Posted on December 17th, 2010 by Roy Clarkson
in Android
, Spring
.

We recently announced the M1 release
of Spring Android
,
and with that release some questions have arisen around how to build an
Android application utilizing the Spring Android Rest Template and
Spring Android Commons Logging libraries. Google provides several
methods for compiling an Android application, including SDK command line
tools, and the ADT (Android Development Tools) Plugin for Eclipse.
Unfortunately, neither of these methods includes integrated dependency
management support.
Overview
As Java developers we have come to appreciate tools such as Maven
and Gradle
for managing external dependencies. While traditional Java
applications run in a JVM, Android applications run on the Dalvik
virtual machine. The Dalvik VM executes files in the Dalvik Executable
(.dex) format. It runs classes compiled by a Java language compiler
that have been transformed into the .dex format. A build tool will need
to support this process if it is going to be able to compile a
compatible Android application with dependencies.
There are basically two options for including external libraries in
your Android application. The first is to manually copy the jars into
the libs directory within your project and update the classpath within
Eclipse. This is the simplest solution, and the one most supported by
the ADT plugin. The disadvantage is that you have to manage the
dependencies manually. Alternatively, a third party plugin such as the Maven Android Plugin
can be utilized to automatically include the dependencies from a Maven repository.
In this post I will walk through the process of using the Android command line tools, Maven, the Maven Android Plugin, and Android Maven artifacts
to compile a sample application that utilizes the Spring Android
libraries, and deploy it to the Android emulator. After you have
configured Maven, it is easy to create a build, deploy it to the
emulator, run tests, and package the app for deployment to the Android
Market. Before running the sample code, we will first highlight the
configuration settings necessary in the pom.xml. The components used in
this example are listed below.
Maven Configuration
This section covers the parts of a pom.xml that are required for developing with Spring Android and the Maven Android Plugin.
Maven Android Plugin
In order to use Maven to build an Android application, you will need
to configure the Maven Android Plugin within your pom.xml file. Android
applications are deployed to the device as an apk file, not a jar. You
must specify this in the the packaging configuration.
1
|
<
packaging
>apk</
packaging
>
|
To configure the Maven Android and Maven Compiler Plugins in the
build task, set the sdk platform to the desired level. In this example
it is set to 9, which corresponds to Android version 2.3.1. The
emulator avd value is the name of the AVD (Android Virtual Device) you
defined in the AVD Manager. In this case, an AVD with the name "9", but
the AVD can be named whatever you like, as long as it matches the name
you specified when creating the AVD. This is a basic configuration for
the plugin that is needed to build and run an Android application.
There are additional parameters that can be included for more
functionality.
02
|
<
sourceDirectory
>src</
sourceDirectory
>
|
03
|
<
finalName
>${project.artifactId}</
finalName
>
|
06
|
<
groupId
>com.jayway.maven.plugins.android.generation2</
groupId
>
|
07
|
<
artifactId
>maven-android-plugin</
artifactId
>
|
08
|
<
version
>2.8.4</
version
>
|
11
|
<
platform
>9</
platform
>
|
16
|
<
deleteConflictingFiles
>true</
deleteConflictingFiles
>
|
17
|
<
undeployBeforeDeploy
>true</
undeployBeforeDeploy
>
|
19
|
<
extensions
>true</
extensions
>
|
22
|
<
artifactId
>maven-compiler-plugin</
artifactId
>
|
23
|
<
version
>2.3.2</
version
>
|
Dependencies
The Android artifacts have been built and published to the Maven repository through the efforts of the Android for Maven project
.
Google prevented the official Android jars from being uploaded to
Maven, so the, third party, Android for Maven project was started to
provide an API compatible Android artifact that could be uploaded to the
Maven repository. There are now artifacts for each major Android
version available in the Maven repository. These are not functional,
however, and only provide stubbed implementations of the API. All
methods in all classes throw a runtime exception. Because an Android
app runs on a device, it will never use these libraries for execution,
but the API compatibility allows an app to be compiled as if it were the
real library. More information can be found here
.
To compile an Android application with dependencies you need to
include the Android version you are targeting for your app. As stated
previously, we are using level 9, which corresponds to version 2.3.1.
Check the Maven Repository
for the available versions. You must set the android dependency scope to provided
, otherwise Maven will try to include the Android jar library into your apk.
2
|
<
groupId
>com.google.android</
groupId
>
|
3
|
<
artifactId
>android</
artifactId
>
|
4
|
<
version
>2.3.1</
version
>
|
5
|
<
scope
>provided</
scope
>
|
Compile against the latest milestone release of Spring Android Rest Template by adding the following dependency.
2
|
<
groupId
>org.springframework.android</
groupId
>
|
3
|
<
artifactId
>spring-android-rest-template</
artifactId
>
|
4
|
<
version
>1.0.0.M2</
version
>
|
Include the repositories for the snapshot and milestone builds to use
the latest build or milestone release of either of the Spring Android
libraries in your app.
