- 浏览: 74235 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 北京
-

文章分类
最新评论
-
george.gu:
lqjacklee 写道怎么解决。。 First: Conf ...
Bad version number in .class file -
lqjacklee:
怎么解决。。
Bad version number in .class file -
flyqantas:
would you pleade left more mate ...
UML Extension
How to use beanshell
beanshell Manual:
http://www.beanshell.org/manual/bshmanual.html
"loosely typed" variables
You can simply omit the types of variables that you use (both primitives and objects).
Beanshell automatically converts them to properly type before execute any operations. BeanShell will only signal an error if you attempt to misuse the actual type of the variable.
Demo 1: loosely typed method signature
take one method for an example:
add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
Interpreter bsh = new Interpreter();
bsh.eval("print(add(1,2))");
bsh.eval("print(add(\"Oh \",\"baby\"))");
bsh.eval("print(add(\"1\",2))");
Demo 2: loosely typed variable in blocks
Demo 3: loosely typed variables in method blocks
add(a, b) {
c=5;
return a + b;
}
Document Friendly Entities
BeanShell supports special overloaded text forms of all common operators to make it easier to embed BeanShell scripts inside other kinds of documents (e.g XML)
| @gt | > |
| @lt | < |
| @lteq | <= |
| @gteq | >= |
| @or | || |
| @and | && |
| @bitwise_and | & |
...
It is very useful when containing beanshell inside XML.
Demo 1:
import bsh.Interpreter;
Interpreter i = new Interpreter(); // Construct an interpreter
i.eval("print(5>4)"); // it will output: true
i.eval("print(\"5>4\")"); // it will output: 5>4
i.eval("print(5@gt4)"); // it will output: true
i.eval("print(\"5@gt4\")"); // it will output: 5@gt4
Demo 2:
Inside XML, we can use the beanshell like following:
if(a @gt b) {
//...
}
Calling beanshell in Java Application
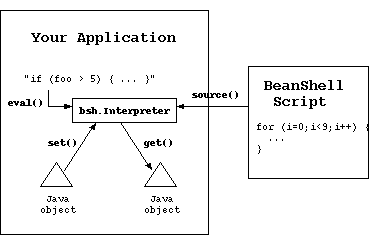
(Image from http://www.beanshell.org/images/embeddedmode.gif)
First, you should add beanshell library into your application classes path. For the moment, it is bsh-1.3.0.jar.
Initial beanshell intercepter
import bsh.Interpreter;
Interpreter i = new Interpreter(); // Construct an interpreter
eval("script_String") to interpret script string
The Interprete eval() method accepts a script as a string and interprets it, optionally returning a result. The string can contain any normal BeanShell script text with any number of Java statements. The Interpreter maintains state over any number of eval() calls, so you can interpret statements individually or all together.
TIt is not necessary to add a trailing ";" semi-colon at the end of the evaluated string. BeanShell always adds one at the end of the string.
Demo 1:
i.eval("foo=\"Foo\""); // it will set a loostly typed varialbe foo with initial value "Foo".
Demo 2:
i.eval("for (i=0;i<5;i++) print(i);") // it will display: 0 1 2 3 4
is not same as:
i.eval("for (i=0;i<5;i++)")
i.eval("print(i);") // it will display: 5
Demo 3:
Eash script string inside eval() should be a entire operation. Follwoing invocation will cause error:
i.eval("for (i=0;i<5;i++) {")
i.eval("print(i);")
i.eval("}")
set(), get() to exchange variables with Interpreter
You can use set(String name, Object value) to set variables into beanshell interpreter.
For example, you have a beanshell script:
c = 5;
foo () {
c = a + b;
//print(c);
return c;
}
You can set a and b like following:
i.set("a", 1);
i.set("b", "2");
Then you can perform an operation by invoke eval():
i.eval("foo()");
Now you can get value of c by invoke get():
i.get("c"); // you will get "12".
unset() and clear() command to eraser variables in current scope
unset(variable) used to remove a variable from the current scope. (Return it to the "undefined" state).
clear() used to Clear all variables, methods and imports from the current scope. It is not embedded in Interpreter class for the moment.
source() to read script from external file
The Interpreter source() method can be used to read a script from an external file:
i.source("/opt/tmp/mybeanshell.bsh");
source("beanshell script file") will read and interprete specified beanshell script file. You can use it to valid and test your beanshell script.
Import referenced classes
It is very important to import classes that will be referenced inside beanshell script. By default, beanshell interpreter import common Java core and extension packages for us. They are, in the order in which they are imported:
- javax.swing.event
- javax.swing
- java.awt.event
- java.awt
- java.net
- java.util
- java.io
- java.lang
Two BeanShell package classes are also imported by default:
- bsh.EvalError
- bsh.Interpreter
You can define classes import in bean shell scipt:
import com.gemalto.wgu.*;
Alternatively, you can also import classes through eval():
i.eval("import com.gemalto.wgu.*");
Scripted Objects, Methods and Interfaces
Here I would like to list four different approaches on how to invoke script in Java Application.
