapter { public void internalFrameIconified(InternalFrameEvent event) { JInternalFrame source = (JInternalFrame)event.getSource(); System.out.println("Iconified: "+source.getTitle()); } public void internalFrameDeiconified(InternalFrameEvent event) { JInternalFrame source = (JInternalFrame)event.getSource(); System.out.println("Deiconified: "+source.getTitle()); } }
 
InternalFrameEventжШѓAWTEventзЪДе≠Рз±їгАВдЄЇдЇЖеЃЪдєЙзФ±AWTEventзЪДpublic int getID()жЦєж≥ХињФеЫЮзЪДеАЉпЉМInternalFrameEventжѓПдЄАдЄ™еПѓзФ®зЪДзЙєеЃЪдЇЛдїґе≠Рз±їеЃЪдєЙдЇЖдЄАдЄ™еЄЄйЗПгАВи°®8-11еИЧеЗЇдЇЖдєЭдЄ™еЄЄйЗПгАВжИСдїђдєЯеПѓдї•йАЪињЗдЇЛдїґзЪДgetInternalFrame()жЦєж≥ХжЭ•иОЈеЊЧеЃЮйЩЕзЪДJInternalFrameгАВ
InternalFrameEventдЇЛдїґе≠Рз±їеЮЛ
| дЇЛдїґе≠Рз±їеЮЛID |
еЕ≥иБФзЪДжО•еП£жЦєж≥Х |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_ACTIVATED |
internalFrameActivated |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_CLOSED |
internalFrameClosed |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_CLOSING |
internalFrameClosing |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_DEACTIVATED |
internalFrameDeactivated |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_DEICONIFIED |
internalFrameDeiconified |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_FIRST |
N/A |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_ICONIFIED |
internalFrameIconified |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_LAST |
N/A |
| INTERNAL_FRAME_OPENED |
internalFrameOpened |
иЗ™еЃЪдєЙJInternalFrameиІВжДЯ
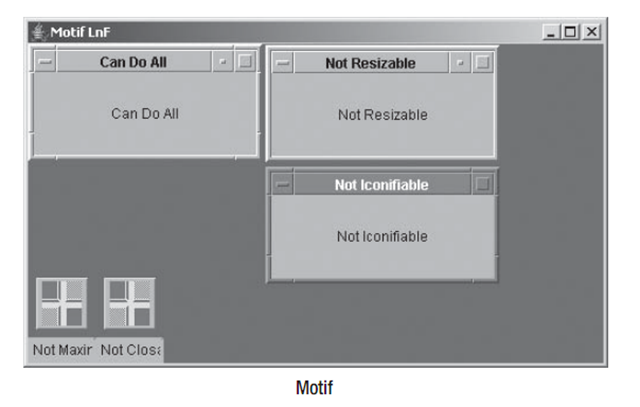
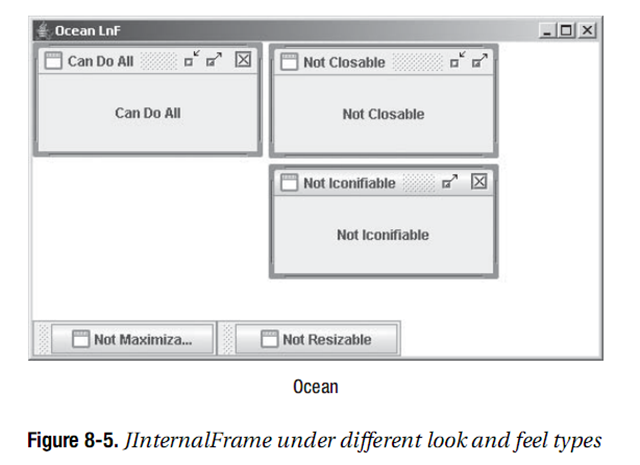
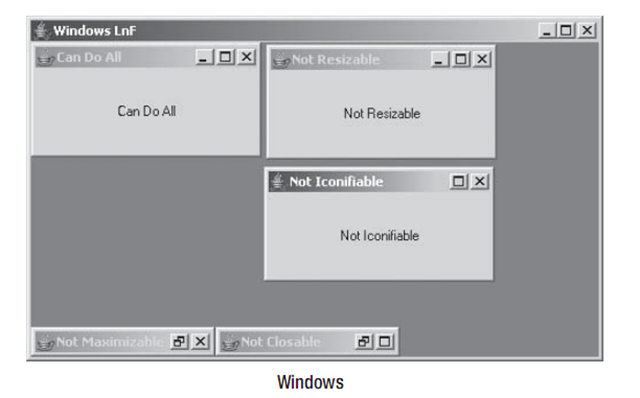
еЫ†дЄЇJInternalFrameжШѓдЄАдЄ™иљїйЗПзЇІзїДдїґпЉМдїЦеЕЈжЬЙеПѓеЃЙи£ЕзЪДиІВжДЯгАВжѓПдЄАдЄ™еПѓеЃЙи£ЕзЪДSwingиІВжДЯжПРдЊЫдЇЖдЄАдЄ™дЄНеРМзЪДJInternalFrameе§ЦиІВдї•еПКйїШиЃ§зЪДUIResourceеАЉйЫЖеРИгАВеЫЊ8-5йҐДеЃЙи£ЕзЪДиІВжДЯз±їеЮЛйЫЖеРИзЪДJWindowз™ЧеП£е§ЦиІВгАВ
и°®8-12дЄ≠еИЧеЗЇдЇЖJInternalFrameзЪДеПѓзФ®UIResourceзЫЄеЕ≥е±ЮжАІзЪДйЫЖеРИгАВеѓєдЇОJInternalFrameеЄЄйЗПпЉМжЬЙ60дЄ™дЄНеРМзЪДе±ЮжАІпЉМеМЕжЛђеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУзЪДж†ЗйҐШйЭҐжЭњзЪДе±ЮжАІгАВ
JInternalFrame UIResourceеЕГзі†
|   | |
|
е±ЮжАІе≠Чзђ¶дЄ≤ |
еѓєи±°з±їеЮЛ |
|
InternalFrame.actionMap |
ActionMap |
|
InternalFrame.activeBroderColor |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.activeTitleBackground |
Color |
|
InternaleFrame.activeTitleForeground |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.activeTitleGradient |
List |
|
InternalFrame.border |
Border |
|
InternalFrame.borderColor |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.borderDarkShadow |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.borderHighlight |
Color |
|
InterenalFrame.borderLight |
Color |
|
InternaleFrame.borderShadow |
Color |
|