04
|
<
id
>org.springframework.maven.snapshot</
id
>
|
05
|
<
name
>Spring Maven Snapshot Repository</
name
>
|
07
|
<
releases
><
enabled
>false</
enabled
></
releases
>
|
08
|
<
snapshots
><
enabled
>true</
enabled
></
snapshots
>
|
12
|
<
id
>org.springframework.maven.milestone</
id
>
|
13
|
<
name
>Spring Maven Milestone Repository</
name
>
|
15
|
<
snapshots
><
enabled
>false</
enabled
></
snapshots
>
|
Development Environment
The Android SDK is required for developing Android applications. As
mentioned earlier, Google provides command line tools, and an Eclipse
plugin for building Android applications, however you are not restricted
to only those options. Other IDE's also provide support for building
Android apps. The Maven Android Plugin makes use of the Android SDK
command line tools to compile and deploy the app to the emulator, so
there is no need for a separate IDE setup or configuration.
The instructions for downloading and installing the Android SDK
can be found on the Android web site. Please note that the Android SDK Revision 8 release
changed the location of some of the tools. In addition to the tools
directory, you must also add the platform-tools
directory to your path.
For example, a .bash_profile on a Mac may look like the following.
1
|
export ANDROID_HOME=~/android-sdk-mac_x86
|
2
|
export PATH=${PATH}:$ANDROID_HOME/tools:$ANDROID_HOME/platform-tools
|
Configure an Android Virtual Device
To run an Android app, you must have an Android Virtual Device
(AVD) configured. An AVD is a configuration of emulator options. In
other words, you are defining the settings to use when running the
emulator. You can save a configuration with a name and use it later.
You can also define multiple AVD's for testing against different Android
versions or hardware configurations.
The pom.xml file included with the sample Android client app
specifies an AVD with the name "9". In order for Maven to be able to
deploy the Android app, you must have an AVD configured with that same
name. This is of particular interest, as all developer machines will
need to have the same AVD configured, since the pom.xml is typically
committed to source control.
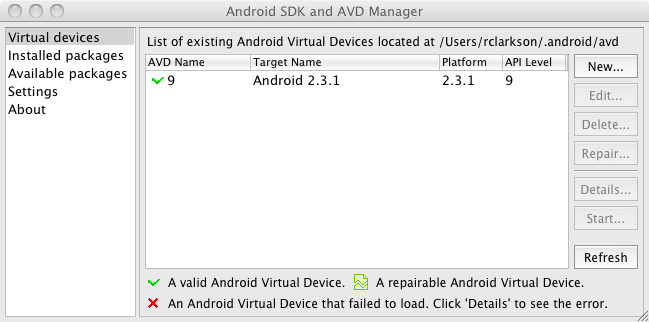
- From the command line, type android
and hit return. This opens the Android SDK and AVD Manager
window.
- Select Virtual devices
in the left hand column and click the New…
button
- Enter 9
in the Name
field
- Select Android 2.3.1- API Level 9
in the Target
selector
- Click Create AVD
to finish
Sample Application
We've set up a samples repository for the Spring Mobile projects.
From the command prompt, clone the repository to your local machine with
the following command.
Start the Server
If you would like to run the server component of the sample
application, to see the interaction between the Android client and a
Spring MVC website, the easiest way to do so is from within the STS IDE.
Navigate to the spring-android-showcase
directory.
There are two directories, "client" for a client Android application,
and "server" for a Spring MVC server application. The client app makes
network requests to the server to illustrate RestTemplate functionality,
so the server must be running for the client to function.
- From STS, select File -> Import…
- In the General
folder, select Existing Projects into Workspace
and click Next
- Click Browse
and navigate to the Server
directory of the spring-android-showcase
directory
- Click Open
to add the project to your workspace
- Highlight the spring-android-showcase-server
project in the Package Explorer
view and drag it to SpringSource tc Server Developer Edition
in the Servers
view to deploy the web app
- Finally, click the Run
button to start the server
Run the Android Client
To build the client app enter the following command from the command line
Enter the following command to start the Android emulator. Maven
tries to start the AVD with the name configured in the pom.xml, which is
why the name needs to match with the name of the actual AVD you
created.
1
|
$ mvn android:emulator-start
|
Finally, deploy the application to the emulator with the following command.
The app is deployed to the emulator as S2Android Showcase. Before
running the app, start up the Android log viewer to see the activity of
the application. You will spend a lot of time with the Android logs
when doing development. To view the logs, execute the following command
at the command prompt.
Congratulations! You have now built and deployed an Android app with Maven managed dependencies.
Conclusion
Adding Maven to your Android development process adds extra
complexity, but it provides the ability to compile an Android app that
includes external dependencies from a Maven repository. Without it, you
would manually have to download the dependencies needed to compile and
run your application. We've shown the benefit of using it for
dependency management to build with the Spring Android libraries. In
the Part 2
post I will cover Android development in Eclipse with the Maven Integration for Android Development Tools
plugin, and the ADT (Android Developer Tools) Plugin for Eclipse
.
Neither the m2eclipse nor ADT plugins support building Android
applications with Maven dependencies. The Maven Integration for Android
Development Tools plugin provides a bridge to the Maven Android Plugin,
enabling Maven dependency management within Eclipse for Android
projects. If you prefer using Eclipse for development, I'll discuss how
to use these plugins in the next post
.