1-->No method definition: Beanshell file content = the body of your function method
Write your function in beanshell script file as global definition without define special method, in this case, your function code will be loaded and executed when interpreter source scripting file.
myfile.bsh:
c = 5 + 6;
print(c);
Interpreter.source("myfile.bsh"); // it will execute "c= 5 + 6" and print "11" directly.
2--> Script Methods and eval(): define your function in script method and call it in your application through eval()
Define your function inside a methods, then invoke method by eval(). If there are some other parameters, you can set("parametername", object_instance ) them.
myfile.bsh:
displayPlainPage(BufferedReader in, PrintStream out) throws IOException { String line; while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) { out.println(line); } }
Interpreter bsh = new Interpreter();
bsh.source("myfile.bsh");
bsh.set("in", BufferedReader Instance);
bsh.set("out", PrintStream Instance);
bsh.eval("displayPlainPage(in, out)"); // it will execute your function code.
Please be note: eval() will return result in "Object" instance to java context.
3--> Script Object and eval()
Interpreter bsh = new Interpreter();
bsh.eval("myObj.displayPlainPage(in, out)");
4--> Implement Interface and return Interface instance in script methods
You can define any java interface for your function:
public inteface IDisplayLog{
public void displayPlainPage(BufferedReader in, PrintStream out) throws IOException;
}
Then write a script method implement this API and return the object instance with explicity cast:
myfile.bsh:
Thanks to its lightly, no need compile, compliant with Java and loosely typed variables (which will be automatically gurranted by beanshell), you can use beanshell to make your application really flexible.
When your application meets one or some of following factors:
- some user defined global macro;
- some components change often and you pay more attention on String parameters parsing;
- your configuration or script need to call other Java clall API.
- ...
Please try beanshell to see if it can solve your issue and save time.
From beanshell manual: http://www.beanshell.org/manual/embeddedmode.html, you can see some general advice on when to use beanshell:
- Highly customized application or your application under intense change. What's more. if some component is really change often and is based on customer business rule, you can try to encapsulate thise part with beanshell.
- Macros and Evaluation: it is also related to customized requirement. you can define global macro and evaluation with beanshell.
- Simplify configuration file: you can define configuration file with beanshell script partition or entire.
In fact, some tools had already embedded beanshell support to provide flexible customized features.
For myself, I am using Jmeter and OsWorkflow engine. Both of them had embedded beanshell support. For example, we can use beanshell in workflow defintion:
<step id="2" name="XXX"> <actions> <action id="1001" name="Action 1" view="Action 1"> <pre-functions> <function type="beanshell" name="XXX"> <arg name="script"> import java.util.*; // Business logical in beanshell. transientVars.put("_simMenuTargetNode", SIMServiceTargetPath); </arg> </function> </pre-functions> <results> //... </results> </action> </actions> </step>
发表评论
-
javax.naming.CommunicationException: remote side declared peer gone on this JVM.
2012-07-11 09:44 2394javax.naming.ServiceUnavailable ... -
Generate special format numbers
2012-04-27 00:06 953DecimalFormat df = new DecimalF ... -
Singleton Service in Weblogic Cluster
2012-03-21 00:12 745http://blog.csdn.net/mobicents/ ... -
Scheduled ThreadPool Executor suppressed or stopped after error happen
2012-03-20 16:54 1051ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor ... -
Bad version number in .class file
2012-01-27 00:35 906Bad version number in .class fi ... -
User Data Header in SMPP SUBMIT_SM
2012-01-25 22:30 2338SMPP optional Parameters for ... -
jQuery study
2011-12-28 00:44 0to be study -
Java is Pass-by-Value or Pass-by-Reference?
2011-12-19 19:18 692What's saved in Object Referenc ... -
java.util.Properties: a subclass of java.util.Hashtable
2011-12-13 06:57 784I met a problem this afternoon ... -
Jmock usage
2011-12-02 05:37 0Discuss how Jmock working. -
Oracle Index Usage
2011-12-15 05:26 637Like a hash mapping for record' ... -
AOP(2):AOP与动态代理JDK Proxy and Cglib Proxy
2011-05-12 16:20 1059使用动态代理(JDK Proxy 或者Cglib Proxy) ... -
AOP(1):应用中的几个小故事
2011-05-09 21:49 981I had heared about AOP almost 7 ... -
异步系统设计:push vs pull
2011-05-02 23:59 1146今天讨论问题时,有个同事说系统A是主动去系统B里“拿”消息,我 ... -
Velocity Usage
2011-04-28 22:52 1012You can find velocity mannua ... -
Java Regular Expression (Java正则表达式)
2011-04-23 06:58 962In current Project, we need to ... -
XML Parser:DOM + XPath
2011-04-23 06:30 1237There are many kinds of XML Par ... -
File upload and download in Java Web Application.
2011-04-21 21:08 1722最近在项目中遇到一个下载文件的老问题。之所以说是老问题,因为在 ... -
Manage zip content using Java APIs
2011-04-21 18:14 1045JDK provide a set of utils to c ... -
OXM: JAXB2.0 in JDK1.6
2011-04-20 22:53 12481.1.1 JAXB 2.0: ObjectàXML ...