InternaleFrame.borderWidth |
Integer |
|
InternalFrame.closeButtonToolTip |
String |
|
InternalFrame.closeIcon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrmae.closeSound |
String |
|
InternalFrame.icon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrame.iconButtonToolTip |
String |
|
InternalFrame.iconifyIcon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrame.inactiveBorderColor |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.inactiveTitleBackground |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.inactiveTitleForeground |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.inactiveTitleGradient |
List |
|
InternalFrame.layoutTitlePaneAtOrigin |
Boolean |
|
InternalFrame.maxButtonToolTip |
String |
|
InternalFrame.maximizeIcon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrame.maximizeSound |
String |
|
InternalFrame.minimizeIcon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrame.minimizeIconBackground |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.minimizeSound |
String |
|
InternalFrame.optionDialogBorder |
Border |
|
InternalFrame.paletteBorder |
Border |
|
InternalFrame.paletteCloseIcon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrame.paletteTitleHeight |
Integer |
|
InternaleFrame.resizeIconHighlight |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.resizeIconShadow |
Color |
|
InternalFrame.restoreButtonToolTip |
String |
|
InternalFrame.restoreDownSound |
String |
|
InternalFrame.restoreUpSound |
String |
|
InternalFrame.titlebuttonHeight |
Integer |
|
InternalFrame.titleButtonWidth |
Integer |
|
InternalFrame.titleFont |
Font |
|
InternalFrame.titlePaneHeight |
Integer |
|
InternalFrame.useTaskBar |
Boolean |
|
InternalFrame.windowBindings |
Object[] |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.closebuttonAccessibleName |
String |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.closebuttonText |
String |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.closeIcon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.iconifyButtonAccessibleName |
String |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.iconifyIcon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.maximizeButtonAccessiblName |
String |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.maximizeButtonText |
String |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.minimizeIcon |
Icon |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.moveButtonText |
String |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.restoreButtonText |
String |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.sizeButtonText |
String |
|
InternalFrameTitlePane.titlePaneLayout |
LayoutManager |
|
InternalFrameTitlePaneUI |
String |
|
InternalFrameUI |
String |