Additional Resources
The Android Chapter of Maven: The Complete Reference
contains a lot of good information about the Android Maven Plugin.
Posted on February 9th, 2011 by Roy Clarkson
in Android
, Spring
.

In Spring Android and Maven (Part 1)
,
I described how to build an Android application from the command-line
using Maven. In this post, I will show you how to build an Android
application with Maven dependency management from the Eclipse IDE. The
application will also showcase the latest features in Spring Android 1.0.0.M2
, which was released this week.
Overview
The Maven Android Plugin lets you build your Android applications
with Maven and benefit from dependency management. Google's Android
Development Tools (ADT) plugin allows you to develop and build Android
applications within the Eclipse IDE. To get Maven dependency management
within Eclipse, the Maven Integration for Android Development Tools
plugin is required, which integrates m2eclipse
, the ADT Plugin, and the Maven Android Plugin
.
This post will show you how to install this plugin and use it to get
Maven-based dependency management working in the Eclipse IDE.
The specific versions of each component used in this post are listed below:
Configure Eclipse
Before building or compiling any code, we need to install and configure the required Eclipse plugins. In Part 1
I discussed installing the Android SDK, so I will assume you have
already done so. However, if you have not, then you will need to
install it before continuing. Additionally, you will need to have
already installed Eclipse
3.5 or newer. In this example I am using SpringSource Tool Suite
2.5.2 which is based on Eclipse 3.6.1.
There are three Eclipse plugins that need to be installed, the ADT
Plugin for Eclipse, Maven Integration for Eclipse, and Maven Integration
for Android Development Tools. You have two options for installing
these plugins, either by using the Eclipse Marketplace Client
, or by manually installing each plugin.
Installing Plugins using the Eclipse Marketplace Client
Depending on your version of Eclipse, you may already have the
Eclipse Marketplace Client installed. The Marketplace Client will
simplify the plugin installation, because it will transitively include
any required plugins.
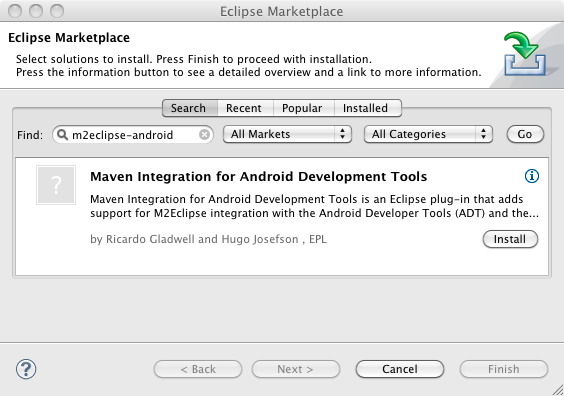
- Open the Eclipse Marketplace Client by selecting Help -> Eclipse Marketplace…
- Enter m2eclipse-android
in the Find:
field, and click the Go
button.
- Click the Install
button next to Maven Integration for Android Development Tools
.
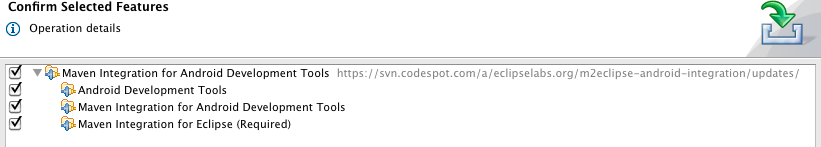
- Click the Next
button to confirm the selected
features. Note that Android Development Tools and Maven Integration for
Eclipse are dependencies.
- Accept the license agreements and click the Finish
button to complete the installation.
- After you restart Eclipse, you need to set the Android SDK Location
as specified in the ADT Plugin installation in the next section.
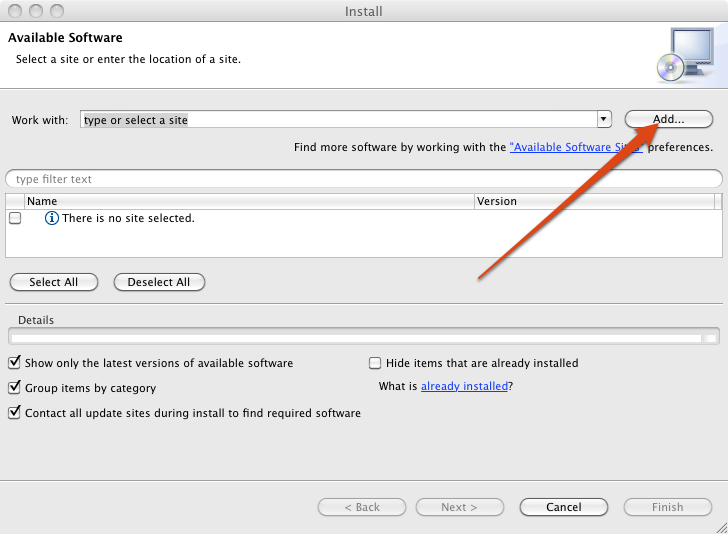
Manual Plugin Installation
The alternative to using the Marketplace Client is to manually
install each plugin. If you installed the plugins from the Marketplace,
then you can skip down to the Sample Android Application section. For
each plugin, from the Eclipse Help
menu, select Install New Software…
and click the Add…
button.