相关推荐
### 使用BeanShell调试Java应用程序的关键知识点 #### 一、引言 在评估Java应用程序的安全性时,特别是客户端-服务器架构的应用程序,往往涉及到修改代码、编译、部署、测试等一系列繁琐的过程。当无法获取源代码时...
BeanShell-简单的Java脚本 BeanShell的官方活动项目主页。注意:待发布新版本唯一推荐的版本是master分支的手动构建。 对旧版本的支持达到了行尾,只能接受针对主版本的问题和拉取请求。 下一个版本将是概述的...
有两种方式启动 BeanShell:图形桌面模式和命令行模式。在图形桌面模式下,可以双击 JAR 文件来启动 BeanShell。在命令行模式下,可以使用以下命令来启动 BeanShell: * java bsh.Console // 运行图形桌面模式 * ...
Bean Shell 是一个轻量级的Java脚本环境,它允许用户在运行时动态地执行Java代码,进行交互式编程或自动化任务。这个压缩包包含了Bean Shell的核心组件和一些相关资源,便于用户在Java环境中进行脚本操作。...
在实践中,你可以通过以下步骤学习 Beanshell: 1. 下载 Beanshell 源码,通常以 `.jar` 文件形式提供。 2. 使用反编译工具(如jd-gui)查看源码,了解其内部工作原理。 3. 实验并调试 Beanshell 脚本,观察其如何...
在本项目中,我们关注的是一个特定实现——"iso8583-server-simulator-beanshell",它利用了Beanshell脚本语言作为请求监听器。Beanshell是一个轻量级、动态的Java脚本环境,允许开发者在运行时执行和修改Java代码,...
标题中的“用BeanShell来运行Java脚本”指的是利用BeanShell这个开源库在Java环境中执行动态的、交互式的Java代码。BeanShell是一个轻量级的Java Scripting引擎,它允许你在运行时执行Java代码,无需编译,极大地...
BeanShell 是一个轻量级的Java脚本语言,它允许开发者使用类似JavaScript的语法来编写和执行Java代码。这个“BeanShell帮助文档和jar包”包含了一切你需要开始使用BeanShell的资源。以下是对BeanShell及其相关文件的...
【标题】:“深入理解JMeter中的BeanShell组件” 【描述】:“本文将详细介绍JMeter的BeanShell组件,包括其使用场景、内置变量和方法,帮助读者掌握如何在接口测试中运用BeanShell进行脚本编写。” 【标签】:...
BeanShell 是一个轻量级的Java脚本环境,它允许开发者使用类似JavaScript的语法来编写和执行Java代码。BeanShell 的设计目标是提供一个灵活、动态的工具,用于测试、原型设计、脚本以及对Java应用程序进行调试。由于...
bsh(BeanShell)是一个轻量级的、动态的Java语言解释器,它允许在运行时执行Java语法和一些扩展语法的脚本。作为Java开发工具,bsh提供了一个强大的环境,开发者可以快速测试代码片段、原型设计、自动化任务,甚至...
Beanshell 是一个轻量级的Java脚本引擎,它允许用户在运行时直接执行Java语法的脚本。这个压缩包包含三个重要的组成部分:`bsh-2.0b4.jar`、`bshjavadoc.zip` 和 `beanshell` 文件夹,这些都是与Beanshell相关的资源...
【标题】: 使用BeanShell构建公式管理系统的实践 【描述】: 在复杂的企业级应用如SCM、CRM和ERP中,常常需要用户根据自身需求调整计算参数,以满足特定时期的业务规则。例如,商品折扣率、员工奖金计算等都需要动态...
Beanshell 是一个轻量级的Java脚本引擎,它允许你在运行时动态执行Java代码。这个源码包可能包含了 Beanshell 的完整源代码,对于学习和理解其内部工作原理非常有帮助。Beanshell 可以作为Java应用程序的一部分,...
BeanShell和Mozilla Rhino是两种在Java环境中用于动态执行和脚本化的工具,它们各自具有独特的特性和用途。 BeanShell是一个轻量级的Java代码解释器,它的主要特点是免费、可嵌入和具备面向对象的脚本语言特性。...
Beanshell 是一个轻量级的Java源码解释器,它允许你在运行时执行Java代码片段或者完整的脚本。这个工具非常适用于快速测试、调试、以及动态编程任务,因为它的语法接近于标准Java,同时又引入了一些脚本语言的便利...
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("/path/to/your/file.xlsx"); Workbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fis); ``` 3. 访问工作簿中的工作表,读取数据。比如获取第一个工作表: ```java Sheet sheet = ...
Java的BeanShell是一个轻量级、动态的脚本语言,它是专门为Java平台设计的,允许在运行时执行Java代码或者类似JavaScript的语法。BeanShell在Java应用中常被用来进行快速原型开发、测试以及扩展,它提供了一种简单的...