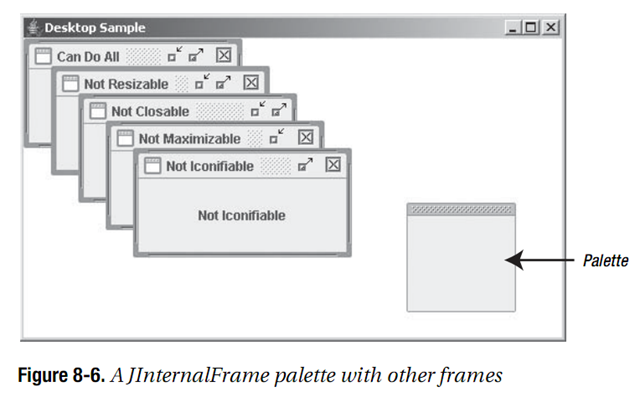
йЩ§дЇЖи°®8-12дЄ≠иЃЄе§ЪеПѓйЕНзљЃе±ЮжАІдї•е§ЦпЉМеѓєдЇОMetalиІВжДЯпЉМжИСдїђињШеПѓдї•йАЪињЗзЙєжЃКзЪДеЃҐжИЈзЂѓе±ЮжАІJInternalFrame.isPaletteжЭ•е∞ЖеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУиЃЊиЃ°дЄЇдЄАдЄ™paletteгАВељУиЃЊзљЃдЄЇBoolean.TRUEжЧґпЉМеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУзЪДе§ЦиІВдЉЪдЄОеЕґдїЦз™ЧдљУзХ•еЊЃдЄНеРМпЉМеєґдЄФеЕЈжЬЙиЊГзЯ≠зЪДж†ЗйҐШж†ПпЉМе¶ВеЫЊ8-6жЙАз§ЇгАВ
е¶ВжЮЬжИСдїђеРМжЧґеЬ®ж°МйЭҐзЪДPALETTE_LAYERдЄКжЈїеК†дЇЖдЄАдЄ™еЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУпЉМеИЩињЩдЄ™з™ЧдљУдЉЪдљНдЇОеЕґдїЦжЙАжЬЙз™ЧдљУдєЛдЄКпЉИе¶ВеЫЊ8-6жЙАз§ЇпЉЙпЉЪ
JInternalFrame palette = new JInternalFrame("Palette", true, false, true, false); palette.setBounds(150, 0, 100, 100); palette.putClientProperty("JInternalFrame.isPalette", Boolean.TRUE); desktop.add(palette, JDesktopPane.PALETTE_LAYER);
 
еИЫеїЇеЫЊ8-6жЙАз§ЇзЪДз®ЛеЇПзЪДеЃМжХідї£з†БжШЊз§ЇеЬ®жЬђзЂ†з®НеРОзЪДеИЧи°®8-6дЄ≠гАВ
дњЃжФєJDesktopIcon
JInternalFrameдЊЭиµЦдЄАдЄ™еЖЕиБФз±їJDesktopIconжЭ•дЄЇJInternalFrameзЪДеЫЊж†ЗеМЦжШЊз§ЇжПРдЊЫUIеІФжЙШгАВињЩдЄ™з±їеП™жШѓзФ®жЭ•ињЩзІНеКЯиГљзЪДдЄАдЄ™зЙєжЃКзЪДJComponentпЉМиАМдЄНжШѓе¶ВеЕґеРНе≠ЧжЪЧз§ЇзЪДдЄАдЄ™зЙєжЃКзЪДIconеЃЮзО∞гАВдЇЛеЃЮдЄКпЉМJDesktopIconз±їзЪДж≥®йЗКи°®жШОињЩдЄ™з±їжШѓдЄіжЧґзЪДпЉМжЙАдї•жИСдїђдЄНеЇФзЫіжО•еѓєеЕґињЫи°МиЗ™еЃЪдєЙгАВпЉИељУзДґпЉМињЩдЄ™з±їдЉЪе≠ШеЬ®дЄАжЃµжЧґйЧігАВпЉЙ
е¶ВжЮЬжИСдїђйЬАи¶БиЗ™еЃЪдєЙJDesktopIconпЉМжИСдїђеПѓдї•дњЃжФєдЄАдЇЫUIResourceзЫЄеЕ≥зЪДе±ЮжАІгАВи°®8-13еИЧеЗЇдЇЖJDesktopIconзїДдїґзЪДеЕЂдЄ™UIResourceзЫЄеЕ≥е±ЮжАІгАВ
JInternalFrame.JDesktopIcon UIResourceеЕГзі†
| е±ЮжАІе≠Чзђ¶дЄ≤ |
еѓєи±°з±їеЮЛ |
| DesktopIcon.background |
Color |
| DesktopIcon.border |
Border |
| DesktopIcon.font |
Font |
| DesktopIcon.foreground |
Color |
| DesktopIcon.icon |
Icon |
| DesktopIcon.width |
Integer |
| DesktopIcon.windowBindings |
Object[] |
| DesktopIconUI |
String |
8.6.2 JDesktopPaneз±ї
дЄОеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУзїДеРИйЕНеРИдљњзФ®зЪДеП¶дЄАдЄ™з±їе∞±жШѓJDesktopPaneз±їгАВж°МйЭҐйЭҐжЭњзЪДзЫЃзЪДе∞±жШѓеМЕеРЂеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУйЫЖеРИгАВељУеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУ襀еМЕеРЂеЬ®дЄАдЄ™ж°МйЭҐйЭҐжЭњдЄ≠жЧґпЉМдїЦдїђе∞ЖеЕґи°МдЄЇзЪДе§ІйГ®еИЖеІФжЙШзїЩж°МйЭҐйЭҐжЭњзЪДж°МйЭҐзЃ°зРЖеЩ®гАВжИСдїђе∞ЖдЉЪеЬ®жЬђзЂ†з®НеРОиѓ¶зїЖдЇЖиІ£DesktopManagerжО•еП£гАВ
еИЫеїЇJDesktopPane
JDesktopPaneеП™жЬЙдЄАдЄ™жЧ†еПВжХ∞зЪДжЮДйА†еЗљжХ∞гАВдЄАжЧ¶еИЫеїЇпЉМжИСдїђйАЪеЄЄе∞ЖеЕґжФЊеЬ®зФ±BorderLayoutзЃ°зРЖзЪДеЃєеЩ®зЪДдЄ≠йГ®гАВињЩеПѓдї•дњЭиѓБж°МйЭҐеН†жНЃеЃєеЩ®зЪДжЙАжЬЙз©ЇйЧігАВ
е∞ЖеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУжЈїеК†еИ∞JDesktopPane
JDesktopPaneеєґж≤°жЬЙеЃЮзО∞RootPaneContainerгАВжИСдїђеєґдЄНиГљзЫіжО•е∞ЖзїДдїґжЈїеК†еИ∞JRootPaneеЖЕзЪДдЄНеРМйЭҐжЭњдЄ≠пЉМиАМжШѓзЫіжО•е∞ЖеЕґжЈїеК†еИ∞JDesktopPaneпЉЪ