ADT Plugin for Eclipse
The first step is to install the ADT (Android Developer Tools) Plugin
for Eclipse. This is the official plugin provided by Google for
developing Android applications. If you already have the ADT Plugin
installed, then verify you have the latest version by running Check for Updates
from the Eclipse Help
menu.
- Enter ADT Plugin
for the Name
, and the following URL for the Location
. Click OK
to continue.
- In the Available Software dialog, select the checkbox next to Developer Tools and click Next.
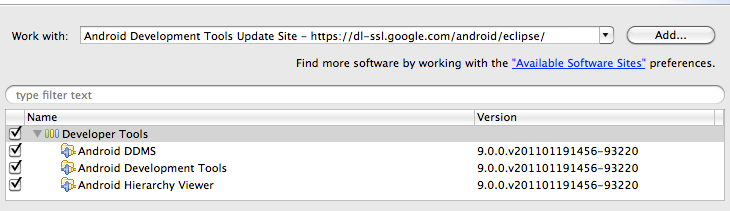
- In the next window, you'll see a list of the tools to be downloaded. Click Next
.
- Read and accept the license agreements, then click Finish
.
- When the installation completes, restart Eclipse.
- After Eclipse restarts, set the Android SDK Location by selecting Preferences
from the Eclipse menu and selecting Android
in the left column. On my machine, the SDK folder is located in my
profile folder. Once the location is configured you should see a list of
SDK Targets.
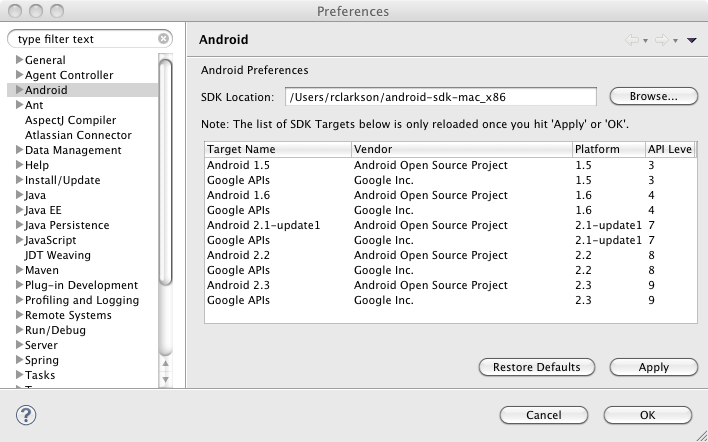
Note: If you have any trouble with the ADT installation, the Android web site
can provide additional information.
Maven Integration for Eclipse
The next step is to install the m2eclipse plugin. STS 2.5.2 comes
with this plugin. However, if you have a previous release, or if you
already have the plugin installed, you need to verify you have the
latest version. The Maven Integration for Android Development Tools
requires version 0.12.0 or higher.
- Enter m2eclipse Core Update Site
for the Name
, and the following URL for the Location
. Click OK
to continue.
- In the Available Software dialog, select the checkbox next to Maven Integration for Eclipse
and click Next
.
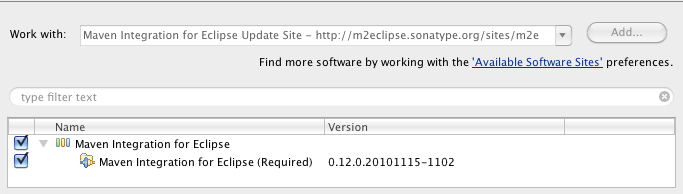
- In the next window, you'll see a list of the components to be downloaded. Click Next
.
- Read and agree to the terms of the Eclipse Public License v1.0, then click Finish
.
- When the installation completes, restart Eclipse.
Maven Integration for Android Development Tools
We've got one more plugin to install, and this is the one that brings
all this functionality together. After you have set up the Android SDK
and configured the ADT Plugin in Eclipse, install the Maven Integration for Android Development Tools
plugin.
- From the Eclipse Help
menu, select Install New Software…
and click the Add…
button
- Enter Maven Integration for Android Development Tools Update Site
for the Name
, and the following URL for the Location
. Click OK
to continue.
- In the Available Software dialog, select the checkbox next to Maven Integration for Android Development Tools
and click Next
.
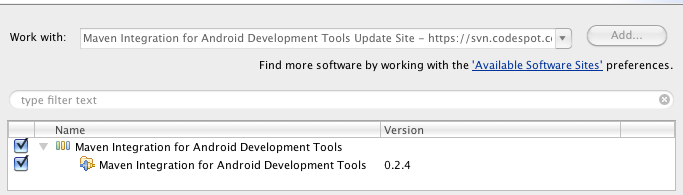
- In the next window, you'll see a list of the components to be downloaded. Click Next
.
- Read and accept the license agreements, then click Finish
.
- When the installation completes, restart Eclipse.