desktop.add(anInternalFrame);
JDesktopPaneе±ЮжАІ
е¶Ви°®8-14жЙАз§ЇпЉМJDesktopPaneжЬЙеЕЂдЄ™е±ЮжАІгАВдљНдЇОallFramesе±ЮжАІжХ∞зїД糥еЉХ0е§ЦзЪДJInternalFrameжШѓдљНдЇОж°МйЭҐеЙНйЭҐзЪДеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУпЉИJInternalFrame f = desktop.getAllFrames()[0]пЉЙгАВйЩ§дЇЖиОЈеПЦJDesktopPaneдЄ≠зЪДжЙАжЬЙз™ЧдљУдї•е§ЦпЉМжИСдїђињШеПѓдї•дїЕиОЈеПЦзЙєеЃЪе±ВзЪДз™ЧдљУпЉЪpublic JInternalFrame[] getAllFramesInLayer(int layer)гАВ
еПѓзФ®зЪДdragModeе±ЮжАІиЃЊзљЃеПѓдї•дЄЇз±їзЪДLIVE_DRAG_MODEдЄОOUTLINE_DRAG_MODEеЄЄйЗПгАВ
JDesktopPaneе±ЮжАІ
| е±ЮжАІеРН |
жХ∞жНЃз±їеЮЛ |
иЃњйЧЃжАІ |
| accessibleContext |
AccessibleContext |
еП™иѓї |
| allFrames |
JInternalFrame[] |
еП™иѓї |
| desktopManager |
DesktopManager |
иѓїеЖЩ |
| dragMode |
int |
иѓїеЖЩзїСеЃЪ |
| opaque |
boolean |
еП™иѓї |
| selectedFrame |
JInternalFrame |
иѓїеЖЩ |
| UI |
DesktopPaneUI |
иѓїеЖЩ |
| UIClassID |
String |
еП™иѓї |
иЗ™еЃЪдєЙJDesktopPaneиІВжДЯ
еЫЮеИ∞еЫЊ8-5пЉМжИСдїђеПѓдї•зЬЛеИ∞JDesktopPaneдЄ≠зЪДJInternalFrameеѓєи±°гАВJDesktopPaneзЪДеЯЇжЬђиІВжДЯдЄОжѓПдЄАдЄ™иІВжДЯзЫЄеРМгАВе¶Ви°®8-15жЙАз§ЇпЉМеѓєJDesktopPaneеєґж≤°жЬЙ姙е§ЪеПѓдї•йЕНзљЃзЪДUIResourceзЫЄеЕ≥е±ЮжАІгАВ
JDesktopPane UIResourceеЕГзі†
| е±ЮжАІе≠Чзђ¶дЄ≤ |
еѓєи±°з±їеЮЛ |
| desktop |
Color |
| Desktop.ancestorInputMap |
InputMap |
| Desktop.background |
Color |
| Desktop.windowBindings |
Object[] |
| DesktopPane.actionMap |
ActionMap |
| DesktopPaneUI |
String |
еЃМжХізЪДж°МйЭҐз§ЇдЊЛ
зО∞еЬ®жИСдїђеЈ≤зїПдЇЖиІ£дЇЖдЄїи¶БзЪДж°МйЭҐзЫЄеЕ≥з±їпЉМзО∞еЬ®жИСдїђжЭ•зЬЛдЄАдЄЛеЃМжХізЪДз§ЇдЊЛгАВеЯЇжЬђзЪДињЗз®ЛеМЕжЛђеИЫеїЇдЄАзїДJInternalFrameеѓєи±°пЉМзДґеРОе∞ЖжФЊеЬ®дЄАдЄ™JDesktopPaneдЄ≠гАВе¶ВжЮЬйЬАи¶БпЉМеПѓдї•еѓєжѓПдЄАдЄ™еЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУзЪДеНХдЄ™зїДдїґињЫи°МдЇЛдїґе§ДзРЖпЉМдєЯеПѓдї•еѓєеНХдЄ™з™ЧдљУињЫи°МдЇЛдїґе§ДзРЖгАВеЬ®ињЩдЄ™з§ЇдЊЛдЄ≠зЃАеНХзЪДдљњзФ®дЇЖеЙНйЭҐзЪДеИЧи°®8-5дЄ≠жЙАзїЩеЗЇзЪДInternalFrameIconifyListenerз±їжЭ•зЫСеРђж≠£еЬ®еЫЊж†ЗеМЦеТМеПЦжґИеЫЊж†ЗеМЦзЪДеЖЕеЃєз™ЧдљУгАВ
еЫЊ8-6жШЊз§ЇдЇЖз®ЛеЇПеРѓеК®жЧґзЪДж†Је≠РгАВдЄАдЄ™зЙєеЃЪзЪДеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУ襀职聰䪯paletteпЉМеєґдЄФеЕБиЃЄдЇЖжЛЦжФЊж®°еЉПгАВ
еИЧи°®8-6жШЊз§ЇдЇЖињЩдЄ™з§ЇдЊЛзЪДеЃМжХідї£з†БгАВ
package swingstudy.ch08; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.JDesktopPane; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JInternalFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.event.InternalFrameListener; public class DesktopSample { /** * @param args */ public static void main(final String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Runnable runner = new Runnable() { public void run() { String title = (args.length==0 ? "Desktop Sample" : args[0]); JFrame frame = new JFrame(title); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); JDesktopPane desktop = new JDesktopPane(); JInternalFrame internalFrames[] = { new JInternalFrame("Can Do All", true, true, true, true), new JInternalFrame("Not Resizable", false, true, true, true), new JInternalFrame("Not Closable", true, false, true, true), new JInternalFrame("Not Maximizable", true, true, false, true), new JInternalFrame("Not Iconifiable", true, true, true, false) }; InternalFrameListener internalFrameListener = new InternalFrameIconifyListener(); int pos = 0; for(JInternalFrame internalFrame: internalFrames) { // Add to desktop desktop.add(internalFrame); // Position and size internalFrame.setBounds(pos*25, pos*25, 200, 100); pos++; // Add listener for iconification events internalFrame.addInternalFrameListener(internalFrameListener); JLabel label = new JLabel(internalFrame.getTitle(), JLabel.CENTER); internalFrame.add(label, BorderLayout.CENTER); // Make visible internalFrame.setVisible(true); } JInternalFrame palette = new JInternalFrame("Palette", true, false, true, false); palette.setBounds(350, 150, 100, 100); palette.putClientProperty("JInternalFrame.isPalette", Boolean.TRUE); desktop.add(palette, JDesktopPane.PALETTE_LAYER); palette.setVisible(true); desktop.setDragMode(JDesktopPane.OUTLINE_DRAG_MODE); frame.add(desktop, BorderLayout.CENTER); frame.setSize(500, 300); frame.setVisible(true); } }; EventQueue.invokeLater(runner); } }
 
DesktopManagerжО•еП£
дљњзФ®ж°МйЭҐзЪДжЬАеРОдЄАйГ®еИЖе∞±жШѓж°МйЭҐзЃ°зРЖеЩ®дЇЖпЉМдїЦжШѓDesktopManagerжО•еП£зЪДеЃЮзО∞пЉМеЕґеЃЪдєЙе¶ВдЄЛпЉЪ
 
ељУJInternalFrameдљНдЇОJDe
public interface DesktopManager { public void activateFrame(JInternalFrame frame); public void beginDraggingFrame(JComponent frame); public void beginResizingFrame(JComponent frame, int direction); public void closeFrame(JInternalFrame frame); public void deactivateFrame(JInternalFrame frame); public void deiconifyFrame(JInternalFrame frame); public void dragFrame(JComponent frame, int newX, int newY); public void endDraggingFrame(JComponent frame); public void endResizingFrame(JComponent frame); public void iconifyFrame(JInternalFrame frame); public void maximizeFrame(JInternalFrame frame); public void minimizeFrame(JInternalFrame frame); public void openFrame(JInternalFrame frame); public void resizeFrame(JComponent frame, int newX, int newY, int newWidth, int newHeight); public void setBoundsForFrame(JComponent frame, int newX, int newY, int newWidth, int newHeight); }
 
sktopPaneдЄ≠жЧґпЉМдїЦдїђдЄНеЇФе∞ЭиѓХдЊЛе¶ВеЫЊж†ЗеМЦжИЦжШѓжЬАе§ІеМЦзЪДжУНдљЬгАВзЫЄеПНпЉМдїЦдїђеЇФиѓ•иѓЈж±ВдїЦдїђжЙАеЃЙи£ЕеЬ®зЪДж°МйЭҐйЭҐжЭњзЪДж°МйЭҐзЃ°зРЖеЩ®жЭ•жЙІи°МињЩдЇЫжУНдљЬпЉЪ
getDesktopPane().getDesktopManager().iconifyFrame(anInternalFrame);
 