Sample Android Application
Now that we have all the necessary plugins installed and configured,
we are ready to try out our setup with a sample Android application. We
will use the same sample app created for the Part 1 blog post, however
the sample app has been updated to run on the latest Android platform
SDK, 2.3.1 API Level 9. If you do not have this SDK platform installed,
you will need to do so before building the sample code.
Fetch the Sample Project
Run the following command to clone the Spring Mobile samples repository.
If the git:// URL is not accessible, you may need to try the alternate URL for the samples repository.
Before opening the source code in Eclipse, navigate to the spring-android-showcase/client
project directory and verify the project builds with the Android Maven Plugin.
Open the Project in Eclipse
Assuming that the project built from the command line successfully, we are ready to open the project in Eclipse.
- From the Eclipse File
menu, select select New
and Project…
- Select the Android Project wizard from the Android
folder and click Next
. If the Android wizard is not available, then the ADT Plugin has not been installed.
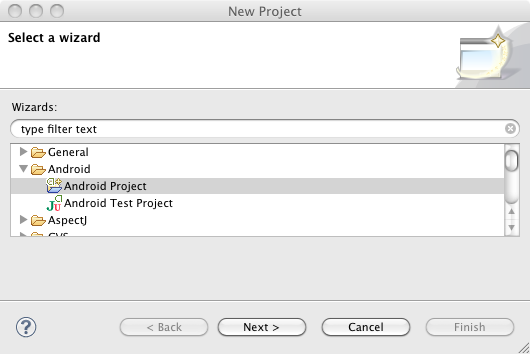
- In the New Android Project
window, enter spring-android-showcase-client
for the Project name
. Select Create project from existing source
, and browse to the Location
of the sample client. Click Finish
to add the project to Eclipse.
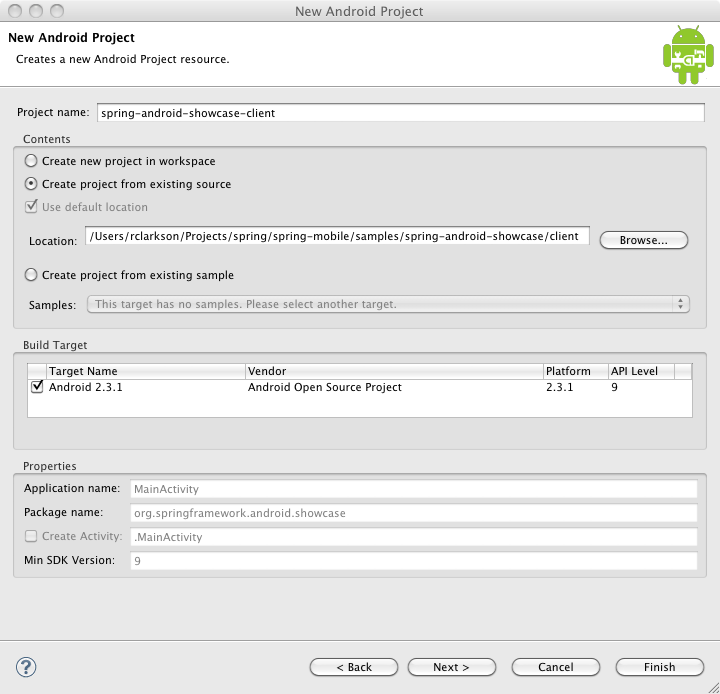
Enabling Maven Dependency Management
The sample project is now loaded into Eclipse. The first thing you
will notice is the big red 'X' over the project in the Package Explorer,
which indicates it currently does not build. Since we have yet to
configure Maven for this project, this is expected behavior.
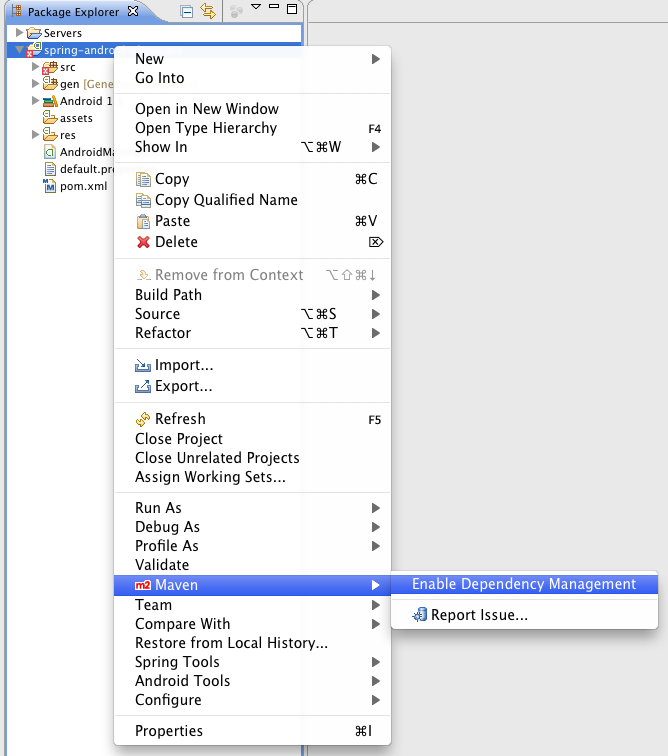
To enable Maven dependency management, right-click on the spring-android-showcase-client
in the Package Explorer
, and select Maven -> Enable Dependency Management
from the context menu.