DefaultDesktopManagerз±їжПРдЊЫдЇЖDesktopManagerзЪДдЄАдЄ™еЃЮзО∞гАВе¶ВжЮЬйїШиЃ§еЃЮзО∞ињШиґ≥е§ЯпЉМиІВжДЯдЉЪжПРдЊЫдїЦдїђиЗ™еЈ±зЪДDesktopManagerеЃЮзО∞з±їпЉМдЊЛе¶ВWindowsиІВжДЯзЪДWindowsDesktopManagerгАВжИСдїђдєЯеПѓдї•еЃЪдєЙиЗ™еЈ±зЪДзЃ°зРЖеЩ®пЉМдљЖжШѓйАЪеЄЄеєґдЄНйЬАи¶БињЩж†ЈгАВ
8.7 е∞ПзїУ
еЬ®жЬђзЂ†дЄ≠пЉМжИСдїђжОҐиЃ®дЇЖJRootPaneз±їпЉМдї•еПКе¶ВдљХеЃЮзО∞дЊЭжНЃJRootPaneеѓєеЖЕйГ®зїДдїґињЫи°МзЃ°зРЖзЪДRootPaneContainerжО•еП£гАВжИСдїђеРМжЧґдЇЖиІ£дЇЖеЬ®SwingдЄ≠жИСдїђе¶ВдљХдљњзФ®JFrame, JDialog, JWindow, JAppletжИЦжШѓJInternalFrameз±їзЪДJRootPaneгАВж†єйЭҐжЭњеПѓдї•еАЯеК©JLayeredPaneжЭ•еЄГе±АзїДдїґпЉМеЕґжЦєеЉПжШѓеЈ•еЕЈжПРз§ЇжЦЗжЬђдї•еПКеЉєеЗЇиПЬеНХжАїжШѓжШЊз§ЇеЬ®зЫЄеЕ≥иБФзїДдїґзЪДдЄКйЭҐгАВ
JInternalFrameеРМжЧґдєЯеПѓдї•е≠ШеЬ®дЇОж°МйЭҐзОѓеҐГдЄ≠пЉМеЬ®ињЩзІНжГЕеЖµдЄЛпЉМJDesktopPaneдї•еПКDesktopManagerзЃ°зРЖе¶ВдљХдї•еПКеЬ®еУ™йЗМжФЊзљЃеєґжШЊз§ЇеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУгАВжИСдїђињШеПѓдї•йАЪињЗе∞ЖInternalFrameListenerеЃЮзО∞дєЯJInternalFrameеЕ≥иБФжЭ•еУНеЇФеЖЕйГ®з™ЧдљУдЇЛдїґгАВ
еЬ®зђђ9зЂ†дЄ≠пЉМжИСдїђе∞ЖдЉЪжОҐиЃ®SwingеЇУдЄ≠зЪДзЙєеЃЪеЉєеЗЇзїДдїґпЉЪJColorChooser, JFileChooserпЉМ JOptionPaneдї•еПКProgressMonitor
- 2011-12-05 11:41
- жµПиІИ 733
- иѓДиЃЇ(0)
- еИЖз±ї:зЉЦз®Лиѓ≠и®А
- жЯ•зЬЛжЫіе§Ъ
еПСи°®иѓДиЃЇ
-
Swing иЊєж°ЖпЉИдЄАпЉЙ
2011-12-05 11:43 896SwingзїДдїґжПРдЊЫдЇЖеѓєзїДдїґеС®еЫізЪДиЊєж°ЖеМЇеЯЯињЫи°МеЃЪеИґзЪДеКЯиГљгАВдЄЇ ... -
Root Pane ContainerпЉИдЄЙпЉЙ
2011-12-05 11:40 7008.3 JWindowз±ї JWindowз±їдЄОJFrame ... -
Root Pane ContainerпЉИдЇМпЉЙ
2011-12-05 11:39 6428.2 JFrameз±ї JFrameз±їжШѓдљњзФ®JRootP ... -
Root Pane Containers (дЄА)
2011-12-05 11:36 759еЬ®зђђ7зЂ†дЄ≠пЉМжИСдїђдЇЖиІ£дљњзФ®SwingзїДдїґеС®еЫізЪДиЊєж°ЖгАВеЬ®жЬђзЂ†дЄ≠ ...





зЫЄеЕ≥жО®иНР
еИЖе±ВдїЛзїНjava SwingзїДдїґ,иѓ¶зїЖиѓіжШОrootPane,LayeredPane,rootPane,contentPaneдєЛйЧізЪДеЕ≥з≥ї
NavigationPaneжШѓиљѓдїґеЉАеПСдЄ≠еЄЄиІБзЪДдЄАзІНзХМйЭҐеЕГзі†пЉМе∞§еЕґеЬ®WindowsеЇФзФ®еТМзІїеК®еЇФзФ®иЃЊиЃ°дЄ≠пЉМеЃГжЙЃжЉФзЭАеѓЉиИ™еТМзїДзїЗеЖЕеЃєзЪДеЕ≥йФЃиІТиЙ≤гАВNavigationPaneжОІдїґйАЪеЄЄзФ®дЇОеИЫеїЇдЄАдЄ™дЊІжїСиПЬеНХпЉМзФ®жИЈеПѓдї•йАЪињЗжїСеК®е±ПеєХжИЦзВєеЗїжМЙйТЃжЭ•е±Хз§ЇжИЦ...
гАРеЙНзЂѓеЉАжЇРеЇУ-contacts-paneгАСжШѓдЄАдЄ™дЄУдЄЇзЃ°зРЖиБФз≥їдЇЇиАМиЃЊиЃ°зЪДеЉАжЇРй°єзЫЃпЉМеЃГжПРдЊЫдЇЖйАЪиЃѓз∞њгАБзїДеТМдЄ™дЇЇиБФз≥їдЇЇзЪДйЂШжХИзЃ°зРЖзХМйЭҐгАВињЩдЄ™еЇУжШѓеЙНзЂѓеЉАеПСдЄ≠зЪДдЄАдЄ™йЗНи¶БеЈ•еЕЈпЉМеЃГжЧ®еЬ®зЃАеМЦWebеЇФзФ®з®ЛеЇПдЄ≠зЪДиБФз≥їдЇЇжХ∞жНЃе§ДзРЖпЉМдЄЇзФ®жИЈжПРдЊЫ...
4pane_5.0.orig.tar.gz 4pane_5.0-2.debian.tar.xz 4pane_5.0-2.dsc 4pane_5.0-2_amd64.deb 4pane_5.0-2_i386.deb 4pane_5.0-2_arm64.deb 4pane_5.0-2_mips64el.deb йЬАи¶БеЫљдЇІжЬНеК°еЩ®жУНдљЬз≥їзїЯжИЦиАЕжЬНеК°еЩ®жУНдљЬз≥їзїЯзЪД...
"folder-pane"е∞±жШѓдЄАдЄ™ињЩж†ЈзЪДеЉАжЇРеЇУпЉМдЄУйЧ®зФ®дЇОеЃЮзО∞жЦЗдїґе§єз™Чж†ЉеКЯиГљпЉМдЄЇзФ®жИЈеЄ¶жЭ•з±їдЉЉжЦЗдїґжµПиІИеЩ®зЪДдЇ§дЇТдљУй™МгАВињЩдЄ™еЇУе∞§еЕґйАВзФ®дЇОйЬАи¶Бе§ДзРЖе§ІйЗПжЦЗдїґжХ∞жНЃгАБжПРдЊЫжЦЗдїґжµПиІИеТМзЃ°зРЖзЪДWebеЇФзФ®гАВ й¶ЦеЕИпЉМжИСдїђи¶БзРЖиІ£дїАдєИжШѓвАЬжЦЗдїґе§є...
гАРеЙНзЂѓеЉАжЇРеЇУ-meeting-paneгАСжШѓдЄАжђЊдЄУдЄЇеЃЮзО∞дЉЪиЃЃеНПдљЬеКЯиГљиЃЊиЃ°зЪДеЙНзЂѓеЇУпЉМеЃГжПРдЊЫдЇЖеЃЮдљУеЕЉеЃєз™Чж†ЉпЉМдљњеЊЧеЬ®еРДзІНиЃЊе§ЗдЄКињЫи°МдЉЪиЃЃеНПеРМеЈ•дљЬеПШеЊЧжЫіеК†дЊњжНЈеТМйЂШжХИгАВеЬ®зО∞дї£зЪДеЬ®зЇњдЉЪиЃЃеЬЇжЩѓдЄ≠пЉМзФ®жИЈйЬАи¶БиГље§ЯеЬ®дЄНеРМеє≥еП∞дЄКй°ЇзХЕеЬ∞еЕ±дЇЂ...
"source-pane"жШѓдЄАдЄ™ињЩж†ЈзЪДеЇУпЉМдЄУдЄЇеЙНзЂѓеЉАеПСиАЕиЃЊиЃ°пЉМеЃГжПРдЊЫдЇЖжЇРз™Чж†ЉзЪДеКЯиГљпЉМеЕБиЃЄзФ®жИЈжЯ•зЬЛеТМзЉЦиЊСдї£з†БеЃЮдљУпЉМе∞§еЕґйАВзФ®дЇОи∞ГиѓХеТМеҐЮеЉЇеЉАеПСдљУй™МгАВеЬ®ињЩдЄ™вАЬжЇРз™Чж†ЉвАЭдЄ≠пЉМжИСдїђеПѓдї•зЬЛеИ∞еЃГ襀职聰жИРдЄАдЄ™еЕЉеЃєеРДзІНеЃЮдљУзЪДзЉЦиЊСеЩ®пЉМ...
иІ£еЖ≥VueеѓєElementдЄ≠зЪДel-tab-paneжЈїеК†@clickдЇЛдїґжЧ†жХИ
еЕґдЄ≠пЉМеѓЉиИ™з™Чж†ЉпЉИNavigation PaneпЉЙжШѓиµДжЇРзЃ°зРЖеЩ®зЪДйЗНи¶БзїДжИРйГ®еИЖпЉМеЃГжПРдЊЫдЇЖењЂйАЯиЃњйЧЃзФµиДСжЦЗдїґе§єгАБеЇУгАБжОІеИґйЭҐжЭњз≠ЙдљНзљЃзЪДжЦєеЉПгАВзДґиАМпЉМз≥їзїЯйїШиЃ§зЪДеѓЉиИ™з™Чж†Љй°єеПѓиГљжЧ†ж≥Хжї°иґ≥жЙАжЬЙзФ®жИЈзЪДдЄ™жАІеМЦйЬАж±ВгАВдЄЇдЇЖиІ£еЖ≥ињЩдЄ™йЧЃйҐШпЉМеЗЇзО∞дЇЖ...
еЬ®дљњзФ®"pane-fixer-centos"дєЛеЙНпЉМдљ†йЬАи¶БеЕИдЄЛиљљй°єзЫЃдЄ≠зЪДиДЪжЬђжЦЗдїґеИ∞жЬђеЬ∞пЉМзДґеРОйАЪињЗзїИзЂѓињРи°Миѓ•иДЪжЬђпЉМиµЛдЇИеЕґжЙІи°МжЭГйЩРпЉИе¶В`chmod +x pane-fixer-centos`пЉЙпЉМжЬАеРОжЙІи°Миѓ•иДЪжЬђпЉИе¶В`./pane-fixer-centos`пЉЙгАВжЙІи°МињЗз®ЛдЄ≠пЉМиДЪжЬђ...
Atom-еШњpaneжШѓдЄАжђЊдЄУдЄЇAtomжЦЗжЬђзЉЦиЊСеЩ®иЃЊиЃ°зЪДжПТдїґпЉМеЕґдЄїи¶БеКЯиГљжШѓжФЊе§ІељУеЙНжіїеК®зЪДз™Чж†ЉпЉМжПРеНЗзФ®жИЈеЬ®зЉЦз®ЛжИЦжЦЗжЬђзЉЦиЊСињЗз®ЛдЄ≠зЪДиБЪзД¶иГљеКЫгАВAtomдљЬдЄЇдЄАдЄ™зФ±GitHubеЉАеПСзЪДеЉАжЇРжЦЗжЬђзЉЦиЊСеЩ®пЉМеИ©зФ®WebжКАжЬѓе¶ВHTMLгАБCSSеТМJavaScript...
Property name for specifying skin to be used on the specific root pane. This property can only be installed on a JRootPane and will affect all the controls in that root pane. The value must be an ...