The sample project already includes the following Maven POM file. If
you did not have an existing POM in your project, Eclipse would have
prompted you to create one. Note the use of the maven-android-plugin
and maven-compiler plugin
in the build
section.
003
|
<
modelVersion
>4.0.0</
modelVersion
>
|
005
|
<
groupId
>org.springframework.android</
groupId
>
|
006
|
<
artifactId
>spring-android-showcase-client</
artifactId
>
|
007
|
<
version
>1.0.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</
version
>
|
008
|
<
packaging
>apk</
packaging
>
|
009
|
<
name
>spring-android-showcase-client</
name
>
|
012
|
<
name
>SpringSource</
name
>
|
017
|
<
android-platform
>9</
android-platform
>
|
018
|
<
android-emulator
>9</
android-emulator
>
|
019
|
<
maven-android-plugin-version
>2.8.4</
maven-android-plugin-version
>
|
020
|
<
maven-compiler-plugin-version
>2.3.2</
maven-compiler-plugin-version
>
|
021
|
<
android-version
>2.3.1</
android-version
>
|
022
|
<
spring-android-version
>1.0.0.M2</
spring-android-version
>
|
023
|
<
jackson-version
>1.7.2</
jackson-version
>
|
024
|
<
simple-version
>2.4.1</
simple-version
>
|
025
|
<
android-rome-version
>1.0.0-r2</
android-rome-version
>
|
029
|
<
sourceDirectory
>src</
sourceDirectory
>
|
030
|
<
finalName
>${project.artifactId}</
finalName
>
|
033
|
<
groupId
>com.jayway.maven.plugins.android.generation2</
groupId
>
|
034
|
<
artifactId
>maven-android-plugin</
artifactId
>
|
035
|
<
version
>${maven-android-plugin-version}</
version
>
|
038
|
<
platform
>${android-platform}</
platform
>
|
041
|
<
avd
>${android-emulator}</
avd
>
|
043
|
<
deleteConflictingFiles
>true</
deleteConflictingFiles
>
|
044
|
<
undeployBeforeDeploy
>true</
undeployBeforeDeploy
>
|
046
|
<
extensions
>true</
extensions
>
|
049
|
<
artifactId
>maven-compiler-plugin</
artifactId
>
|
050
|
<
version
>${maven-compiler-plugin-version}</
version
>
|
057
|
<
groupId
>com.google.android</
groupId
>
|
058
|
<
artifactId
>android</
artifactId
>
|
059
|
<
version
>${android-version}</
version
>
|
060
|
<
scope
>provided</
scope
>
|
063
|
<
groupId
>org.springframework.android</
groupId
>
|
064
|
<
artifactId
>spring-android-rest-template</
artifactId
>
|
065
|
<
version
>${spring-android-version}</
version
>
|
069
|
<
groupId
>org.codehaus.jackson</
groupId
>
|
070
|
<
artifactId
>jackson-mapper-asl</
artifactId
>
|
071
|
<
version
>${jackson-version}</
version
>
|
075
|
<
groupId
>org.simpleframework</
groupId
>
|
076
|
<
artifactId
>simple-xml</
artifactId
>
|
077
|
<
version
>${simple-version}</
version
>
|
080
|
<
artifactId
>stax</
artifactId
>
|
081
|
<
groupId
>stax</
groupId
>
|
084
|
<
artifactId
>stax-api</
artifactId
>
|
085
|
<
groupId
>stax</
groupId
>
|
091
|
<
groupId
>com.google.code.android-rome-feed-reader</
groupId
>
|
092
|
<
artifactId
>android-rome-feed-reader</
artifactId
>
|
093
|
<
version
>${android-rome-version}</
version
>
|
100
|
<
id
>android-rome-feed-reader-repository</
id
>
|
101
|
<
name
>Android ROME Feed Reader Repository</
name
>
|
106
|
<
id
>org.springframework.maven.snapshot</
id
>
|
107
|
<
name
>Spring Maven Snapshot Repository</
name
>
|
109
|
<
releases
><
enabled
>false</
enabled
></
releases
>
|
110
|
<
snapshots
><
enabled
>true</
enabled
></
snapshots
>
|
114
|
<
id
>org.springframework.maven.milestone</
id
>
|
115
|
<
name
>Spring Maven Milestone Repository</
name
>
|
117
|
<
snapshots
><
enabled
>false</
enabled
></
snapshots
>
|
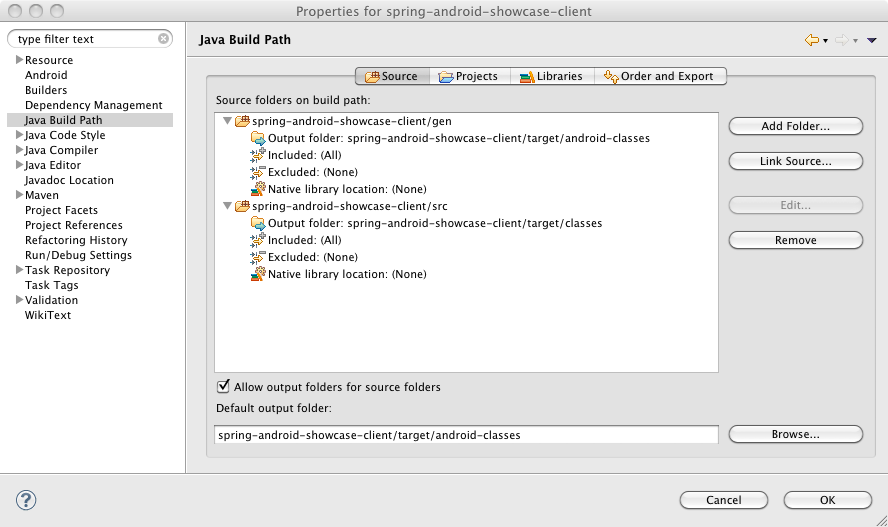
Maven will now update the required dependencies and Eclipse should
successfully build the project. Once Eclipse is finished building the
project, you should now see the Maven Dependencies
classpath container in the Package Explorer
window.
There are a couple things to note. First you may see there is a bin
folder in the project. You can see from the Java Build Path
properties (below) that the default output folder is the Target
folder. So it is safe to remove the bin
folder.
Second, you may also notice that there is a JRE System Library
classpath container that was added to the project. Since we are
building an Android app that utilizes the Android JVM you should not
need to reference the JRE. If you have created a new Android app in
Eclipse with the ADT, you know that it does not add a classpath
container for the JRE. I have discussed this with the Maven Integration
for Android Development Tools developer, Ricardo Gladwell, and he
created a ticket
to research the issue. I have removed the JRE from the sample project
without any obvious, negative effects. But you may want to keep watch
on that issue for more information.
Start the Spring Android Showcase Sample App
To run the sample application, simply select the spring-android-showcase-client
in the Package Explorer
, and click the Run
button. The Maven POM file in the sample client is configured to look
for an Android Virtual Device (AVD) named "9". As mentioned earlier,
the samples project has been updated to run on the Android Platform SDK
2.3.1. You need to have an AVD configured for this platform for the
samples to run.

The first time you run the app, you should see something like the following in the Eclipse console:
01
|
[2011-02-08 14:00:49 - spring-android-showcase-client] ------------------------------
|
02
|
[2011-02-08 14:00:49 - spring-android-showcase-client] Android Launch!
|
03
|
[2011-02-08 14:00:49 - spring-android-showcase-client] adb is running normally.
|
04
|
[2011-02-08
14:00:49 - spring-android-showcase-client] Performing
org.springframework.android.showcase.MainActivity activity launch
|
05
|
[2011-02-08 14:00:49 - spring-android-showcase-client] Automatic Target Mode: launching new emulator with compatible AVD '9'
|
06
|
[2011-02-08 14:00:49 - spring-android-showcase-client] Launching a new emulator with Virtual Device '9'
|
07
|
[2011-02-08
14:00:50 - Emulator] 2011-02-08 14:00:50.936 emulator[5951:903] Warning
once: This application, or a library it uses, is using NSQuickDrawView,
which has been deprecated. Apps should cease use of QuickDraw and move
to Quartz.
|
08
|
[2011-02-08 14:00:50 - spring-android-showcase-client] New emulator found: emulator-5554
|
09
|
[2011-02-08 14:00:50 - spring-android-showcase-client] Waiting for HOME ('android.process.acore') to be launched...
|
10
|
[2011-02-08 14:01:21 - spring-android-showcase-client] HOME is up on device 'emulator-5554'
|
11
|
[2011-02-08 14:01:21 - spring-android-showcase-client] Uploading spring-android-showcase-client.apk onto device 'emulator-5554'
|
12
|
[2011-02-08 14:01:23 - spring-android-showcase-client] Installing spring-android-showcase-client.apk...
|
13
|
[2011-02-08 14:01:50 - spring-android-showcase-client] Success!
|
14
|
[2011-02-08
14:01:50 - spring-android-showcase-client] Starting activity
org.springframework.android.showcase.MainActivity on device
emulator-5554
|
15
|
[2011-02-08
14:01:52 - spring-android-showcase-client] ActivityManager: Starting:
Intent { act=android.intent.action.MAIN
cat=[android.intent.category.LAUNCHER]
cmp=org.springframework.android.showcase/.MainActivity }
|
The AVD will start and display the locked screen. Slide the green
lock from left to right to "open" the Android device. Once opened, the
app should now display:
Conclusions
In this post we've reviewed how to build a sample Android application
in Eclipse that utilizes Maven dependency management. To accomplish
this, we've used Eclipse, the Android Development Tools (ADT) Plugin for
Eclipse, the Maven Android Plugin, the Maven Integration for Android
Development Tools plugin, and the Maven Integration for Eclipse
(m2eclipse) plugin. There are a lot of pieces involved, but once you
have everything configured, it is easy to build and deploy to the
Android emulator. If you are using third party libraries within your
Android application, you should consider using these tools to help
manage those dependencies.