DotnetBar 8.1.0.6жХЩз®Л-NavigationPane дїОеЃШжЦєзљСзЂЩдЄЛиљљзЪДжХЩз®ЛпЉМжШѓзФ®VBжЉФз§ЇзЪДе¶ВдљХдљњзФ®DotnetBarзЪДпЉМжШѓиЛ±жЦЗзЙИзЪДгАВ еЬ®C#дЄ≠зФ®иµЈжЭ•дЄАж†ЈпЉМдљЖжДњеѓєе§ІеЃґжЬЙзФ®гАВ
ж†ЗйҐШдЄ≠зЪД"pane-management-жЇРз†Б.rar"и°®жШОињЩжШѓдЄАдЄ™еЕ≥дЇОвАЬpaneзЃ°зРЖвАЭзЪДжЇРдї£з†БеОЛзЉ©еМЕпЉМеПѓиГљжШѓжЯРдЄ™иљѓдїґжИЦз≥їзїЯзїДдїґзЪДдЄАйГ®еИЖпЉМзФ®дЇОе§ДзРЖзФ®жИЈзХМйЭҐдЄ≠зЪДpaneеЄГе±АеТМзЃ°зРЖгАВзДґиАМпЉМзФ±дЇОж≤°жЬЙеЕЈдљУзЪДж†Зз≠ЊжЭ•жМЗжШОињЩжШѓеУ™зІНзЉЦз®Лиѓ≠и®АжИЦиАЕ...
**FilePaneдљњзФ®жХЩз®Л** FilePaneжШѓдЄАжђЊдЄУдЄЇMac OSеє≥еП∞иЃЊиЃ°зЪДйЂШжХИеЈ•еЕЈпЉМеЃГжЮБе§ІеЬ∞зЃАеМЦдЇЖзФ®жИЈеЬ®е§ДзРЖжЦЗжЬђеТМеЫЊзЙЗжЧґзЪДе§НеИґгАБз≤ШиііжУНдљЬгАВйАЪињЗFilePaneпЉМдљ†еПѓдї•жЧ†йЬАе§НжЭВзЪДйФЃзЫШењЂжНЈйФЃпЉМеП™йЬАзЃАеНХзЪДжЛЦжФЊеК®дљЬе∞±иГљеЃМжИРжЦЗдїґеТМдњ°жБѓзЪД...
Chat-pane жШѓдЄАдЄ™дЄУдЄЇеЙНзЂѓеЉАеПСиЃЊиЃ°зЪДеЉАжЇРеЇУпЉМдЄїи¶БзФ®дЇОжЮДеїЇиБК姩з™ЧеП£еКЯиГљгАВеЃГжПРдЊЫдЇЖдЄАзІНйЂШжХИгАБеПѓеЃЪеИґзЪДжЦєеЉПжЭ•еЃЮзО∞еРДзІНз±їеЮЛзЪДиБК姩зХМйЭҐпЉМе¶ВеЃЮжЧґйАЪдњ°гАБеЃҐжИЈжЬНеК°еѓєиѓЭж°ЖжИЦз§ЊдЇ§е™ТдљУзЪДзІБдњ°еКЯиГљгАВдљЬдЄЇдЄАдЄ™еЉАжЇРй°єзЫЃпЉМChat-pane ...
Vueе§ЪеИЖеЙ≤з™Чж†Љ еЯЇдЇОVue.jsзЪДзїДдїґгАВ жПРдЊЫжЧ†йЩРзЪДеПѓи∞ГжХіе§Іе∞ПзЪДе§Ъз™Чж†ЉжФѓжМБгАВ жЉФз§ЇзЙИ | | | еЃЙи£Е npm i vue-multi-split-pane ... onPaneCollapsed ( paneIndex , paneClass , containerClass ) { console . log
гАРж†ЗйҐШгАС"Cupertino Pane MasterжЇРз†БиІ£жЮР" еЬ®ITи°МдЄЪдЄ≠пЉМжЇРз†БжШѓзРЖиІ£иљѓдїґеЈ•дљЬеОЯзРЖзЪДеЕ≥йФЃпЉМзЙєеИЂжШѓеѓєдЇОеЉАеПСиАЕиАМи®АпЉМжЈ±еЕ•з†Фз©ґжЇРз†БжЬЙеК©дЇОжПРеНЗжКАиГљеТМиІ£еЖ≥йЧЃйҐШгАВжЬђзѓЗе∞Жиѓ¶зїЖжОҐиЃ®"cupertino-pane-master"й°єзЫЃпЉМињЩжШѓдЄАдЄ™дЄОiOS...
VueеИЖеЙ≤з™Чж†ЉдљњзФ®Vue.jsзЪДеПѓи∞ГжЛЖеИЖз™Чж†ЉеЃЙи£Е# yarn (recommend)$ yarn add vue-split-pane# npm$ npm install vue-split-pane --saveзФ®ж≥ХCDN < script src =" https://unpkg.com/vue-split-pane " > </ ...
еЬ®жЬђжЦЗдЄ≠пЉМжИСдїђе∞ЖжЈ±еЕ•жОҐиЃ®е¶ВдљХиІ£еЖ≥VueдЄ≠`el-tab-pane`еИЗжНҐжЧґйБЗеИ∞зЪДйЧЃйҐШпЉМдї•еПКе¶ВдљХдЉШеМЦеТМзЃ°зРЖзїДдїґзЪДжЄ≤жЯУгАВ й¶ЦеЕИпЉМйЧЃйҐШеЗЇзО∞еЬ®ељУзФ®жИЈеЬ®дЄНеРМжХ∞йЗПзЪД`el-tab-pane`дєЛйЧіеИЗжНҐжЧґпЉМ`el-dialog`еПѓиГљдЉЪдњЭжМБдєЛеЙНзЪДзКґжАБпЉМињЩйАЪеЄЄжШѓ...