分享到:




























相关推荐
基于spring boot + maven + opencv 实现的图像深度学习Demo项目,包含车牌识别、人脸识别、证件识别等功能,贯穿样本处理、模型训练、图像处理、对象检测、对象识别等技术点。 基于spring boot + maven + opencv ...
**Spring Framework 5.2.x Maven 版本详解** Spring Framework是Java开发中不可或缺的开源框架,它为构建高效、灵活且可测试的Java应用程序提供了基础。5.2.x是其一个重要的版本,引入了许多新特性和改进。在这个...
《Android Maven Gradle 插件:与Android库项目兼容的构建工具详解》 在Android开发领域,构建工具的不断更新迭代对于开发者来说既是机遇也是挑战。Android Maven Gradle 插件,作为Android库项目与Maven集成的重要...
Android Maven 插件是将Android项目与Maven构建系统集成的一种工具。在传统的Android开发中,我们通常使用Gradle作为构建系统,但Maven在Java领域有着广泛的应用,因此对于那些习惯于Maven或者需要利用Maven生态的...
Java使用Maven导入Spring依赖
标题中的"spring4 mvc maven"指的是一个使用Spring MVC框架和Maven构建工具的Web应用程序项目。这个项目的核心是Spring MVC,它是Spring框架的一部分,专门用于构建Web应用,提供了模型-视图-控制器(MVC)架构模式...
这个项目"springmvc spring hibernate jpa maven 整合"就是这样一个例子,它整合了四个关键的技术组件:Spring MVC、Spring、Hibernate和JPA,以及依赖管理工具Maven。让我们详细探讨这些技术及其在项目中的作用。 ...
Maven 插件 Spring Boot Maven Plugin Spring Boot Maven Plugin 是一个 Maven 插件,用于简化 Spring Boot 项目的构建和打包过程。该插件提供了许多有用的功能,例如重新打包可执行的存档、自定义层配置、继承 ...
**Spring Boot 2 Maven 模板详解** Spring Boot 2 是一个基于 Java 的框架,它旨在简化Spring应用程序的初始设置和常规配置。Maven作为Java项目管理工具,可以帮助我们管理和构建Spring Boot应用。本模板是专为学习...
标题提到的“maven包,spring boot的maven包”,指的是包含Spring Boot相关依赖的Maven仓库文件。这些文件通常以`.jar`或`.pom`格式存在,存储在`repository`目录下,用于离线环境下搭建Spring Boot工程。离线搭建...
在这个带有中文注释的maven版本中,我们能够更方便地理解和学习Spring的源码。 Maven 是一个项目管理和综合工具,它帮助开发者管理项目依赖、构建流程以及提供了一种标准化的项目结构。在Spring Framework 5.1.x的...
【maven】说明:Gradle maven工件发布与maven、maven发布、android maven Gradle插件的演练。该项目包含..., (Gradle maven artifacts publishing walkaround with maven , maven-publish , android-maven gradle ...
在IT行业中,Spring框架与Maven的整合是开发Java企业级应用时不可或缺的一部分。Spring作为一个强大的轻量级应用框架,提供了全面的后端服务管理,包括依赖注入、AOP(面向切面编程)、数据访问、Web开发等。而Maven...
标题中的“maven仓库中org下的springframework”指的是在Maven的本地或远程仓库中,位于`org`组织下的`springframework`项目。Spring Framework是Java开发中的一个核心框架,由Pivotal Software公司维护,它为构建...
Spring Annotation和Maven的结合使用是现代Java项目中常见的配置方式,它们为开发者提供了高效、灵活的开发环境。本篇文章将深入探讨Spring注解和Maven的配置及其重要性。 **Spring注解** Spring注解是Spring框架...
### Spring Boot 框架与 Maven 项目的搭建详解 #### 一、Spring Boot与Maven简介 - **Spring Boot**:是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定...
在Spring Boot项目中,`maven install` 是一个常见的构建步骤,它用于将项目打包成可部署的格式,如JAR或WAR,并将其安装到本地Maven仓库。然而,当出现错误 `[ERROR] Failed to execute goal org.springframework....
《Spring in Action》一书是Spring框架的实践指南,它深入介绍了如何使用Maven构建Spring工程。Maven是一个流行的项目管理和综合工具,它通过提供一套标准化的构建过程,简化了Java项目的构建、依赖管理和部署。在...
在这个“Spring Security Maven 示例”中,我们可以通过官方提供的Maven项目来深入理解并实践Spring Security的核心概念和技术。 首先,让我们从Maven开始。Maven是一个项目管理和综合工具,它简化了构建、依赖管理...
在IT行业中,构建一个高效、可维护的企业级Web应用程序常常会采用MVC(Model-...通过这样的配置,开发者可以快速构建起一个基于Spring MVC、Spring和MyBatis的Web应用,同时利用Maven的便利性进行项目的构建和管理。